Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (14): 2291-2296.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.14.027
Spermatogonial stem cells and their biological characteristics: current situation, advances and applications
Luo Yue-ji1, 2, Zeng Jie2, Tang Rui-ling1, Wang Xing-ming1, Fan Li-qing1
- 1Research Institute of Reproduction and Stem Cell Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410078, Hunan Province, China; 2Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Changsha Medical University, Changsha 410219, Hunan Province, China
-
Revised:2015-03-05Online:2015-04-02Published:2015-04-02 -
Contact:Fan Li-qing, M.D., Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Research Institute of Reproduction and Stem Cell Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410078, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Luo Yue-ji, Master, Lecturer, Research Institute of Reproduction and Stem Cell Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410078, Hunan Province, China; Department of Basic Medical Sciences Changsha Medical University, Changsha 410219, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Plan Project of Hunan Province, No. 2011SK3263
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Yue-ji, Zeng Jie, Tang Rui-ling, Wang Xing-ming, Fan Li-qing. Spermatogonial stem cells and their biological characteristics: current situation, advances and applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2291-2296.
share this article
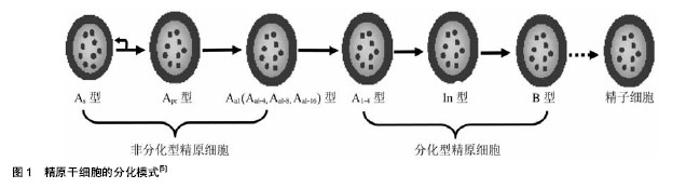
2.1 精原干细胞的起源 哺乳动物原始生殖系细胞起源于胚胎外胚层,以小鼠为例,在小鼠胚胎11.5 d时,原始生殖系细胞陆续从尿囊基部沿后肠迁移到双侧生殖嵴,大约在胚胎13.5 d时原始生殖系细胞停止分裂[4]。在雄性生殖腺嵴,原始生殖系细胞被支持细胞-Sertoli前体细胞包围,共同形成被称为生精索的实体细胞团,此时的原始生殖系细胞的形态发生改变,成为精原母细胞或性原细胞,之后随着发育的进行,精索逐渐形成腔隙,增殖10 000倍后停止在G0/G1期直到出生;而在雌性个体发育过程中,原始生殖系细胞经减数分裂后失去干细胞潜能,成为卵母细胞。与卵母细胞相反,精母细胞仍然保持并具有干细胞潜能,出生后精原母细胞继续增殖,在出生后六七天迁移至曲细精管基底膜并发育成精原干细胞[5]。 2.2 精原干细胞的生物学特性 2.2.1 精原干细胞的形态学特征及数量 哺乳动物精原干细胞紧贴曲细精管基膜,与其他成体干细胞一样呈现圆形或是卵圆形,直径为9-12 μm,细胞核大,核呈圆形或轻微卵圆形,直径约7 μm,胞质内除核糖体、线粒体外,其他细胞器均不发达[6]。精原干细胞的细胞核常染色质丰富且均匀,异染色质较少,核仁偏向于核膜处,数目不定,有的是1个,有的是3-5个;细胞质中的线粒体呈圆或椭圆状,内有板层状线粒体嵴。