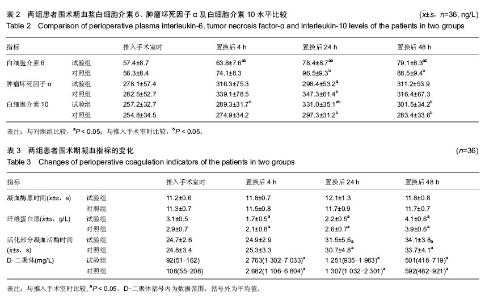
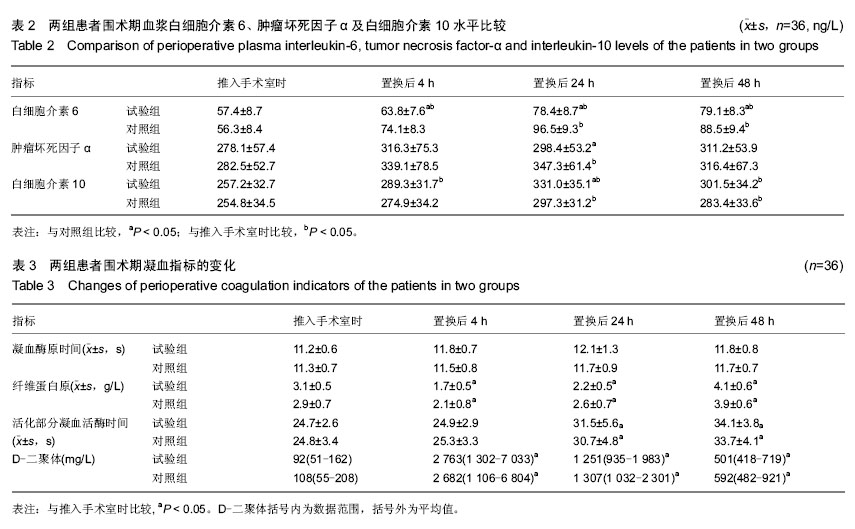
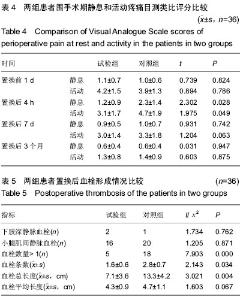
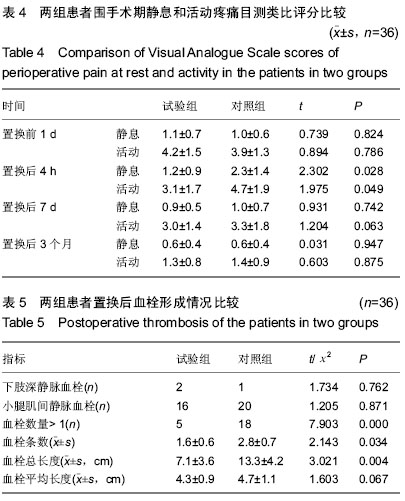
| [1] 吴立新,张海彬,李晓辉,等. 全膝关节置换后类风湿关节炎生化指标及受累关节功能变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(39): 6896-6901.
[2] 聂志奎,李林.人工全膝关节置换术治疗膝关节骨关节炎的疗效观察[J].中国现代医生, 2011,49(4):111-112.
[3] 马骏,李国庆,曹力.全膝关节置换术中不同压力止血带对术后肿胀及疼痛影响的临床研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(13): 1297-1301.
[4] Chung LH, Chen WM, Chen CF, et al. Deep vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty in asian patients without prophylactic anticoagulation. Orthopedics. 2011;34(1):15.
[5] 刘伟恒,关雪梅,牛涧峰.乌司他丁的药理及临床应用效果观察[J]. 中国医药指南, 2014,12(19):103-104.
[6] 姜俪凡,冯艺,安海燕.人工全膝关节置换术康复锻炼期镇痛方式对关节功能恢复的影响[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志, 2014,20(2): 90-94.
[7] 俞一瑾,魏昌伟,陈易,等.加温输血对关节置换术患者术后恢复质量的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志, 2014,30(1):17-20.
[8] 陈易,俞一瑾,倪新莉.术后恢复质量量表分析全麻苏醒期躁动的预警指标[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2013,29(8):782-784.
[9] 刘万超,金立民,王金,等.乌司他丁对老年腹主动脉瘤手术患者的肾保护作用[J].中国老年学杂志, 2012,32(3):626-628.
[10] 唐智权,邢蓉,陶勇,等.乌司他丁心肌保护作用的临床影响因素分析[J].重庆医学, 2013,42(23):2745-2746,2749.
[11] 王春波,唐颖,李佳,等.乌司他丁治疗急性肺损伤/急性呼吸窘迫综合征的疗效观察[J].中国医药导报, 2011,8(29):71-72.
[12] 秦成伟,吴吉智.乌司他丁辅助全身麻醉对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者血清炎症因子水平的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2014, 24(36): 39-42.
[13] 雷亿群,张建平,俞春钊,等.乌司他丁对急性胰腺炎患者炎性因子的影响[J]. 中国生化药物杂志, 2012,33(6):900-901.
[14] 赵若光,陈彦青,姚玉笙,等.乌司他丁对剖宫产患者凝血及血小板聚集功能的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志, 2011,27(6):566-568.
[15] 田昭涛,冯慧远,李慧丽,等.乌司他丁对术后炎症反应和血液高凝状态的影响机制研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2014,24(4): 853-856.
[16] 葛叶盈,徐云,成建庆,等.乌司他丁对老年髋关节置换患者术后并发症影响的病例对照研究[J]. 中国骨伤, 2011,24(6):459-462.
[17] 刘泽文,严国胜,刘会长.乌司他丁对人工关节置换术患者凝血和纤溶系统的影响[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2012,11(18): 1451-1452,1455.
[18] Nagareddy P, Smyth SS. Inflammation and thrombosis in cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Hematol. 2013;20(5): 457-463.
[19] 武迪,段敏,王卫青.全膝关节置换术后膝关节肿胀、疼痛程度对膝关节功能的影响及护理[J].中国医药导报, 2012,9(9): 128-129,134.
[20] 孙扬,杨明敏,李亦梅.人工全膝关节置换围术期镇痛方法:多模式方案及最佳疼痛管理[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(44): 7188-7193.
[21] 陈睿,刘东宁.预见性护理在预防人工全髋或全膝关节手术后深静脉血栓中的应用[J].中国医学创新, 2010,7(17):97-98.
[22] 陈虎,曹力,杨德盛,等. 麻醉方式与全膝关节置换术后深静脉血栓发生率分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2012,20(5):402-405.
[23] 姜文娟.全膝关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓的预防及护理[J]. 中国社区医师(医学专业),2011,13(33):233-234.
[24] 乔志,王义生,殷力,等.全髋及全膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成的季节因素[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(13):2000-2005.
[25] Royse CF, Newman S, Chung F, et al. Development and feasibility of a scale to assess postoperative recovery: the post-operative quality recovery scale. Anesthesiology. 2010; 113(4):892-905.
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
|