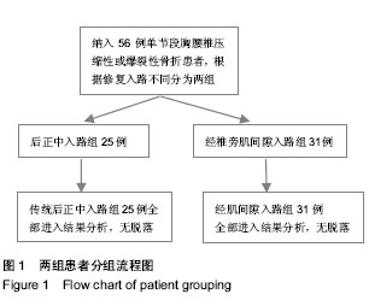
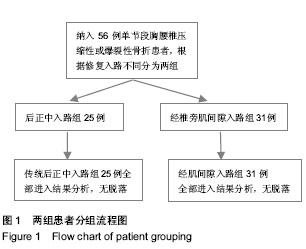
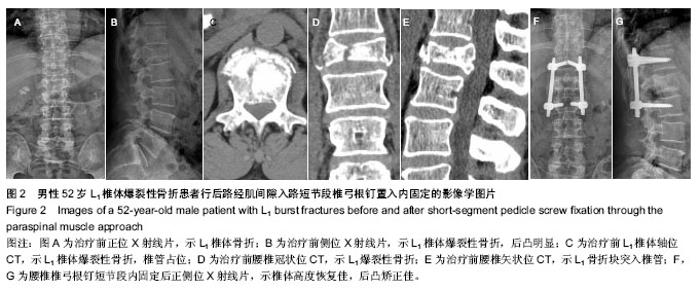
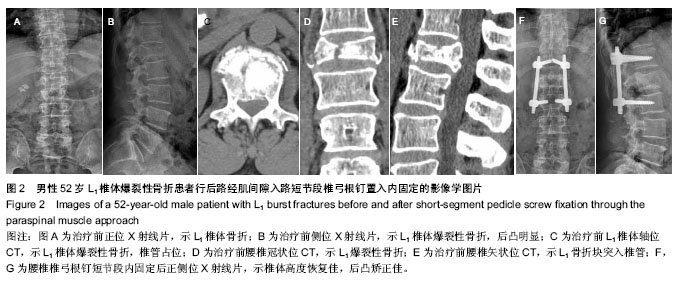
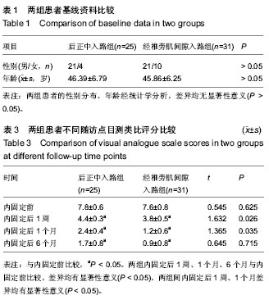
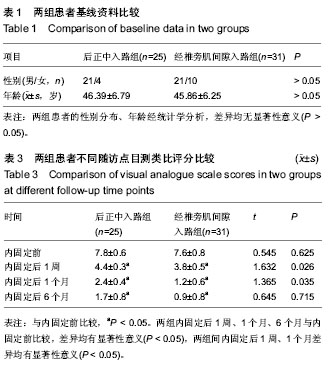
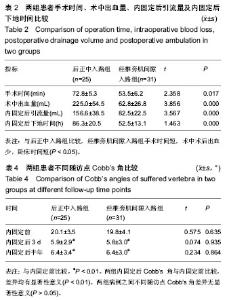
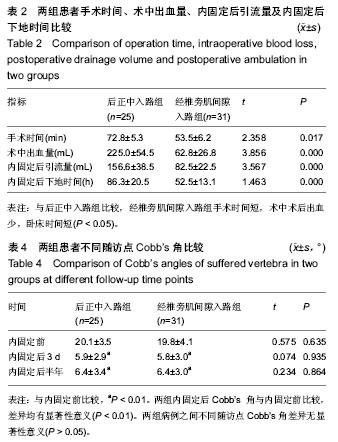
| [1] 池永龙,徐华梓,林众,等.微创经皮穿刺椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的初步报道[J].中华外科杂志,2004,42(24): 1307-1311.
[2] Kim DY,Lee SH, chung SK,et al.Compation of multifidus muscle atrophy and trunk extension muscle Strength: Percutaneos versue open Pedicle Scren fixation. Spine. 2005;30(1):123-129.
[3] 陈晓陇,尚平,温月凤,等.椎旁肌间隙入路与传统后正中入路在胸腰椎后路手术中的应用比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(10): 925-930.
[4] 李玉茂,王剑火,林奇益.椎旁肌间隙入路与传统后入路在胸腰椎骨折后路手术中的比较[J].颈腰痛杂志,2012,33(05):340-344.
[5] Barbagallo GM,Yoder E,Dettori JR,et al. Percutaneous minimally invasive versus open spine surgery in the treatment of fractures of the thoracolumbar junction:a comparative effectiveness review. Evid Based Spine Care J. 2012;3(3):43-49.
[6] Wiltse LL, Spencer CW. New uses and refinements of the pamspinaI approach to the lumbar spine.Spine.1988;13(6):69-706.
[7] 赵斌,赵轶波,马迅,等.经椎旁肌间隙入路在胸腰椎骨折治疗中的应用.中华骨科杂志,2011,31(10):1147-1151.
[8] Vaccaro AR, Lehman RA Jr, Hurlbert RJ, et al. A new classification of thoracolumbar injuries:the importance of injury morphology, the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex, and neurologic status.Spine. 2005;30(20):2325-2333.
[9] Wiltse LL, Bateman JG, Hutchinson RH, et al. The paraspinal sacrospinalis-splitting approach to the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1968;50(5):919-926.
[10] Kawaguchi Y, Yabuki S, Styf J, et al. Back muscle injury after posterior lumbar spine surgery.Topographic evaluation of intramuscular pressure and blood flow in the porcine back muscle during surgery.Spine. 1996;21:2683-2688.
