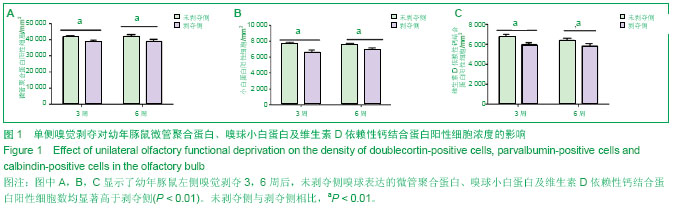
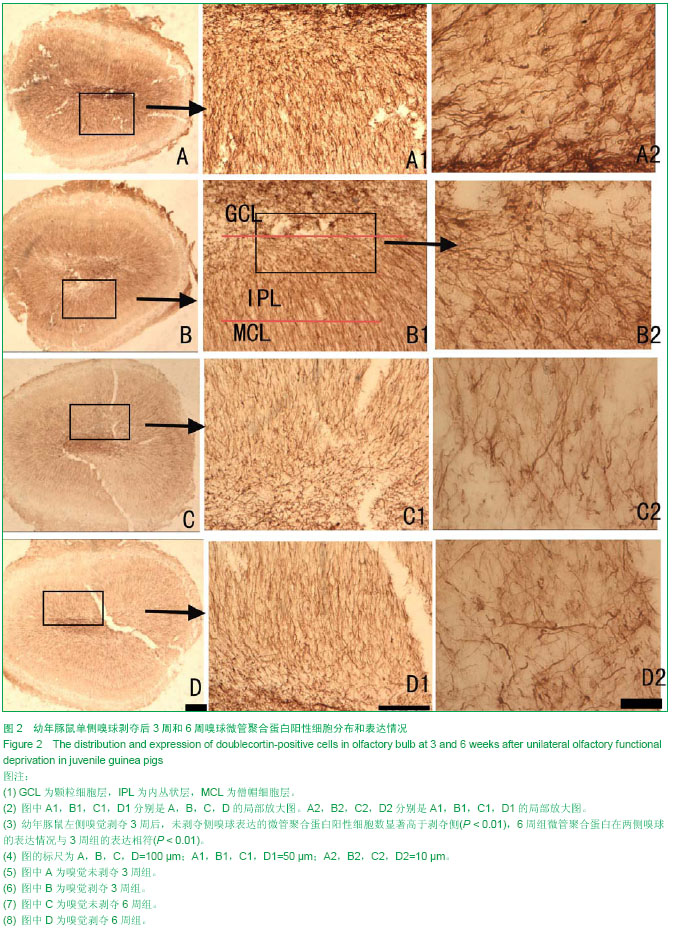
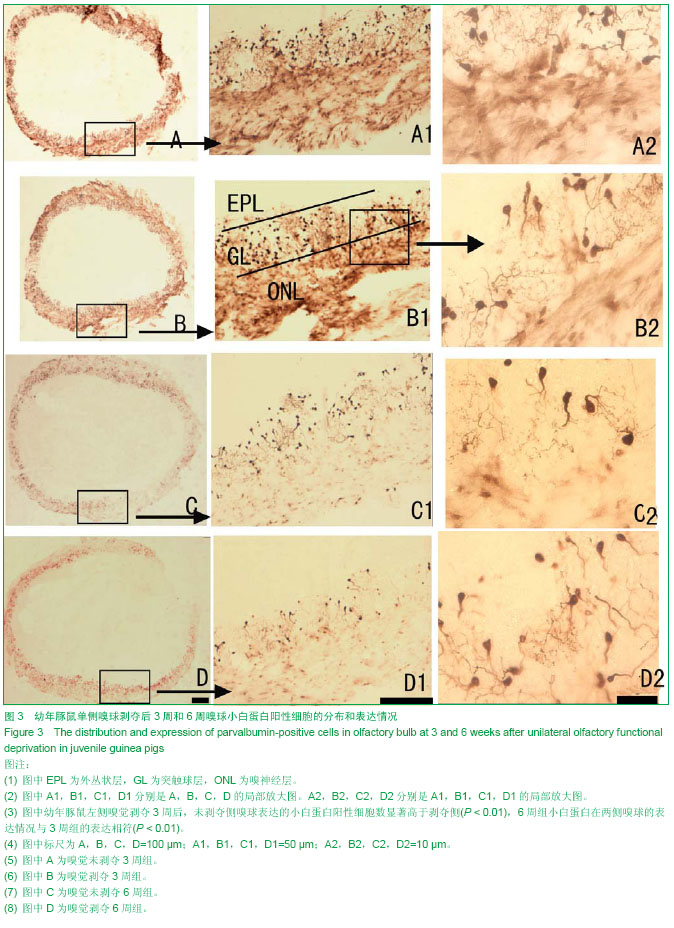
| [1] Leinwand SG, Chalasani SH. Olfactory networks: from sensation to perception. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011;21(6): 806-811.[2] Pan A, Li M, Gao JY, et al. Experimental epidural hematoma causes cerebral infarction and activates neocortical glial and neuronal genesis in adult guinea pigs. J Neurosci Res. 2013; 91(2): 249-261.[3] Mu Y, Lee SW, Gage FH. Signaling in adult neurogenesis. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010;20(4): 416-423.[4] Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH. Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell. 2008;132(4): 645-660.[5] Ma DK, Bonaguidi MA, Ming GL, et al. Adult neural stem cells in the mammalian central nervous system. Cell Res. 2009; 19(6): 672-682.[6] Chen R, Lin C, You Y, et al. Characterization of immature and mature 5-hydroxytryptamine 3A receptor-expressing cells within the adult SVZ-RMS-OB system. Neuroscience. 2012; 227: 180-190.[7] Oboti L, Savalli G, Giachino C, et al. Integration and sensory experience-dependent survival of newly-generated neurons in the accessory olfactory bulb of female mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2009;29(4): 679-692.[8] Moreno-Lopez B, Romero-Grimaldi C, Noval JA, et al. Nitric oxide is a physiological inhibitor of neurogenesis in the adult mouse subventricular zone and olfactory bulb. J Neurosci. 2004;24(1): 85-95.[9] Bovetti S, Veyrac A, Peretto P, et al. Olfactory enrichment influences adult neurogenesis modulating GAD67 and plasticity-related molecules expression in newborn cells of the olfactory bulb. PLoS One. 2009;4(7): e6359.[10] Nissant A, Bardy C, Katagiri H, et al. Adult neurogenesis promotes synaptic plasticity in the olfactory bulb. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12(6): 728-730.[11] Ma DK, Kim WR, Ming GL, et al. Activity-dependent extrinsic regulation of adult olfactory bulb and hippocampal neurogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1170: 664-673.[12] Francis F, Koulakoff A, Boucher D, et al. Doublecortin is a developmentally regulated, microtubule-associated protein expressed in migrating and differentiating neurons. Neuron. 1999;23(2): 247-256.[13] Couillard-Despres S, Winner B, Schaubeck S, et al. Doublecortin expression levels in adult brain reflect neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21(1): 1-14.[14] Gleeson JG, Lin PT, Flanagan LA, et al. Doublecortin is a microtubule-associated protein and is expressed widely by migrating neurons. Neuron. 1999;23(2): 257-271.[15] Couillard-Despres S, Winner B, Schaubeck S, et al. Doublecortin expression levels in adult brain reflect neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21(1): 1-14.