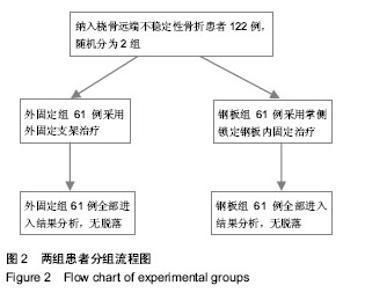
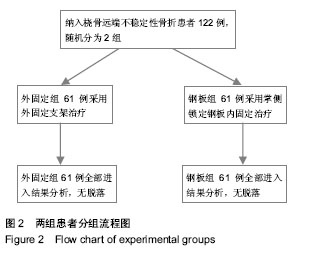
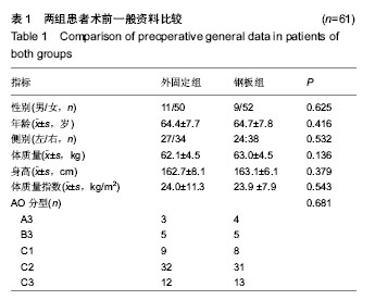
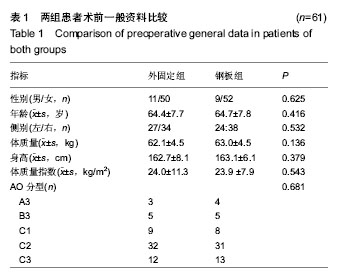
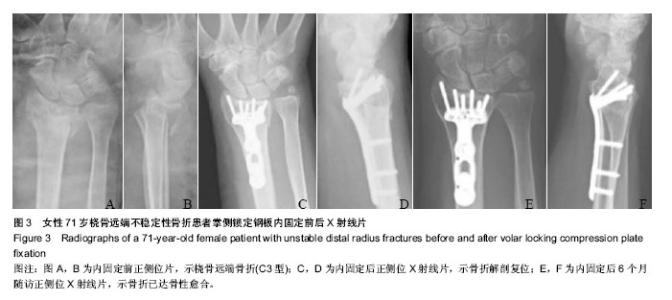
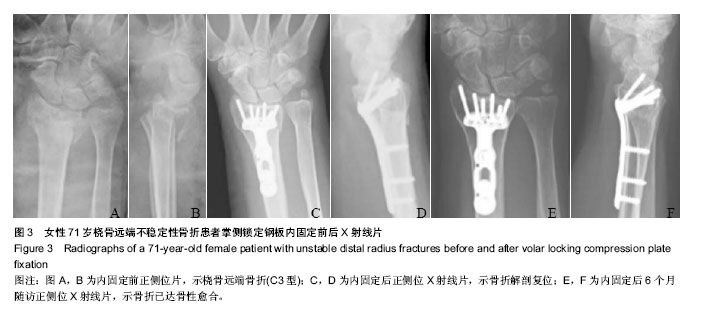
| [1] 金粉勤,薛锋,徐雪荣,等.外固定支架与钢板内固定治疗桡骨远端不稳定型骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(1): 87-89.
[2] Porrino JA Jr, Maloney E, Scherer K, et al. Fracture of the distal radius: epidemiology and premanagement radiographic characterization. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203(3): 551-559.
[3] Kumbaraci M, Kucuk L, Karapinar L, et al. Retrospective comparison of external fixation versus volar locking plate in the treatment of unstable intra-articular distal radius fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014; 24(2):173-178.
[4] Moradi A, Ebrahimzadeh MH, Jupiter JB. Intra-articular fractures of the distal radius: bridging external fixation in slight flexion and ulnar deviation along articular surface instead of radial shaft. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2014; 18(1):41-50.
[5] Paksima N, Panchal A, Posner MA, et al. A meta-analysis of the literature on distal radius fractures: review of 615 articles. Bull Hosp Joint Dis. 2004;62(1-2):40-46.
[6] Bass RL, Blair WF, Hubbard PP. Results of combined internal and external fixation for the treatment of severe AO-C3 fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg.1995; 20(3): 373-381.