[11] Gejo R,Malsui H, Kawaguchi Y, et al.Serial changes in trunk muscle performance after posterior lumbar surgery.Spine. 1999;24:1023-1028.
[12] 林达生,郭林新,丁真奇,等.椎旁肌间隙入路经伤椎椎弓根植骨内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华外科杂志,2011,49(2):125-129.
[13] 涂来勇,阚瑞,杨明坤,等.经多裂肌间隙单侧椎弓根钉固定椎间融合治疗腰椎退行性疾病的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(7):629-631.
[14] 王洪伟,孙连星,王尚忠,等.微创经多裂肌间隙单侧椎弓根钉固定TLIF术治疗椎间盘源性腰痛的疗效评价[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(9):817-819.
[15] Olivier LL, Beldame J, Slimane MO, et al.Comparison between one midline ctltaneous incision and two lateral incisions in the lumb”paraspinal approach by Wiltse:a cadaver surdy. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006;28:494-498.
[16] Stephen T.Failed back syndrome.Neurologis. 2004;10(5):257-264.
[17] Kim KT, Lee SH, Suk KS, et al.The quatitative analysis of tissue injury markeIs after mini-open lumbar fusion. Spine. 2006;3l(6):712-716.
[18] Stevens KJ, Spenciner DB, Griffiths KL, et al.Comparison of minimally invasive and conventional open posterolateral lumbar fusion using magnetic resonance imaging and restraction pressure studies.J Spinal Disrod Tech. 2006;19(2): 77-86.
[19] Dick W, Kluger P, Magerl F, et al. A new device for interal fixation of thoracolumbar and lumbar spin fratures: the firateur in terne. Paraplegia.1985;23(4):225-232.
[20] 晏礼,宋文慧,王春强.胸腰椎骨折分类及治疗研究新进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(12):1202-1205.
[21] 宋升,孙振中,芮永军,等.椎弓根钉棒系统置入复位内固定胸腰段椎体爆裂骨折的椎管形态学变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17 (22):4047-4054.
[22] 聂锋锋,张英华,黄寿国,等.经皮微创椎弓根螺钉内固定与开放手术治疗胸腰椎骨折:Cobb’s 角与椎体前缘高度恢复的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(44):7094-7099.
[23] 丁磊,丁伟伟,闫生亮,等.后路经伤椎单侧椎弓根通道植骨并置钉短节段内固定修复胸腰段椎体爆裂性骨折[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(44):7100-7105.
[24] 王秀会,陆耀刚,付备刚,等.经多裂肌间隙入路伤椎单侧置钉短节段固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014,29 (5):427-429.
[25] 王洪伟,李长青,周跃,等.微创与传统开放附加伤椎经椎弓根螺钉内固定手术治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(2):112-116.
[26] 刘良乐,汤呈完,杨国敬.胸椎椎弓根螺钉置入技术的研究现状与展望[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(2):148-150.
[27] 方摇钧,郑季南,洪庆南,等.经伤椎椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(4):364-367.
[28] 罗卫华,朱剑,叶峥.经伤椎椎弓根内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(1):8-10.
[29] 厉晓龙,王生介,刘伟峰,等.经椎弓根固定结合硫酸钙椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(4):369-371
[30] 何海龙,叶晓健,袁文,等.经伤椎椎弓根钉固定治疗重度胸腰椎爆裂性骨折的临床疗效研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2009,7(3): 153-156.
[31] 张蒲,谢幼专,孙月华,等.经伤椎椎弓根钉固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2009,12( 5):516-518.
[32] Barbagallo GM, Yoder E, Dettori JR, et al. Percutaneous minimally invasive versus open spine surgery in the treatment of fractures of the thoracolumbar junction:a comparative effectiveness review. Evid Based Spine Care J. 2012;3(3): 43-49.
[33] Turner NM, Van de Leemput AJ, Draaisma JM, et al. Validity of the visual analogue scale as an instrument to measure self -efficacy in resuscitation skills. Med Educ. 2008;42(5):503.
[34] 尹占民.经伤椎椎弓根椎体内植骨结合短节段钉棒系统内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折37例分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012, 20(4):369-371.
[35] Yaray O, Akesen B, Aydinli U. Long -term outcome after surgicalt reatment of thoracolumbar fractures versus a control group of healthy volunteers. Acta Orthop Belg. 2011;77(1):93-96.
[36] 林达生,郭林新,丁真奇,等.椎旁肌间隙入路经伤椎椎弓根植骨内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华外科杂志,2011,49(2):125-129.
[37] 涂来勇,阚瑞,杨明坤,等.经多裂肌间隙单侧椎弓根钉固定椎间融合治疗腰椎退行性疾病的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013,28(7):629-631.
[38] 蔡福金,朱建平,骆宇春,等.经椎旁肌间隙入路椎弓根钉棒系统置入内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折:与传统方法比较[J].中国组织工程究,2012,16(30): 5676-5680.
[39] 文坤树,蒋波,蔡勇平,等.椎弓根钉棒系统治疗胸腰椎骨折56例体会[J].重庆医学, 2012,41(15):1496-1498.
[40] 印飞,孙振中,殷渠东,等.伤椎植骨植钉与跨节段椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014,28(2):227-232.
[41] 刘军,项良碧,陈语,等."触摸法"经皮椎弓根钉内固定治疗不稳定胸腰椎骨折[J].颈腰痛杂志,2010,31(5):330-334. |