Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (17): 2775-2781.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2598
Previous Articles Next Articles
tau protein and Alzheimer’s disease
Wang Jinchun1, Liu Huiying1, Cao Yunpeng2
- 1Department of Neurology, the Fifth People's Hospital of Shenyang, Shenyang 110023, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Neurology, the First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2019-03-07Revised:2019-03-15Accepted:2019-05-08Online:2020-06-18Published:2020-03-30 -
Contact:Cao Yunpeng, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Neurology, the First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Jinchun, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Neurology, the Fifth People's Hospital of Shenyang, Shenyang 110023, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81371227
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jinchun, Liu Huiying, Cao Yunpeng. tau protein and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(17): 2775-2781.
share this article
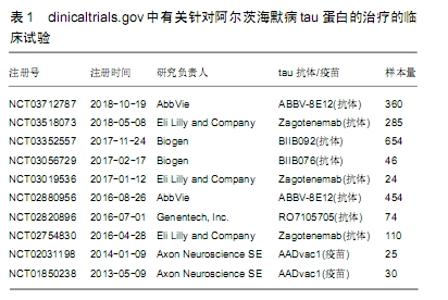
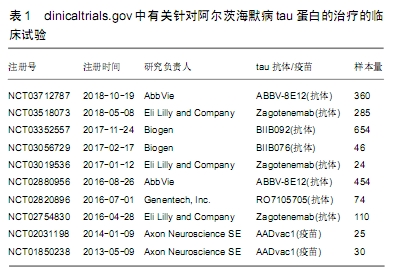
2.1 tau蛋白假说 2.1.1 tau蛋白产生的生物学过程 神经元纤维缠结的异常沉积是阿尔茨海默病等神经退行性疾病的特征常见的病理现象,而神经元纤维缠结的主要成分为成对螺旋丝,tau蛋白是组成成对螺旋丝和神经元纤维缠结的惟一必需成分。神经元纤维缠结的沉积与阿尔茨海默病中的认知衰退密切相关[24-25],这些都与tau蛋白的病理变化相关,这表明tau在神经变性中起着至关重要的作用。 tau蛋白广泛分布于中枢神经系统的神经元中,是一种微管相关的蛋白质,其可调节微管蛋白的稳定性。人tau基因位于17号染色体。在成人的大脑中存在6种tau异构体,均为伴有或不伴有外显子2,3和10信使mRNA替代拼接的结果。外显子10包含微管结合区,外显子10的插入可提供4个重复(4R)tau等异构体,而3个重复(3R)tau异构体则不需要外显子10参与。成年人的大脑表达了3R和4R tau等形式[26],在正常的生理条件下,它们主要位于成年神经元轴突。tau假说认为阿尔茨海默病的主要致病物质原因是tau。如果是在神经元细胞体中形成的,这些病理内含物被称为神经原纤维缠结。这些发现表明,对tau的错误分类可能会导致tau病理变化[27]。在微管蛋白C末端结合位点附近发生重复的疾病,导致了微管结合的能力减弱,并削弱了微管结合微管的能力,提示微管调节损伤。局部错误定位的tau也会引起微管调控的损伤。这些tau像上面描述的那样被超磷酸化,并形成了沉积和纤维种子。此外,与正常的tau蛋白相比,突变体和超磷酸化蛋白的稳定性增加了[28]。稳定的tau蛋白与丝状的肌动蛋白的异常相互作用导致了肌动蛋白的不稳定、突触的损伤、线粒体的完整性缺陷[29-31]。因此,tau蛋白病变会对细胞运输系统、细胞骨架系统、信号传导系统以及线粒体完整性等造成广泛的损害。因此推测在一部分脑细胞中,tau会聚集成一组,传播到其他区域,从而导致神经退化和疾病的发生。 磷酸化tau蛋白分为可溶性的磷酸化tau和不可溶性的以配对螺旋丝结构存在的成对螺旋丝两种。磷酸化tau与微管蛋白竞争结合正常tau蛋白及其他微管相关蛋白,可导致微管解聚,在神经元内形成成对螺旋丝,影响tau蛋白的正常生理功能[8]。 在阿尔茨海默病患者大脑中,纤维缠结普遍存在,磷酸化tau蛋白增加了数倍[32],说明磷酸化tau蛋白聚积对突触和神经元的毒性作用。可以肯定的是患者认知障碍的程度与神经元纤维缠结的密度正相关,这点与可溶性Aβ的作用相似[33]。与Aβ淀粉病变相比,tau病变与痴呆的相关性更强,因此,当认知障碍变得明显时,在疾病的后期阶段,通过清除tau蛋白,可以获得更大的临床疗效。 2.1.2 tau蛋白磷酸化与阿尔茨海默病的关系 阿尔茨海默病患者大脑中tau蛋白总量多于正常人,且正常tau蛋白减少而异常过度磷酸化tau蛋白大量增加。阿尔茨海默病患者大脑中可出现3种形式的tau蛋白:可溶型非磷酸化tau蛋白、可溶型磷酸化tau蛋白和不可溶性的双股螺旋丝聚合tau蛋白。磷酸化tau蛋白是神经元纤维缠结的主要成分。正常老年人颞叶和其他神经系统变性病变时也可见神经元纤维缠结,但阿尔茨海默病患者tau蛋白过度磷酸化后,遍及整个大脑,常见于海马和内嗅皮质,与突触损伤和认知减退有关。磷酸化tau蛋白通过自身的的增多减慢Aβ增长形成一个负反馈环,从而阻碍Aβ增多。随着疾病进展到晚期,磷酸化tau继续形成双股螺旋丝,与此同时,Aβ斑块沉积进入平台期。 tau蛋白的生理作用是稳定微管,微管在阿尔茨海默病、额颞叶痴呆和其他变性病的发病机制中受到破坏。在阿尔茨海默病的发病机理中,神经内部的tau蛋白积聚首先出现在内溴皮质,随后在海马体和新皮质中[34],这一过程强调了tau病理学的传播机制,目前还不清楚。有研究假设tau可以一种类似于灵长类的朊蛋白病的方式从神经元扩散到神经元[35]。最近,在直接注射到小鼠体内,或从人类表达tau蛋白神经元到缺乏人类tau蛋白表达的神经细胞时[36],已经显示出了tau蛋白播散的病理特点,这导致了tau病变的后续进展。 tau蛋白是一种微管结合蛋白,但与微管分离并在神经元中聚集,它在多个位点被高度磷酸化后,导致微管装配和功能的损伤。越来越多的证据表明这2个特征在阿尔茨海默病中是紧密相关的。在转染tau基因的SH-SY5Y细胞中,tau蛋白与微管结合,增强微管的稳定性,有时诱导微管成束。成束可能是受tau蛋白影响,是微管稳定性增强的结果[37]。 超过20年的遗传和分子研究所产生的压倒性证据支持淀粉样级联的假说这种假设,即Aβ沉积是形成阿尔茨海默病的基础;然而在淀粉样蛋白前体转基因小鼠中,认知损伤是必须在tau蛋白存在下[38]。tau蛋白沉积的程度与阿尔茨海默病认知下降的相关程度质疑了Aβ沉积作为触发tau发病机理的作用。 tau蛋白异常过度磷酸化并形成成对螺旋丝,被认为是阿尔茨海默病神经元退化的基础。