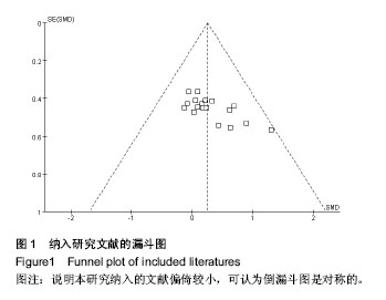
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (15): 2455-2460.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.15.030
Acute exercise leads to varying peptide YY levels in adults: a Meta-analysis
Wu Na-na, Wang Ru, Wang Xue-qiang, Guan Yan-fei
- Key Laboratory of Exercise and Health Sciences (Shanghai University of Sport), Ministry of Education, Shanghai 200438, China
-
Revised:2015-03-13Online:2015-04-09Published:2015-04-09 -
Contact:Wang Ru, Associate professor, Doctoral supervisor, Key Laboratory of Exercise and Health Sciences (Shanghai University of Sport), Ministry of Education, Shanghai 200438, China -
About author:Wu Na-na, Studying for master’s degree, Key Laboratory of Exercise and Health Sciences (Shanghai University of Sport), Ministry of Education, Shanghai 200438, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31000522, 81472148; the Visiting Scholar Project in Shanghai University of Sport, No. stfx20140204
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Na-na, Wang Ru, Wang Xue-qiang, Guan Yan-fei. Acute exercise leads to varying peptide YY levels in adults: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(15): 2455-2460.
share this article
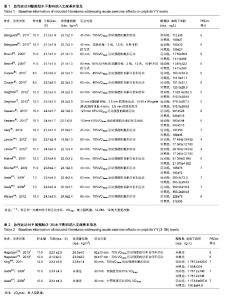
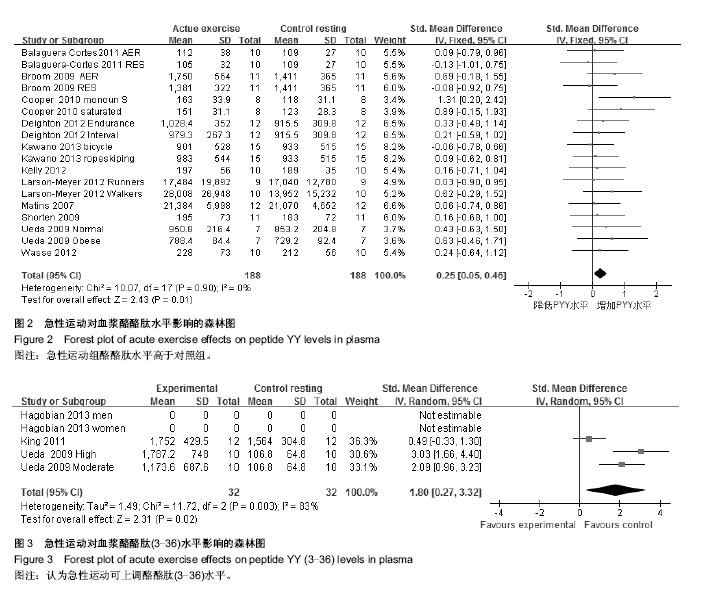
2.1 检索结果分析及质量评价 通过检索PubMed、Google Scholar、Web of Knowledge、Sport Dicus和CNKI数据库,发现急性运动与酪酪肽水平相关的研究英文文献757篇,未发现其他语种文献。 根据文献标题、摘要及纳入和排除标准,剔除不相关文献603;对文献进一步鉴定后,删除不合要求文献140篇,其中123篇无运动干预,11为长期运动运动干预不是急性运动干预,4篇文章受试者是儿童,2篇未报道酪酪肽的曲线下面积,最后剩余文献14篇,共23项随机对照实验。其中19项为高质量(PEDro评分≥6分),4项为低质量(PEDro评分< 6分)。 研究运动影响酪酪肽水平一共纳入11篇文献,包括18个随机对照试验,188名受试者。受试者年龄范围为20.8- 25.9岁(median:23岁),体质量指数19.8-30.0 kg/m2 (median:22.5 kg/m2),体脂率12.9%-35.7%(median:15.1%),运动干预时间45-120 min (median:60 min)。纳入文献详细信息见表1。运动影响酪酪肽(3-36)水平的研究一共纳入3篇文献,包括5个试验,53名受试者。受试者年龄21.0-23.4岁(median:23.4岁),体质量指数22.8-26.4 kg/m2 (median 22.5 kg/m2),体脂率:12.9%-35.7% (median:15.1%),运动干预时间:45-90 min (median:82 min)。纳入文献信息见表2。"
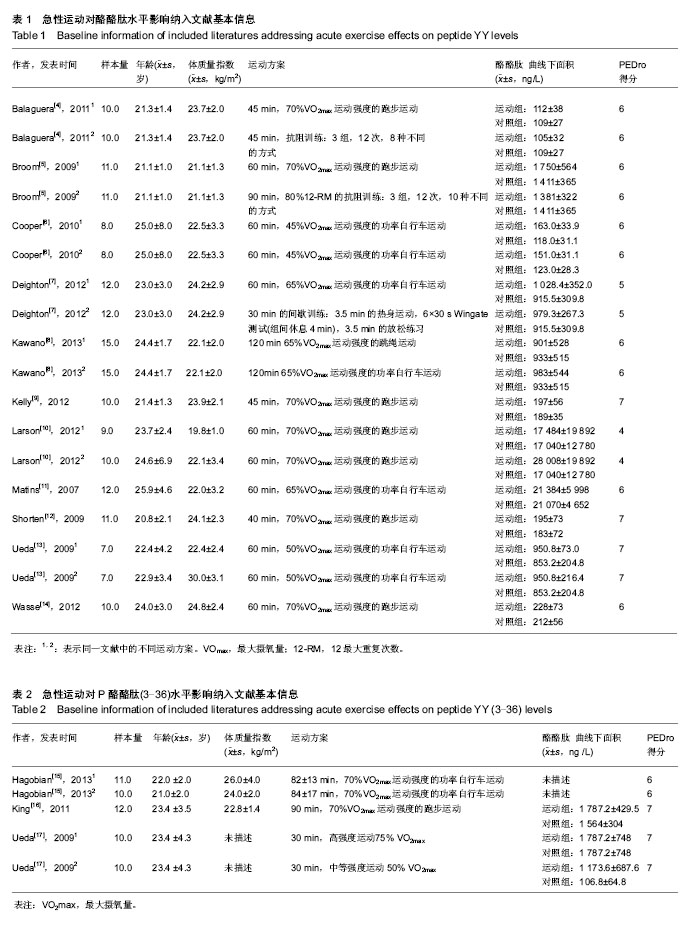
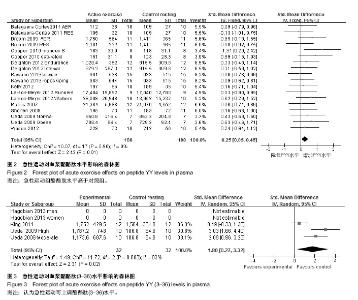
2.3 研究异质性检验及合并统计效应量结果 2.3.1 急性运动对酪酪肽水平的影响 对纳入11篇文献进行异质性检验,χ2=10.07,df=17,P=0.90,I2=0%,I2 < 50%,表明资料具有同质性,可用Meta分析中的固定效应模型进行分析。在森林图见图2,该研究中,合并标准化加权均数差标准化均数差(SMD)=0.25,95%CI为[0.05,0.46],整体效果检验(test for overall effect)的Z=2.43,P=0.01。剔除权重最大Cooper等[6]的研究数据进行敏感性分析,观察结果无变化,证明了结果的稳定性和可靠性,标准化均数差(SMD)的95%CI横线落在无效竖线右侧,急性运动组酪酪肽水平高于对照组。 2.3.2 急性运动对酪酪肽(3-36)水平的影响 由于Hagobian的文章没有索要到原始数据,只有3个随机对照试验,32个受试者纳入分析运动对酪酪肽(3-36)影响。异质性检验χ2=11.72,df=2,P=0.03,I2=83%,I2=83% > 50%,异质性较明显,故采用随机效应模型进行分析。急性运动对酪酪肽(3-36)水平的影响的森林图见图3,合并标准化均值差标准化均数差(SMD)=1.80,95%CI为[0.27,3.32],整体效果检验的Z=2.31,P=0.02,标准化均数差(SMD)的95%CI横线落在无效竖线右侧,故可认为急性运动可上调酪酪肽(3-36)水平。"