[16] Klempin F, Kronenberg G, Cheung G, et al. Properties of doublecortin-(DCX)-expressing cells in the piriform cortex compared to the neurogenic dentate gyrus of adult mice. PLoS One. 2011;6(10): e25760.[17] Winner B, Couillard-Despres S, Geyer M, et al. Dopaminergic lesion enhances growth factor-induced striatal neuroblast migration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008;67(2): 105-116.[18] Kronenberg G, Wang LP, Geraerts M, et al. Local origin and activity-dependent generation of nestin-expressing protoplasmic astrocytes in CA1. Brain Struct Funct. 2007; 212(1): 19-35.[19] Shapiro LA, Ng KL, Kinyamu R, et al. Origin, migration and fate of newly generated neurons in the adult rodent piriform cortex. Brain Struct Funct. 2007;212(2): 133-148.[20] Walsh CA. Genetics of neuronal migration in the cerebral cortex. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2000; 6(1): 34-40.[21] Xiong K, Cai Y, Zhang XM, et al. Layer I as a putative neurogenic niche in young adult guinea pig cerebrum. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2010;45(2): 180-191.[22] Hu H, Tomasiewicz H, Magnuson T, et al. The role of polysialic acid in migration of olfactory bulb interneuron precursors in the subventricular zone. Neuron. 1996;16(4): 735-743.[23] Meyer A, Galizia CG. Elemental and configural olfactory coding by antennal lobe neurons of the honeybee (Apis mellifera). J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2012;198(2): 159-171.[24] Andrews-Zwilling Y, Bien-Ly N, Xu Q, et al. Apolipoprotein E4 causes age- and Tau-dependent impairment of GABAergic interneurons, leading to learning and memory deficits in mice. J Neurosci. 2010;30(41): 13707-13717.[25] Lledo PM, Merkle FT, Alvarez-Buylla A. Origin and function of olfactory bulb interneuron diversity. Trends Neurosci. 2008; 31(8): 392-400.[26] Bastien-Dionne PO, David LS, Parent A, et al. Role of sensory activity on chemospecific populations of interneurons in the adult olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol. 2010;518(10): 1847-1861.[27] Batista-Brito R, Close J, Machold R, et al. The distinct temporal origins of olfactory bulb interneuron subtypes. J Neurosci. 2008;28(15): 3966-3975.[28] 李瑞锡,彭裕文,大谷修,等. 大鼠杏仁体基底外侧核中小白蛋白反应阳性神经元受抑制性神经网络支配(英文)[J]. 神经解剖学杂志, 2004, 20(1): 12-20.[29] Guthrie KM, Wilson DA, Leon M. Early unilateral deprivation modifies olfactory bulb function J Neurosci. 1990;10(10): 3402-3412.[30] Brunjes PC, Smith-Crafts LK, Mccarty R. Unilateral odor deprivation: effects on the development of olfactory bulb catecholamines and behavior. Brain Res. 1985;354(1): 1-6.[31] Brunjes PC. Unilateral naris closure and olfactory system development. