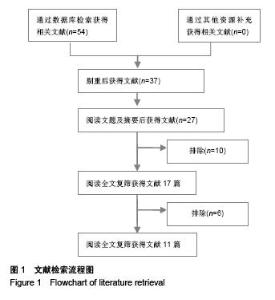
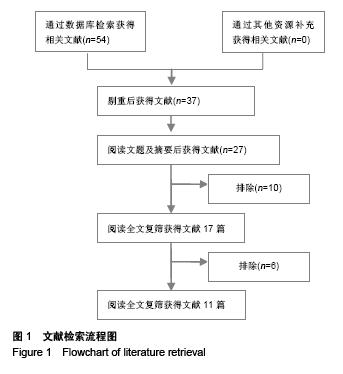
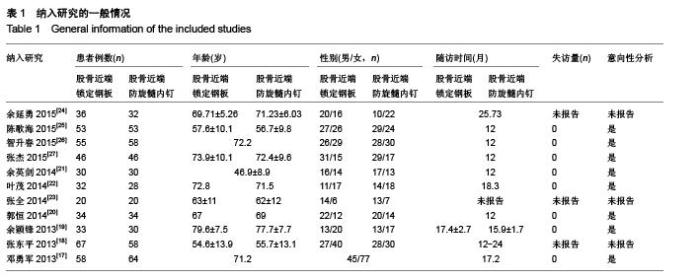
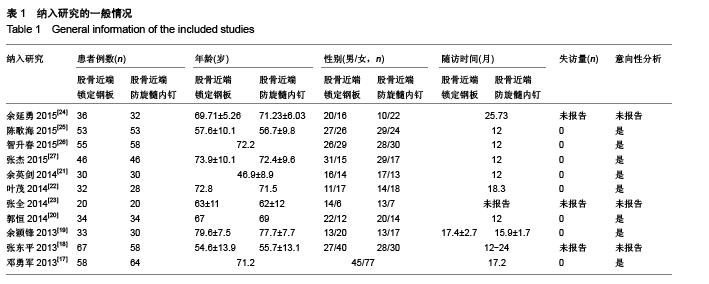
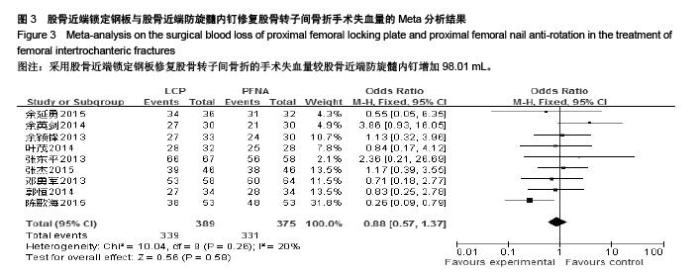
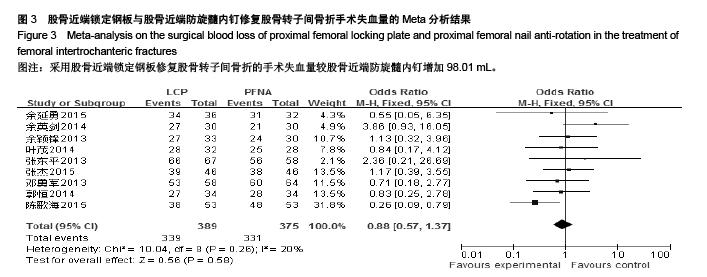
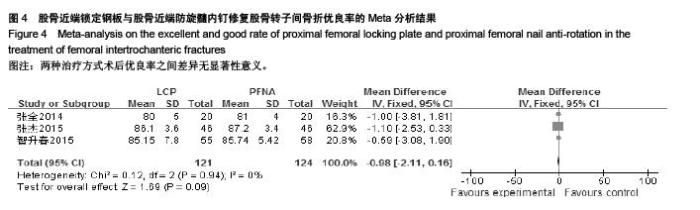
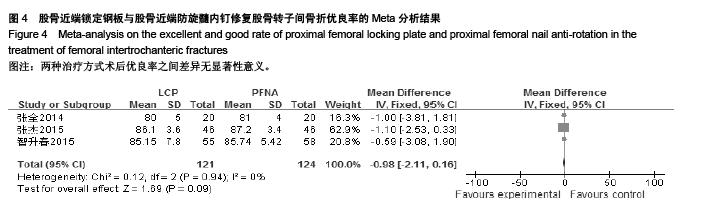
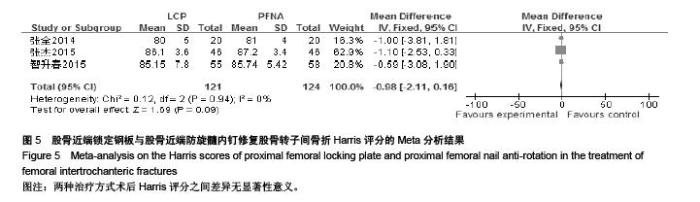
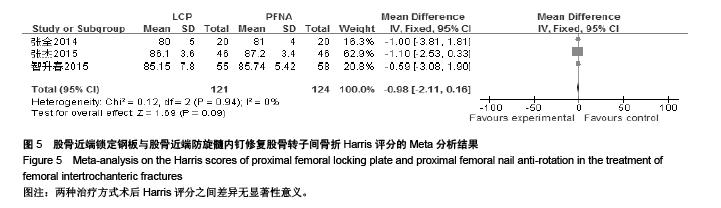
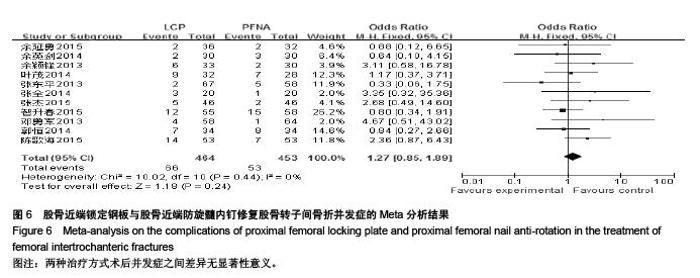
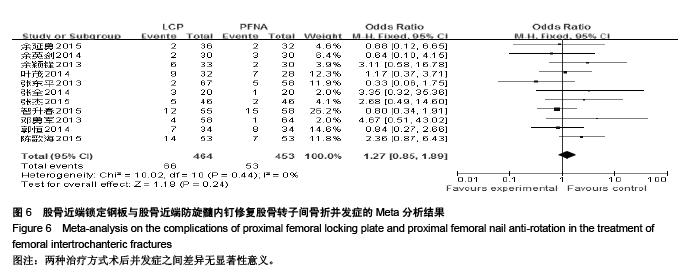
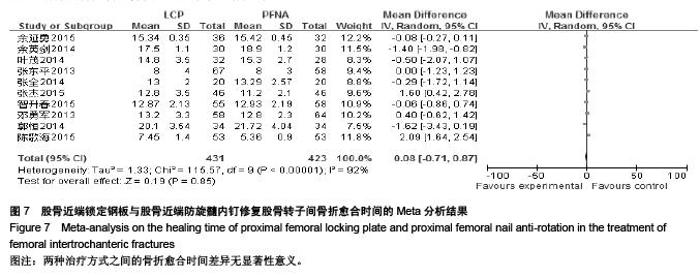
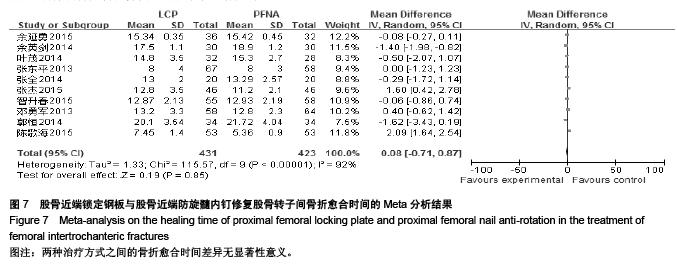
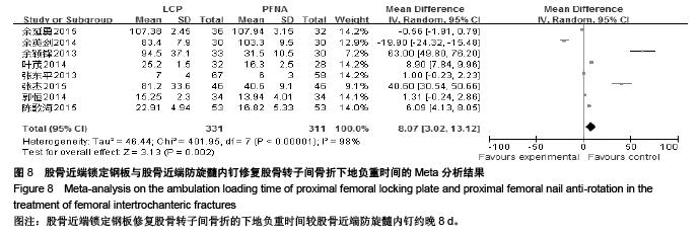
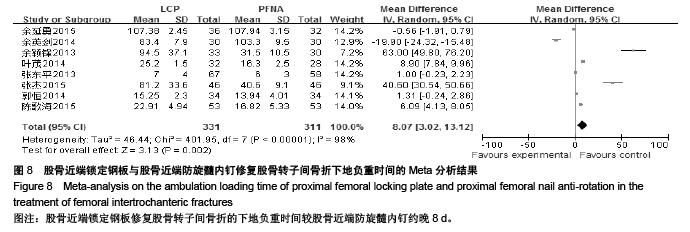
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (53): 8677-8684.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.53.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Proximal femoral nail anti-rotation and locking plate for treating femoral intertrochanteric fractures: a systematic review
Wang Feng, Li Zhen-wu, Yin Rui-feng, Li Zhi-an
- Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang 473009, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2015-10-05Online:2015-12-24Published:2015-12-24 -
About author:Wang Feng, Master, Attending physician, Nanyang City Center Hospital, Nanyang 473009, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Feng, Li Zhen-wu, Yin Rui-feng, Li Zhi-an. Proximal femoral nail anti-rotation and locking plate for treating femoral intertrochanteric fractures: a systematic review[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(53): 8677-8684.
