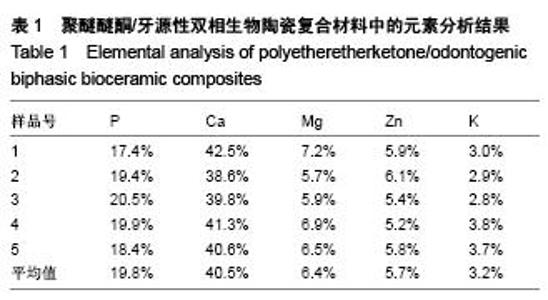
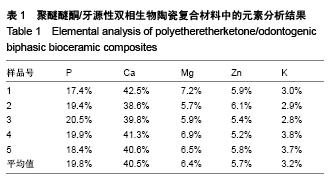
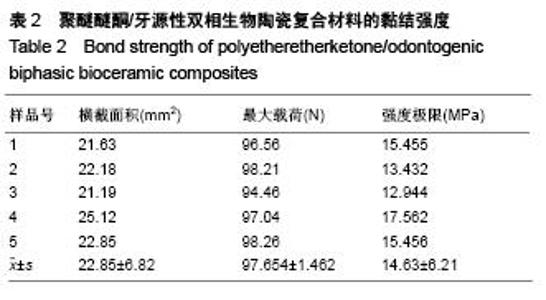
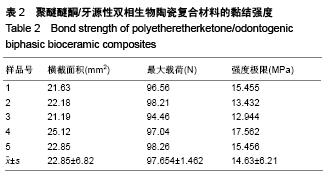
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (52): 8418-8422.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.52.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and mechanical properties of polyetheretherketone/odontogenic biphasic bioceramic composites
Leng Wei-dong1, Liu Cai-yun1, Huang Cui2, Ai Jun1, Shi Cong-yu1,Yu He-dong1
- 1Oral Medical Center, Hospital Affiliated to Hubei University of Medicine (Taihe Hospital of Shiyan City), Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Prosthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2015-10-30Online:2015-12-17Published:2015-12-17 -
Contact:Yu He-dong, Master, Physician, Department of Prosthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Leng Wei-dong, M.D., Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Oral Medical Center, Hospital Affiliated to Hubei University of Medicine (Taihe Hospital of Shiyan City) , Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51541202; General Program of Health and Family Planning Commission of Hubei Province of China, No. 2015MB289
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Leng Wei-dong, Liu Cai-yun, Huang Cui, Ai Jun, Shi Cong-yu,Yu He-dong. Preparation and mechanical properties of polyetheretherketone/odontogenic biphasic bioceramic composites[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(52): 8418-8422.
share this article
| [1] Dennes JT,Schwartz J.A nanoscale adhesion layer to promote cell attachment on PEEK.J Am Chem Soc,2009; 131:3456-3457. [2] 蔡卫全,马睿,翁履谦,等.原位聚合羟基磷灰石/聚醚醚酮复合材料[J].化工新型材料,2010,38(6):55-63. [3] Kyomoto M,Ishihara K.Self-initiated surface graft polymerization of 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine on poly(ether ether ketone)by photoirradiation.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2009;1(3):537-542. [4] Briem D,Strametz S,Schroder K,et al.Response of primary fibroblasts and osteoblasts to plasma treated polyetheretherketone(PEEK)surfaces.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2015;16(7):671-677. [5] Dorozhkin SV.Calcium orthophosphates in nature,biology and medicine.Materials. 2009;2:399-498. [6] Katzer A,Marquardt H,Westendorf J,et al. Polyetheretherketone cytotoxicity and mutagenicity in vitro.Biomaterials.2012;23(8):1749-1759. [7] Gonverse GL,Conrad TL,Merrill CH,et al.Hydroxxyapatite whisker reinforced polyetherketoneketone.Acta Boimaterials. 2010;6:856-863. [8] Converse GL,Conrad TL,Roeder RK.Hydroxyapatite whisker reinforced polyetherketoneketone bone ingrowth scaffolds.Acta Boimaterials.2010;32:856-863. [9] Masayuki K,Toru M.Self-initiated surface grafting with poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine)on poly(ether-ether-ketone).Biomaterials.2010;31:1017-1024. [10] Cheol MH,Lee EJ.The electron beam deposition of titanium on polyetheretherketone (PEEK)and the resulting enhanced biological properties. Biomaterials. 2010;31: 3465-3470. [11] Lim JY,Shaughnessy MC,Zhou ZY,et al.Surface energy effects on osteoblast spatial growtfi and mineralization. Biomaterials.2008;29:1776-1784. [12] Kay S,Thapa A,Haberstroh KM,et al.Nanostructured polymer/nanophase ceramic composites enhance osteoblast and chondrocyte adhesion.Tissue Eng. 2012;8:753-761. [13] Lee JH,Jang HL,Lee KM,et al.In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the bioactivity of hydroxyapatite-coated polyetheretherketone biocomposites created by cold spray technology.Acta Biomaterials.2013;9:6177-6187. [14] Simona S,Antonella P,Stefania L,et al.Improved functions of human hepatocytes on NH3 plasma-grafted PEEK-WC-PU membranes.Biomaterials.2009;30:4348-4356. [15] Dennes TJ,Jeffrey S.A Nanoscale Adhesion Layer to Promote Cell Attachment on PEEK.J Am Chem Soc.2009; 131(10):3456-3457. [16] Wang M,Bonfield W.Chemically coupled hydroxyapatite- polyethylene composites:structure