| [1] Ballantyne GH. Peptide YY(1-36) and peptide YY(3-36): Part I. Distribution, release and actions. Obes Surg.2006;16(5):651-658. [2] King NA, Blundell JE. High-fat foods overcome the energy expenditure induced by high-intensity cycling or running. Eur J Clin Nutr.1995;49(2):114-123. [3] Schubert MM, Sabapathy S, Leveritt M, et al. Acute exercise and hormones related to appetite regulation: a meta-analysis. Sports Med.2014;44(3):387-403. [4] Balaguera-Cortes L, Wallman KE, Fairchild TJ, et al.Energy intake and appetite-related hormones following acute aerobic and resistance exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab.2011;36(6): 958-966. [5] Broom DR, Batterham RL, King JA, et al. Influence of resistance and aerobic exercise on hunger, circulating levels of acylated ghrelin, and peptide YY in healthy males. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.2009;296(1):R29-R35. [6] Cooper JA, Watras AC, Paton CM, et al.Impact of exercise and dietary fatty acid composition from a high-fat diet on markers of hunger and satiety. Appetite.2011;56(1):171-178. [7] Deighton K, Barry R, Connon CE, et al. Appetite, gut hormone and energy intake responses to low volume sprint interval and traditional endurance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol.2013; 113(5):1147-1156. [8] Kawano H, Mineta M, Asaka M, et al. Effects of different modes of exercise on appetite and appetite-regulating hormones. Appetite.2013;66:26-33. [9] Kelly PJ, Guelfi KJ, Wallman KE, et al. Mild dehydration does not reduce postexercise appetite or energy intake. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2012;44(3):516-524. [10] Larson-Meyer DE, Palm S, Bansal A, et al.Influence of running and walking on hormonal regulators of appetite in women. J Obes.2012;2012:730409. [11] Martins C, Morgan LM, Bloom SR, et al. Effects of exercise on gut peptides, energy intake and appetite. J Endocrinol.2007; 193(2):251-258. [12] Shorten AL, Wallman KE, Guelfi KJ. Acute effect of environmental temperature during exercise on subsequent energy intake in active men.Am J Clin Nutr.2009;90(5): 1215-1221. [13] Ueda SY, Yoshikawa T, Katsura Y, et al.Changes in gut hormone levels and negative energy balance during aerobic exercise in obese young males.J Endocrinol.2009;201(1): 151-159. [14] Wasse LK, Sunderland C, King JA, et al. Influence of rest and exercise at a simulated altitude of 4,000 m on appetite, energy intake, and plasma concentrations of acylated ghrelin and peptide YY. J Appl Physiol (1985).2012;112(4):552-559. [15] Hagobian TA, Yamashiro M, Hinkel-Lipsker J, et al. Effects of acute exercise on appetite hormones and ad libitum energy intake in men and women. