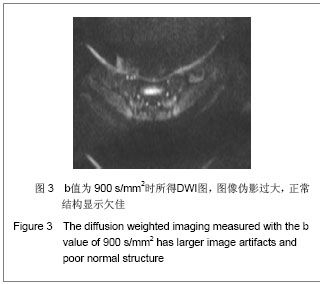
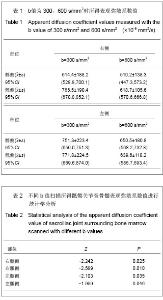
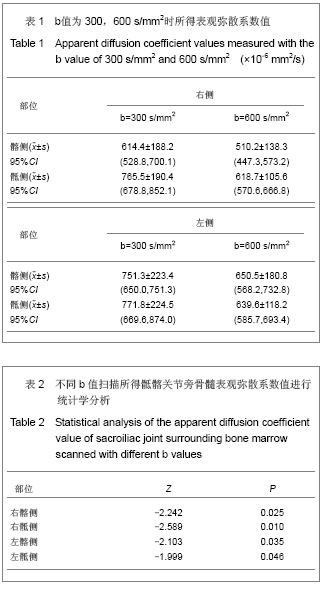
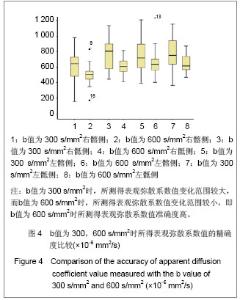
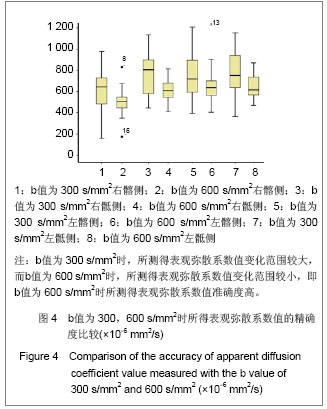
| [1] Zhang YT,Yu ZX. Beijing:People’s Medical Publishing House. 2010:126. 张云亭,于兹喜.医学影像检查技术学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2010:126.[2] Zhang CY, Rong R, Wang XY.Age-related changes of bone marrow of normal adult man on diffusion weighted imaging. Chin Med Sci J. 2008;23(3):162-165.[3] Kwee TC, Takahara T, Ochiai R,et al. Whole-body diffusion- weighted magnetic resonance imaging.Eur J Radiol. 2009; 70(3):409-417.[4] Bammer R. Basic principles of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2003;45(3):169-184.[5] Zhong JY,Guo ZF,Wang DH,et al. Shiyong Yiyuan Linchuang Zazhi. 2012;9(5):129-131.钟建勇,郭贞芳,王大浒,等.急性脑梗死122例的低场强磁共振弥散加权成像特征分析[J].实用医院临床杂志,2012,9(5): 129-131.[6] Fan Y,Li YC,Liu GR,et al. Zhonghua Shenjingke Zazhi. 2012; 45(12):879-882.樊宇,李月春,刘国荣,等.弥散加权成像对短暂性脑缺血发作患者临床转归的诊断价值[J].中华神经科杂志,2012,45(12): 879-882.[7] Fen XG,Zhang JH,Yang J,et al. Zhonghua Xingwei Yixue yu Naokexue Zazhi. 2012;21(3):255-257.冯勋刚,张俊湖,杨君,等.急性期脑梗死患者弥散加权成像皮质层状坏死表现的临床意义[J].中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2012, 21(3):255-257.[8] Chen QF,Zhang J. Zhongguo Shiyong Yiyao. 2012;7(29):82.陈庆丰,张杰.低场磁共振弥散加权成像(DWI)对超急性期脑梗死的诊断价值[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(29):82. [9] Wang Y,Zhang H,Song P,et al. Zhonghua Laonian Xinnao Xueguanbing Zazhi. 2012;14(6):639-643.王勇,张晖,宋鹏,等.应用高场强磁共振弥散加权成像评价神经生长因子治疗犬脑梗死疗效的研究[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2012,14(6):639-643.[10] Xu S,Zhou SQ,Sen SG. Zhonghua Linchuang Yishi Zazhi: Diziban. 2012;6(7):128-129.徐钐,周四清,温生贵.磁共振弥散加权成像对胰腺囊肿性病变的鉴别诊断价值[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2012,6(7): 128-129.[11] Zhang H,Qin DJ,Jiang XY,et al. Zhonghua Linchuang Yishi Zazhi:Diziban. 2012;6(6):1473-1476.张虎,秦东京,姜兴岳,等.磁共振弥散加权成像对肝脏常见占位性病变诊断应用价值的研究[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2012, 6(6):1473-1476.[12] Fan XJ,Pan WD,Qin MW. Zhongguo Yixue Kexueyuan Xuebao. 2012;34(5):534-538.范小晶,潘卫东,秦明伟.弥散加权成像在直肠癌诊断中的应用价值[J].中国医学科学院学报,2012,34(5):534-538.[13] Wang J,Yao XZ,Rao SX,et al. Yixue Yingxiangxue Zazhi. 2012;22(1):91-93.王健,姚秀忠,饶圣祥,等.3.0T磁共振弥散加权成像在胰腺癌中的应用价值[J].医学影像学杂志,2012,22(1):91-93.[14] Qi J. Shiyong Fangshexue Zazhi. 2009;25(2):224-227.齐静.肌炎的弥散加权成像的定量分析:骨骼肌弥散各向异性初步研究[J].实用放射学杂志,2009,25(2):224-227.[15] Dietrich O, Raya JG, Sommer J, et al. A comparative evaluation of a RARE-based single-shot pulse sequence for diffusion-weighted MRI of musculoskeletal soft-tissue tumors. Eur Radiol. 