Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (17): 2734-2739.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.17.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
3.0 T magnetic resonance imaging diffusion-weighted imaging in evaluation of the reasons for lumbar disc degeneration
Ma Xiao-hui, Zhang Wei, Gao Yu, Zhao Jian, Li Shi-ling, Zhang Xu-jing, Zhao Zhen-jiang, Jiang Zhen
- Third Hospital, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Orthopedic Biomechanics, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China
-
Revised:2014-03-08Online:2014-04-23Published:2014-04-23 -
Contact:Zhang Wei, Associate chief physician, Third Hospital, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Orthopedic Biomechanics, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Ma Xiao-hui, Associate chief technician, Third Hospital, Hebei Medical University, Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Orthopedic Biomechanics, Shijiazhuang 050051, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Hebei Provincial Medical Research Key Project, No.20120344
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Xiao-hui, Zhang Wei, Gao Yu, Zhao Jian, Li Shi-ling, Zhang Xu-jing, Zhao Zhen-jiang, Jiang Zhen. 3.0 T magnetic resonance imaging diffusion-weighted imaging in evaluation of the reasons for lumbar disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(17): 2734-2739.
share this article
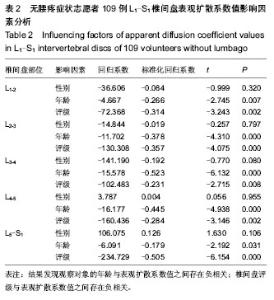
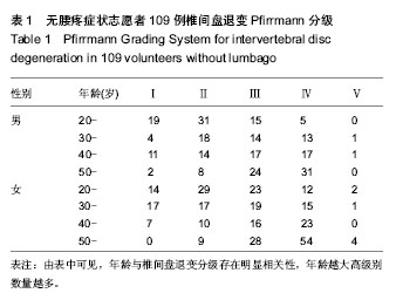
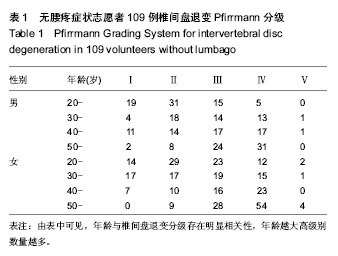
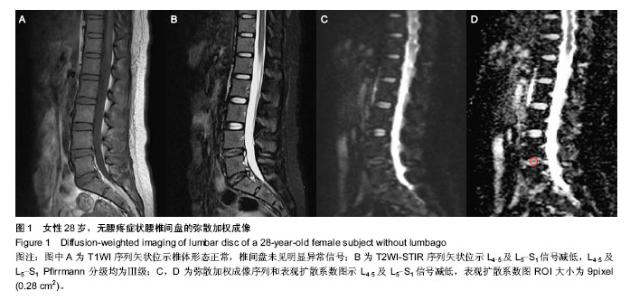
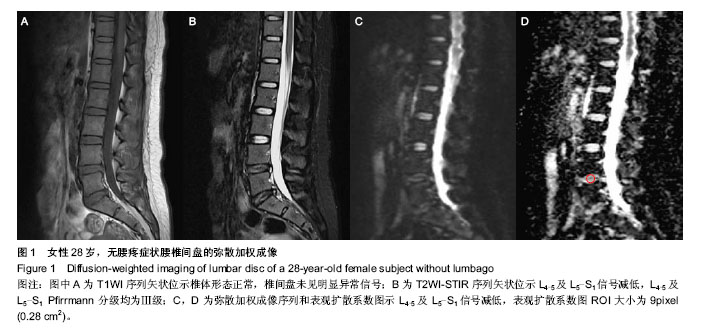
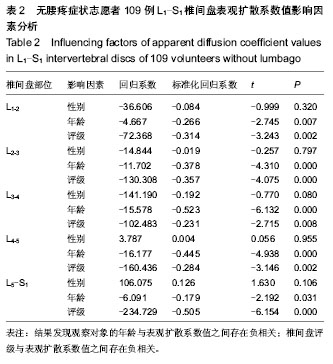
2.5 不同部位椎间盘表观扩散系数值的比较 受试对象L1-2椎间盘的表观扩散系数1=(1.631±0.217)×10-3 mm2/s,L2-3椎间盘的表观扩散系数值表观扩散系数2= (1.581± 0.383)×10-3 mm2/s,L3-4椎间盘的表观扩散系数值表观扩散系数3=(1.547±0.368)×10-3 mm2/s,L4-5椎间盘的表观扩散系数值表观扩散系数4=(1.441±0.450)×10-3 mm2/s,L5-S1椎间盘的表观扩散系数值表观扩散系数5=(1.388± 0.420)×10-3 mm2/s。 采用随机区组设计方差分析,5个椎间盘的表观扩散系数值存在统计学差异(F=8.071,P < 0.001)。进一步采用S-N-K法进行两两比较,表观扩散系数1、表观扩散系数2与表观扩散系数3之间不存在统计学差异;表观扩散系数4与表观扩散系数5之间不存在统计学差异;表观扩散系数1/表观扩散系数2/表观扩散系数3与表观扩散系数4/表观扩散系数5椎间盘的表观扩散系数值之间存在统计学差异。 2.6 L1-S1椎间盘表观扩散系数值影响因素分析 性别对表观扩散系数1的影响:采用两独立样本t 检验,结果发现男性与女性表观扩散系数值之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05,表2)。 年龄与表观扩散系数值的关系:采用线性相关分析,结果发现研究对象的年龄与表观扩散系数值之间存在负相关(P < 0.05,表2)。 椎间盘评级与表观扩散系数值的关系:采用秩相关分析,结果发现研究对象的椎间盘评级与表观扩散系数值之间存在负相关(P < 0.05,表2)。"
| [1] Freemont AJ. Review The cellular pathobiology of the degenerate intervertebral disc and discogenic back pain. Rheumatology (Oxford).2009;48(1):5-10. [2] Videman T, Gibbons LE, Battié MC.Age- and pathology-specific measures of disc degeneration.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008;33(25):2781-2788. [3] Hadjipavlou AG, Tzermiadianos MN, Bogduk N,et al.The pathophysiology of disc degeneration: a critical review. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2008; 90(10):1261-1270. [4] Costi JJ, Stokes IA, Gardner-Morse MG,et al. Frequency-dependent behavior of the intervertebral disc in response to each of six degree of freedom dynamic loading: solid phase and fluid phase contributions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008; 33(16):1731-1738. [5] O'Connell GD, Guerin HL, Elliott DM.Theoretical and uniaxial experimental evaluation of human annulus fibrosus degeneration. J Biomech Eng.2009; 131(11):111007. [6] Stokes IA,Iatridis JC.Review Mechanical conditions that accelerate intervertebral disc degeneration: overload versus immobilization. