Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (11): 2040-2047.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.11.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Stress distribution of needle body during the process of acupuncture
Wang Xi-ming, Zhang Hui, Zhou Yong-jun
- Department of Physics, Xianyang Normal College, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2012-11-02Revised:2012-11-24Online:2013-03-12Published:2013-03-12 -
About author:Wang Xi-ming, Professor, Department of Physics, Xianyang Normal College, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China wxm332@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xi-ming, Zhang Hui, Zhou Yong-jun. Stress distribution of needle body during the process of acupuncture[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(11): 2040-2047.
share this article
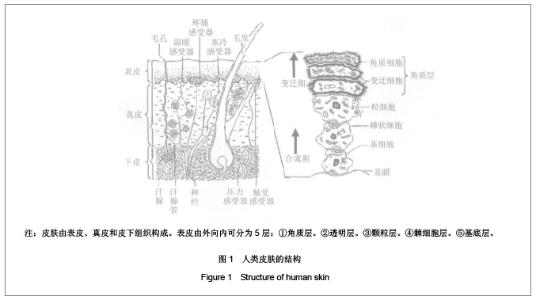
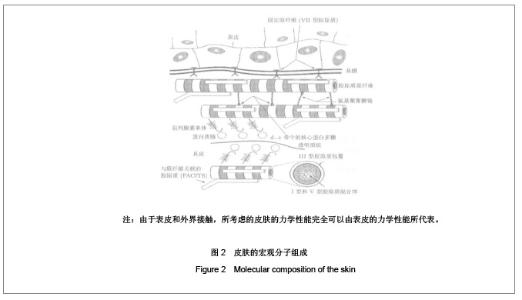
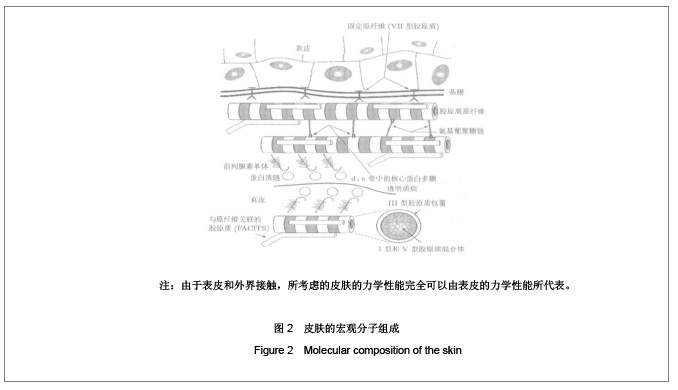
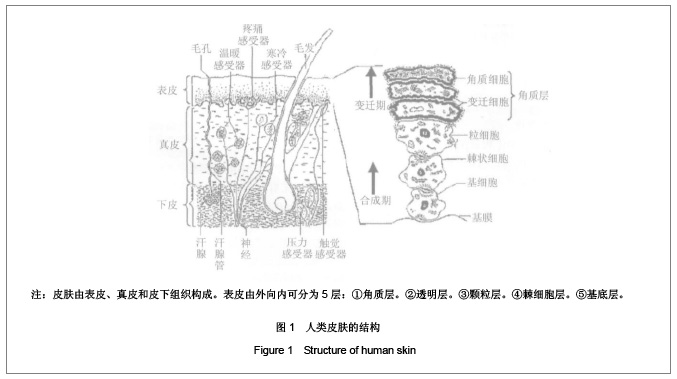
1 皮肤组织及其力学性能 1.1 皮肤组织结构 皮肤是人体最大的器官,总质量占体质量的5%-15%,总面积为1.5-2 m2,厚度因人或因部位而异,为0.5-4 mm。 皮肤由表皮、真皮和皮下组织构成。表皮是皮肤最外面的一层,平均厚度为0.2 mm,根据细胞的不同发展阶段和形态特点,由外向内可分为5层:①角质层:由数层角化细胞组成,含有角蛋白。它能抵抗摩擦,防止体液外渗和化学物质内侵。②透明层:由两三层核已消失的扁平透明细胞组成,含有角母蛋白。能防止水分,电解质和化学物质的透过,故又称屏障带。③颗粒层:由2-4层扁平梭形细胞组成,含有大量嗜碱性透明角质颗粒。④棘细胞层:由4-8层多角形的棘细胞组成,由下向上渐趋扁平,细胞间借桥粒互相连接,形成所谓细胞间桥。⑤基底层:由1层排列呈栅状的圆柱细胞组成。此层细胞不断分裂(经常有3%-5%的细胞进行分裂),逐渐向上推移、角化、变形,形成表皮其他各层,最后角化脱落。由于表皮和外界接触,所考虑的皮肤的力学性能完全可以由表皮的力学性能所代表,见图1,2。"

1.2 皮肤的几个主要力学性能 杨氏模量:弹性模量是描述材料力学性能的最常用的参数,其单位是每单位面积上的力。均质材料的传统力学特性对于皮肤来说并不适用,皮肤既没有独特的单一杨氏模量,也没有单一的剪切模量,对皮肤而言杨氏模量并不是常数。但是作为皮肤力学性能最重要的参数之一,人类皮肤的体内杨氏模量和体外杨氏模量已经得到了广泛的测量,因为这些材料参数能够反映人类皮肤的基本弹性行为方式。皮肤杨氏模量测量值之间存在着很大的差异,范围从0.02-100 MPa,主要取决于推倒材料参数所用的模型和所施加的应力[7]。针刺过程中破皮的一瞬间,针尖施加在皮肤单位面积上的力很大,杨氏模量值相应的也很大,代表参数应该是角质层测量参数。 压缩系数:体积压缩系数是指固体受到压力时体积变量和原体积乘所受压力之比。实验发现,人体的软组织(皮肤、皮下组织和内脏)具有0.30 m2/GN到0.38 m2/GN的体积压缩系数,这说明人类皮肤的可压缩性不如蒸馏水(0.46 m2/GN)[8]。这些实验结果表明,人的皮肤是很难压缩的。 摩擦因数:当两个物体表面接触挤压并且相对运动时,在两个物体的接触表面就会产生动摩擦力。摩擦因数是表征物体摩擦性能的重要参量,摩擦因数的大小主要取决于摩擦物体表面的材质,不同材质之间的摩擦因数是不同的。