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab.2013; 38(1): 66-72. [16] King JA, Wasse LK, Ewens J, et al. Differential acylated ghrelin, peptide YY3-36, appetite, and food intake responses to equivalent energy deficits created by exercise and food restriction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2011;96(4):1114-1121. [17] Ueda SY, Yoshikawa T, Katsura Y, et al. Comparable effects of moderate intensity exercise on changes in anorectic gut hormone levels and energy intake to high intensity exercise. J Endocrinol.2009;203(3):357-364. [18] le Roux CW, Batterham RL, Aylwin SJ, et al. Attenuated peptide YY release in obese subjects is associated with reduced satiety. Endocrinology.2006;147(1):3-8. [19] Korner J, Bessler M, Cirilo LJ, et al. Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery on fasting and postprandial concentrations of plasma ghrelin, peptide YY, and insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2005;90(1):359-365. [20] Batterham RL, Cohen MA, Ellis SM, et al. Inhibition of food intake in obese subjects by peptide YY3-36. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(10): 941-948. [21] Roth CL, Enriori PJ, Harz K, et al.Peptide YY is a regulator of energy homeostasis in obese children before and after weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(12): 6386-6391. [22] le Roux CW, Batterham RL, Aylwin SJ, et al. Attenuated peptide YY release in obese subjects is associated with reduced satiety. Endocrinology.2006;147(1): 3-8. [23] Karra E, Batterham RL. The role of gut hormones in the regulation of body weight and energy homeostasis. Mol Cell Endocrinol.2010;316(2): 120-128. [24] Gibbons C, Caudwell P, Finlayson G, et al. Comparison of postprandial profiles of ghrelin, active GLP-1, and total PYY to meals varying in fat and carbohydrate and their association with hunger and the phases of satiety. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(5): E847-E855. |
| [1] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [2] | Li Xiangze, Bu Xianmin, Li Dongmei, Chi Yulei, Su Qiang, Jin Xintong, Zhao Jian, Zhang Gaotian, Wu Bin, Meng Chunyang . Stem cells, cytokines, hormones, neuropeptides and genes in traumatic brain trauma to promote fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3057-3063. |
| [3] | Wu Qi, Liao Ying, Sun Guanghua, Zhou Guijuan, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Zhong Peirui, Cheng Guo, Deng Chengyuan, Wang Tiantian. Changes of subchondral bone in rat models of knee osteoarthritis treated by elcatonin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 709-715. |