share this article
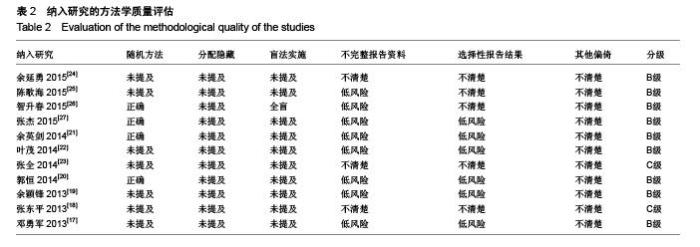
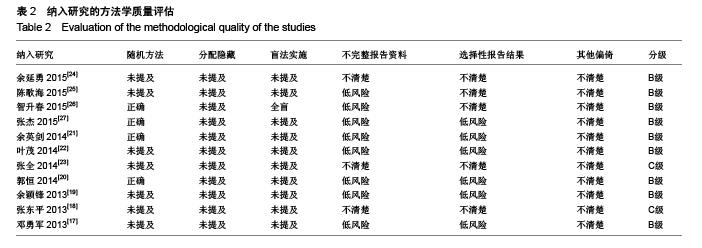
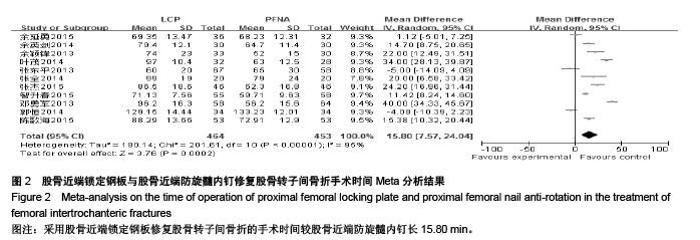
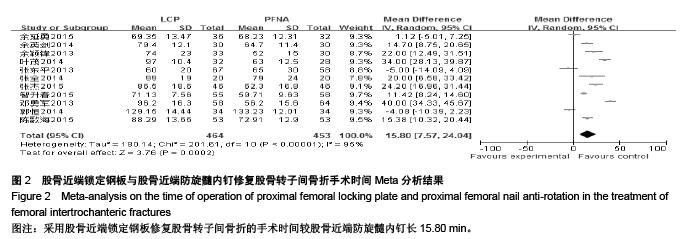
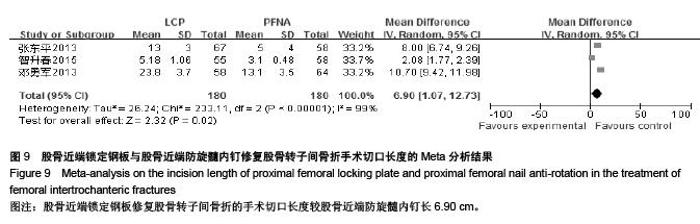
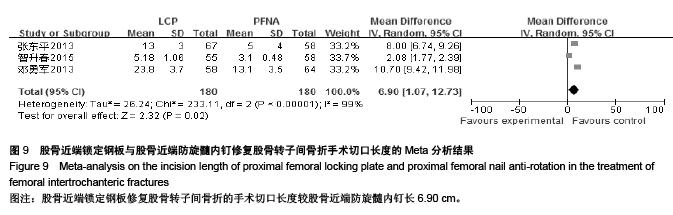
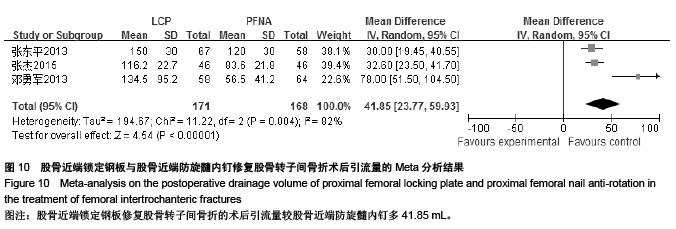
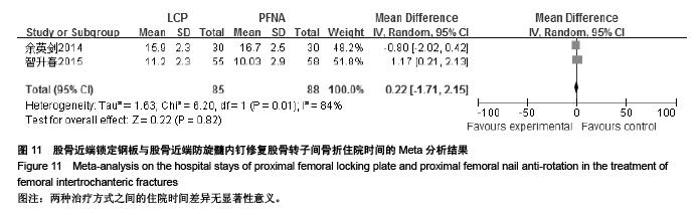
| [1] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].4版.北京:人民军医出版社,2012:947-948. [2] Bohl DD, Basques BA, Golinvaux NS,et al.Extramedullary compared with intramedullary implants for intertrochanteric hip fractures: thirty-day outcomes of 4432 procedures from the ACS NSQIP database. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96(22):1871-1877. [3] McCormack R, Panagiotopolous K, Buckley R, et al.A multicentre,prospective, randomised comparison of the sliding hip screw with the Medoff sliding screw and side plate for unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures.Injury. 2013; 44(12): 1904-1909. [4] Taylor AJ, Gary LC, Arora T, et al.Clinical and demographic factors associated with fractures among older Americans. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(4):1263-1274. [5] Le-Wendling L, Bihorac A, Baslanti TO,et al.Regional anesthesia as compared with general anesthesia for surgery in geriatric patients with hip fracture: does it decrease morbidity, mortality, and health care costs? Results of a single-centered study. Pain Med. 2012;13(7):948-956. [6] Daugaard CL, Jorgensen HL, Riis T,et al.Is mortality after hip fracture associated with surgical delay or admission during weekends and public holidays? A retrospective study of 38,020 patients.Acta Orthop. 2012;83(6):609-613. [7] 黎裕明,黄宗贵,戴海,等.切开复位和闭合复位DHS内固定治疗股骨粗隆间骨折临床对比分析[J].医学理论与实践,2015,28(7): 848-850,862 [8] Werner BC, Fashandi AH, Gwathmey FW, et al.Trends in the management of intertrochanteric femur fractures in the United States 2005-2011. Hip Int. 2015;25(3):270-276. [9] 肖柳斌,付朝霞,汪清华,等.髓内固定与髓外固定治疗Evans- JensenⅢ型股骨转子间骨折疗效比较[J].华西医学, 2014, 29(11): 2023-2027. [10] Swart E, Makhni EC, Macaulay W,et al.Cost-effectiveness analysis of fixation options for intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2014;96(19):1612-1620. [11] 翟生,吕青.