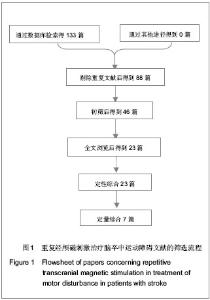
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficiency of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on rehabilitation of motor function in patients with stroke: A systematic review
Zhu Yi, Yang Yu-jie, Gu Yi-huang, Xie Bin, Jin Hong-zhu
- Second School of Clinical Medicine of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210046, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2013-09-18Online:2013-12-10Published:2013-12-10 -
Contact:Jin Hong-zhu, Doctoral supervisor, Professor, Second School of Clinical Medicine of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210046, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhu Yi★, Master, Lecturer, Second School of Clinical Medicine of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210046, Jiangsu Province, China zhuyi1010@163.com Yang Yu-jie, Second School of Clinical Medicine of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210046, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Higher Learning School “Qinglan Engineering” Project of Jiangsu Province in 2012*; the Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu Province, No. SBL201220091*; the State Science and Technology Support Project during the 12th Five-Year Plan Period, No. 2013BAI10B00*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Yi, Yang Yu-jie, Gu Yi-huang, Xie Bin, Jin Hong-zhu. Efficiency of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on rehabilitation of motor function in patients with stroke: A systematic review[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.50.022.
share this article
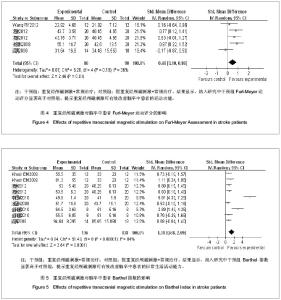
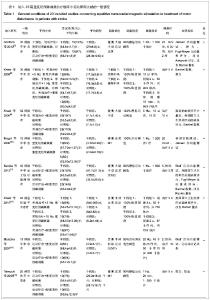
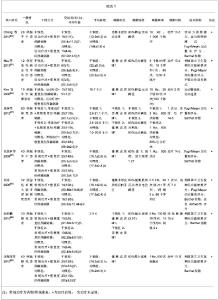
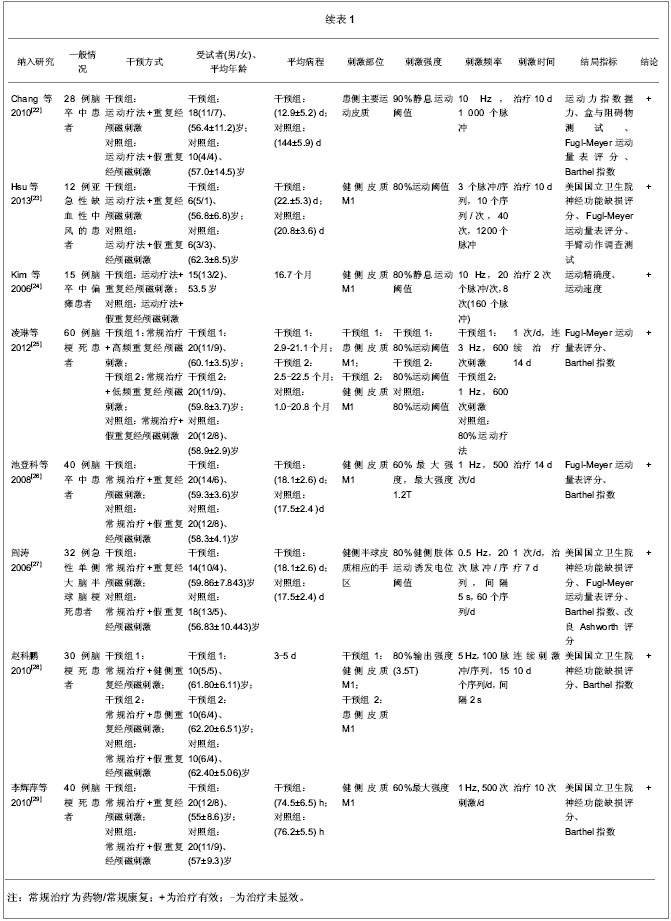
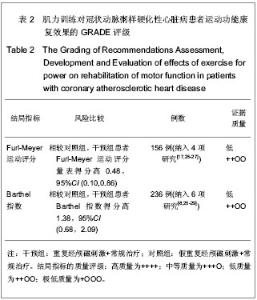
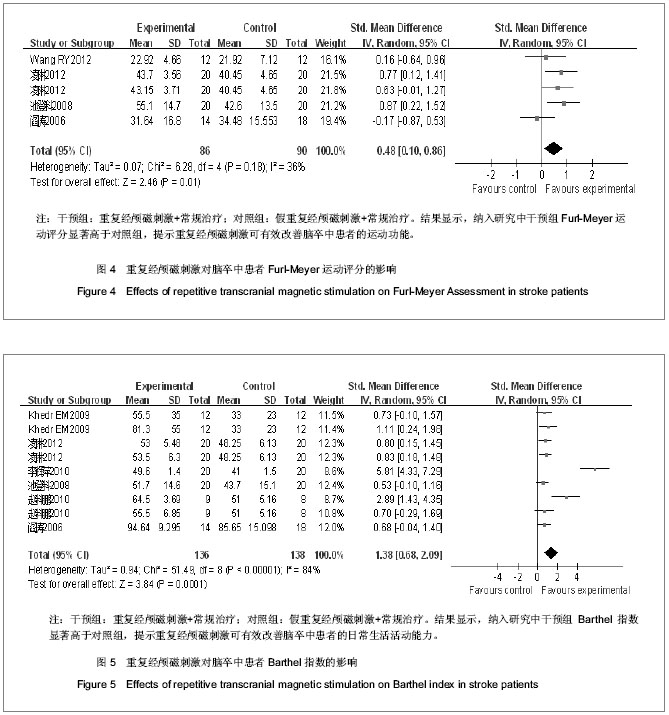
2.4 重复经颅磁刺激的治疗与康复效果评价 2.4.1 重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中患者运动功能的影响 主要评价指标Fugl-Meyer运动评分 有4项研究报道了重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中患者Fugl-Meyer运动评分的影响[17, 25-27],共计156例患者。采用随机效应模型进行分析。结果显示,重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中患者运动功能的治疗效果与对照组相比,其差异有显著性意义[SMD=0.48,95%CI(0.10,0.86)],见图4。因研究数量有限,未能进行漏斗图分析。 2.4.2 重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中患者日常生活活动能力的影响 主要评价指标为Barthel指数:有6项研究报道了重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中患者Barthel指数的影 响[8, 25-29],共计236例患者。采用随机效应模型进行分析。结果显示,重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中患者日常生活活动能力的影响与对照组相比,其差异有显著性意义[SMD=1.38,95%CI(0.68,2.09)],见图5。因研究数量有限,未能进行漏斗图分析。 2.4.3 重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中患者其他能力的影响 本文共纳入23项研究,其中英文18项,中文5项。定量分析7项研究,其中英文2项,中文5项。其余16项英文研究,作描述性分析,结果如下: Conforto等[7]2012年的研究结果显示,低频重复经颅磁刺激作用于早期脑卒中患者,治疗2周后患者的Jebsen手功能测试结果有明显提高,尤其1个月后患者“捡小物”、“叠加跳棋”的能力有明显改善,提示重复经颅磁刺激能有效改善脑卒中偏瘫患者手的运动功能。 Khedr等[9]2005年的研究结果显示,对早期脑卒中患者进行连续10 d的重复经颅磁刺激治疗,患者的斯堪的纳维亚卒中量表得分、美国国立卫生院神经功能缺损评分、Barthel指数均有明显改善。 Fregni等[10]2006年的研究结果显示,连续5 d的低频重复经颅磁刺激治疗,脑卒中患者手的运动功能有明显改善,且治疗效果可持续到2周。研究提示,随治疗周期增加重复经颅磁刺激的疗效可能得到了累积。"
