Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (48): 7825-7830.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.48.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
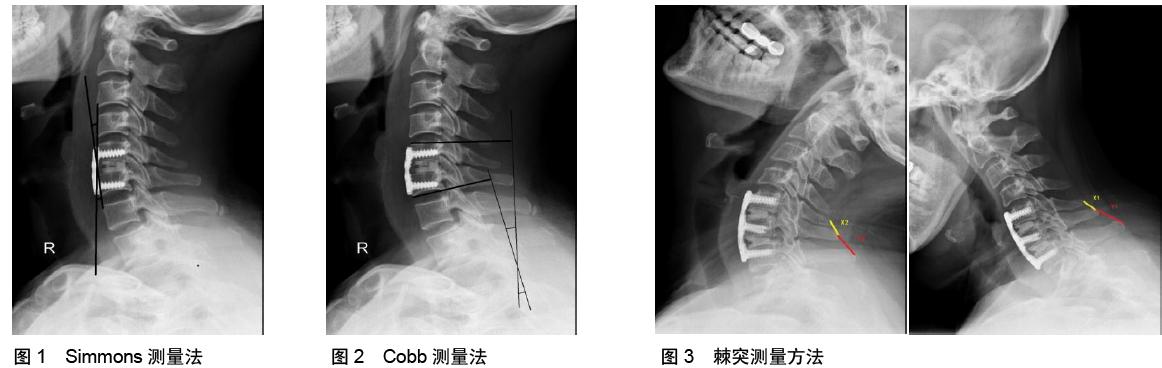
Imaging evaluation strategy of spinal interbody fusion
Gao Zhi-qiang1, Li Yang2, Luo Fei2
- 1Outpatient Department, Chongqing Communication Institute, Chongqing 400035, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Chongqing Southwest Hospital, Chongqing 400038, China
-
Received:2015-09-16Online:2015-11-26Published:2015-11-26 -
Contact:Luo Fei, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Chongqing Southwest Hospital, Chongqing 400038, China -
About author:Gao Zhi-qiang, Associate chief physician, Outpatient Department, Chongqing Communication Institute, Chongqing 400035, China -
Supported by:Spinal Fusion; Cervical Vertebrae; Lumbar Vertebrae; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Tissue Engineering
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Zhi-qiang, Li Yang, Luo Fei . Imaging evaluation strategy of spinal interbody fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(48): 7825-7830.
share this article
| [1] Fh A. Transplantation of a portion of the tibia into the spine for Pott's desease. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1911;57: 885-886.[2] Fischgrund JS, Mackay M, Herkowitz HN, et al. 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(24): 2807-2812.[3] Carreon LY, Djurasovic M, Glassman SD, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and reliability of fine-cut CT scans with reconstructions to determine the status of an instrumented posterolateral fusion with surgical exploration as reference standard. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(8): 892-895.[4] Brantigan JW, Steffee AD. A carbon fiber implant to aid interbody lumbar fusion. Two-year clinical results in the first 26 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(14): 2106-2107.[5] Min SH, Yoo JS. The clinical and radiological outcomes of multilevel minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(5): 1164-1172.[6] Fogel GR, Toohey JS, Neidre A, et al. Fusion assessment of posterior lumbar interbody fusion using radiolucent cages: X-ray films and helical computed tomography scans compared with surgical exploration of fusion. Spine J. 2008; 8(4): 570-577.[7] Santos ER, Goss DG, Morcom RK et al. Radiologic assessment of interbody fusion using carbon fiber cages. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(10): 997-1001.[8] McAfee PC, Regan JJ, Geis WP, et al. Minimally invasive anterior retroperitoneal approach to the lumbar spine. Emphasis on the lateral BAK. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998; 23(13): 1476-1484.[9] Christensen FB, Laursen M, Gelineck J, et al. Interobserver and intraobserver agreement of radiograph interpretation with and without pedicle screw implants: the need for a detailed classification system in posterolateral spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(5): 538-543; discussion 543-534.[10] Shah RR, Mohammed S, Saifuddin A, et al. Comparison of plain radiographs with CT scan to evaluate interbody fusion following the use of titanium interbody cages and transpedicular instrumentation. Eur Spine J. 2003;12(4): 378-385.[11] Cleveland M, Bosworth DM, Thompson FR. Pseudarthrosis in the lumbosacral spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1948. 30: 302-312.[12] Simmons JW. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with posterior elements as chip grafts. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;(193): 85-89.[13] McAlister WH, Shackelford GD. Measurement of spinal curvatures. Radiol Clin North Am. 1975;13(1): 113-121.[14] Hutter CG. Posterior intervertebral body fusion. A 25-year study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;(179): 86-96.[15] Goldstein C, Drew B. When is a spine fused? Injury. 2011; 42(3): 306-313.[16] Behrbalk E, Uri O, Parks RM, et al. Fusion and subsidence rate of stand alone anterior lumbar interbody fusion using PEEK cage with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(12): 2869-2875.[17] Korovessis P, Koureas G, Zacharatos S, et al. Correlative radiological, self-assessment and clinical analysis of evolution in instrumented dorsal and lateral fusion for degenerative lumbar spine disease. Autograft versus coralline hydroxyapatite. Eur Spine J. 2005; 14(7): 630-638.[18] Glaser J, Stanley M, Sayre H, et al. A 10-year follow-up evaluation of lumbar spine fusion with pedicle screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(13): 1390-1395.