阿尔茨海默病早期的脑损伤可能是可逆的。高度磷酸化的tau蛋白介导了阿尔茨海默病时的轴突运输障碍[39]。tau蛋白的异常磷酸化成为目前阿尔茨海默病研究的热点。tau蛋白磷酸化程度取决于体内多种特异蛋白激酶的磷酸化和蛋白磷酸酶去磷酸化之间的相互作用。 2.2 tau蛋白通过Aβ途径诱发阿尔茨海默病 β-淀粉蛋白级联假说提出脑内的Aβ过度沉积,由于Aβ清除减少和Aβ生成过多造成的,是一系列致病事件的起始因子,包括神经元纤维缠结、氧化应激、神经炎症、突触功能障碍和神经元丧失,最终导致阿尔茨海默病痴呆。淀粉样斑块的形成由Aβ异常沉积导致,这被认为是Aβ生成与清除之间的动态平衡被打破造成的。 2.2.1 Aβ产生的生物学过程 淀粉样蛋白前体基因突变可以增加Aβ的产生和沉积,并选择性的增加Aβ42的水平。迄今为止,已经明确至少20个位点的淀粉样蛋白前体基因突变参与家族性早发性阿尔茨海默病的发病过程[40-41]。β分泌酶和γ分泌酶连续分解淀粉样蛋白前体,致淀粉样蛋白前体序列断裂形成Aβ[42]。淀粉样蛋白前体和Aβ在神经元和突触的发育过程中发挥营养作用。Aβ可能存在多种形式,包括单体、寡聚体和原纤维,而只有寡聚体被认为具有更大的神经毒性。Aβ单体和淀粉样蛋白前体作用涉及神经系统的发育和可塑性,并促进认知能力和记忆力。不仅仅是Aβ肽段(Aβ40和Aβ42)影响神经功能,而且这种Aβ肽段的寡聚体(2-12个小肽段)实际上对大脑功能的损害比老年斑的作用更大。Aβ肽段也可以生长成纤维,将自己排列成折叠的薄片,形成一种不溶性的淀粉样蛋白。表明Aβ寡聚体在神经元功能障碍和阿尔茨海默病发展方面起着关键作用。 γ分泌酶分解淀粉样蛋白前体产生Aβ42和Aβ40,淀粉样蛋白前体在高尔基体内形成Aβ42,在内质网形成Aβ40。正常老年人和阿尔茨海默病患者脑内均存在Aβ40,Aβ42主要位于阿尔茨海默病患者脑内[43-46]。细胞产生的Aβ40远比Aβ42多,但Aβ42更易沉积,最终形成β淀粉样蛋白,是老年斑的主要组成成分,Aβ42的寡聚体和原纤维形式还直接或间接对神经元产生毒性作用,因此γ-分泌酶与阿尔茨海默病的发病存在密切的关系。从Aβ单体聚合而成的Aβ寡聚体被认为是阿尔茨海默病的最初起因,与认知功能障碍有直接关系[47-51]。 2.2.2 tau蛋白是Aβ级联反应的目标 Aβ在脑内沉积被普遍认为是阿尔茨海默病病理改变的中心环节。目前已知家族性早发型阿尔茨海默病与编码Aβ代谢的基因突变密切相关[1]。Aβ通过对敏感神经细胞的毒性,促进tau超磷酸化,扰乱蛋白质组活动[52],触发突触功能障碍[53],最终促进阿尔茨海默病病理进程。在β淀粉样级联假说中,tau被认为是Aβ的主要下游目标之一,并产生神经毒性。 Aβ加速神经细胞的神经退化,而不是在缺乏tau蛋白的神经元中[54]。此外,在突变转基因小鼠体内的tau损耗阻止了学习和记忆障碍的发展[55]。 2.3 tau蛋白、Aβ和阿尔茨海默病的相互关系 阿尔茨海默病的病因和发病机制尚不完全明确,Aβ的生成和清除失调是可能是阿尔茨海默病发病的起始因素[56]。阿尔茨海默病的β淀粉蛋白级联假说提出脑内的Aβ沉积,由生产和清除之间的不平衡引起,是一系列致病事件的起始因子,包括神经原纤维缠结、氧化应激、神经炎症、突触功能障碍和神经元丧失,最终导致阿尔茨海默病痴呆。Aβ通过增加糖原合酶激酶3活性来促进生成神经元纤维缠结的生成,从而导致tau蛋白的超磷酸化,超磷酸化的tau开始自行组装形成成对螺旋丝和神经元纤维缠结,而tau蛋白的超磷酸化则会促进Aβ聚集。Aβ斑块,一种可溶解的低聚物,和神经元纤维缠结干扰正常的神经元细胞功能,干扰神经连接的突触信号传导,异常蛋白质的累积会导致神经损伤进展。目前研究发现,Aβ和tau蛋白存在相互作用,tau蛋白可加剧Aβ导致的神经元毒性,进而导致记忆损害和学习障碍[57]。 超磷酸化tau蛋白通过自身的的增多减慢Aβ增长形成一个负反馈环[58],从而阻碍Aβ增多。随着疾病进展到晚期,超磷酸化tau继续形成双股螺旋丝,与此同时,Aβ斑块沉积进入平台期。可溶性的Aβ寡聚体,而不是空斑或可溶性Aβ单体,已经出现并继续存在,吸引作为主要的有毒形式Aβ注意。这些寡聚体可能会随着Aβ斑块的形成而不断积累,它们可能会在解释Aβ和超磷酸化tau之间的联系方面建立一个关键的联系[59]。神经元纤维缠结在大脑中形成后,Aβ斑块的清除并不影响神经元纤维缠结的消除,但是早期干预可以预防超磷酸化tau的发展[60]。 大量研究结果证实,磷酸化tau蛋白与Aβ寡聚体协同产生神经毒性作用,导致阿尔茨海默病的发病。Aβ需要借助tau蛋白磷酸化后形成的沉积物产生毒性作用[57,61]。Aβ作用于缺乏内源性tau蛋白表达的海马神经元细胞,不会引起细胞的退行性改变[54]。另有动物模型研究提示任何有效的干预措施都应同时减少Aβ和tau蛋白的产生,阿尔茨海默病小鼠的认知功能才能改善,仅降Aβ低寡聚体的水平,不能缓解阿尔茨海默病小鼠的学习记忆障碍[62]。 2.3.1 Aβ促进tau的过度磷酸化 Aβ寡聚体水平已经被证明直接诱导糖原合酶激酶3β活化和tau蛋白磷酸化[63],有报道说被动免疫降低Aβ寡聚体的水平,已经有证明了Aβ会诱导在培养的隔膜中胆碱能神经元产生tau磷酸化和毒性Aβ纤维丝加速了在一种转基因老鼠中异常磷酸化的神经原纤维缠结[64]。最近有研究证实,Aβ寡聚体沉积通过在树突里内源性tau错误的分类导致了异常的tau磷酸化和形态学的改变。从阿尔茨海默病大脑中分离出来的自然产生的Aβ二聚体就足以诱导阿尔茨海默病-tau磷酸化,从而导致神经营养不良[65]。特异激活τau激酶的Aβ寡聚体,导致tau蛋白过磷酸化,Aβ寡聚体也是细胞蛋白酶的强力催化剂,并导致tau蛋白裂解和聚合。过度磷酸化的tau和截短的tau都容易在神经元中发生自聚集和聚合。 目前的证据表明,tau蛋白的超磷酸化和聚合是一种阿尔茨海默病中驱动神经退化的重要途径,Aβ沉积作为tau超磷酸化,聚合以及受影响的神经元的后续退化的备用触发条件,在3xg-AD(APPswe/PS1/Tauvlw)小鼠中,只有在早期的,而不是晚期的磷酸化的人类tau蛋白可被一种抗体注射到大脑中抗抗体所清除[66]。 tau蛋白对Aβ的毒性也起到调节作用,Aβ和tau蛋白存在相互作用,tau蛋白可加剧Aβ导致的神经元毒性、微管丢失、神经炎症变化等致病效应,进而导致记忆损害和学习障碍。 2.3.2 Aβ调节tau蛋白的可能途径 tau-FcyⅡb-Aβ途径:一种假说认为非受体型酪氨酸蛋白激酶家族成员Fcy是tau蛋白和Aβ的连接枢纽之一[67-68]。KAM等[69]研究了Aβ和FcyIIb之间的相互作用是否可以调节神经元内的tau蛋白的磷酸化作用。研究表明,在阿尔茨海默病大脑神经元中,FcgRIIb在酪氨酸273上被磷酸化,而这个磷酸化的过程则需要包含(SHIP2,INPPL1)的SH2增加PtdIns(3,4)P2的水平,用于tau蛋白超磷酸化。将Aβ淀粉样蛋白添加到大鼠神经元中,导致tau蛋白被过度磷酸化。然而,从神经细胞中除去FcyⅡb受体,阻止了Aβ淀粉样蛋白这一效应。当Aβ与FcIIb受体结合时,受体就会被磷酸化。这反过来又引发了一系列的磷酸化事件,最终导致了一种分子水平变化,在神经元内部传递来自细胞受体的信号—称为SHIP2,会增加tau蛋白磷酸化。减少SHIP2的活动或数量的效果,表现在阿尔茨海默症的症状上,就是减少了它们神经元中的tau蛋白过度磷酸化,并将其记忆恢复到正常水平。