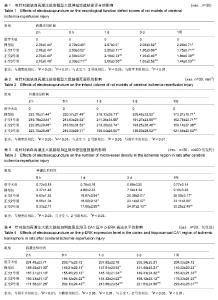
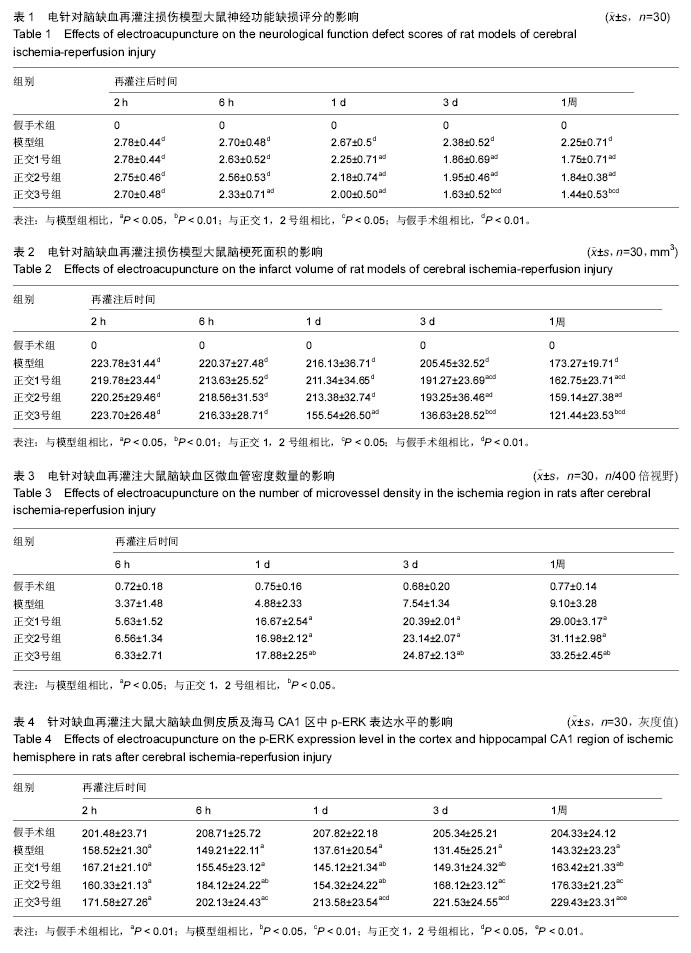
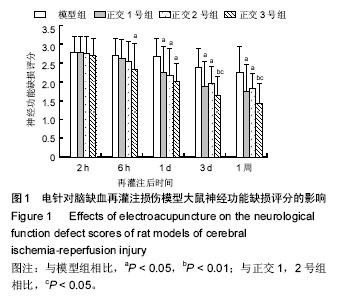
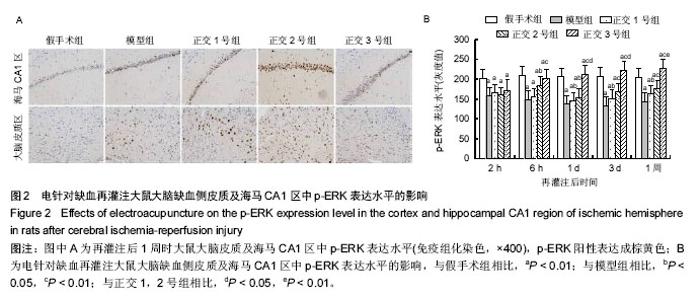
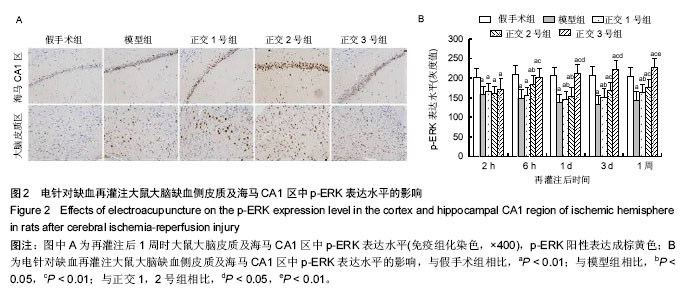
| [1] Schulz JB, Weller M, Moskowitz MA. Caspases as treatment targets in stroke and neurodegenerative diseases. Ann Neurol. 1999;45(4):421-429.
[2] 于淼,高维娟,钱涛.脑缺血/再灌注信号转导通路的研究进展[J].承德医学院学报,2010,27(1):65-67.
[3] 张海湃,苏思骢,周垚,等.近5年电针治疗脑缺血再灌注损伤的实验研究进展[J].辽宁中医杂志,2014,41(8): 1780-1781.
[4] Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.
[5] 李辞蓉,华兴邦,周浩良,等.豚鼠针灸穴位图谱的研制[J].上海针炙杂志,1992(2):28-30.
[6] 李忠仁.实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2003.
[7] Weidner N. Current pathologic methods for measuring intratumoral microvessel density within breast carcinoma and other solid tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995;36(2):169-180.
[8] 朱惠斌,陈懿,谭琥,等.脑泰方提取物对局灶性脑缺血大鼠CD34表达的影响[J]中药新药与临床药理,2011,22(2): 141-144.
[9] 曹莹,戴建武,胡志兵,等.依达拉奉联合电刺激小脑顶核治疗急性脑梗死疗效观察[J].中国医药导报,2009,6(16): 100-101.
[10] Beretta S, Pastori C, Sala G, et al. Acute lipophilicity-dependent effect of intravascular simvastatin in the early phase of focal cerebral ischemia. Neuropharmacology. 2011;60(6):878-885.
[11] Jin H, Hwang SK, Yu K, et al. A high inorganic phosphate diet perturbs brain growth, alters Akt-ERK signaling, and results in changes in cap-dependent translation. Toxicol Sci. 2006;90(1):221-229.
[12] Shioda N, Han F, Fukunaga K. Role of Akt and ERK signaling in the neurogenesis following brain ischemia. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009;85:375-387.
[13] 田北方.MAPK级联途径在脑发育与损伤修复中的作用[J].国外医学:生理病理科学与临床分册,2000,20(3): 184-186. |