人们已经设计出各种各样的实验来测定皮肤和不同物体之间的摩擦因数[9]。目前测出的皮肤表面的摩擦因数一般在0.12-0.7,大部分的测量值集中在0.2-0.5。存在测量区间的差别,是因为受到皮肤的干燥度和在人体上的不同部位等因素引起的。有人做过人腹部皮肤和直径10 mm不锈钢针之间的摩擦因数测定,当载荷从5 g(0.049 N)到45 g(0.44 N)变化时,它们之间的摩擦因数存在从1.1-0.51之间的变化差异,可以看出摩擦因数随压力的增加而减小[10]。丁光宏等[11]根据自己研制的仪器测出针刺人体曲池穴位时,针尖对皮肤的破皮压力为0.5-1.0 N,此时的摩擦因数应该在0.4-0.5之间。"


2 真皮、皮下组织及其力学性能 2.1 真皮和皮下组织结构 真皮来源于中胚叶,由纤维、基质和细胞构,真皮分为乳头层(又称真皮浅层)和 网状层(又称真皮深层)。皮下组织也来源于中胚叶,在真皮的下部,由疏松结缔组织和脂肪小叶组成,其下紧临肌膜。真皮和皮下组织主要都是由结缔组织组成,区分在于真皮主要是由致密结缔组织组成,而皮下组织主要是由疏松结缔组织组成。疏松结缔组织广泛存在于各器官之间、组织之间、甚至细胞之间。其结构特点是基质多,纤维少,结构疏松,呈蜂窝状,故又称蜂窝组织。这里考虑的皮下组织是一种广义的概念,也可以包含肌间隔疏松结缔组织、神经血管束疏松结缔组织、器官门疏松结缔组织等。从解剖学知,无论是致密结缔组织还是疏松结缔组织中均含有大量的纤维,而主要的纤维是胶原纤维和弹力纤维。 2.2 真皮和皮下组织的力学性能 真皮及以下的组织为黏弹性组织,和表皮大不相同,黏弹性接近于液体性质,只是黏性比液体大。又因为它们为结缔组织,胶原纤维和弹性纤维的力学性能代表了其主要生物力学性能,下面主要讨论这两种纤维的力学性质。 2.2.1 胶原纤维及其力学性质 胶原蛋白借分子间的交联聚合形成胶原原纤维并继而由后者聚合形成胶原纤维。胶原纤维为真皮的主要成分,约占95%,集合组成束状。在皮下组织中胶原纤维含量没有真皮大,多为平行状组成,在空腔器官壁上多呈三维排列。胶原纤维是黏弹性体,有明显的滞后、应力松弛特性,很小的应变就会引起很高的应力,应力-应变关系为非线性。在拉伸试验中,胶原纤维开始伸长量较小,但随着载荷增加,伸长量和载荷成正比例直线增加,随后载荷与变形呈非线性关系,在终点处产生破坏[12]。可见,胶原纤维韧性大、抗张力性强。生长发育、创伤修复和某些病理过程中,由于应力的变化,胶原纤维的合成与障碍发生适应性改变,包括各型胶原含量和空间排列的重建[13]。反之,由外界施加影响使胶原纤维发生应力变化,可以修复创伤并治理某些疾病。 2.2.2 弹性纤维及其力学性质 弹性纤维新鲜状态下呈黄色,又名黄纤维。在苏木精-伊红标本中,着色轻微,不易与胶原纤维区分。弹性纤维较细,直行,分支交织,粗细不等(0.2-1.0 μm),表面光滑,断端常卷曲。电镜下,弹性纤维的核心部分电子密度低,由均质的弹性蛋白组成,核心外周覆盖微原纤维,直径约10 nm。弹性蛋白分子能任意卷曲,分子间借共价键交联成网。在外力牵拉下,卷曲的弹性蛋白分子伸展拉长;除去外力后,弹性蛋白分子又回复为卷曲状态。弹性纤维富于弹性而韧性差,与胶原纤维交织在一起,使疏松结缔组织既有弹性又有韧性,有利于器官和组织保持形态位置的相对恒定,又具有一定的可变性。弹性纤维除了具有胶原纤维所具有的基本力学性能外,它的另一个显著性能是,弹性纤维变形和熵的变化有关。经络和穴位处有丰富的弹性纤维聚集,弹性纤维的这一独特性能可能对针刺过程中能量传递起着关键作用。"

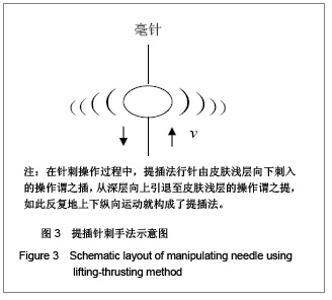
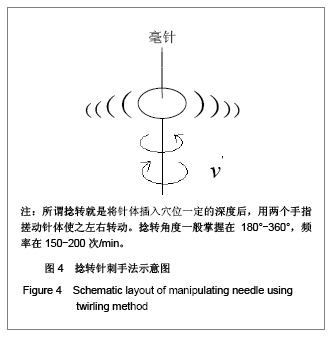
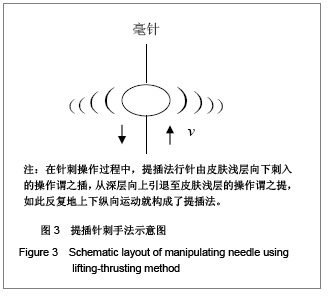
3 两种主要针刺手法及其模型 目前针刺手法很多,但是最基本的针刺手法仍然是提插法和捻转法两种。本课题组设计的实验研究也是以它们为基础,下面根据这两种针刺手法的特点建立相应的研究模型。 3.1 提插针刺手法和麦克斯韦(Maxwell)体模型 在针刺操作过程中,提插法行针由皮肤浅层向下刺入的操作谓之插,从深层向上引退至皮肤浅层的操作谓之提,如此反复地上下纵向运动就构成了提插法。提插法是上下直进式动作,必然在皮肤及结缔组织中产生一个以针体为中心,以r为半径的很小范围内的圆柱形速度梯度分布 。这种速度不断改变方向引起针体周围皮肤及结缔组织上下震动。 提插行针过程中,提插的上下运动幅度就是弹性体振动源的振幅,它也是皮肤及结缔组织的最大振幅,这个振幅以针体为中心随着半径增大而衰减。皮肤及结缔组织对针体的阻力必然形成了弹性体的串联阻尼。所以,提插法行针过程就是一个典型的麦克斯韦(Maxwell)体模型。