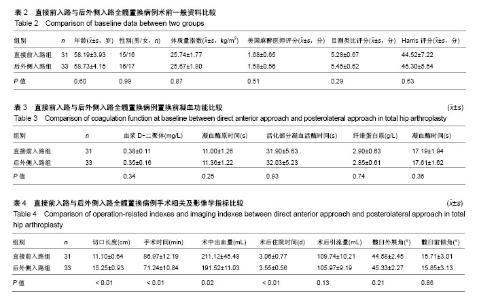
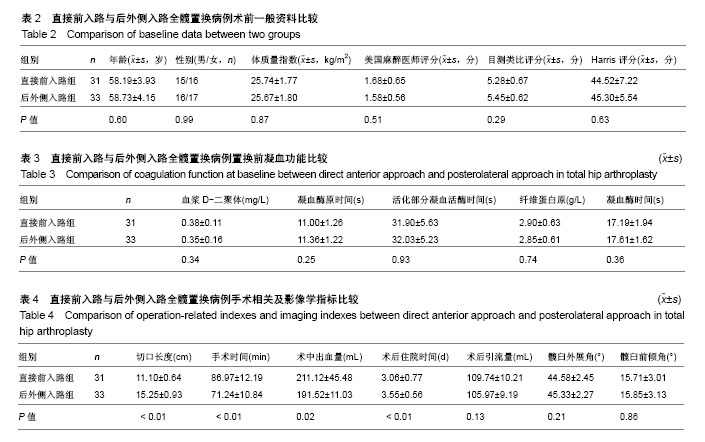
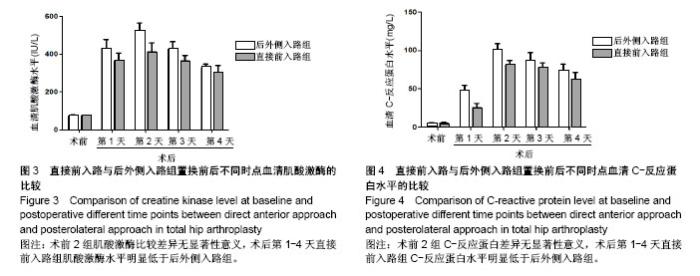
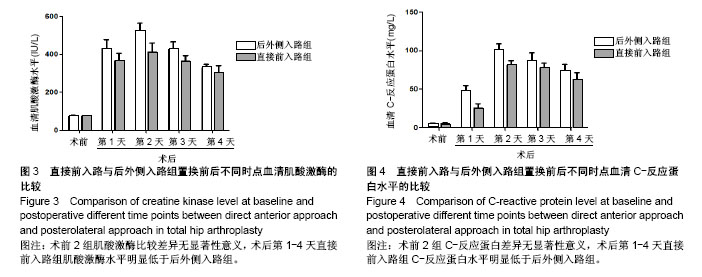
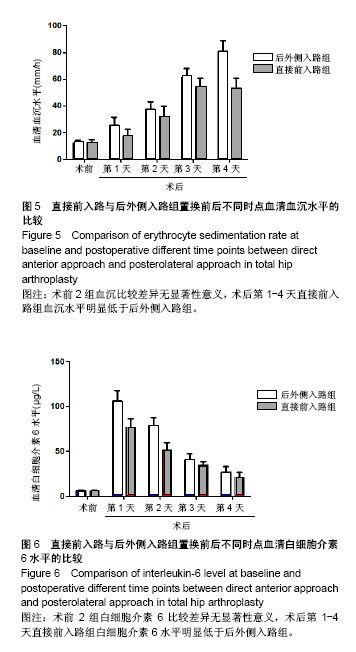
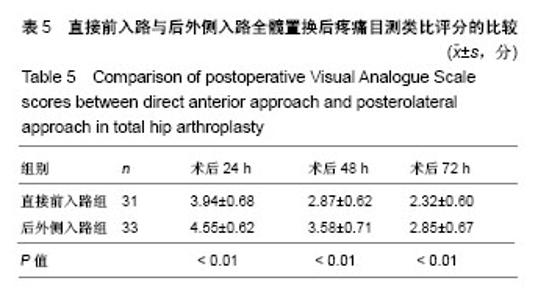
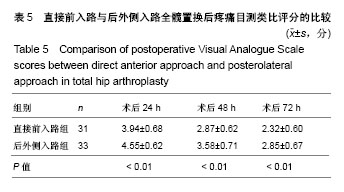
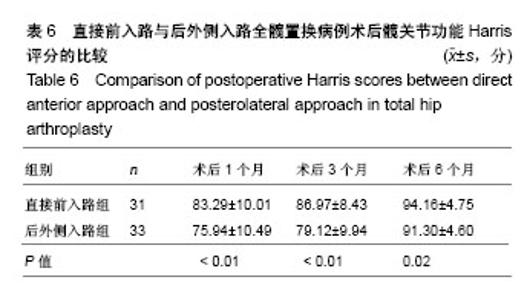
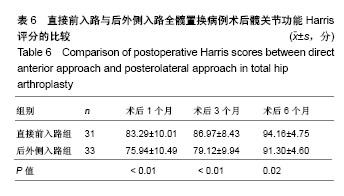
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (35): 5583-5589.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Early effects of direct anterior approach versus posterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty
Zha Xiaowei, Cheng Wendan, Lü Hao, Li Ziyu, Liu Wei, Qi Lei, Yu Shuisheng, Jing Juehua
- Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China
-
Online:2018-12-18Published:2018-12-18 -
Contact:Jing Juehua, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Zha Xiaowei, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230000, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81671204; the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (General Program), No. 1608085MH167
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zha Xiaowei, Cheng Wendan, Lü Hao, Li Ziyu, Liu Wei, Qi Lei, Yu Shuisheng, Jing Juehua. Early effects of direct anterior approach versus posterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(35): 5583-5589.
share this article
| [1] 俞银贤, 马金忠. 微创直接前方入路髋关节置换术相关研究[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2014, 35(1):33-35.[2] Reichert JC, Volkmann MR, Koppmair M, et al. Comparative retrospective study of the direct anterior and transgluteal approaches for primary total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2015;39(12):2309-2313.[3] Clyburn TA. CORR Insights(®): anterior and anterolateral approaches for tha are associated with lower dislocation risk without higher revision risk. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(11):3401-3408.[4] Witzleb WC, Stephan L, Krummenauer F, et al. Short-term outcome after posterior versus lateral surgical approach for total hip arthroplasty - a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Med Res. 2009;14(6):256.[5] Cheng TE, Wallis JA, Taylor NF, et al. A prospective randomized clinical trial in total hip arthroplasty-comparing early results between the direct anterior approach and the posterior approach. J Arthroplasty. 2016; 32(3):883-890.[6] Yang C, Zhu Q, Han Y, et al. Minimally-invasive total hip arthroplasty will improve early postoperative outcomes: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Ir J Med Sci. 2010;179(2):285-290.[7] Christensen CP, Jacobs CA. Comparison of patient function 6 weeks after direct anterior or posterior tha: a randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(9 Suppl):94-97.