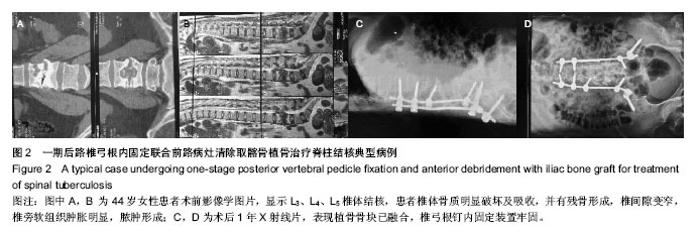
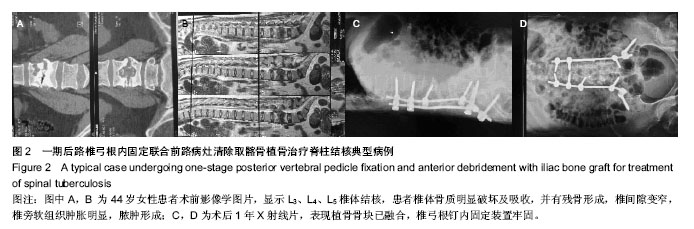
| [1] Talu U, Gogus A, Ozturk C,et al.The role of posterior instrumentation and fusion after anterior radical debridement and fusion in the surgical treatment of spinal tuberculosis: experience of 127 cases. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(8): 554-559.
[2] Kim DJ, Yun YH, Moon SH, et al.Posterior instrumentation using compressive laminar hooks and anterior interbody arthrodesis for the treatment of tuberculosis of the lower lumbar spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(13):E275-279.
[3] Mouhsine E, Wettstein M, Schizas C, et al.Modified triangular posterior osteosynthesis of unstable sacrum fracture.Eur Spine J. 2006;15(6):857-863.
[4] Sagi HC. Technical aspects and recommended treatment algorithms in triangular osteosynthesis and spinopelvic fixation for vertical shear transforaminal sacral fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2009; 23(5):354-360.
[5] 张伟,郭兴峰,张竞,等.应用椎弓根系统经腰-髂间固定治疗骶骨骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,5(24):521-524.
[6] Crocker M, James G, Ibrahim A, et al.Posterior approach vertebrectomy in the thoracolumbar spine with expandable cage reconstruction: indications and techniques based on eight cases.Br J Neurosurg. 2008;22(2):235-240.
[7] Moghtaderi A, Alavi-Naini R, Rahimi-Movaghar V.Tuberculous myelopathy: current aspects of neurologic sequels in the southeast of Iran.Acta Neurol Scand. 2006;113(4):267-272.
[8] 肖联平,江毅,田永刚,等.前路经腹腔一期病灶清除植骨融合内固定术治疗腰骶段脊柱结核[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009, 23(8):913-916.
[9] 崔虎山,李勋,郑炳周,等.后路病灶清除、椎体间融合及器械内固定术治疗结核性脊柱炎的安全性和有效性[J].临床骨科杂志, 2011, 14(1):6-8.
[10] 曾小军,杨述华,禹志宏,等.一期后路病灶清除植骨椎弓根钉系统内固定治疗胸腰椎结核[J].临床骨科杂志,2009,12(6):510-513.
[11] 马君,宋滇文,邵将,等.一期前后路联合手术治疗下腰椎结核[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(1):13-16.
[12] Tsutsumimoto T, Shimogata M, Ohta H, et al.Mini-open versus conventional open posterior lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis: comparison of paraspinal muscle damage and slip reduction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009 15;34(18):1923-1928.
[13] 梁柱德,宁金沛,庞彤.一期前路病灶清除、自体髂骨植骨联合后路椎弓根内固定治疗腰骶椎结核——附52例报告[J].新医学, 2012,43(1):48-50
[14] 欧云生,权正学,蒋电明,等.一期后路椎弓根内固定前路病灶清除植骨治疗腰骶段脊柱结核并后凸畸形[J].重庆医科大学学报, 2008, 33(1):119-121.
[15] Bridwell KH,Baldus C,Berven S,et al.Changes in radiographic and clinical outcomes with primary treatment adult spinal deformity surgeries from two years to threeto five years follow up Spine(Phila Pa 1976),2010,35(20):1849-1854.
[16] Chen WJ, Chen CH, Shih CH.Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylitis. 50 patients followed for 2-8 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 1995;66(2):137-142.
[17] 瞿东滨,金大地.正确认识脊柱结核病灶清除术[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(8): 565-567.
[18] Jin D, Qu D, Chen J, et al.One-stage anterior interbody autografting and instrumentation in primary surgical management of thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis.Eur Spine J. 2004;13(2):114-121.
[19] 张前法,庞清江,葛志斌,等.骨盆后环损伤内固定重建方法的选择[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006, 20(12):1214-1216.
[20] Xu L, Zhi-Ming Y, Xue-Mei L.An experimental study of bioderived bone to repair bone defects as a scaffold of tissue engineering.Int Surg. 2008;93(6):377-380.
[21] Jain AK, Dhammi IK, Prashad B, et al.Simultaneous anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation of the tuberculous spine using an anterolateral extrapleural approach.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(11):1477-1481.
[22] Jain AK, Dhammi IK, Jain S, et al. Simultaneously anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation by extrapleural retroperitoneal approach in thoracolumbar lesions. Indian J Orthop. 2010;44(4):409-416.
[23] Lan X, Yang ZM, Ge BF, et al. Culture of osteoblasts on bio-derived bones. Chin J Traumatol, 2005, 8(2): 86-90.
[24] Sandhu HS.Bone morphogenetic proteins and spinal surgery.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28(15 Suppl):S64-73. |