提插针刺过程是机械压力或者膨扩皮肤及结缔,在短时间内将机械能转变成经络物质的振动能量的过程,见图3。 3.2 捻转针刺手法和开耳芬(Kelvin)体模型 在针刺操作过程中,另一种主要手法是捻转法。所谓捻转就是将针体插入穴位一定的深度后,用两个手指搓动针体使之左右转动。捻转角度一般掌握在180°-360°,频率在150-200次/min。一般来说,捻转角度越大,频率越快,刺激量就越大,反之,刺激量就越小。 捻转行针时,针体转动带动穴位处皮肤及结缔组织一同扭转,也会在皮肤及结缔组织中产生一个以针体为中心,以不同r为半径的很小范围内的圆柱形转动速度梯度 ,形成了以针体为中心的多个薄圆面。同样,这个速度也在不断的改变方向,引起皮肤及结缔组织左右扭转,甚至引起弹性纤维在针体上的缠绕,见图4。"

4 行针过程中针体所受的阻力分布分析 1991年诺贝尔奖获得者、法国物理学家德热纳(P. G. De Gennes)在颁奖大会上提出了软物质的概念。固体是具有固定形状的物体,液体是可以随意流动的物体,而软物质是介于固体和液体之间的一类物体,人体就是典型的软物质。根据以上研究,因为人的皮肤表皮近似具有固体的力学性质,把它从软物质中剥离出来,可以看成准固体物质;真皮和皮下结缔组织是黏弹性体,直接看作软物质。结合本课题组近年来的系统研究成果[5,14-22],吸收同领域里其他方面的成果,下面从行针过程中的提插法麦克斯韦体模型和捻转法开耳芬体模型为基础来进行阻力分析。 4.1 提插法行针过程中针体所受阻力分布 若将开始提插作为有效的行针起点,在提插行针过程中,针体将受到两个区域的阻力:表皮区域的阻力和真皮及以下的结缔组织区域的阻力。表皮为准固体物质,坚硬而致密,进针口处相对粗糙,在针体上下提插的过程中阻力很大。而真皮和皮下结缔组织为软物质,柔软而疏松,相对针体滑腻且阻力较小。在行针过程中当针体上提时可以看见皮肤有明显的隆起状,这主要是表皮的阻力所引起的。所以在提插法行针过程非“得气”情况下,针体受到的主要阻力应该来自表皮,部分机械能以摩擦形式转换成热能,其余能量将以机械能形式贡献给穴位,引起穴位的一系列生理反应。 上面提到过,对于表皮的生物力学性质已经有很多学者进行了实验研究[23],从实验结论知皮肤强度很强,韧度很大且很难压缩,皮肤表面的摩擦因数也较大。皮肤表面摩擦因数的准确测定对于提插法行针过程关系很大。目前,测定皮肤摩擦因数的实验大致分为两类:一类为利用受已知法向力作用并在皮肤上旋转的探针或转轮进行测量,另一类则是利用在皮肤上滑动的探针进行测量。 作者所在的课题组研究了提插法行针过程所产生的针刺信号循经传播机制,认为该信号是一种次声波信号。按次声声压公式计算,若已知目前所用银针规格为:直径d=0.45-0.23 mm,则针尖面积s=1.6×10-7-4.15× 10-8 m2 ,考虑到穴位入口处皮肤的黏滞阻力,一般表皮组织的受力面积为s’=10-5-10-7 m2的数量级,若取行针时针尖压力F=0.2-0.02 N,可估算出声压压强和声强分别为P=2×103-2×105 Pa,L=160-180 dB甚至更大[5]。针刺过程中针体受力监控系统等的研制成功,对准确测量摩擦因数将会起到积极的帮助。 在“得气”状况下,针体所受阻力应该有所变化。作者计算了丁光宏等[24]用针体受力监控系统监测提插法针刺过程在“得气”情况下的实验结果,发现“得气”时针体受力比非“得气”时针体受力大1倍多,见图5,丁光宏自己所作的波形分析图也证实了这一点。"

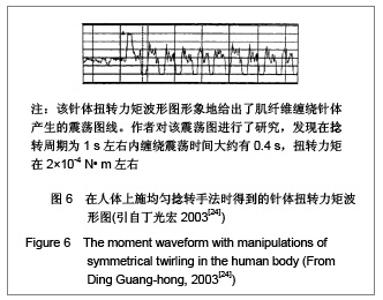
如果“得气”是由结缔组织收缩所引起的,在短时间内,纤维细胞的收缩将伴随着可溶性肌动蛋白的聚合和其受力纤维的形成,那么针体受到的主要阻力就是受力纤维的“紧抱”针体引起的。根据作者前期研究,在提插行针过程中麦克斯韦体模型下,松弛弹性模量、复弹性模量和内摩擦力均成正比例关系[17]。这个研究结论也说明在“得气”情况下,皮下部分内摩擦力增加,针体受力点必然下移,但是表皮的阻力也不应忽略。提插的过程实际上就是在寻找合适的刺激点,刺激结缔组织收缩,促使可溶性肌动蛋白的聚合和受力纤维的形成,并以这些物质为基础帮助针刺信号以次声波的形式沿经络线传播。根据本节讨论,提插行针过程中非“得气”时阻力主要来自表皮部分。在“得气”状况下阻力应该来自表皮和结缔组织中的纤维细胞共同作用,对针体而言,进入皮肤的所有针体部分都是受力点,只是靠近针尖部分的针体受力稍大一些,但是随着提插操作,进入皮肤的针体长度不断在发生变化。 4.2 捻转法行针过程中针体所受阻力分布 和提插法行针过程一样,在捻转法行针过程中,开始捻转应该是有效的行针起点,针体同样受到两个区域的阻力:表皮和真皮及皮下的结缔组织。因为表皮的厚度很小 (0.2 mm),对于捻转法行针过程而言,它的阻力可以忽略不计,这样,针体的主要阻力应该来自于结缔组织。前面提到,有学者在电子显微镜的观测下已经确认,捻转法行针时针体在穴位处提出后带有的残留物质是一些弹性和胶原纤维缠绕在针体上。从而可以确认,捻转法行针的阻力主要来自结缔组织中的弹性纤维和胶原纤维缠绕,其他阻力则来自针体和结缔组织之间的摩擦。有人用自己研制的“动态监测系统”监测了捻转手法行针过程[24],该针体扭转力矩波形图形象地给出了肌纤维缠绕针体产生的震荡图线。作者对该震荡图进行了研究,发现在捻转周期为1 s左右内缠绕震荡时间大约有0.4 s,扭转力矩在2×10-4 N• m左右,见图6。"