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(23): 2724-2732. [7] Shirazi-Adl A,Taheri M,Urban JP.Analysis of cell viability in intervertebral disc: Effect of endplate permeability on cell population. J Biomech.2010; 43(7):1330-1336. [8] Eskola PJ,Lemmelä S,Kjaer P,et al.Genetic association studies in lumbar disc degeneration: a systematic review. PLoS One.2012;7(11):e49995. [9] Smith LJ, Kurmis AP, Slavotinek JP, et al.In vitro evaluation of a manganese chloride phantom-based MRI technique for quantitative determination of lumbar intervertebral disc composition and condition. Eur Spine J.2011; 20(3):434-439. [10] Kettler A, Wilke H. Review of existing grading systems for cervical or lumbar disc and facet joint degeneration.Eur Spine J.2006;15(6):705-718. [11] Antoniou J, Demers CN, Beaudoin G,et al.Apparent diffusion coefficient of intervertebral discs related to matrix composition and integrity.Magn Reson Imaging.2004;22(7): 963-972. [12] Williams JR.The Declaration of Helsinki and public health. Bull World Health Organ.2008;86(8):650-652. [13] Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine.2001;26(17):1873-1878. [14] Campana S,Charpail E, Guise J,et al.Relationships between viscoelastic properties of lumbar intervertebral disc and degeneration grade assessed by MRI.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2011;4(4):593-599. [15] Sharp CA, Roberts S, Evans H, et al.Disc cell clusters in pathological human intervertebral discs are associated with increased stress protein immunostaining. Eur Spine J.2009; 18(11):1587-1594. [16] Setton L, Chen J. Mechanobiology of the intervertebral disc and relevance to disc degeneration.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(Suppl 2):52-57. [17] Haefeli M, Kalberer F, Saegesser D, et al.The course of macroscopic degeneration in the human lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine.2006;31(14):1522-1531. [18] Rajasekaran S, Babu JN, Arun R, et al. ISSLS prize winner: a study of diffusion in human lumbar discs: a serial magnetic resonance imaging study documenting the influence of the endplate on diffusion in normal and degenerate discs. Spine. 2004;29(23):2654-2667. [19] Beattie PF, Morgan PS, Peters D. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of normal and degenerative lumbar intervertebral discs: a new method to potentially quantify the physiologic effect of physical therapy intervention. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther.2008;38(2):42-49. [20] Antoniou J, Demers CN, Beaudoin G, et al.Apparent diffusion coefficient of intervertebral discs related to matrix composition and integ-rity. Magn Reson Imaging.2004; 22(7):963-972. [21] Kealey SM, Aho T, Delong D, et al. Assessment of apparent diffusion coefficient in normal and degenerated intervertebral lumbar disks: initial experience. Radiology.2005; 235(2): 569-574. [22] Anderson DG, Tannoury C.Molecular pathogenic factors in symptomatic disc degeneration.Spine J.2005;5(6):260-266. [23] Roughley PJ.Biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: involvement of the extracellular matrix. Spine.2004;29(23):2691-2699. [24] Roberts S, Evans H, Trivedi J.Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2006; 88(2):10-14. [25] Urban JP, Winlove CP.Pathophysiology of the intervertebral disc and the challenges for MRI.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;25(2):419-432. [26] Adams MA, McNally DS, Dolan P.‘Stress’ distributions inside intervertebral discs: the effects of age and degeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1996;78(6):965-972. [27] Brown MF, Hukkanen MV, McCarthy ID, et al.Sensory and sympathetic innervation of the vertebral endplate in patients with degenerative disc disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1997; 79(1):147-153. [28] Ohtori S,Inoue G,Ito T,et al.Tumor necrosis factor-immunoreactive cells and PGP 9.5-immunoreactive nerve fibers in vertebral endplates of patients with discogenic low back pain and Modic type 1 or type 2 changes on MRI. Spine.2006; 31(9): 1026-1031. [29] Ren J,Huan Y, Wang H,et al. Dynamic contrast -enhanced MR imaging of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic carcinoma: correlation with angiogenesis. Clin Radiol.2008; 63(2): 153-159. [30] Siemionow K, An H, Masuda K.The effects of age, sex, ethnicity, and spinal level on the rate of intervertebral disc degeneration: a review of 1712 intervertebral discs. Spine. 2011;8(17): 1333-1339. [31] Boos N, Weissbach S, Rohrbach H, et al.Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo Award in basic science. Spine. 2002;27(23):2631-2644. [32] 徐宝山,杨强,夏群.腰椎间盘退变的分子病理学变化及发病机制[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复.2011,15(2):335-338. [33] 王娟,周义成,夏黎明,等.使用ADC值评估正常及退变腰椎间盘的初步研究[J].医学影像学杂志. 2006,16 (10): 1093-1096. [34] 郭家川,杨汉丰,杜勇,等. ADC值在腰椎间盘退行性变诊断中价值的初步研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2011, 30(2): 239-242. [35] 常英娟,颜蕾,任静等,正常和变性腰椎间盘ADC值定量研究[J].国际医学放射杂志, 2011, 34(3):211-214. [36] Keller TS, Colloca CJ,Harrison DD, et al.Influence of spine morphology on intervertebral disc loads and stresses in asymptomatic adults: implications for the ideal spine. Spine. 2005;5(3):297-309. [37] Takatalo J,Karppinen J,Niinimäki J ,et al. Prevalence of degenerative imaging findings in lumbar magnetic resonance imaging among young adults. Spine. 2009; 34(16): 1716- 1721. [38] Takatalo J, Karppinen J, Niinimäki J, et al.Association of modic changes, Schmorl's nodes, spondylolytic defects, high-intensity zone lesions, disc herniations, and radial tears with low back symptom severity among young Finnish adults. Spine.2012;37(14):1231-1239. [39] Wang YX, Griffith JF, Ma HT. Relationship between gender, bone mineral density, and disc degeneration in the lumbar spine: a study in elderly subjects using an eight-level MRI-based disc degeneration grading system. Osteoporosis Int. 2011;22(1):91-96. [40] Wang YX, Griffith JF.Effect of menopause on lumbar disk degeneration: potential etiology. Radiology. 2010; 257(2): 318-320. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Yi Meizhi, Luo Guanghua, Xiao Yawen, Hu Rong, Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng. MRI findings of anatomical variations of the talus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3888-3893. |