| [4] | Gong Lei, Zhang Xi. Antineoplastic mechanism of antimicrobial peptides: selective membrane destruction and non-membrane dissolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 643-649. |
| [5] | Tian Haiqing, Zhang Yunian, Zhang Hejiang, Fan Yinglu, La Xiaolin. Time for preparing a mouse model of autoimmune premature ovarian failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5168-5172. |
| [6] | Zhang Xi, Gong Lei. Antimicrobial mechanism of antimicrobial peptide and research progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1634-1640. |
| [7] | Chen Meihong, Dang Yini, Zhu Xudong, Li Xuan, Peng Lei, Yang Jiajia, Zhang Guoxin. Feasibility of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell sheet transplantation for wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 790-796. |
| [8] | Xiong Na, Liu Yanfei, Wei Wei . Self-assembling peptide hydrogels and bone tissue construction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5531-5537. |
| [9] | Zhang Yuantong. Body composition and bone mineral density of juvenile basketball players versus ordinary middle school students: data from a middle school [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 341-347. |
| [10] | Lan Qingshi. Participation degree and control ability of human latissimus dorsi, trapezius, triceps, musculus and deltoid during cross support of hand ring: analysis on contribution rate of major muscle group [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 361-366. |
| [11] | Kong Lingyao, Li Tao, Zeng Xinglin, Li Jian, Xiong Yan. Synovial chondromatosis: how to improve the diagnosis accuracy and clearance rate of tumor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4570-4575. |
| [12] | Wu Tingyun, Wang Detang, Zhu Youjia, Ruan Qiong, Wu Aimin, He Shangqun, Zeng Xiaofang. Effects of different types of fluoride-free toothpaste on the remineralization of enamel after acid erosion: an in vivo study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2842-2846. |
| [13] | Yu Hong, Liu Yan. Strength of knee flexor and extensor in football athletes after vibration training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2327-2331. |
| [14] | Zhu Yaojia1, Huo Hongfeng1, 2. Balance ability and foot type characteristics during different postures of standing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2345-2349. |
| [15] | Li Xintong1, Pan Weimin2, Qin Huasheng1, Qu Lei1, Zhang Hengyin1, Zhu Xinrui1. Blood flow restriction training: a new method for accelerating musculoskeletal rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2415-2420. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||