在这个时间范围内,针刺对纤维产生的拉伸足可以促使可溶性肌动蛋白的聚合和其受力纤维的形成。同时在纤维缠绕时间内产生连续性的小震荡,说明缠绕的阻力很大,也说明纤维是在拉伸和收缩的弹性震荡中吸收针体能量的。纤维产生的震荡频率应该是等于或者稍大于捻针频率的,也就是说纤维激发的肯定是次声波。捻转行针时,针体对于黏弹性的弹性纤维等扭转,形成了以针体为中心的多个薄圆面。从能量输入角度讲,捻转法行针过程就是复合阻力型的开耳芬(Kelvin)体模型,复合阻力主要来自皮肤和皮下结缔组织扭转、弹性纤维对针体的缠绕等。同样,松弛弹性模量、复弹性模量和内摩擦力均成正比例关系,内摩擦因数tanδ可以由相应的公式给出[15-17]。 弹性纤维是典型的软物质,前面提到,弹性纤维一般呈卷曲状,在外力的作用下会伸长,撤去外力它又会恢复卷曲状。Hearle在1958年就用X射线观察到,纤维的结构含有分子规则排列的结晶区和分子无规则排列的非结晶区,因而其性能介于结晶体与非结晶体之间[12]。在外力的作用下弹性纤维的变性会引起两种效果:内能的变化和熵的变化,其弹性主要由熵的变化而产生的。捻转行针过程中会引起弹性纤维产生拉伸形变,必然导致纤维内能的增加和熵的变化。内能增加引起纤维强力振动,一般捻转行针过程中产生的主频率在次声频率范围内,根据次声在介质中的传播特点,这些振动能量会无衰减的沿经络传播出去[5];熵变化会引起纤维及经络组织温度的变化。捻转行针过程中“得气”以后施针者会有捻转费力的明显感觉,也就是施针者会有更多的能量输出,根据目前的研究可知,这些能量一部分促使可溶性肌动蛋白的聚合和其受力纤维的形成并被纤维所吸收,另一部分产生内能和熵的变化。熵的变引起纤维及经络组织温度升高。“得气”以后患者产生凉簌簌的感觉和蚁走样的感觉是熵和温度变化的表现。 根据本节讨论,捻转行针过程,无论是否“得气”,在穴位组织区域受力点集中在真皮及其以下的结缔组织中,对针体而言受力点主要集中在针尖及附近部位。"

| [1] Fei L, Cheng HS, Cai DH, et al. Kexue Tongbao. 1988;43(6): 658. 费伦,承焕生,蔡得亨,等.经络物质基础及其功能性特征的实验探索和研究展望[J].科学通报,1988,43(6):658.[2] Dung HC. Anatomical features contributing to the formation of acupuncture. Brookline MA:Paradigm,1991.[3] Langevin HM, Churchill DL, Fox JP, et al. Biomechanical response to acupuncture needling in humans. J Appl Physical. 2001;91:2471.[4] Kolodney MS, Wysolmersky RB. Isometric contraction by fibroblasts and endothelial cells in tissue culture:a quantitative study. J Cell Biol. 1992;117:73.[5] Wang XM. Zhongguo Zhenjiu. 2009;29(3):223-226. 王西明.针刺次声能量治病机制的分析[J].中国针灸,2009,29(3):223-226.[6] Yuan L, Yao DW, Tang L, et al. Jiepou Xuebao. 2004;35(4): 337-343. 原林,姚大卫,唐雷,等. 针灸经穴的数字解剖学研究[J].解剖学报,2004,35(4):337-343.[7] Maurel W, Wu Y, Magnenat Thalmann N, et al. Biomechanical Models for Soft Tissue Simulation.Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 1998.