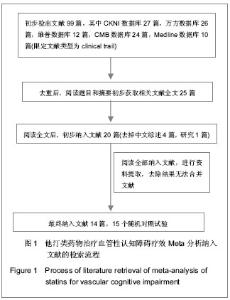
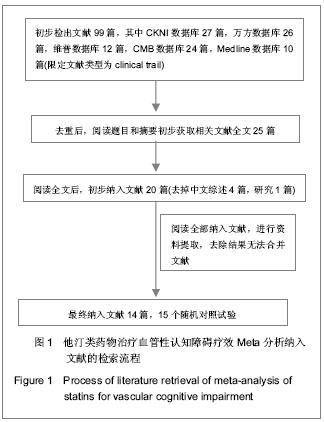
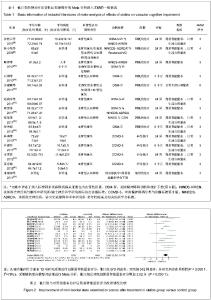
| [1] |
Huang Yong, Zhu Weimin, Lu Wei, Ouyang Kan, Peng Liangquan, Liu Haifeng, Li Hao, Feng Wenzhe, Xu Jian, Zhong Mingjin, Chen Kang, Li Ying, Deng Zhenhan.
Safety of steroid-containing cocktail periarticular injection
after knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1449-1456.
|
| [2] |
Deng Jinman, Fang Guanjun, Wang Yu, Ding Shaobo.
Efficacy and characteristics of parecoxib and celecoxib in
the treatment of pain after orthopedic surgery: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1471-1476.
|
| [3] |
Mou Zichao, Wang Dan, Wang Xiaoyan, Li Siyu, Wang Zhiqiang, Wang Qingsong.
Oral simvastatin for 3 continuous months improves learning and memory ability of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4190-4195.
|
| [4] |
Gu Yingxuan, Huang Linfeng, Hu Xiaohui, Quan Xiaoming, Kang Liangqi, Zhou Linghan, Wang Xiaojun.
Platelet-rich plasma combined with negative pressure for chronic refractory wounds: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4257-4264.
|
| [5] |
Yan Xianke.
Total knee arthroplasty through a midvastus approach reduces
postoperative adverse reactions and accelerates functional recovery of the knee
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3336-3340.
|
| [6] |
Yan Yan, Zhao Yan, Fu Fanyu, He Haijun.
Systematic evaluation and meta-analysis of total hip
arthroplasty with three-dimensional printing model in preoperative planning
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3423-3429.
|
| [7] |
Ma Xin, Zhang Wenhui, Yang Yuping, Yuan Zhiguo.
Meta-analysis of barbed suture versus traditional suture in primary total knee arthroplasty
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3430-3437.
|
| [8] |
Deng Kaifeng, Shang Xinyang, Zhu Shengwang, Li Shuzhen, Zhu Ying, Chen Rilan.
Meta-analysis of the effect of acupoint injection on pain
improvement and joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2879-2887.
|
| [9] |
Wang Jinchun, Liu Huiying, Cao Yunpeng.
tau protein and Alzheimer’s disease
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(17): 2775-2781.
|
| [10] |
Zhang Chi, Lü Haoyuan, Zhang Xiaoyun, Lin Zonghan, Chen Yueping, Dong Panfeng, Feng Yang.
Hip function after total hip arthroplasty through different approaches: a network meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1248-1257.
|
| [11] |
Zhang Zhiliang, Han Pengfei, Ren Guangzong, Chen Chenglong, Li Pengcui, Wei Xiaochun.
Effectiveness and safety of knotless barbed suture for primary total knee or hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1258-1264.
|
| [12] |
Lu Chao, Liu Wengang, Wu Huai, Ye Guozhu, Chen Guocai, Chen Jin.
Sealing of intramedullar femoral canal for blood loss after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 636-642.
|
| [13] |
Zhong Qiusheng1, Xia Weichao1, Guo Meizhen1, Zhu Haiqing1, Zhong Cuiqiong1, Shao Jieqi1, He Xiaohong2, Chen Xiumin2.
Sandwiched Moxibustion plus Bushen Quhan recipe for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5670-5675.
|
| [14] |
Liu Dongqi1, Li Rongmei1, Zhang Meiqi1,Chen Yanyan1, Zhang Haiping2 .
Meta-analysis of the effect of aerobic exercise on mild cognitive impairment in the elderly
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5727-5731.
|
| [15] |
Gong Jiao, Liu Ming.
Human induced pluripotent stem cell transplantation for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonatal mice
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5322-5327.
|