精原干细胞由于胞质分裂不完全,细胞之间以间桥相连,苏木精-伊红染色后由于核内染色质呈强碱性,染成蓝紫或深蓝色,胞质呈弱碱性,染成淡蓝色[7]。 根据有关数据的估测,在成年小鼠睾丸中大约有细胞的总数量是108个,精原干细胞的数量为2×104个,仅占总数的0.02%-0.03%[8],其余大部分生殖细胞为高度特化时期的精子细胞、正在进行减数分裂的精母细胞和有丝分裂的精原细胞[9]。所以,精原干细胞的数量少也是其显著特征之一。 2.2.2 精原干细胞的发育微环境——龛位(niche) 干细胞在机体组织中的居所被称为干细胞巢,也称之为干细胞龛境(niche)或壁龛,最初是在造血系统中提出,目前研究发现,睾丸组织中也同样存在于龛境[10]。睾丸中精原干细胞生存发育的龛境是由周围的支持细胞以及所有控制干细胞增殖与分化的外部信号所构成的微环境(microenvironment)或分子环境(molecular milieu)。精原干细胞的生存发育受其自身因素和龛境的双重影响,例如为了保持自身群体数量恒定而调整增殖更新速度,大量精原细胞分化以维持器官功能等[11-13]。一旦精原干细胞脱离这样的微环境,其干细胞生物学特征将不再保持,而是朝着既定方向分化,精原干细胞移植研究进一步证实了干细胞龛位的存在。精原干细胞数量以及精原干细胞的微环境为研究组织特异性干细胞生物学提供了很宝贵的线索,它为治疗一些疾病提供新途径[14]。 2.2.3 精原干细胞具有分化潜能和迁移能力 精子的发生是一个组织性极强的复杂过程。原始生殖细胞是在胚胎发育的外胚层中被鉴定出来的,它是形成动物配子的前体,随着胚胎发育的进行迁移到生殖腺嵴,进而转化为精母细胞,在个体出生后精母细胞再发育(图1),发育过程存在两步重要的阶段:第一步存在于单个型(A single,As)精原细胞与对称型(A paired,Apr)精原细胞之间,单个型精原细胞能自我更新或者分裂形成由两个通过胞质桥相连的精原细胞,即对称型精原细胞;第二步存在于排列型(A aligned,Aal)精原细胞与A1型之间,对称型精原干细胞进一步分裂形成4个、8个或16个排列型精原细胞。排列型精原细胞不经过有丝分裂即分化为A1精原细胞,A1精原细胞通过严格时效控制的连续6次的细胞分裂,分化形成A2精原细胞、A3精原细胞、A4精原细胞及中间型精原细胞,最终分化为B型精原细胞。B型精原细胞经过数次分裂后,体积增大并分化为初级精母细胞,再经过减数分裂产生圆形精子,最终变形成为成熟的精子,完成生精过程[15]。 精原干细胞具有一定的迁移能力,成年动物生精上皮中的精原干细胞受到有害因素影响时会造成生精细胞损失和退化,例如经过X射线照射或是腹腔注射入烷化剂二甲磺酸丁二醇二酯等。如果去除有害因素,部分存活的精原干细胞在生精小管内能重新进行分布和定居,重新建立起精原干细胞群,启动精子发生[16]。除此之外精原干细胞移植实验也表明了它的迁移能力,移植的精原干细胞在受体睾丸中能从生精小管管腔迁移到生精上皮基膜处,随着时间的延长,还能继续扩张其领地[5,17-18]。 2.3 精原干细胞自我更新和分化的调控 2.3.1 微环境对精原干细胞的调控 在高等脊椎动物中,干细胞生存的微环境是体内成体干细胞的集中存储部位,它是由细胞群落中特定的细胞外基质及周围细胞所组成,对维护干细胞自我更新、决定干细胞分化命运至关重要。微环境中存在调控干细胞自我更新和分化的各类生长和细胞因子,并具有排除已发生分化干细胞的作用[19]。精原干细胞的微环境包括精原干细胞本身及周边细胞和结构,如支持细胞、管周肌样细胞等细胞以及附着在胞外基质上的各种生长和细胞因子等[20],因此相对于其他成体干细胞而言,精原干细胞的微环境较为复杂。有文献报道,微环境对精原干细胞的调节分为两种途径:首先是机体其他组织和器官间接调控精原干细胞的增殖和分化,主要是通过产生一些活性物质进入内分泌系统运输到睾丸,作用于微环境,被称为外源性调节;其次,自身微环境中的各类因素通过网络式调控机制直接或间接作用于精原干细胞的增殖、分化、代谢及功能活动,被称为内源性调节[21]。 2.3.2 精原干细胞自我更新的调控 精原干细胞通过增殖和分化最终会发育成为成熟的精子,此过程复杂有序,要求有一个可以数量恒定且连续分化的细胞群,所以精原干细胞必须具备不断自我更新和复制的能力。目前,虽然关于精原干细胞自我更新和维持其数量恒定的具体机制仍然有待进一步研究,但已有大量研究表明,许多基因及生长因子参与了这一过程,如早幼粒细胞白血病锌指蛋白、胶质细胞源神经营养因子、ERM/Etv等。 早幼粒细胞白血病锌指蛋白(the promyelocytic leukaemia zinc finger ,Plzf):早幼粒细胞白血病锌指蛋白基因是国内生物医学领域中第一个克隆出的新的人类疾病的基因,在生物大分子相互作用水平和转基因小鼠模型中证实了其致白血病的作用。早幼粒细胞白血病锌指蛋白可与特异性DNA序列结合起到转录抑制作用,属于转录因子,在睾丸中广泛表达于单个型精原细胞、对称型精原细胞、排列型精原细胞,不仅能维持精原干细胞的活性[22],在精子发生过程中也起到了重要作用[23]。