[8] North JF, Gibson F. Volume compressibility of human abdominal skin. J Biomech.1978;11(4): 203-207.[9] Sivamani RK, Goodman J, Gitis NV, et al. Coefficient of friction: tribological studies in man-an overview. Skin Res Technol. 2003;9(3):227-234.[10] Sivamani RK, Goodman J, Gitis NV, et al. Friction coefficient of skin in real-time. Skin Res Technol. 2003;9(3):235-239.[11] Ding GH, Shen XY, Dai JH, et al. Shengwu Yixue Gongchengxue Zazhi. 2003;20(1):121-124. 丁光宏,沈雪勇,戴建华,等.中医针刺过程中针体受力的动态监测系统研制[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2003,20(1):121-124.[12] Feng YZ. Beijing: Science Press. 1983: 124-134. 冯元桢. 生物力学[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1983: 124-134. [13] Oryan A. Role of collagen in soft connective tissue wound healing. Transplant. 1995;27(5):2759. [14] Wang XM. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(39):7382-7385. 王西明.针刺频率和输入能量的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(39):7382-7385.[15] Wang XM. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(22):4346-4348. 王西明.针刺能量的物理学分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(22):4346-4348.[16] Deng YR, Wang XM, Zhang WH. Xianyang Shifan Xueyuan Xuebao. 2010;25(4):24-26. 邓亚荣,王西明,张卫华.针刺能量输入模型及动力学方程[J].咸阳师范学院学报,2010,25(4):24-26.[17] Wang XM. Beijing Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng. 2008;27(2): 202-204. 王西明.针刺过程能量的输入[J]. 北京生物医学工程,2008, 27(2): 202-204.[18] Wang XM. Beijing Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng. 2009;28(3): 309-312. 王西明.针刺治病是次声能量的有效利用[J].北京生物医学工程, 2009,28(3):309-312.[19] Wang XM. Xi′an: Xi′an Jiaotong University Press. 2007: 1372-1375. 王西明.熵变概念的再拓展——对人体系统和外界作用规律的研究.生物医学进展[M]. 西安:西安交通大学出版社, 2007: 1372-1375.[20] Wang XM. Shanxi Shifan Daxue Xuebao. 2003;(3):62-64. 王西明. 熵变概念的拓展[J]. 陕西师范大学学报,2003,(3): 62-64.[21] Wang XM. Zhongguo Zhenjiu: Wangluoban. 2007. 王西明. 人体腧穴和外界交换能量(信息)规律的探讨[J].中国针灸: 网络版,2007.[22] Wang XM. Zhongguo Zhenjiu. 2011;31(1):71-74. 王西明. 提插与捻转手法输入能量的比较分析[J]. 中国针灸,2011,31(1):71-74.[23] Lu TJ, Xu F. Luxue Jinzhan. 2008;38(4):393-426. 卢天健,徐峰. 皮肤的力学性能概述[J]. 力学进展,2008,38(4): 393-426.[24] Ding GH, Shen XY, Dai JH, et al. Zhongguo Zhenjiu. 2002; 22(10):679-681. 丁光宏,沈雪勇,戴建华,等.中医针刺过程中针体受力的动态监测系统研制[J].中国针灸,2002,22(10):679-681. |