2005;15(4):772-783.[16] Chan JH, Tsui EY, Luk SH, et al. MR diffusion-weighted imaging of kidney: differentiation between hydronephrosis and pyonephrosis.Clin Imaging. 2001;25(2):110-113.[17] Gaspersic N, Sersa I, Jevtic V, et al. Monitoring ankylosing spondylitis therapy by dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.Skeletal Radiol. 2008;37(2):123-131.[18] Bozgeyik Z, Ozgocmen S, Kocakoc E. Role of diffusion-weighted MRI in the detection of early active sacroiliitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191(4):980-986.[19] Ding QG,Jia CH,Lu YM,et al. Linchuang Fangshexue Zazhi. 2012; 31(5):693-696.丁庆国,贾传海,陆永明,等. MRI联合DWI在强直性脊柱炎诊断中的价值[J].临床放射学杂志, 2012, 31(5):693-696.[20] Bulakbasi N, Guvenc I, Onguru O,et al.The added value of the apparent diffusion coefficient calculation to magnetic resonance imaging in the differentiation and grading of malignant brain tumors. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2004;28(6):735-746.[21] van Rijswijk CS, Kunz P, Hogendoorn PC, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI in the characterization of soft-tissue tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;15(3):302-307.[22] Deng SH,Liu Y. Yingxiang Zhenduan yu Jieru Fangshexue. 2007; 16(3):141-144.邓世华,刘源.MRI诊断强直性脊柱炎中轴骨关节病变的展望[J]. 影像诊断与介入放射学,2007,16(3):141-144.[23] Sheng HQ,Zhao B,Geng L. Linchuang Fangshexue Zazhi. 2008; 27(8):1091-1094.盛华强,赵斌,耿丽.强直性脊柱炎的骶髂关节病变:MRI与螺旋CT对照研究[J].临床放射学杂志, 2008, 27(8):1091-1094.[24] Guo HL,Shui GH,Kong FG. Shiyong Fangshexue Zazhi. 2007; 23(11):1493-1496.郭会利,水根会,孔凡国.影像学对强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变的诊断价值[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2007, 23(11):1493-1496.[25] Goie The HS, Steven MM, van der Linden SM, et al. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison of the Rome, New York and modified New York criteria in patients with a positive clinical history screening test for ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1985;24(3):242-249. [26] Jin HH,Cheng RQ,Wang HM. Shiyong Fangshexue Zazhi. 2010; 26(8):1166-1168,1180.金红花,程若勤,王化敏.强直性脊柱炎的MRI分析[J].实用放射学杂志, 2010,26(8):1166-1168,1180.[27] Cui LF,Song HC,Li HF,et al. Zhonghua Fengshibingxue Zazhi. 2003; 7(1):55-56.崔刘福,宋海澄,李宏芬,等.HLA-B27等位基因与强直性脊柱炎的相关性研究[J].中华风湿病学杂志, 2003, 7(1):55-56.[28] Sheng CY,Han MJ. Fangshexue Shijian. 2007; 22(12): 1344-1346.盛翠云,韩铭钧.强直性脊柱炎的影像诊断研究进展[J].放射学实践, 2007, 22(12):1344-1346.[29] Huang ZG,Zhang XZ,Hong W,et al. Linchuang Fangshexue Zazhi. 2011; 30(12):1797-1801.黄振国,张雪哲,洪闻,等.脊柱关节病脊柱的MRI表现[J].