[8] Zawadsky MW, Paulus MC, Murray PJ, et al. Early outcome comparison between the direct anterior approach and the mini-incision posterior approach for primary total hip arthroplasty: 150 consecutive cases. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(6):1256-1260.[9] Reichert JC, Volkmann MR, Koppmair M, et al. Comparative retrospective study of the direct anterior and transgluteal approaches for primary total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2015;39(12):2309-2313.[10] Zhao HY, Kang PD, Xia YY, et al. Comparison of early functional recovery after total hip arthroplasty using a direct anterior or posterolateral approach: a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(11):3421-3428.[11] Zhang Z, Wang C, Yang P, et al. Comparison of early rehabilitation effects of total hip arthroplasty with direct anterior approach versus posterior approach. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018;32(3):329-333. [12] Graves SC, Dropkin BM, Keeney BJ, et al. Does surgical approach affect patient-reported function after primary tha? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 474(4):971-981.[13] Lee GC, Marconi D. Complications following direct anterior hip procedures: costs to both patients and surgeons. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(9):98-101.[14] Purcell RL, Parks NL, Cody JP, et al. Comparison of wound complications and deep infections with direct anterior and posterior approaches in obese hip arthroplasty patients. J Arthroplasty. 2017; 33(1):20-223.[15] Connolly KP, Kamath AF. Direct anterior total hip arthroplasty: Literature review of variations in surgical technique. World J Orthop. 2016;7(1):38.[16] Rossini M, Adami S, Bertoldo F, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis, prevention and management of osteoporosis. Reumatismo. 2016; 68(1):1.[17] Bergin PF, Doppelt JD, Kephart CJ, et al. Comparison of minimally invasive direct anterior versus posterior total hip arthroplasty based on inflammation and muscle damage markers. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(15):1392-1398.[18] Lewinnek GE, Lewis JL, Tarr R, et al. Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978;60(2): 217-220.[19] Malek IA, Royce G, Bhatti SU, et al. A comparison between the direct anterior and posterior approaches for total hip arthroplasty: the role of an 'Enhanced Recovery' pathway. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(6): 754-760.[20] Faldini C, Perna F, Mazzotti A, et al. Direct anterior approach versus posterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: effects on early post-operative rehabilitation period. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2017;31(4 suppl 1):75-81.[21] Matta JM, Shahrdar C, Ferguson T. Single-incision anterior approach for total hip arthroplasty on an orthopaedic table. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;441:115-124.[22] Kenanidis EI, Potoupnis ME, Papavasiliou KA, et al. Re: Prospective randomized study of two surgical approaches for total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(5):671-679.[23] 吕明, 张金庆, 王兴山, 等. 直接前入路髋关节置换术及其早期临床疗效[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2017, 49(2):206-213.[24] Jewett BA, Collis DK. High complication rate with anterior total hip arthroplasties on a fracture table. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(2): 503-507.[25] Leder S, Knahr K. Instability following total hip arthroplasty: etiology and treatment options. Semin Arthroplasty. 2012;23(4):200-205.[26] Rodriguez JA, Deshmukh AJ, Rathod PA, et al. Does the direct anterior approach in tha offer faster rehabilitation and comparable safety to the posterior approach? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(2): 455-463.[27] Berend KR, Jr LA, Seng BE, et al. Enhanced early outcomes with the anterior supine intermuscular approach in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91 Suppl 6(11):107.[28] 史占军, 徐祎骏, 王健, 等. 透析患者全髋关节置换术围手术期下肢深静脉血栓预防策略[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2015,9(6):756-761.[29] Bender B, Nogler M, Hozack WJ. Direct anterior approach for total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;22(9):595.[30] 邱淳烈. 小切口外侧入路微创全髋关节置换术的临床效果观察[J]. 中国医药指南, 2016, 14(29):101-102. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [4] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [5] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [6] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [7] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [8] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [9] | Yao Rubin, Wang Shiyong, Yang Kaishun. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis improves lumbar-pelvic balance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1387-1392. |
| [10] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [11] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [12] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [14] | Zhang Lei, Ma Li, Fu Shijie, Zhou Xin, Yu Lin, Guo Xiaoguang. Arthroscopic treatment of greater tuberosity avulsion fractures with anterior shoulder dislocation using the double-row suture anchor technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 895-900. |
| [15] | Liu Lihua, Sun Wei, Wang Yunting, Gao Fuqiang, Cheng Liming, Li Zirong, Wang Jiangning. Type L1 steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through femoral head and neck junction decompression by fenestration: a single-center prospective clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 906-911. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||