and properties. Biomaterials.2011;22:1311-1320. [17] Hooshmand T,van Noort R,Keshwad A.Storage effect of a pre-activated silane on the resin to ceramic bond.Dental Material.2014;20:635-642. [18] Dorozhkin sv.Biphasic,triphasic and multiphasic calcium orthophosphates.Acta Biomaterialia.2012;8:963-977. [19] Levengood SK,Poellmann MJ,Clark SG,et al.Human endothelial colony forming cells undergo vasculogenesis within biphasic calcium phosphate bone tissue engineering constructs.Acta Biomaterialia.2011;7(12):4222-4228. [20] Prabhakaran MP,Ghasemi-Mobarakeh L,Ramakrishna S.Eleetrospun composite nanofibers for tissue regeneration. J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2011;11:3039-3057. [21] Zhang H.Eleetrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/multiwalled carbon nanotubes composite scaffolds for guided bone tissue regeneration.J Bioact Compat Polym.2011;26:16-23. [22] Zou D,Zhang Z,He J,et al.Repairing critical-sized calvarial defects with BMSCs modified by a constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and a phosphate cement scaffold.Biomaterials.2011;32:9707-9718. [23] Sturgeon JL,Brown PW.Effects of carbonate on hydroxyapatite formed from CaHP04 and Ca4(P04)20.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2009;20:1787-1794. [24] Chen G,Li W,Yu X,et al.Study of the cohesion of TTCP/DCPA phosphate cement through evolution of cohesion time and remaining percentage.J Mater Sci. 2009;44:828-834. [25] Sayer M,Stratilatov AD,Reid JW,et al.Structure and composition of siliconstabilized tricalcium phosphate. Biomaterials.2013;24:369-382. [26] Reid JW,Pietak AM,Sayer M,et al.Phase formation and evolution in the silicon substituted tricalcium phosphate/ apatite system. Biomaterials. 2015;26:2887-2897. [27] Jang JH,Castano O,Kim HW.Electrospun materials as potential platforms for bone tissue engineering.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2009;61:1065-1083. [28] Arcangeli E,Kon E,Delcogliano M,et al.Nanocomposite biomimetic scaffold in knee osteochondral defect regeneration:An animal study.J Appl Biomater Biomech. 2009;7:52-62. [29] Khadka A,Li JH,Li YB,et al.Evaluation of hybrid porous biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 6 and bone marrow-derived stem cell construct in repair of calvarial critical size defect.J Craniofac Surg.2011;22:1852-1858. [30] Schneider OD,Weber F,Bninner TJ,et al.In vivo and in vitro evaluation of flexible,cottonwool-like nanocomposites as bone substitute material for complex defects.Acta Biomater. 2009;5:1775-1784. [31] Gupta V,Aseh A,Rios CN,et al.Fabrication and characterization of silk fibroin-derived curcumin nanoparticles for cancer therapy.Int J Nanomed.2009;4:115-122. [32] Chow LC.Next generation calcium phosphate-based biomaterials.Dent Mater J.2009;28:1-10. [33] Ishikawa K.Bone substitute fabrication based on dissolution-precipitation reactions. Materials. 2010;3: 1138-1155. [34] Becker A,Epple M,Mttller KM,et al.A comparative study of clinically well-characterized human atherosclerotic plaques with histological,chemical and ultrastructural methods.J Inorg Biochem.2014;98(12):2032-2038. [35] Dorozhkin SV.Amorphous calcium(ortho)phosphates.Acta Biomater.2010;6:4457-4475. [36] Sinyaev VA,Shustikova ES,Levchenko LV,et al.Synthesis and dehydration of amorphous calcium phosphate.Inorg Mater.2011;37:619-622. [37] Kumar R,Cheang P,Khor KA.Phase composition and heat of crystallization of amorphous calcium phosphate in ultra-fine radio frequency suspension plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite powders.Acta Mater.2014;52:1171-1181. [38] Wu YJ,Tseng YH,Chan JCC.Morphology control of fluorapatite crystallites by citrate ions.Cryst Growth Des. 2010;10:4240-4242. [39] Choi WY,Kim HE,Kim MJ,et al.Production and characterization of calcium phosphate(CaP) whisker-reinforced poly(e-caprolactone)composites as bone regenerative.Mater Sci Eng C.2010;30:1280-1284. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||