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1994;19(1):146-160.[32] Coppola DM. Studies of olfactory system neural plasticity: the contribution of the unilateral naris occlusion technique. Neural Plast. 2012;2012: 351752.[33] Zhang XM, Xiong K, Cai Y, et al. Functional deprivation promotes amyloid plaque pathogenesis in Tg2576 mouse olfactory bulb and piriform cortex. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;31(4): 710-721.[34] Kolb B, Whishaw IQ. Brain plasticity and behavior. Annu Rev Psychol. 1998;49: 43-64. [35] Meisami E. Effects of olfactory deprivation on postnatal growth of the rat olfactory bulb utilizing a new method for production of neonatal unilateral anosmia. Brain Res. 1976; 107(2): 437-444. [36] 谭洁,罗敏敏. 嗅球对嗅觉信息的处理[J]. 生物物理学报, 2010, 26(3): 194-208.[37] Haehner A, Rodewald A, Gerber JC, et al. Correlation of olfactory function with changes in the volume of the human olfactory bulb. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; 134(6): 621-624.[38] Cummings DM, Knab BR, Brunjes PC. Effects of unilateral olfactory deprivation in the developing opossum, Monodelphis domestica. J Neurobiol. 1997;33(4): 429-438.[39] Korol DL, Brunjes PC. Unilateral naris closure and vascular development in the rat olfactory bulb. Neuroscience. 1992; 46(3): 631-641.[40] 郑小敏,沈新生,吴凯,等. 早期嗅觉剥夺对SD鼠发育的影响[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2011, 34(1): 8-11.[41] Corotto FS, Henegar JR, Maruniak JA. Odor deprivation leads to reduced neurogenesis and reduced neuronal survival in the olfactory bulb of the adult mouse. Neuroscience. 1994; 61(4): 739-744.[42] 贺旭. 单侧嗅觉功能剥夺对成年豚鼠嗅觉中枢DCX阳性细胞表达的实验研究[D].中南大学, 2012.[43] Lledo PM, Saghatelyan A, Lemasson M. Inhibitory interneurons in the olfactory bulb: from development to function. Neuroscientist. 2004;10(4): 292-303.[44] Kelsch W, Mosley CP, Lin CW, et al. Distinct mammalian precursors are committed to generate neurons with defined dendritic projection patterns. PLoS Biol. 2007;5(11): e300.[45] Li WL, Yu SP, Ogle ME, et al. Enhanced neurogenesis and cell migration following focal ischemia and peripheral stimulation in mice. Dev Neurobiol. 2008;68(13): 1474-1486.[46] 李辉,吴乐,李云庆. 大鼠延髓背角内5-羟色胺、脑啡肽、γ-氨基丁酸、甘氨酸或P-物质能终末与钙结合蛋白阳性神经元间的联系(英文)[J]. 神经解剖学杂志,2006, 22(1): 1-13.[47] Suzuki N, Bekkers JM. Inhibitory interneurons in the piriform cortex. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007;34(10): 1064-1069.[48] Celio MR. Parvalbumin in most gamma-aminobutyric acid-containing neurons of the rat cerebral cortex. Science. 1986;231(4741): 995-997.[49] Kutsuna N, Suma T, Takada Y, et al. Decrease in doublecortin expression without neuronal cell death in rat retrosplenial cortex after stress exposure. Neuroreport. 2012;23(4): 211-215. |