在3xTg-AD小鼠体内的缺乏FcyⅡb对任何一种蛋白质都会产生抑制作用,都表明了在Aβ诱导的tau病理中,FcgRIIb-SHIP2轴的重要性。KAM等的研究结果也为阿尔茨海默症的治疗方法提供新方向[53]。 tau-糖原合酶激酶3-Aβ途径:糖原合酶激酶3是Aβ调节tau蛋白磷酸化的重要激酶之一[70],tau-糖原合酶激酶3-Aβ途径也是传统的比较公认的Aβ调节tau蛋白的重要途径。糖原合酶激酶3对Aβ和tau蛋白产生具有双向调节作用[39,71]。糖原合酶激酶3分为糖原合酶激酶3α和糖原合酶激酶3β两型,其中糖原合酶激酶3β在调控Aβ生成和tau蛋白磷酸化的过程中发挥主要作用[72],并在中枢神经系统大量表达。 以Aβ疫苗免疫可减少Aβ和tau两种病变,分析可能是由于主动和被动免疫产生的Aβ抗体生成导致Aβ减少;而tau蛋白生成减少是由于间接机制,源于 Aβ生成减少导致更少的tau激酶激活,因此导致tau磷酸化降低。既往研究结果提示,Aβ还与许多受体结合,包括阿尔法尼古丁乙酰胆碱受体、N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体、高级糖基末端的受体产物、Aβ-乙醇脱氢酶、Ephrin型B2受体、细胞朊蛋白、配对免疫类蛋白受体B等[71]。尽管这些受体被证明是对Aβ神经毒性负责的,尤其是在阿尔茨海默病小鼠记忆损伤中,但它们作为神经元受体,在a7和N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体位点显示对Aβ诱导的tau病理中的作用是有限的[73]。 2.3.3 tau蛋白和Aβ在阿尔茨海默病发病中的作用 Aβ与tau蛋白都在阿尔茨海默病的发病中起着至关重要的作用,含有Aβ细胞外斑块和超磷化tau蛋白形成的细胞内神经原纤维缠结是阿尔茨海默病的两大重要神经病理特征,但对两者相互之间的关系及具体作用机制尚不明了。目前公认的假说,Aβ在阿尔茨海默病的发病机制中起着核心作用,包括记忆损伤、突触丢失和神经元细胞死亡。但Aβ诱导tau磷酸化引发记忆缺陷中的机理仍然不明确。两者在阿尔茨海默病发病过程中都与线粒体的损伤与突触功能障碍密切相关,同时伴有自身构象的变化。在阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织中发现,Aβ和磷酸化tau可共同聚集在神经元突触终端[74],以及营养不良的树突和轴突中[75]。tau蛋白可与Aβ结合形成可溶性复合体,生成稳定的复合物[76]。复合物通过激活-糖原合酶激酶3β前体,使糖原合酶激酶3β活化,诱导tau蛋白磷酸化,同时加速Aβ沉积[77]。这种协同作用在动物水平也得到了证实[78]。有研究表明散发性早老性痴呆发病机制中tau蛋白是不依赖Aβ启动而独立发挥致病作用的,和Aβ为两条独立的致病途径[39,79]。 2.4 tau蛋白与阿尔茨海默病诊治进展 目前还没有治愈阿尔茨海默病这种疾病的方法,药物研发是一个费用巨大且耗时的过程。在过去的14年里,尽管科学家和制药公司积极努力,并没有新药物问世。迄今为止,已经有大约400项阿尔茨海默病药物临床试验以失败告终,同时已经被批准用于临床的药物的疗效仍然难以令人满意,可用的治疗方法只是针对症状,而且随着阿尔茨海默病病情的进展,疗效也会下降。目前阿尔茨海默病药物研发的进程不顺利主要是以下几个原因:①阿尔茨海默病的发病机制只是假说,许多关键机制都仍不清楚;②还没有非常标准的动物模型用于阿尔茨海默病的相关研究;③治疗的靶点多关注于Aβ,而非tau蛋白;④预防性药物治疗的使用时机不准确,不能起到阻止病情进展的效果;⑤药物缺乏有效载体,比如难以通过血脑屏障,并且易产生抗药性等。 基于tau蛋白、Aβ和阿尔茨海默病的相互关系的治疗策略,期待通过减少脑中的Aβ含量,不触发Aβ级联反应,减少tau的过度磷酸化,从而阻止病变的进一步发展,但近20年来,包括针对Aβ的主动免疫接种和针对抗-Aβ抗体的被动免疫接种的免疫疗法进行了研究。ROSENBERG等[80]研究首次发现Aβ42全肽段基因疫苗主动免疫3xTg-AD小鼠会导致海马Aβ40/Aβ42比值下降和淀粉样斑块减少,与此同时Aβ42全肽段基因疫苗主动免也显著减少3xTg-AD鼠大脑的tau蛋白的表达水平。然而,研制出来Aβ疫苗或Aβ抗体没有一种能够成功地改善Ⅲ期临床试验患者的记忆缺陷。投入临床试验的相关药物未显示出明显疗效。 鉴于针对Aβ治疗靶点的各项治疗措施均失败,因而推测Aβ仅是一种中和病理因子的、具有保护作用的螯合剂,阿尔茨海默病的病理学是触发淀粉样蛋白前体的代谢障碍,阿尔茨海默病的形成和进展更主要与tau蛋白相关,据此推测tau蛋白相关治疗可能比Aβ相关治疗在改善阿尔茨海默病的临床表现等方面表现更优。因此近年来,tau蛋白相关的免疫阿尔茨海默病治疗研究在受到了广泛的关注及发展。tau蛋白已成为阿尔茨海默病及tau蛋白相关疾变性病的重要治疗靶点。虽然目前阿尔茨海默病还没有有效的疗法,但许多针对tau蛋白的新治疗方法正在临床试验中,见表1。一些针对阿尔茨海默病疾病修饰疗法目的是对病理tau蛋白的寡聚体产生、聚集和沉积进行阻止、减慢或改变其构型。 "
| [1] ASHLEY S, BRADBURN S, MURGATROYD C. A meta-analysis of peripheral tocopherol levels in age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease. Nutr Neurosci. 2019. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2019.1681066. [2] Alzheimer’s Disease International. World Alzheimer Report 2015: The Global Impact of Dementia. An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Costand Trends. London: Alzheimer’s Disease International, 2015 [2019-03-07]. https://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2015.pdf. [3] MORTON RE, ST JOHN PD, TYAS SL. Migraine and the risk of all-cause dementia, Alzheimer's disease, and vascular dementia: A prospective cohort study in community-dwelling older adults. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2019;34(11):1667-1676. [4] STOCKER H, NABERS A, PERNA L, et al. Prediction of Alzheimer's disease diagnosis within 14 years through Aβ misfolding in blood plasma compared to APOE4 status, and other risk factors. Alzheimers Dement. 2019. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2019.08.189. [5] XU W, TAN L, WANG HF, et al. Education and Risk of Dementia: Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(5):3113-3123. [6] WASHINGTON PM, VILLAPOL S, BURNS MP. Polypathology and dementia after brain trauma: Does brain injury trigger distinct neurodegenerative diseases, or should they be classified together as traumatic encephalopathy?. Exp Neurol. 2016;275 Pt 3(0 3):381-388. [7] MASTERS CL, SIMMS G, WEINMAN NA, et al. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985;82(12):4245-4249. [8] LEE VM, GOEDERT M, TROJANOWSKI JQ. Neurodegenerative tauopathies. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:1121-1159. [9] SEABROOK TJ, THOMAS K, JIANG L, et al. Dendrimeric Abeta1-15 is an effective immunogen in wildtype and APP-tg mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28(6):813-823. [10] BOHRMANN B, BAUMANN K, BENZ J, et al. Gantenerumab: a novel human anti-Aβ antibody demonstrates sustained cerebral amyloid-β binding and elicits cell-mediated removal of human amyloid-β. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;28(1):49-69. [11] KIM SH, CARNEY DF, HAMMER CH, et al. Nucleated cell killing by complement: effects of C5b-9 channel size and extracellular Ca2+ on the lytic process. J Immunol. 1987;138(5):1530-1536. [12] ROGERS J, COOPER NR, WEBSTER S, et al. Complement activation by beta-amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992; 89(21):10016-10020. [13] YANG LB, LI R, MERI S, et al. Deficiency of complement defense protein CD59 may contribute to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 2000;20(20):7505-7509. [14] YANG L, LINDHOLM K, KONISHI Y, et al. Target depletion of distinct tumor necrosis factor receptor subtypes reveals hippocampal neuron death and survival through different signal transduction pathways. J Neurosci. 2002;22(8):3025-3032. [15] SHEN Y, YANG L, LI R. What does complement do in Alzheimer's disease? Old molecules with new insights. Transl Neurodegener. 2013;2(1):21. [16] LIAN H, YANG L, COLE A, et al. NFκB-activated astroglial release of complement C3 compromises neuronal morphology and function associated with Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 2015;85(1):101-115. [17] KRSTIC D, KNUESEL I. Deciphering the mechanism underlying late-onset Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013;9(1):25-34. [18] MCGEER PL, MCGEER EG. The amyloid cascade-inflammatory hypothesis of Alzheimer disease: implications for therapy. Acta Neuropathol. 2013;126(4):479-497. [19] SPIRES-JONES T, KNAFO S. Spines, plasticity, and cognition in Alzheimer's model mice. Neural Plast. 2012;2012:319836. [20] TOSUN D, JOSHI S, Weiner MW; Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Neuroimaging predictors of brain amyloidosis in mild cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol. 2013;74(2):188-198. [21] SELKOE DJ. Alzheimer's disease is a synaptic failure. Science. 2002; 298(5594):789-791. [22] VOSSEL KA, ZHANG K, BRODBECK J, et al. Tau reduction prevents Abeta-induced defects in axonal transport. Science. 2010;330(6001): 198. [23] SCHMITT K, GRIMM A, KAZMIERCZAK A, et al. Insights into mitochondrial dysfunction: aging, amyloid-β, and tau-A deleterious trio. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012;16(12):1456-1466. [24] YAMADA M. [Senile Dementia of the Neurofibrillary Tangle Type (SD-NFT)]. Brain Nerve. 2018;70(5):533-541. [25] HUBER CM, YEE C, MAY T, DHANALA A, MITCHELL CS. Cognitive Decline in Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease: Amyloid-Beta versus Tauopathy. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;61(1):265-281. [26] IQBAL K, LIU F, GONG CX. Tau and neurodegenerative disease: the story so far. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12(1):15-27. [27] ZEMPEL H, MANDELKOW E. Lost after translation: missorting of Tau protein and consequences for Alzheimer disease. Trends Neurosci. 2014;37(12):721-732. [28] YAMADA K, PATEL TK, HOCHGRÄFE K, et al. Analysis of in vivo turnover of tau in a mouse model of tauopathy. Mol Neurodegener. 2015;10:55. [29] CABRALES FONTELA Y, KADAVATH H, BIERNAT J, et al. Multivalent cross-linking of actin filaments and microtubules through the microtubule-associated protein Tau. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1981. [30] ZHOU L, MCINNES J, WIERDA K, et al. Tau association with synaptic vesicles causes presynaptic dysfunction. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15295. [31] BARDAI FH, WANG L, MUTREJA Y, et al. A Conserved Cytoskeletal Signaling Cascade Mediates Neurotoxicity of FTDP-17 Tau Mutations In Vivo. J Neurosci. 2018;38(1):108-119. [32] MATSUO ES, SHIN RW, BILLINGSLEY ML, et al. Biopsy-derived adult human brain tau is phosphorylated at many of the same sites as Alzheimer's disease paired helical filament tau. Neuron. 1994;13(4): 989-1002. [33] GÓMEZ-ISLA T, HOLLISTER R, WEST H, et al. Neuronal loss correlates with but exceeds neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1997;41(1):17-24. [34] GOEDERT M, KLUG A, CROWTHER RA. Tau protein, the paired helical filament and Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006; 9(3 Suppl):195-207. [35] DE CALIGNON A, POLYDORO M, SUÁREZ-CALVET M, et al. Propagation of tau pathology in a model of early Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 2012;73(4):685-697. [36] CLAVAGUERA F, BOLMONT T, CROWTHER RA, et al. Transmission and spreading of tauopathy in transgenic mouse brain. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(7):909-913. [37] LI B, CHOHAN MO, GRUNDKE-IQBAL I, et al. Disruption of microtubule network by Alzheimer abnormally hyperphosphorylated tau. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;113(5):501-511. [38] AMNIAI L, BARBIER P, SILLEN A, et al. Alzheimer disease specific phosphoepitopes of Tau interfere with assembly of tubulin but not binding to microtubules. FASEB J. 2009;23(4):1146-1152. [39] SMALL SA, DUFF K. Linking Abeta and tau in late-onset Alzheimer's disease: a dual pathway hypothesis. Neuron. 2008;60(4):534-542. [40] MCGOWAN E, ERIKSEN J, HUTTON M. A decade of modeling Alzheimer's disease in transgenic mice. Trends Genet. 2006;22(5): 281-289. [41] ZHANG YW, THOMPSON R, ZHANG H, et al. APP processing in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Brain. 