现已有实验证明早幼粒细胞白血病锌指蛋白对于精原干细胞的增殖是必需的一类生殖细胞自主性的细胞因子,与支持细胞介导的信号通路相互作用来完成生物学功能,如GDNF和SCF通路[24]。在对luxoid 突变体小鼠的研究发现,此类突变小鼠只能产生少量的精子,出生后随着年龄的增长生殖细胞将会消失[25]。2004年Buaas等[26]对luxoid突变体小鼠研究时发现编码早幼粒细胞白血病锌指蛋白的基因中有一个无义突变,这个突变是在基因的Zfp145序列上,对Zfp145序列进行靶向断裂,这样的小鼠随着长大会丢失一部分的精原细胞,支持细胞不受影响,但生精小管会发生结构的变化,细胞凋亡增加,这项研究也进一步证实了早幼粒细胞白血病锌指蛋白基因上的Zfp145 序列对精原干细胞的自我更新有一定的调控作用[27]。"

胶质细胞源神经营养因子(glial cell line- derivedneurotrophic factor,GDNF):胶质细胞源神经营养因子于1993年由Lin等从大鼠神经胶质细胞系B49的培养液中首先纯化并命名,目前已在多种神经细胞和神经相关细胞中发现胶质细胞源神经营养因子表达,并有靶源性神经营养因子的作用。在小鼠睾丸中,支持细胞分泌胶质细胞源神经营养因子[28],在支持细胞、分化的生殖细胞、管周肌样细胞及间质细胞均有胶质细胞源神经营养因子mRNA表达,调节精原干细胞增殖和分化的比例。有大量研究表明胶质细胞源神经营养因子对精原干细胞自我更新的维持起到了非常关键的作用,是体外培养需添加的细胞因子之一[29-30]。胶质细胞源神经营养因子家族的神经营养因子信号是通过复合受体途径实现的,胶质细胞源神经营养因子的受体也表达在生殖细胞里,复合受体由两部分组成,第一部分是糖基化的磷脂酰肌醇(glycosyl-phosphatidyl inositol,GPI)锚定到细胞表面的蛋白分子,称为胶质细胞源神经营养因子家族受体α(GDNF Family Recepter alpha,GFRα);另一部分为原癌基因c-ret编码的产物蛋白Ret,它是一种受体酪氨酸激酶。前者特异性地结合胶质细胞源神经营养因子家族成员,促使Ret磷酸化,磷酸化的Ret激活其下游的丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)等,导致一系列胞内途径的激活,从而产生多种生物效应,在精原干细胞中可直接导致有丝分裂的发生[31-32]。 Tadokoro等[33]利用睾丸没有生育能力的小鼠研究精原干细胞自我更新机制,发现在未分化的精原细胞有GFRa1 mRNA的表达,且GFRa1的剂量调控胶质细胞源神经营养因子的信号转导,从而对单个型精原细胞增殖和分化起着双向调节作用:高剂量时诱导其自我增殖、低剂量时诱导其分化,同时还发现胶质细胞源神经营养因子浓度的主要调控因素为卵泡刺激素。Meng等[34]研究表明,未分化精原细胞的增殖受胶质细胞源神经营养因子调节,无胶质细胞源神经营养因子等位基因的靶基因小鼠没有精原干细胞,而过度表达胶质细胞源神经营养因子的小鼠存在大量精原干细胞,且可能引起非转移性睾丸瘤。刘欢欢等[35]研究中发现胶质细胞源神经营养因子通过与精原干细胞膜上受体GFRα1结合形成GDNF-GFRα1复合物,并活化RET,最后激活MAPK、SFK和PI3K-AKT信号通路并达到调控精原干细胞自我更新和分化的目的。由此看来胶质细胞源神经营养因子是影响精原干细胞进行自我更新的重要生长因子。 Etv5/ERM对精原干细胞的调控:Ets转录因子家族一共有30多个成员,具有调节细胞增殖、分化、凋亡等作用[21]。Etv5/ERM在精原干细胞的自我更新发生中起重要的调节作用。转录因子Ets家族的一个重要成员是转录因子Ets差异基因5(Ets variant 5,Etv5),Etv5基因靶向敲除后小鼠模型的精原干细胞在第一次精子发生后会逐渐减少,最终会导致无精症和唯支持细胞综合征[36-37]。所以,Etv5 被认为维持精子的持续发生以及在精原干细胞的更新、分化中起着重要作用。 ERM是Ets亚家族中的一员,包括ER81和PEA3。有研究表明,小鼠ERM的缺失将导致睾丸和身体发育的异常,ERM功能缺失小鼠在出生4周后表现出正常精子的发生过程,但其精原干细胞会随着时间的推移逐渐减少并最终消失;此外,其附睾中仍会存在活动的精子,但已丧失受精能力,对这类小鼠的基因进行分析表明,精原细胞特定表达的基因如Stra8、Dazl及Plzf等表达量会明显减少[38]。 另外,TATA 盒结合蛋白相关因子(Tafs)、集落刺激因子1(CSF1)等都是精原干细胞自我更新的调节蛋白及生长因子。 2.3.3 精原干细胞分化的调控 精原干细胞经历了3个关键分化点,第一个是从单个型到对称型精原细胞,此分化点之后所形成的细胞均由细胞间桥相连,这是精子形成的第一步,也是分化的开端;第二个关键点是从排列型到A1精原细胞的转变,排列型精原干细胞分裂形成A1精原干细胞的过程是不可逆的,紧接着会进行6次分裂注定导致这些细胞不可避免的走向减数分裂;第三个关键点是从A1向B型精原细胞的转化,此时精原细胞的增殖表现出高度同步化。