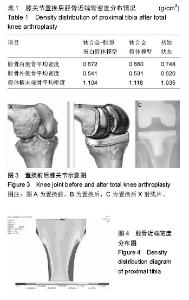
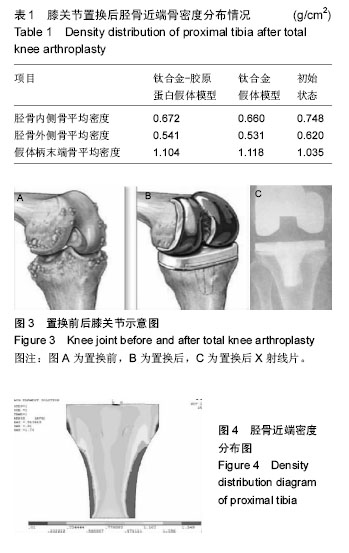
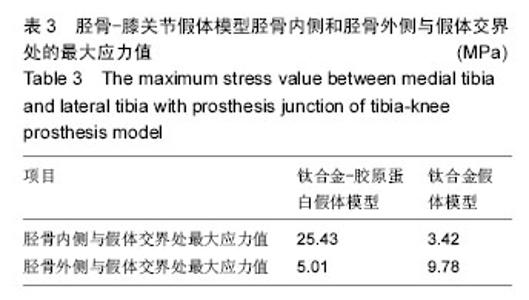
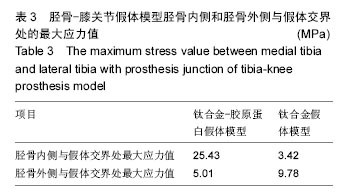
| [1] Petersen SG,Saxne T,Heinegard D,et al. Glucosamine but not ibuprofen alters cartilage turnover in osteoarthritis patients in response to physical training.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(1): 34-40.
[2] Bauerova K,Ponist S,Kuncirova V,et al. Chondroitin sulfate effect on induced arthritis in rats.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(11):1373-1379.
[3] Lammers G,Roth G,Heck M,et al.Construction of a microstructured collagen membrane mimicking the papillary dermis architecture and guiding keratinocyte morphology and gene expression.Macromol Biosci. 2012;12(5):675-691.
[4] Pecchi E,Priam S,Mladenovic Z,et al. A potential role of chondroitin sulfate on bone in osteoarthritis: inhibition of prostaglandin E2 and matrix metalloproteinases synthesis in interleukin-1β- stimulated osteoblasts. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(2):127-135.
[5] Fardellone P,Zaim M,Saurel AS,et al. Comparative efficacy and safety study of two chondroitin sulfate preparations from different origin(avian and bovine) in symptomatic osteoarthritis of the knee.Open Rheumatol J. 2013;7:1-12.
[6] 张弛,叶斌,张海林,等. 抗骨质疏松治疗对老年性膝关节骨关节炎疗效的影响[J]. 实用老年医学,2011,25(4): 346-347.
[7] 彭溶,潘小莉. 糖皮质激素在膝骨性关节炎中的合理应用[J].中国现代医药杂志,2011,13(3):110 -111.
[8] Bostan B,Sen U,Günes T,et al. Comparison of intra-articular hyalu-ronic acid injections and mud-pack therapy in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2010;44(1):42-47.
[9] 石国勋,任天丽,周红霞,等. 透明质酸盐对骨性关节炎关节液中OPG/ODF的影响[J].吉林医学, 2014,35(9): 1833.
[10] 袁长深,梅其杰,潘奔洲. 膝骨关节炎运动疗法的国外研究进展[J]. 重庆医学,2011,40(22):2281-2283.
[11] Sampson S,Reed M,Silvers H, et al. Injection of platelet-rich plasma in patients with primary and secondary knee osteoarthritis: a pi1ot study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;89(12): 961-969.
[12] Kon E,Buda R,Filardo G,et al. Platelet-rich plasma: intra-articular knee injections produced favorable results on degenerative cartilage lesions. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(4): 472-479.
[13] 郭文青,南秋生,耿登峰. 关节骨关节病综合疗法86例疗效观察[J]. 健康研究,2011,31(5):332-334.
[14] 徐剑锋. 骨性关节炎中关节镜的临床应用分析[J].中国医药指南,2013, 11(10):99-100.