2011;4:3. [42] SCHONROCK N, MATAMALES M, ITTNER LM, et al. MicroRNA networks surrounding APP and amyloid-β metabolism--implications for Alzheimer's disease. Exp Neurol. 2012;235(2):447-454. [43] BENILOVA I, KARRAN E, DE STROOPER B. The toxic Aβ oligomer and Alzheimer's disease: an emperor in need of clothes. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15(3):349-357. [44] ZHENG YL, KESAVAPANY S, GRAVELL M, et al. A Cdk5 inhibitory peptide reduces tau hyperphosphorylation and apoptosis in neurons. EMBO J. 2005;24(1):209-220. [45] DEBELJUH N, BARROW CJ, HENDERSON L, et al. Structure inducing ionic liquids-enhancement of alpha helicity in the Abeta(1-40) peptide from Alzheimer's disease. Chem Commun (Camb). 2011;47(22):6371-6373. [46] GARZON-RODRIGUEZ W, SEPULVEDA-BECERRA M, MILTON S, et al. Soluble amyloid Abeta-(1-40) exists as a stable dimer at low concentrations. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(34):21037-21044. [47] CLEARY JP, WALSH DM, HOFMEISTER JJ, et al. Natural oligomers of the amyloid-beta protein specifically disrupt cognitive function. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(1):79-84. [48] CHIANG ACA, FOWLER SW, REDDY R, et al. Discrete Pools of Oligomeric Amyloid-β Track with Spatial Learning Deficits in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer Amyloidosis. Am J Pathol. 2018;188(3):739-756. [49] GOÑI F, MARTÁ-ARIZA M, HERLINE K, et al. Anti-β-sheet conformation monoclonal antibody reduces tau and Aβ oligomer pathology in an Alzheimer's disease model. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2018;10(1):10. [50] RUSBRIDGE C, SALGUERO FJ, DAVID MA, et al. An Aged Canid with Behavioral Deficits Exhibits Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid Amyloid Beta Oligomers. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:7. [51] SUN L, ZHONG Y, GUI J, et al. A hydrogel biosensor for high selective and sensitive detection of amyloid-beta oligomers. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:843-856. [52] LAFERLA FM, GREEN KN, ODDO S. Intracellular amyloid-beta in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(7):499-509. [53] KAM TI, GWON Y, JUNG YK. Amyloid beta receptors responsible for neurotoxicity and cellular defects in Alzheimer's disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71(24):4803-4813. [54] RAPOPORT M, DAWSON HN, BINDER LI, et al. Tau is essential to beta -amyloid-induced neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002; 99(9):6364-6369. [55] ROBERSON ED, SCEARCE-LEVIE K, PALOP JJ, et al. Reducing endogenous tau ameliorates amyloid beta-induced deficits in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Science. 2007;316(5825):750-754. [56] SEINO Y, KAWARABAYASHI T, WAKASAYA Y, et al. Amyloid β accelerates phosphorylation of tau and neurofibrillary tangle formation in an amyloid precursor protein and tau double-transgenic mouse model. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88(16):3547-3554. [57] NUSSBAUM JM, SCHILLING S, CYNIS H, et al. Prion-like behaviour and tau-dependent cytotoxicity of pyroglutamylated amyloid-β. Nature. 