以下几个因素调控了精原干细胞分化的机制,例如SCF/c-Kit系统、维生素等。 干细胞因子(stem cell factor,SCF)及受体c-Kit:在以上众多分子中,SCF/c-Kit研究较多。干细胞因子是一种作用广泛的多肽生长因子,它是受体原癌基因蛋白质(c-kit)的配体,两者可发生特异性的结合而诱导受体的磷酸化从而对生殖细胞增殖、分化及原始生殖细胞迁徙、存活等有重要的调控作用。还有资料表明, 在原始生殖细胞和其他阶段生殖细胞发育过程中SCF/c-Kit系统也起到了重要的调控作用[39]。SCF/c-Kit系统在生精细胞的发育过程中可维持分化A型精原细胞状态,而对未分化A型精原细胞没有影响。体内实验已证实动物出生后不久,睾丸中支持细胞就会生成较多的干细胞因子,干细胞因子与A型精原细胞表达的c-Kit酪氨酸激酶受体发生特异性的结合,维持干细胞状态和影响A型精原细胞分化[40]。在体外,经X射线照射后,干细胞因子可刺激残留的A型精原干细胞的存活和分化。在精原细胞培养中,干细胞因子诱导DNA复制,注入抗c-kit抗体后会阻断精原细胞的增殖,生精过程开始阶段受阻,在分化型A1-A2精原细胞DNA合成受抑制和雄性不育时,减数分裂开始时c-kit表达终止[41]。 维生素:正常精子的发生过程中脂溶性维生素A、E和水溶性维生素C都发挥了至关重要的作用。维生素A的活性形式之一视黄酸是促进单个型精原干细胞自我更新和分化的细胞因子,大鼠维生素A缺乏将导致其生殖细胞分化的终止[21]。在维生素A缺乏症动物模型中,大量A型精原干细胞退化[42]。维生素C和E则是精原干细胞的存活因子,培养基中添加维生素C和E虽不刺激精原干细胞增殖,但可维持其存活[43],在精子的发生过程中维生素C和E是抗氧化剂,可清除体内的超氧自由基,提高的精子活力,保护精子免受伤害。 2.4 精原干细胞的应用 2.4.1 男性功能的保存及不育的治疗 每年有很多年轻癌症患者在接受放化疗时会破坏内源性精子的发生,从而可能会导致永久或长时间的不育,针对这种情况,可在治疗前低温储存精原干细胞,待患者治愈后将低温贮藏的精原干细胞复苏移植回体内,开始精子发生及恢复生育能力[44]。目前关于精原干细胞分离纯化和体外培养技术正在不断的进步和完善,获得临床应用也正在不断的努力中。 人类不育的原因大部分来自男性,其中尤其以精子发生出现障碍为主,临床上称为精子产生异常。无精子症和少精子症就是由于精子发生障碍而导致的男性不育,但这些患者睾丸中精原干细胞浓度通常较高,当有少量的精子或处于单倍体时期生殖细胞时,可以采用体外受精、胞质内精子注射、胚胎移植等辅助生殖技术进行治疗。解放军北京军区总医院生殖医学中心张水文等[45]介绍非梗阻性无精子症的诊疗大都采用精子库提供的精子而满足当父亲的愿望。精原干细胞是哺乳动物成体睾丸生精上皮内惟一可复制的多潜能二倍体细胞,它能在体外分离、纯化、培养、冻存及同体或异体移植。近年来,随着精原干细胞移植技术的发展,将为这一难题探索出一种新的治疗方法。 2.4.2 转基因动物 目前转基因动物的研究在医学和农业等领域有着广泛的应用前景。这项技术涉及到细胞工程、组织胚胎工程及基因工程,是现代生物技术的一项重要实验手段。精原干细胞在转基因动物上的研究机制是将外源基因转染体外培养的精原干细胞,使之整合在细胞染色体上,传代培养后再移植回受体动物睾丸,该雄性动物产生的精子就有可能携带外源基因的信息,由精子受精获得的子代动物就可以携带外源基因[46]。从原理上讲,这项技术有着比转染和筛选胚胎干细胞更为简便的优点,所以备受人们的关注。 2.4.3 其他 除了上述应用,精原干细胞移植技术为精子的发生提供了新的方法和手段,解决了一些问题,已成为研究生殖细胞和精子发生机制的有力工具。体外培养精原干细胞及遗传信息的体外操作可修正生殖细胞的遗传缺陷,再进一步培养增殖,回植到受体睾丸或者在体外通过诱导将精原干细胞增殖分化为精子,通过人工受精矫正家族性遗传疾病,为遗传病的治疗提供新途径。"

| [1] Hamra FK, Schultz N, Chapman KM, et al. Defining the spermatogonial stem cell. Dev Biol. 2004;269(2):393-410.
[2] Dobrinski I, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL.Transplantation of germ cells from rabbits and dogs into mouse testes. Biol Reprod. 1999;61(5):1331-1339.