| [1] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [2] | Xu Yinqin, Shi Hongmei, Wang Guangyi. Effects of Tongbi prescription hot compress combined with acupuncture on mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, in degenerative intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 713-718. |
| [3] | Bai Shengchao, Gao Yang, Wang Bo, Li Junping, Wang Ruiyuan. Dynamic changes of mitochondrial function of the skeletal muscle after acupuncture intervention in rats with heavy load exercise-induced injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3648-3653. |
| [4] | Liu Jiahui, Zhang Zhongjiu, Jia Dianxiang, Zhai Aoqing, Niu Guangyun, Jiang Haibo. Research status and clinical application of artificial knee joint testing machine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2895-2901. |
| [5] | Yin Yuhui, Zhan Jiawen, Wang Shangquan, Shao Chenchen, Zhou Liang. Meta-analysis of acupuncture combined with massage in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2719-2726. |
| [6] | Zhang Chongfeng, Li Xianlin, Peng Weibing, Jia Hongsheng, Cai Lei. Treating lumbar disc herniation of blood stasis type with Chinese herbs, acupuncture, moxibustion, and massage: a Bayesian network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2781-2788. |
| [7] | Zhu Shiqiang, Xu Jianfeng, Hei Xiaoyan, Chen Yundong, Tian Xinbao, Zhang Jinchen, Lin Ruizhu. Effect of internal heat-type acupuncture needle therapy on the expression of type I collagen, matrix metalloproteinase-3 and osteopontin in the subchondral bone of rabbit knee osteoarthritis model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2636-2642. |