2012;485(7400):651-655. [58] SUN L, WANG X, LIU S, et al. Bilateral injection of isoproterenol into hippocampus induces Alzheimer-like hyperphosphorylation of tau and spatial memory deficit in rat. FEBS Lett. 2005;579(1):251-258. [59] XU G, GONZALES V, BORCHELT DR. Abeta deposition does not cause the aggregation of endogenous tau in transgenic mice. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2002;16(3):196-201. [60] ODDO S, CACCAMO A, SHEPHERD JD, et al. Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease with plaques and tangles: intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron. 2003;39(3):409-421. [61] AMADORO G, CORSETTI V, CIOTTI MT, et al. Endogenous Aβ causes cell death via early tau hyperphosphorylation. Neurobiol Aging. 2011;32(6):969-990. [62] ODDO S, VASILEVKO V, CACCAMO A, et al. Reduction of soluble Abeta and tau, but not soluble Abeta alone, ameliorates cognitive decline in transgenic mice with plaques and tangles. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(51):39413-39423. [63] ZEMPEL H, THIES E, MANDELKOW E, et al. Abeta oligomers cause localized Ca(2+) elevation, missorting of endogenous Tau into dendrites, Tau phosphorylation, and destruction of microtubules and spines. J Neurosci. 2010;30(36):11938-11950. [64] JIN M, SHEPARDSON N, YANG T, et al. Soluble amyloid beta-protein dimers isolated from Alzheimer cortex directly induce Tau hyperphosphorylation and neuritic degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(14):5819-5824. [65] SHIPTON OA, LEITZ JR, DWORZAK J, et al. Tau protein is required for amyloid {beta}-induced impairment of hippocampal long-term potentiation. J Neurosci. 2011;31(5):1688-1692. [66] BOUTAJANGOUT A, QUARTERMAIN D, SIGURDSSON EM. Immunotherapy targeting pathological tau prevents cognitive decline in a new tangle mouse model. J Neurosci. 2010;30(49):16559-16566. [67] ITTNER LM, KE YD, DELERUE F, et al. Dendritic function of tau mediates amyloid-beta toxicity in Alzheimer's disease mouse models. Cell. 2010;142(3):387-397. [68] HAASS C, MANDELKOW E. Fyn-tau-amyloid: a toxic triad. Cell. 2010; 142(3):356-358. [69] KAM TI, SONG S, GWON Y, et al. FcγRIIb mediates amyloid-β neurotoxicity and memory impairment in Alzheimer's disease. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(7):2791-2802. [70] RESENDE R, FERREIRO E, PEREIRA C, et al. ER stress is involved in Abeta-induced GSK-3beta activation and tau phosphorylation. J Neurosci Res. 2008;86(9):2091-2099. [71] KIM T, VIDAL GS, DJURISIC M, et al. Human LilrB2 is a β-amyloid receptor and its murine homolog PirB regulates synaptic plasticity in an Alzheimer's model. Science. 2013;341(6152):1399-1404. [72] TERWEL D, MUYLLAERT D, DEWACHTER I, et al. Amyloid activates GSK-3beta to aggravate neuronal tauopathy in bigenic mice. Am J Pathol. 2008;172(3):786-798. [73] STANCU IC, VASCONCELOS B, TERWEL D, et al. Models of β-amyloid induced Tau-pathology: the long and "folded" road to understand the mechanism. Mol Neurodegener. 2014;9:51. [74] FEIN JA, SOKOLOW S, MILLER CA, et al. Co-localization of amyloid beta and tau pathology in Alzheimer's disease synaptosomes. Am J Pathol. 2008;172(6):1683-1692. [75] TAKAHASHI RH, CAPETILLO-ZARATE E, LIN MT, et al. Co-occurrence of Alzheimer's disease ß-amyloid and τ pathologies at synapses. Neurobiol Aging. 