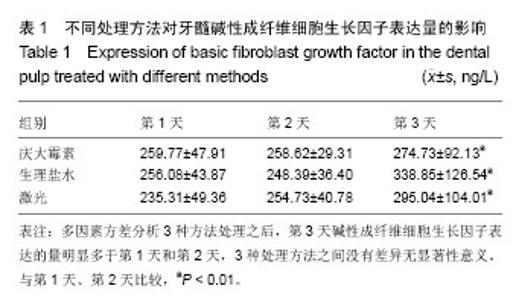
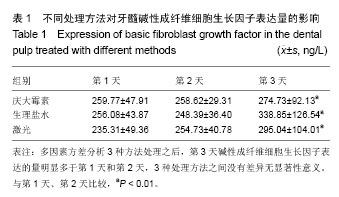
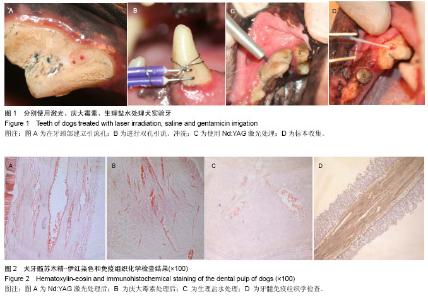
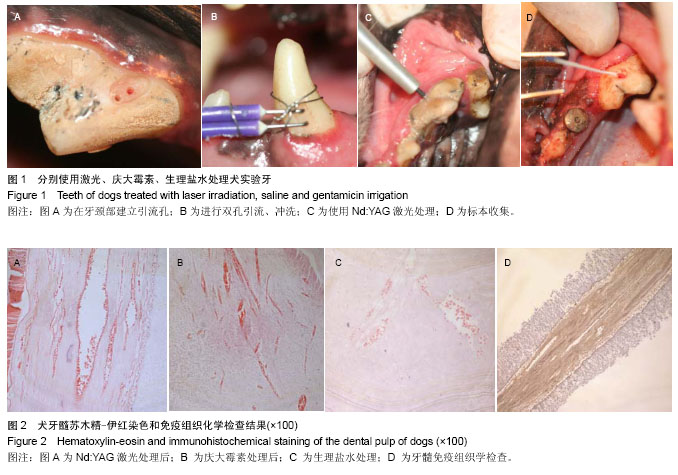
| [1] 林仰东,赵博,殷恺.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对体外培养人牙周膜细胞的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(20): 3184-3189.
[2] Pandiar D, Shameena P.Immunohistochemical expression of CD34 and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in oral submucous fibrosis. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2014;18(2): 155-161.
[3] Yoo MG, Kim IH.Keloids and hypertrophic scars: characteristic vascular structures visualized by using dermoscopy. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26(5):603-609.
[4] 张笋,陈涛,葛立宏.应用Er:YAG 激光治疗儿童龋齿的效果评价[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2013,45 (1):87-91.
[5] Porcaro G, Amosso E, Scarpella R, et al.Doxycycline fluorescence-guided Er:YAG laser ablation combined with Nd:YAG/diode laser biostimulation for treating bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2014;10. S2212-4403 (14)00465-9.
[6] Firoozmand L,Faria R,Araujo MA,et al.Temperature rise in cavities prepared by high and low torque handpieces and Er: YAG laser.Br Dent J.2008;205(1): 28 -29.
[7] 郭怡丹,张笋.Er: YAG 激光治疗对牙髓的作用[J].中国激光医学杂志,2013,22(3):165-171.
[8] Colucci V,Amaral FL,Pecora JD,et al.Water flow on erbium: yttrium-aluminun-garnet laser irradiation: effect on dental tissues.Lasers.Med Sci.2009;24(5): 811-818.
[9] TakimotoK, KawashimaN, Suzuki N, et al.Down-regulation of Inflammatory Mediator Synthesis and Infiltration of Inflammatory Cells by MMP-3 in Experimentally Induced Rat Pulpitis. JEndod. 2014;40(9):1404-1409.
[10] 姚敏,方勇,王莹.激光医学与组织修复[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2010,13(12):1451-1454.