股骨近端髓内固定与动力髋钢板修复成人股骨转子间骨折的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(22):3595- 3603. [12] Mereddy P,Kamath S,Ramakrishnan M,et al.The A0/ASIF proximal femoral nail anti-rotation(PFNA):a new design for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. InJury.2009; 40(4):428-432. [13] Unger AC, Wilde E, Kienast B,et al.Treatment of Trochanteric Fractures with the Gamma3 Nail - Methodology and Early Results of a Prospective Consecutive Monitored Clinical Case Series.Open Orthop J. 2014;8:466–473. [14] Wu D, Ren G, Peng C, et al. InterTan nail versus Gamma3 nail for intramedullary nailing of unstable trochanteric fractures. Diagn Pathol.2014;9:191. [15] Aktselis I, Kokoroghiannis C, Fragkomichalos E,et al. Prospective randomised controlled trial of an intramedullary nail versus a sliding hip screw for intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. Int Orthop. 2014;38(1):155-161. [16] Bradley JP, Elkousy H. Decision making: operative versus nonoperat ive treatment of acromioclavicular joint in juries. Clin Sports Med. 2003;22(2):277-290. [17] 邓勇军,周学文,王强.LCP和PFNA治疗老年人股骨转子间骨折的临床疗效比较[J].浙江创伤外科,2013,18(4):504-506. [18] 张东平,徐雄,钱腾飞.股骨近端锁定加压接骨板与股骨近端抗旋转髓内钉治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效分析[J].重庆医科大学学报, 2013,38(11):1278-1281. [19] 余颖锋,谢文伟,姚汉刚,等.股骨近端锁定解剖钢板和PFNA治疗老年股骨粗隆间粉碎性骨折的疗效比较[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2013,7(4):477-480. [20] 郭恒,石明国,杨占辉,等.不同内固定治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(12):1133-1135. [21] 余英剑,李桂涛,洪翔,等.经皮微创钢板内固定技术结合锁定加压钢板与股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的效果比较[J].中国医药导报,2014,11(19):47-50. [22] 叶茂,王奎,邹毅,等.PFNA 与 PF-LCP 治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效分析[J].贵州医药,2014,38(9):828-830. [23] 张全.锁定钢板和PFNA治疗股骨粗隆间骨折疗效对比[J].现代诊断与治疗,2014,25(21):4996-4997. [24] 于延勇,张锴.锁定加压钢板与股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折疗效分析[J].滨州医学院学报,2015,38(1):22-25,53. [25] 陈歌海,郑建河,黄济嘉,等.PFNA与股骨近端锁定钢板治疗不稳定股骨转子骨折的疗效分析[J].中国医学创新,2015,12(16):4-6. [26] 智春升,金冶华,刘军,等.经皮解剖锁定接骨板与股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的临床对比研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2015,8(2):151-156. [27] 张杰,张保红,马震.PFNA与锁定钢板治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折疗效比较[J].现代医学,2015,43(2):221-224. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||