[15] 肖尚领,任宗凯,陈思嘉. 胫骨高位截骨治疗伴膝内翻的膝骨性关节炎[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(19): 587-588.
[16] 乐婉娜.物理疗法联合运动训练治疗膝关节骨性关节炎疗效观察[J].现代实用医学,2010,22(12):1394-1395.
[17] 王玉丽.针灸疗法与物理疗法(超短波和中频) 联合治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的疗效分析[J].健康之路,2013,12(7): 117-118.
[18] 翁茂盛. 硫酸氨基葡萄糖对膝关节骨性关节炎患者MMP-3表达的影响[J].放射免疫学杂志,2012,25(1): 96-98.
[19] 沈兰娟.硫酸氨基葡萄糖治疗膝关节骨性关节炎130例的疗效及护理[J].中国药业,2013,22(7):63-64.
[20] 鲍晓毅.盐酸氨基葡萄糖治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床观察[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病,2010,9(4):339-341.
[21] 王义斌.中药治疗膝关节骨性关节炎120例[J].中国中医药现代远程教育, 2012,10(24):26.
[22] 赵强,冯伟.针灸推拿为主治疗膝关节骨性关节炎临床观察[J].天津中医药, 2012,29 (2):196.
[23] 常英,刘亚彬.小针刀治疗膝关节骨性关节炎58例临床观察[J].河北中医, 2011,33(11):1688-1689.
[24] 陈桂新.玻璃酸钠关节内注射治疗膝关节骨性关节炎112例[J].中国药业, 2012,21(23):87.
[25] 黄建新,杨升平,梁庆广.医用臭氧治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的疗效观察[J].中国当代医药,2012,19(7): 51-52.
[26] 王建业,曾锦峰,黄连明.综合方法治疗膝关节骨性关节炎70 例[J].中国医药科学,2012,2(1):64-65.
[27] 吴华军,王新华.五步综合疗法治疗骨性膝关节炎的疗效观察[J].中医正骨,2012,24(2):51-52.
[28] 杨健.透明质酸钠注射联合针刀闭合性手术治疗膝关节骨关节炎65例疗效观察[J].中国医学创新,2010,7(33) : 51-53.
[29] 徐盛文.膝关节骨性关节炎关节镜下治疗体会[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(2):198-199.
[30] 梁慧,王小铁,靳江涛.胫骨高位截骨术治疗膝骨关节炎并膝内翻体会[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2011,17(8): 704 -706.
[31] 陈显辉.膝关节置换术后感染的治疗策略[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2010,4(3): 415-418.
[32] 陈福灵,张健.膝关节骨性关节炎治疗进展[J].检验医学与临床,2013,10(12):1596-1598.
[33] 彭侃.人工单髁膝关节置换术治疗膝骨关节炎[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(2):106-108.
[34] 杨小春.全膝关节置换术中髌骨置换与髌骨成形对膝关节功能的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(3):241 -245.
[35] 崔鲁霞.全膝关节置换术治疗膝骨关节炎57膝的临床观察[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2011,5(6):787-790.
[36] 祝天经.人工膝关节置换手术的疗效评定及功能评定[J].现代康复,2011,5(5):10-11.
[37] 刘建华,余世明,徐栋梁.不同固定表面生物型人工膝关节假体的骨长入实验研究[J].中华关节外科杂志,2012,6(3): 432-437.
[38] 张亚平,高家成,王勇.人工关节材料的研究与展望[J].世界科技研究与发展,2000,22(1):47-52.
[39] 邹俭鹏,阮建明,周忠诚.功能梯度材料设计与制备及性能评价[J].粉末冶金材料科学与工程,2005,10(2):78-87.
[40] Nyman JS, Rodrigo JJ, Hazelwood SJ, et al. Predictions on Preserving Bone Mass in Knee Arthroplasty With Bisphosphonates. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(1):106-113.
[41] Tawakol AE, Nadia EB. Material selection in the design of the tibia tray component of cemented artificial knee using finite element method. Mat Des. 2013;44: 454-460.
[42] Marjan B, Sahari BB, Edwards KL, et al. Material tailoring of the femoral component in a total knee replacement to reduce the problem of aseptic loosening. Mat Des. 2013;52:441-451. |