[11] 崔卫新,李云川,邵鸣凯,等.鼻内镜下射频及Nd:YAG激光治疗鼻出血临床效果观察[J].北京医学,2010,32 (2):103-106
[12] Schwarz F, Hegewald A, John G, et al.Four-year follow-up of combined surgical therapy of advanced peri-implantitis evaluating two methods of surface decontamination.J Clin Periodontol. 2013;40(10):962-967.
[13] 冯向辉,路瑞芳,和璐.应用Er: YAG激光治疗慢性牙周炎的短期临床疗效观察[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2011;43(6):886-890.
[14] Matsumoto A, Tamura A, Fukami K, et al. Single-pulse underwater laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with nongated detection scheme.Anal Chem. 2013;85(8): 3807-3811.
[15] 林实,吴为良,詹振林,等.Er:YAG激光辐射后不同牙本质粘结界面的微观形态观察[J].中国激光,2011;38(3):121-126.
[16] 李鑫,陈新梅,郭蓝,等.Er:YAG激光联合3M ESPE Adper Easy-one粘结剂堵塞牙本质小管的体外研究[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2012,22(2):92-95.
[17] 郭晓钰,吴友农,陈慧芬,等.Nd:YAg激光照射治疗牙本质敏感症的能量密度范围的离体牙研究[J].口腔医学研究,2014,30(5): 430-437.
[18] Lopes AO, Aranha AC.Comparative evaluation of the effects of Nd:YAG laser and a desensitizer agent on the treatment of dentin hypersensitivity: a clinical study.Photomed Laser Surg. 2013;31(3):132-138.
[19] 王华,赵彬,姚蔚.氧化锆陶瓷表面喷砂及牙本质表面Er:YAG激光处理对树脂黏结强度影响研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2013, 6(1):24-27.
[20] 李阳,贾兴亚,杜健男.表面处理方法对激光预备牙本质黏结强度的影响[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2014;7(5):283-286.
[21] 王思箭.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的生物活性及应用[J].中国医院药学杂志,2013;33(13):1081-1083.
[22] 张进,刘艳丽,孟秋菊,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对人牙髓细胞生物学活性的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2013, 23(7) : 450-453.
[23] 关雪莲,侯丽淳,王辰,等.大鼠脑出血周边组织谷氨酸、脑水含量和细胞凋亡的变化及碱性成纤维生长因子的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2013,30(4):325-328.
[24] 赵姝哲,周婷婷,黄继红,等.低强度激光照射对实验性牙齿移动牙周组织中P物质表达的影响[J].中国激光医学杂志,2010, 19(3): 152-155.
[25] 刘琨,张惠民,申丽丽,等.Nd: YAG激光对3种树脂水门汀与牙本质粘接强度的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志.2012,30(5):509-513
[26] 关为群,王学莹,杨宾.Nd:YAG激光治疗对慢性牙周炎患者牙周袋深度和附着丧失的改善效果研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2014,3(4):231-235.
[27] 关为群,杨宾,王清妹.Nd:YAG激光照射对人牙周膜成纤维细胞影响的体外研究[J].当代医学,2010,16(19):7-9.
[28] Ishikawa K, Maruyama T, Kusaka M, et al. The state of antimicrobial prophylaxis for holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: HoLEP and the results of a questionnaire survey. Hinyokika Kiyo.2011;57(10):539-543.
[29] 向学熔,晏莺,杨梅.Nd:YAG激光非手术疗法在老年牙周炎患者中的应用前景[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2014,7(2):85-88.
[30] Ramalho KM, de Freitas PM, Correa-Aranha AC, et al.Lasers in esthetic dentistry: soft tissue photobiomodulation, hard tissue decontamination, and ceramics conditioning. Case Rep Dent. 2014;2014:927429.
[31] Kert J,Rose L.Clinical laser therapy low level laser therapy laser therapy[M].Denmark: Scandinavian Medical Laser Technology.1989: 5-6.
[32] Acar O, Tuncer D, Yuzugullu B, et al. The effect of dentin desensitizers and Nd:YAG laser pre-treatment on microtensile bond strength of self-adhesive resin cement to dentin. J Adv Prosthodont. 2014;6(2):88-95.
[33] 陆铃,李菊,刘鲁川.脉冲Nd:YAG激光对犬牙活髓切断术后组织修复的影响[J].四川医学,2010,31(12):1745-1747. |