| [1] 吴兆苏,姚崇华,赵冬. 我国人群脑卒中发病率、死亡率的流行病学研究[J] . 中华流行病学杂志,2003,24(1):236-239.[2] 王伊龙,王拥军,吴敌,等. 中国卒中防治研究现状[J]. 中国卒中杂志,2007,2(1):20-37.[3] 姚滔涛,王宁华,陈卓铭. 脑卒中运动功能训练的循证医学研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2010,25(6):565-570.[4] Barker AT, Jalinous R, Freeston IL. Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet. 1985;325(8437): 1106-1107.[5] 王晓明,谢建平,周树舜.重复经颅磁刺激技术及其临床应用进展[J].国外医学:物理医学与康复学分册, 2004, 24(1): 43-45.[6] Griškova I, Höppner J, Rukš?nas O, et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: the method and application. Medicina (Kaunas). 2006;42(10): 792-804.[7] Conforto AB, Anjos SM, Saposnik G, et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in mild to severe hemiparesis early after stroke: a proof of principle and novel approach to improve motor function. J Neurology. 2012;259(7): 1399-1405.[8] Khedr EM, Abdel-Fadeil MR, Farghali A, et al. Role of 1 and 3 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor function recovery after acute ischaemic stroke. Eur J Neurology. 2009;16(12): 1323-1330.[9] Khedr EM, Ahmed MA, Fathy N, et al. Therapeutic trial of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation after acute ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2005;65(3): 466-468.[10] Fregni F, Boggio PS, Valle AC, et al. A sham-controlled trial of a 5-day course of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the unaffected hemisphere in stroke patients. Stroke. 2006; 37(8): 2115-2122.[11] Seniów J, Bilik M, Le?niak M, et al. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Combined With Physiotherapy in Rehabilitation of Poststroke Hemiparesis A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Repair. 2012;26(9): 1072-1079.[12] Khedr EM, Etraby AE, Hemeda M, et al. Long‐term effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor function recovery after acute ischemic stroke. Acta Neurol Scand. 2010;121(1): 30-37.[13] Malcolm MP, Triggs WJ, Light KE, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation as an adjunct to constraint-induced therapy: an exploratory randomized controlled trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;86(9): 707-715.[14] Takeuchi N, Chuma T, Matsuo Y, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of contralesional primary motor cortex improves hand function after stroke. Stroke. 2005;36(12): 2681-2686.[15] Takeuchi N, Tada T, Toshima M, et al. Inhibition of the unaffected motor cortex by 1 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation enhances motor performance and training effect of the paretic hand in patients with chronic stroke. J Rehabil Med. 2008;40(4): 298-303.[16] Sasaki N, Mizutani S, Kakuda W, et al. Comparison of the effects of high-and low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on upper limb hemiparesis in the early phase of stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013; 22(4): 413-418.[17] Wang RY, Tseng HY, Liao KK, et al. rTMS Combined With Task-Oriented Training to Improve Symmetry of Interhemispheric Corticomotor Excitability and Gait Performance After Stroke A Randomized Trial. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2012;26(3): 222-230.[18] Theilig S, Podubecka J, Bösl K, et al. Functional neuromuscular stimulation to improve severe hand dysfunction after stroke: does inhibitory rTMS enhance therapeutic efficiency? Exp Neurol. 2011;230(1): 149-155.[19] Ackerley SJ, Stinear CM, Barber PA, et al. Combining theta burst stimulation with training after subcortical stroke. Stroke. 2010;41(7):1568-1572.[20] Emara TH, Moustafa RR, Elnahas NM, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation at 1Hz and 5Hz produces sustained improvement in motor function and disability after ischaemic stroke. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(9):1203-1209.[21] Chang WH, Kim YH, Yoo WK, et al. rTMS with motor training modulates cortico-basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuits in stroke patients. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2012;30(3): 179-189.[22] Chang WH, Kim YH, Bang OY, et al. Long-term effects of rTMS on motor recovery in patients after subacute stroke. J Rehabil Med. 2010;42(8): 758-764.[23] Hsu YF, Huang YZ, Lin YY, et al. Intermittent theta burst stimulation over ipsilesional primary motor cortex of subacute ischemic stroke patients: a pilot study. Brain Stimul. 2013;6(2): 166-174.[24] Kim YH, You SH, Ko MH, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation–induced corticomotor excitability and associated motor skill acquisition in chronic stroke. Stroke. 2006;37(6): 1471-1476.[25] 凌琳, 黄国志. 不同频率重复经颅磁刺激对脑梗死患者运动功能影响的研究[J].中华神经医学杂志, 2012, 11(2): 169-172.[26] 池登科, 吴爱玲, 龚凌云, 等. 重复经颅磁刺激在卒中后运动功能康复中的作用[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2008, 6(6): 743-744.[27] 阎涛.经颅磁刺激对急性脑梗死预后的早期评价及治疗的试验研究[D].天津:天津医科大学, 2006.[28] 赵科鹏. 5HZ高频rTMS对急性期脑梗死患者运动功能恢复的影响[D]. 苏州:苏州大学, 2010.[29] 李辉萍, 徐伟, 宋治, 等.重复经颅磁刺激对急性脑梗死患者血清白介素-6水平及神经功能康复的影响[J].中国全科医学, 2010, 13(33): 3709-3711.[30] 庄立. 重复经颅磁刺激改善缺血性脑卒中动功能的作用机制[J]. 中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志, 2009, 16(3): 213-216.[31] Corti M, Patten C, Triggs W. Repetitive transcranial magneticstimulation of motor cortex after stroke: a focused review. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;91(3):254-270.[32] Khedr EM, Fetoh NA. Short- and long-term effect of rTMS on motor function recovery after ischemic stroke. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2010,28(4):545-559.[33] 沈滢, 单春雷, 殷稚飞,等.重复经颅磁刺激在脑卒中后运动功能康复中的应用[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2012, 27(12): 1162-1166.[34] 户东梅, 程肖蕊, 周文霞, 等. 重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中后认知功能障碍治疗的研究进展[J]. 生理科学进展, 2012, 43(6): 411-416. |
| [1] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(在线): 3-. |
| [2] | Zhang Peigen, Heng Xiaolai, Xie Di, Wang Jin, Ma Jinglin, Kang Xuewen. Electrical stimulation combined with neurotrophin 3 promotes proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1076-1082. |