[19] Kuslich SD, Ulstrom CL, Griffith SL, et al. The Bagby and Kuslich method of lumbar interbody fusion. History, techniques, and 2-year follow-up results of a United States prospective, multicenter trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998; 23(11): 1267-1278; discussion 1279.[20] McAfee PC, Boden SD, Brantigan JM, et al. Symposium: a critical discrepancy-a criteria of successful arthrodesis following interbody spinal fusions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(3): 320-334.[21] Burkus JK, Foley K, Haid RW, et al. Surgical Interbody Research Group--radiographic assessment of interbody fusion devices: fusion criteria for anterior lumbar interbody surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2001;10(4): E11.[22] Kanayama M, Hashimoto T, Shigenobu K, et al. A prospective randomized study of posterolateral lumbar fusion using osteogenic protein-1 (OP-1) versus local autograft with ceramic bone substitute: emphasis of surgical exploration and histologic assessment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(10): 1067-1074.[23] Lee CS, Chung SS, Choi SW, et al. Critical length of fusion requiring additional fixation to prevent nonunion of the lumbosacral junction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(6): E206-211.[24] Ghiselli G, Wharton N, Hipp JA, et al. Prospective analysis of imaging prediction of pseudarthrosis after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: computed tomography versus flexion-extension motion analysis with intraoperative correlation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(6): 463-468.[25] Cannada LK, Scherping SC, Yoo JU, et al. Pseudoarthrosis of the cervical spine: a comparison of radiographic diagnostic measures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(1): 46-51.[26] Taylor M, Hipp JA, Gertzbein SD, et al. Observer agreement in assessing flexion-extension X-rays of the cervical spine, with and without the use of quantitative measurements of intervertebral motion. Spine J. 2007;7(6): 654-658.[27] Ito Z, Imagama S, Kanemura T, et al. Volumetric change in interbody bone graft after posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF): a prospective study. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(10): 2144-2149.[28] Carreon LY, Glassman SD, Djurasovic M. Reliability and agreement between fine-cut CT scans and plain radiography in the evaluation of posterolateral fusions. Spine J. 2007; 7(1): 39-43.[29] Stradiotti P, Curti A, Castellazzi G, et al. Metal-related artifacts in instrumented spine. Techniques for reducing artifacts in CT and MRI: state of the art. Eur Spine J. 2009;18 Suppl 1: 102-108.[30] Williams AL, Gornet MF, Burkus JK. CT evaluation of lumbar interbody fusion: current concepts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(8): 2057-2066.[31] Siepe CJ, Stosch-Wiechert K, Heider F, et al. Anterior stand-alone fusion revisited: a prospective clinical, X-ray and CT investigation. Eur Spine J. 2014.[32] Takeuchi M, Kamiya M, Wakao N, et al. Large volume inside the cage leading incomplete interbody bone fusion and residual back pain after posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Neurosurg Rev. 2015.[33] Biswas D, Bible JE, Bohan M, et al. Radiation exposure from musculoskeletal computerized tomographic scans. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(8):1882-1889.[34] Fazel R, Krumholz HM, Wang Y, et al. Exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation from medical imaging procedures. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(9): 849-857.[35] Gruskay JA, Webb ML, Grauer JN. Methods of evaluating lumbar and cervical fusion. Spine J. 2014;14(3): 531-539.[36] Albert TJ, Pinto M, Smith MD, et al. Accuracy of SPECT scanning in diagnosing pseudoarthrosis: a prospective study. J Spinal Disord. 1998;11(3): 197-199.[37] Concia E, Prandini N, Massari L, et al. Osteomyelitis: clinical update for practical guidelines. Nucl Med Commun. 2006; 27(8): 645-660.[38] Buchowski JM, Liu G, Bunmaprasert T, et al. Anterior cervical fusion assessment: surgical exploration versus radiographic evaluation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(11): 1185-1191.[39] Carreon LY, Glassman SD, Schwender JD, et al. Reliability and accuracy of fine-cut computed tomography scans to determine the status of anterior interbody fusions with metallic cages. Spine J. 2008;8(6): 998-1002.[40] Sugiyama S, Wullschleger M, Wilson K, et al. Reliability of clinical measurement for assessing spinal fusion: an experimental sheep study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(9): 763-768. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||