[3] Brinster RL, Zimmermann JW. Spermatogenesis following male germ-cell transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(24):11298-11302.
[4] Molyneaux K, Wylie C. Primordial germ cell migration. Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48(5-6):537-544.
[5] 张学明,李德雪,于家傲,等.精原干细胞的生物学特性[J]. 细胞生物学杂志,2006,28(1):37-41
[6] Weiss L.Histology cell and tissue biology[M].Fifth ed. New York: Elsevier Science Publishing Co., 1983:1056-1016.
[7] 薛振华,刘国世,王永彬,等.精原干细胞研究进展[J].中国畜牧杂志,2007,43(23):41-45.
[8] Bellvé AR, Millette CF, Bhatnagar YM, et al. Dissociation of the mouse testis and characterization of isolated spermatogenic cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977;25(7): 480-494.
[9] de Rooij DG1, Griswold MD. Questions about spermatogonia posed and answered since 2000. J Androl. 2012;33(6): 1085-1095.
[10] Wong MD, Jin Z, Xie T. Molecular mechanisms of germline stem cell regulation. Annu Rev Genet. 2005;39:173-195.
[11] Tran J, Brenner TJ, DiNardo S. Somatic control over the germline stem cell lineage during Drosophila spermatogenesis. Nature. 2000;407(6805):754-757.
[12] Watt FM, Hogan BL. Out of Eden: stem cells and their niches. Science. 2000;287(5457):1427-1430.
[13] Spradling A, Drummond-Barbosa D, Kai T. Stem cells find their niche. Nature. 2001;414(6859):98-104.
[14] 李靳,彭奔,刘苗苗,等.精原干细胞niche的研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(3):554-557
[15] de Rooij DG. Proliferation and differentiation of spermatogonial stem cells. Reproduction. 2001;121(3): 347-354.
[16] Choi YJ, Mendoza L, Rha SJ, et al. Role of p53-dependent activation of caspases in chronic obstructive uropathy: evidence from p53 null mutant mice. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12(5):983-992.
[17] Ogawa T. Spermatogonial transplantation: the principle and possible applications. J Mol Med (Berl). 2001;79(7):368-374.
[18] Ryu BY, Orwig KE, Avarbock MR, et al. Stem cell and niche development in the postnatal rat testis. Dev Biol. 2003;263 (2):253-263.
[19] 萨初拉,顾婷玉,何志颖,等.哺乳动物精原干细胞的研究进展[J], 中国细胞生物学学报,2014, 36(3): 392-399.
[20] de Rooij DG. The spermatogonial stem cell niche. Microsc Res Tech. 2009;72(8):580-585.
