Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (49): 8005-8009.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.49.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
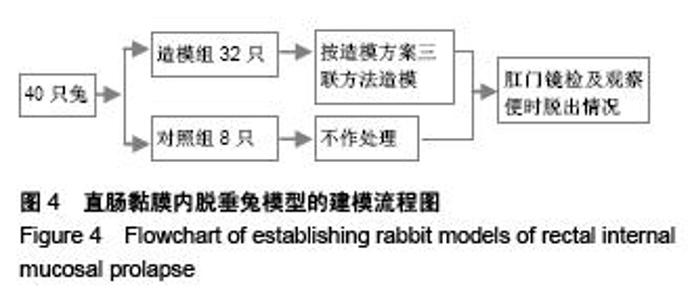
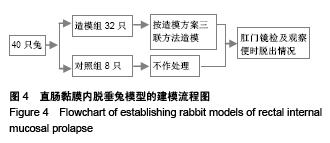
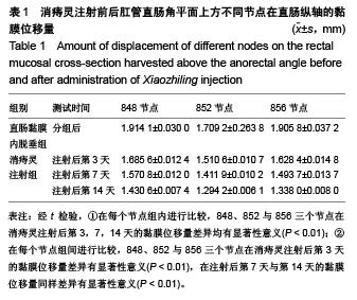
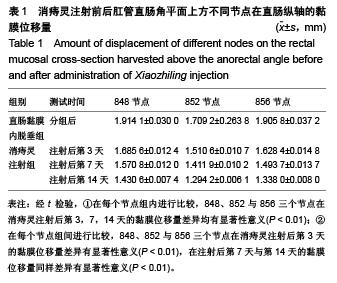
Evaluation of Xiaozhiling injection effect on rectal internal mucosal prolapse based on the amount of displacement of mucosal nodes in a finite element model of rabbit anorectum
Ke Min-hui1, Ye Ling1, Chen Li-wu1, Niu Su-sheng2, Zheng Ming-xiao1, Zhang Zhi-xi3
- 1Department of Anorectal Surgery, Second People’s Hospital of Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China; 2College of Osteopathy, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; 3Laboratory of Photoelasticity, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350108, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-06Online:2015-11-30Published:2015-11-30 -
Contact:Ye Ling, Chief physician, Department of Anorectal Surgery, Second People’s Hospital of Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Ke Min-hui, Master, Attending physician, Department of Anorectal Surgery, Second People’s Hospital of Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81173272; the Natural Foundation of Fujian Province of China, No. 2015J01402
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ke Min-hui, Ye Ling, Chen Li-wu, Niu Su-sheng, Zheng Ming-xiao,Zhang Zhi-xi. Evaluation of Xiaozhiling injection effect on rectal internal mucosal prolapse based on the amount of displacement of mucosal nodes in a finite element model of rabbit anorectum[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(49): 8005-8009.
share this article
| [1] 何永恒,凌光烈.中医肛肠科学[M].北京:清化大学出版社,2011: 181. [2] Wijffels NA,Jones OM,Cunningham C,et al.What are the symptoms of internal rectal prolapse?. Colorectal Dis.2013; 15(3):368-373. [3] Hompes R, Jones OM, Cunningham C,et al. What causes chronic idiopathic perineal pain?. Colorectal Dis.2011;13(9): 1035-1039. [4] Tokunaga Y.Clinical utility of sclerotherapy with a New agent for treatment of rectal prolapse in patients with Risks.J Clin Gastroenterol.2014; 48(4):356-359. [5] 韩宝,聂广军.消痔灵注射治疗直肠脱垂266例[J].人民军医,2008, 51(3):812-813. [6] 叶玲,高献明.消痔灵注射治疗直肠内脱垂型便秘148例临床观察[J].中国现代药物应用,2009,3(18):109-110. [7] 李华山,崔国策,王晓锋.注射疗法治疗直肠脱垂的研究现状[J].世界华人消化杂志,2011,19(23):2480-2485. [8] 王政,刘贵麟.实验性家兔肛门括约肌损伤直肠测压研究[J].中华小儿外科杂志,1999,1(20):41-42. [9] 柯敏辉,叶玲,陈立武,等.兔直肠黏膜内脱垂模型的建立[J].世界中医药,2013,8(12):1458-1460. [10] 柯敏辉,叶玲,陈立武,等.兔肛门直肠三维有限元模型的建立[J].世界华人消化杂志,2013,21(25):2585-2589. [11] 王冬冬,高峰,程杰平,等.治疗股骨转子间骨折时头颈拉力螺钉不同置入位置的有限元计算[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(17): 2667-2672 [12] 梁志红,薛俊杰,王洪军.减阻牵张远移上颌尖牙的三维有限元分析[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,2014,49(08):1132-1136. [13] Erdemir A, Guess TM, Halloran J, et al. Considerations for reporting finite element analysis studies in biomechanics. J Biomech.2012;45: 625-633. [14] Mousavi SR, Khalaji I, Sadeghi Naini A,et al.Statistical finite element method for real-time tissue mechanics analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin.2012;15:595-608. [15] 王荣洁,曾融生,朱凯.应用有限元法预测正颌术后三维软组织形变的初步探讨[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2012,10(2):90-95 [16] Martins JA, Pato MP, Pires EB. Finite element studies of the deformation of the pelvic floor. Ann N Y Acad Sci.2007;101(5): 316-318. [17] 宋红芳,雷玲玲,黄跃,等.基于磁共振图像的女性盆底组织三维几何重建[J].中华妇幼临床医学杂志,2012,8(4):348-349 [18] 孙源,周奇,王志刚.有限元方法分析直肠电极在直肠角的生物电学效应[J].重庆理工大学学报:自然科学,2013,27(12):101-105 [19] 刘守尧,王云亭,蔡蓉蓉,等.家兔腓肠肌拉伸试验设备和夹具的选择[J].中日友好医院学报,2014,28(2):110-112 [20] 彭传刚,杨琦,李鹏.青年与老年人脊柱黄韧带的力学特性[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,9(33):4455-4456. [21] 赵奕李,新颖,李鹏,等.人脊柱棘间韧带与黄韧带应力松弛实验的研究[J].生物医学工程研究,2014,33(3):162-165. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||