2010;31(7):1145-1152. [76] MILLER Y, MA B, NUSSINOV R. Synergistic interactions between repeats in tau protein and Aβ amyloids may be responsible for accelerated aggregation via polymorphic states. Biochemistry. 2011;50(23):5172-5181. [77] GUO JP, ARAI T, MIKLOSSY J, et al. Abeta and tau form soluble complexes that may promote self aggregation of both into the insoluble forms observed in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(6):1953-1958. [78] IIJIMA K, GATT A, IIJIMA-ANDO K. Tau Ser262 phosphorylation is critical for Abeta42-induced tau toxicity in a transgenic Drosophila model of Alzheimer's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19(15): 2947-2957. [79] YOSHIYAMA Y, LEE VM, TROJANOWSKI JQ. Therapeutic strategies for tau mediated neurodegeneration. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013;84(7):784-795. [80] ROSENBERG RN, FU M, LAMBRACHT-WASHINGTON D. Active full-length DNA Aβ42 immunization in 3xTg-AD mice reduces not only amyloid deposition but also tau pathology. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2018; 10(1):115. [81] JADHAV S, AVILA J, SCHÖLL M, et al. A walk through tau therapeutic strategies. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7(1):22. [82] VITALE F, GILIBERTO L, RUIZ S, et al. Anti-tau conformational scFv MC1 antibody efficiently reduces pathological tau species in adult JNPL3 mice. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018;6(1):82. [83] NOVAK P, SCHMIDT R, KONTSEKOVA E, et al. FUNDAMANT: an interventional 72-week phase 1 follow-up study of AADvac1, an active immunotherapy against tau protein pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2018;10(1):108. |
| [1] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [2] | Li Ying, Guan Hantian, Zhou Yu. Semantic memory impairment and neuroregulation in patients with mild cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5236-5242. |
| [3] |
Mou Zichao, Wang Dan, Wang Xiaoyan, Li Siyu, Wang Zhiqiang, Wang Qingsong.
Oral simvastatin for 3 continuous months improves learning and memory ability of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4190-4195. |
| [4] | Liu Dongqi1, Li Rongmei1, Zhang Meiqi1,Chen Yanyan1, Zhang Haiping2 . Meta-analysis of the effect of aerobic exercise on mild cognitive impairment in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5727-5731. |
| [5] | Gong Jiao, Liu Ming. Human induced pluripotent stem cell transplantation for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonatal mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5322-5327. |
| [6] | Guo Bo, Liu Jia, Cui Xiaolan, Shi Han, Zhang Sheyi, Wang Jia, Shan Xia, Wang Yizhong. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells combined with immunotherapy for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2016-2021. |
| [7] | Li Sen, Xu Wan-peng. Meta-analysis of statins for treatment of vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(50): 8769-8774. |
| [8] | Liu Yin, Tian Jing. Monoclonal antibody for treatment of multiple myeloma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(20): 3746-3755. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