[21] 金波,刘洋,岳占碰,等.精原干细胞自我更新和分化的调控[J].生命科学,2011,23(3):244-248.
[22] Buaas FW, Kirsh AL, Sharma M, et al. Plzf is required in adult male germ cells for stem cell self-renewal. Nat Genet. 2004; 36(6):647-652.
[23] Oatley JM, Avarbock MR, Telaranta AI, et al. Identifying genes important for spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(25):9524-9529.
[24] 孙大林,张新东.精原干细胞增殖和分化相关因子的研究进展[J].中华男科学杂志,2010,17(3):268-272.
[25] Costoya JA, Hobbs RM, Barna M, et al. Essential role of Plzf in maintenance of spermatogonial stem cells. Nat Genet. 2004;36(6):653-659.
[26] Buaas FW, Kirsh AL, Sharma M, et al. Plzf is required in adult male germ cells for stem cell self-renewal. Nat Genet. 2004; 36(6):647-652.
[27] Kotaja N, Sassone-Corsi P. Plzf pushes stem cells. Nat Genet. 2004;36(6):551-553.
[28] de Rooij DG. Proliferation and differentiation of spermatogonial stem cells. Reproduction. 2001;121(3): 347-354.
[29] Kanatsu-Shinohara M, Ogonuki N, Iwano T, et al. Genetic and epigenetic properties of mouse male germline stem cells during long-term culture. Development. 2005;132(18): 4155-4163.
[30] Oatley JM, Avarbock MR, Telaranta AI, et al. Identifying genes important for spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(25):9524-9529.
[31] Soler RM, Dolcet X, Encinas M, et al. Receptors of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family of neurotrophic factors signal cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in spinal cord motoneurons. J Neurosci. 1999;19(21):9160-9169.
[32] 胡红梅,李伟,吴绍华.生长因子对精原干细胞增殖、分化影响的研究现状[J].四川解剖学杂志,2006,14(1):41-43.
[33] Tadokoro Y, Yomogida K, Ohta H, et al. Homeostatic regulation of germinal stem cell proliferation by the GDNF/FSH pathway. Mech Dev. 2002;113(1):29-39.
[34] Meng X, Lindahl M, Hyvönen ME, et al. Regulation of cell fate decision of undifferentiated spermatogonia by GDNF. Science. 2000;287(5457):1489-1493.
[35] 刘欢欢,陈曦,余树民,等.以GDNF为核心的哺乳动物精原干细胞调控网络[J].基础医学与临床,2015,35(3):409-412.
[36] Morrow CM, Hostetler CE, Griswold MD, et al. ETV5 is required for continuous spermatogenesis in adult mice and may mediate blood testes barrier function and testicular immune privilege. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1120:144-151.
[37] Eo J, Song H, Lim HJ. Etv5, a transcription factor with versatile functions in male reproduction. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2012;39(2):41-45.
[38] Chen C, Ouyang W, Grigura V, et al. ERM is required for transcriptional control of the spermatogonial stem cell niche. Nature. 2005;436(7053):1030-1034.
[39] 李泽廷,桂耀庭,蔡志明.精子发生中几个关键基因的研究进展[J].国际泌尿系统杂志,2006,26(2):240-244.
[40] Rossi P, Sette C, Dolci S, et al. Role of c-kit in mammalian spermatogenesis. J Endocrinol Invest. 2000;23(9):609-615.
[41] Vincent S, Segretain D, Nishikawa S, et al. Stage-specific expression of the Kit receptor and its ligand (KL) during male gametogenesis in the mouse: a Kit-KL interaction critical for meiosis. Development. 1998;125(22):4585-4593.
[42] McLean DJ, Russell LD, Griswold MD. Biological activity and enrichment of spermatogonial stem cells in vitamin A-deficient and hyperthermia-exposed testes from mice based on colonization following germ cell transplantation. Biol Reprod. 2002;66(5):1374-1379.
[43] 李德雪,张学明,李子义,等.小鼠精原干细胞体外培养的一般特性[J].中国兽医学报,2001,21(2):160-163.
[44] Brinster RL. Male germline stem cells: from mice to men. Science. 2007;316(5823):404-405.
[45] 张水文,杨玟,李建华.精原干细胞治疗非梗阻性无精子症的前景展望[J].中国优生与遗传杂志,2014,22(11):68-70.
[46] 周燕,吴绍华.哺乳动物精原干细胞技术的研究进展[J].国际遗传学杂志,2006,29(1):77-80. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||