| [3] | Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng, Hu Rong, Luo Guanghua, Liu Jincai . Correlation of infrapatellar fat pad edema with trochlear and patellofemoral joint morphology: MRI evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2410-2415. |
| [4] | Li Ying, Guan Hantian, Zhou Yu. Semantic memory impairment and neuroregulation in patients with mild cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5236-5242. |
| [5] | Li Wei, Chu Zhanfei, Yu Zechen, Yu Jinghong, Jia Yanbo, Wang Zongbo. T2-mapping quantitative imaging technique based on sequence optimization in the ankle talus osteochondral injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4333-4337. |
| [6] | Song Yancheng, Kang Liqing, Shen Canghai, Liu Fenghai, Feng Yongjian. Application of task-state fMRI in evaluating disease severity and prognosis of cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3341-3346. |
| [7] | Shen Canghai, Feng Yongjian, Song Yancheng, Liu Gang, Liu Zhiwei, Wang Ling, Dai Haiyang. Value of quantitative MRI T2WI parameters in predicting surgical outcome of thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2893-2899. |
| [8] |
Huang Xuejie, Chang Xiaodan, Zhao Dewei.
Focused research of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic
resonance imaging in bone and joint |
| [9] | Xie Yuchen, Chen Wendong, Ma Li . Anatomical differences in three-dimensional finite element model of difficult airway patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 562-566. |
| [10] | Liu Bin, Liu Xiangyang, Wang Guoping, Shen Xiongjie, Chang Lei, Peng Shuai, Zhang Mingyan. Measurement of paravertebral muscle indicators on MRI in the patients with osteoporotic vertebral fracture and its clinical significance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 578-583. |
| [11] | Zong Qiang, Xu Yanan, Qu Tianyi, Li Lijun, Hai Miti·Abuduaini, Ni Dongkui. Magnetic verapamil nanoparticles promote peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5425-5429. |
| [12] | Cao Jingli1, 2, Marina S. Ferguson3, Sun Jie3, Zhang Dong1, Liu Li1, Li Zirui1, Wang Yajie1, Sui Binbin1, Shen Mi1, Gao Peiyi1, 4, Thomas S. Hatsukami3, Zhao Xihai5, Yuan Chun1, 3, 5. An en bloc paraffin embedding method for serial sectioning of carotid atherosclerotic plaque [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 5041-5045. |
| [13] | Wang Jian, Zhang Xiaodong. Magnetic resonance imaging-based 3D printing technology: advantages and prospects in clinical application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(30): 4897-4904. |
| [14] | Zhao Heng, Hu Rong, Liu Jincai, Luo Guanghua, Qing Weipeng, Peng Zhaojie. MR anatomical variation of sacroiliac joints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4516-4521. |
| [15] |
Guo Juan, Qian Lixia, Wang Xiaodong.
Magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of hallux valgus deformity: changes in the structure and position of the metatarsophalangeal joints
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3857-3861.
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||