临床放射学杂志, 2011, 30(12):1797-1801.[30] Xiao ZY,Zeng QY. Zhonghua Fengshibingxue Zazhi. 2004; 8(8):479-481.肖征宇,曾庆馀.儿童型强直性脊柱炎的早期诊断—24例前瞻性分析[J].中华风湿病学杂志, 2004, 8(8):479-481.[31] Fei WY,Wang H,Wang JC. Shiyong Fangshexue Zazhi. 2007; 23(11):1558-1561.费文勇,王骅,王静成.强直性脊柱炎影像学早期诊断研究进展[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2007, 23(11):1558-1561.[32] Bennett AN, McGonagle D, O'Connor P, et al. Severity of baseline magnetic resonance imaging-evident sacroiliitis and HLA-B27 status in early inflammatory back pain predict radiographically evident ankylosing spondylitis at eight years. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(11):3413-3418.[33] Huang ZG,Zhang XZ,Hong W,et al. Zhonghua Fangshexue Zazhi. 2011; 45(11):1040-1044.黄振国,张雪哲,洪闻,等.早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变的X线、CT和MRI对比研究[J].中华放射学杂志, 2011, 45(11): 1040-1044.[34] Vander Cruyssen B, Muñoz-Gomariz E, Font P, et al. Hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis: epidemiology and risk factors associated with hip replacement surgery. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49(1):73-81. [35] Baraliakos X, Braun J. Hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis: what is the verdict. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010; 49(1):3-4.[36] Qian QR,Jia LS,Gao JX. Linchuang Guke Zazhi. 2002; 5(1): 1-5.钱齐荣,贾连顺,高建新.骶髂关节面形态的测量及其生物力学意义[J].临床骨科杂志, 2002, 5(1):1-5.[37] Zhang YQ,Liu W,Fu XY,et al. Zhongguo Linchuang Jiepouxue Zazhi. 2009; 27(1):73-75.张英琦,刘伟,付小勇,等.骶髂关节的放射解剖学观测[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2009, 27(1):73-75.[38] Liu BM,Wang SM,Cui JL,et al. Linchuang Fangshexue Zazhi. 2008; 27(12):1786-1789.刘丙木,王淑梅,崔建岭,等.10~20岁健康志愿者骶髂关节软骨MRI序列对照研究[J].临床放射学杂志, 2008, 27(12):1786- 1789.[39] Puhakka KB, Jurik AG, Schiottz-Christensen B, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of sacroiliitis in early seronegative spondylarthropathy. Abnormalities correlated to clinical and laboratory findings. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004;43(2):234-237.[40] Zhang XZ. Zhonghua Fangshexue Zazhi. 2007; 41(12): 1425-1426.张雪哲. 强直性脊柱炎[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2007, 41(12): 1425-1426.[41] Wang QW,Zeng QY,Xiao ZY,et al. Zhonghua Neike Zazhi. 2004; 43(11):832-836.王庆文,曾庆馀,肖征宇,等.脊柱关节病患者骶髂关节细针活检的病理表现及其临床意义[J].中华内科杂志, 2004, 43(11):832- 836.[42] Maksymowych WP, Inman RD, Salonen D,et al. Spondyloarthritis research Consortium of Canada magnetic resonance imaging index for assessment of sacroiliac joint inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;53(5):703-709. |