| [3] | Yan Yan, Zhao Yan, Fu Fanyu, He Haijun. Systematic evaluation and meta-analysis of total hip arthroplasty with three-dimensional printing model in preoperative planning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3423-3429. |
| [4] | Ma Xin, Zhang Wenhui, Yang Yuping, Yuan Zhiguo. Meta-analysis of barbed suture versus traditional suture in primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3430-3437. |
| [5] | Zhang Chi, Lü Haoyuan, Zhang Xiaoyun, Lin Zonghan, Chen Yueping, Dong Panfeng, Feng Yang. Hip function after total hip arthroplasty through different approaches: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1248-1257. |
| [6] | Han Jian. Post-stroke dysarthria treated by acupuncture combined with speech-language training: bibliometric analysis and verification of clinical efficacy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1013-1017. |
| [7] | Xia Ling, Wang Pan, Wu Chunfang, Zhang Zhaobo. Application value of surface electromyography in the repair of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1142-1148. |
| [8] | An Taijian, Zhang Wei, Yang Hong, Wang Qingfeng. Potential mechanisms of bone marrow stem cells in the treatment of ischemic stroke based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5249-5255. |
| [9] | Cao Jingli1, 2, Marina S. Ferguson3, Sun Jie3, Zhang Dong1, Liu Li1, Li Zirui1, Wang Yajie1, Sui Binbin1, Shen Mi1, Gao Peiyi1, 4, Thomas S. Hatsukami3, Zhao Xihai5, Yuan Chun1, 3, 5. An en bloc paraffin embedding method for serial sectioning of carotid atherosclerotic plaque [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 5041-5045. |
| [10] | Zhou Jing, Yang Dan, Wei Meng, Huang Caihong, Zhao Yan. Effects of MOTOmed lower limb function trainer on lower limb function in stroke patients with hemiplegia: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(30): 4913-4920. |
| [11] | Zhong Yanchun, Liu Lulin, Xiao Jianhua, Ouyang Xunyan, Huang Weimin, Liu Wuyang. postoperative blood loss of intertrochanteric fracture: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4584-4592. |
| [12] | Ma Shanxin, Xu Jianwen, Long Yaobin, Huang Lang, Fu Shuisheng, Su Yiji, Liu Ying. Botulinum toxin type A under ultrasound guidance for treating plantar flexor spasticity on different stages after stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(27): 4300-4304. |
| [13] |
Zhao Jiangbo, Tian Jianing, Li Yan, Chen Desheng.
Treatment efficacy of cementless versus cemented prosthesis in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3916-3923.
|
| [14] |
Wang Lei, Li Zilong, Yuan Binbin, Wu Qingwei, Tang Fengming.
Clinical effect of locking plate versus anterograde intramedullary nail in the treatment of adult humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3924-3930.
|
| [15] | Zhou Yan, Wang Lin, Pei Shuang, Li Yanfei, Chen Xuemei, Jia Yanjie. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce the activation of type A1 astrocytes after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3294-3301. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||