[7] Huch K, Hunerbein M, Meeder PJ. External fixation of intra-articular fracture of the distal radius in young and old adults. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1996;115(1):38-42.
[8] Kawaguchi S, Sawada K, Nabeta Y, et al. Recurrent dorsal angulation of the distal radius fracture during dynamic external fixation. J Hand Surg Am. 1998; 23(5):920–925.
[9] Cronier P, Talha A, Toulemonde JL, et al. Results of distraction by way of external metacarporadial fixation in fracture of the distal end of the radius. Apropos of 97 cases. J Chir (Paris). 1991;128(1):8-12.
[10] Kandemir U, Matityahu A, Desai R, et al. Does a volar locking plate provide equivalent stability as a dorsal nonlocking plate in a dorsally comminuted distal radius fracture? A biomechanical study. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(9):605-610.
[11] 姜宗圆,马涛,夏江,等. 蝶形锁定钢板在复杂桡骨远端骨折中的应用[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(6):665-668.
[12] Laulan J, Bismuth JP, Clément P,et al.An analytical classification of fractures of the distal radius: The "M.E.U." classification.Chir Main. 2007; 26(6):293-299.
[13] Cooney WP, Bussey R, Dobyns JH, et al. Difficult wrist fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;(214):136-147.
[14] Haus BM, Jupiter JB. Intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius in young adults: reexamined as evidence-based and outcomes medicine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(12): 2984-2991.
[15] Koo KO, Tan DM, Chong AK. Distal radius fractures: an epidemiological review. Orthop Surg. 2013;5(3):209-213.
[16] 殷兵,刘磊,陈伟,等.2003年至2012年河北医科大学第三医院成人尺桡骨远端骨折的流行病学研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014, 16(4):316-319.
[17] Grewal R, MacDermid JC, King GJ, et al. Open reduction internal fixation versus percutaneous pinning with external fixation of distal radius fractures: a prospective, randomized clinical trial. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36(12):1899-1906.
[18] Abramo A, Kopylov P, Geijer M, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation compared to closed reduction and external fixation in distal radial fractures: a randomized study of 50 patients. Acta Orthop. 2009;80(4):478-485.
[19] Grewal R, Perey B, Wilmink M, et al. A randomized prospective study on the treatment of intra-articular distal radius fractures: open reduction and internal fixation with dorsal plating versus mini open reduction, percutaneous fixation, and external fixation. J Hand Surg. 2005;30(4): 764-772.
[20] Rozental TD, Blazar PE. Functional outcomes for unstable distal radial fractures treated with open reduction and internal fixation or closed reduction and percutaneous fixation. A prospective randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91(8):1837-1846.
[21] Xu GG, Chan SP, Puhaindran ME, et al. Prospective randomised study of intra-articular fractures of the distal radius: comparison between external fixation and plate fixation. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2009;38(7):600-606.
[22] 吕浩然,邹云雯,何二兴,等.两种方法治疗老年桡骨远端不稳定型骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(5):447-450.
[23] Kreder HJ, Hanel DP, Agel J, et al. Indirect reduction and percutaneous fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for displaced intra-articular fractures of the distal radius: a randomised, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg. 2005; 87(6):829-836.
[24] Leung F, Tu YK, Chew WY, et al. Comparison of external and percutaneous pin fixation with plate fixation for intra-articular distal radial fractures. A randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90(1):16-22.
[25] MacDermid JC, Turgeon T, Richards RS, et al. Patient rating of wrist pain and disability: a reliable and valid measurement tool. J Orthop Trauma. 1998;12(8):57-586.
[26] Imaeda T, Uchiyama S, Wada T, et al. Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the Japanese version of the Patient-Rated Wrist Evaluation. J Orthop Sci. 2010; 15(4):509-517.
[27] 杨召,马信龙,马剑雄,等.动态外固定架与静态外固定架治疗不稳定桡骨远端骨折远期疗效的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(10):880-885.
[28] Tarallo L, Mugnai R, Zambianchi F, et al. Volar plate fixation for the treatment of distal radius fractures: analysis of adverse events. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(12):740-745. |