| [8] | Zhou Xiaohong, Li Bocun, Li Jia, Peng Rui. Relationship between joint function and circadian rhythm in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis undergoing acupuncture and moxibustion at acupoints selected based on liver theory [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2192-2198. |
| [9] | Wang Donghui, Wu Xin, Sun Ningning, Zhang Han, Gao Jianfeng. Electroacupuncture intervention on the expression of synaptic plasticity-related proteins in the hippocampi of mice with radiation-induced brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2205-2210. |
| [10] | Liu Jie, Fan Ruoxun, Gao Jiazi, Zeng Sheng, Liu Jun. Mechanical responses of the degenerated lumbar spines with different degrees at low frequency vibration generated by vehicle driving using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1371-1377. |
| [11] | Xu Guofeng, Li Xuebin, Tang Yifan, Zhao Yin, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun. The role of autophagy in ossification of the human ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1174-1181. |
| [12] | Fei Jing, Zheng Hongdi, Yu Liya, Li Leiji. Involvement of GDNF/PI3K/AKT pathway in promoting facial nerve regeneration using electroacupuncture in a rabbit model of facial nerve crush injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1094-1100. |
| [13] | Zhang Jinhuan, Yuan Weiqu, Chen Chen, Huang Xingxian, Yu Haibo. Different acupuncture therapies for treating periarthritis of the shoulder: overview of systematic reviews and network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5723-5732. |
| [14] | Fang Yulu, Yi Bingcheng, Shen Yanbing, Tang Han, Zhang Yanzhong. Potential of corn husk fibers reinforced chitosan-based hydrogels in cartilage tissue engineering scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5493-5501. |
| [15] | Wei Weibing, Zhou Binbin, Zhang Hongsheng, Yang Yu, Cui Junwu, Li Zhenxing. Effect of Electroacupuncture at Zusanli and Futu acupoints on expression of apoptosis factor Caspase-3 in spinal cord injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5151-5157. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||