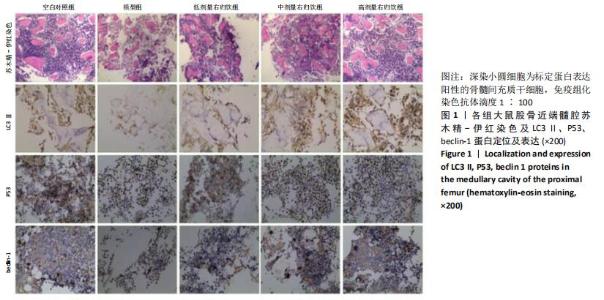
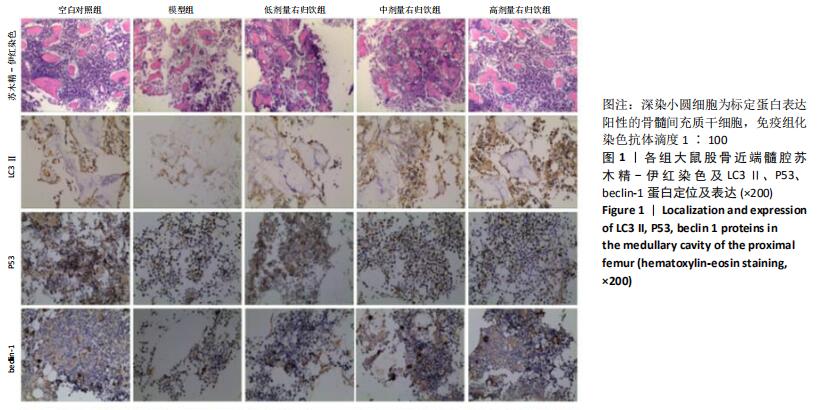
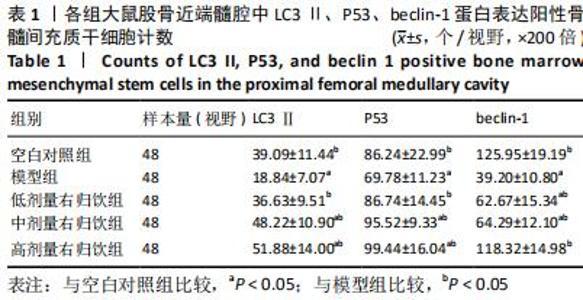
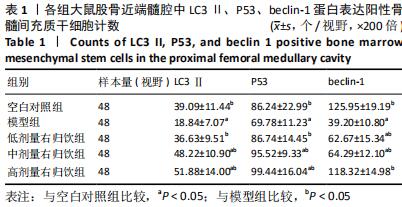
[1] NAKASHIMA Y, YAMAMOTO T, FUKUSHI JI, et al. Transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy for avascular necrosis of the femoral head after unstable slipped capital femoral epiphysis: 10-year clinical results. J Orthop Sci. 2016;21(6):831-835.
[2] YOON BH, JONES LC, CHEN CH, et al. Etiologic Classification Criteria of ARCO on Femoral Head Osteonecrosis Part 1: Glucocorticoid-Associated Osteonecrosis. J Arthroplasty. 2019; 34(1):163-168.
[3] HAN Y, ZHANG L, XING Y, et al. Autophagy relieves the function inhibition and apoptosis‑promoting effects on osteoblast induced by glucocorticoid. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(2):800-808.
[4] 刘锌,金翔,杜斌,等.右归饮加减方对兔激素性股骨头坏死的干预作用及其机制研究[J].江苏中医药,2019,51(9):81-85.
[5] 刘锌,杜斌,孙光权,等.带缝匠肌肌蒂髂骨瓣移植配合中药治疗早中期股骨头坏死近期疗效观察[J].山东中医杂志,2016,35(5): 409-414.
[6] JIA J, YAO W, GUAN M, et al. Glucocorticoid dose determines osteocyte cell fate. FASEB J. 2011;25(10):3366-3376.
[7] TRACHANA V, PETRAKIS S, FOTIADIS Z, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells with enhanced telomerase activity acquire resistance against oxidative stress-induced genomic damage. Cytotherapy. 2017; 19(7):808-820.
[8] GOU WL, LU Q, WANG X, et al. Key pathway to prevent the collapse of femoral head in osteonecrosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015; 19(15):2766-2774.
[9] ZHOU W, QU M, LV Y, et al. New Advances in Stem Cell Therapy for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019; 14(3):226-229.
[10] PENG WX, WANG L. Adenovirus-Mediated Expression of BMP-2 and BFGF in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Combined with Demineralized Bone Matrix For Repair of Femoral Head Osteonecrosis in Beagle Dogs. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(4): 1648-1662.
[11] 孟晨阳,刘万林,白锐,等.激素性股骨头缺血性坏死发病机制中的细胞自噬[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(8): 1280-1287.
[12] 李云隆,赵振群,刘万林.激素性股骨头缺血坏死中PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路对自噬的调控[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(12): 1921-1929.
[13] LIAO Y, ZHANG P, YUAN B, et al. Pravastatin Protects Against Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head via Autophagy. Front Physiol. 2018;9:307.
[14] LUO P, GAO F, HAN J, et al. The role of autophagy in steroid necrosis of the femoral head: a comprehensive research review. Int Orthop. 2018;42(7):1747-1753.
[15] 张舟,凌晓宇,李嫦,等.右归饮治疗骨伤科疾病临床研究进展[J].新中医, 2017,49(12):170-172.
[16] 童培建,金红婷,沈彦,等.右归饮联合MSCs介入治疗早期股骨头缺血性坏死的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009,22(4): 456-462.
[17] 范连霞,章建华,尹华,等.右归饮通过Wnt/ERK信号通路交叉串扰影响成骨细胞相关蛋白的表达[J].中华中医药杂志,2016,31(10): 4249-4252.
[18] 蔡运火.右归饮对假体周围骨溶解大鼠OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路的影响研究[D].杭州:浙江中医药大学,2013.
[19] 宋才渊,沈兴潮,吕帅杰,等.右归饮对激素性股骨头坏死大鼠血液骨矿物质盐及骨密度的影响[J].中医杂志,2015,56(14): 1239-1242.
[20] 郭燕威,许士兵,单乐天,等.右归饮对激素性股骨头坏死大鼠血清脂联素影响的实验研究[J].内蒙古中医药,2015,34(11):140-141.
[21] 徐涛涛,金红婷,廖菲,等.右归饮含药血清促进人血管内皮细胞增殖及抗氧化损伤的作用研究[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2014,38(8): 933-938. |