Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (19): 3027-3032.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0793
Previous Articles Next Articles
Three-dimensional finite element analysis on the novel absorbable screw and traditional screw for fixing Lange-Hansen type 1 medial malleolus fracture
Chen Fan-cheng, Yu Bao-qing, Shi Ji-fei, Ao Rong-guang, Zhang Xu, Li De-jian, Qian Zhi
- Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Shanghai 201399, China
-
Online:2018-07-08Published:2018-07-08 -
Contact:Yu Bao-qing, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Shanghai 201399, China Shi Ji-fei, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Shanghai 201399, China -
About author:Chen Fan-cheng, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Shanghai 201399, China -
Supported by:a grant from the Health and Family Planning Commission of Shanghai City, No. 201440062, ZK2015B17
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Fan-cheng, Yu Bao-qing, Shi Ji-fei, Ao Rong-guang, Zhang Xu, Li De-jian, Qian Zhi . Three-dimensional finite element analysis on the novel absorbable screw and traditional screw for fixing Lange-Hansen type 1 medial malleolus fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(19): 3027-3032.
share this article
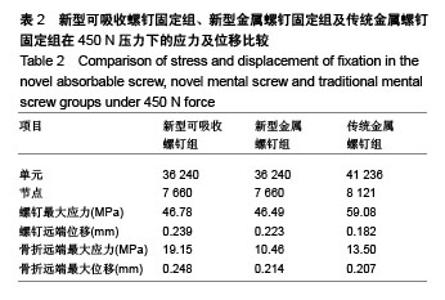
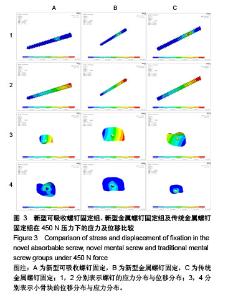
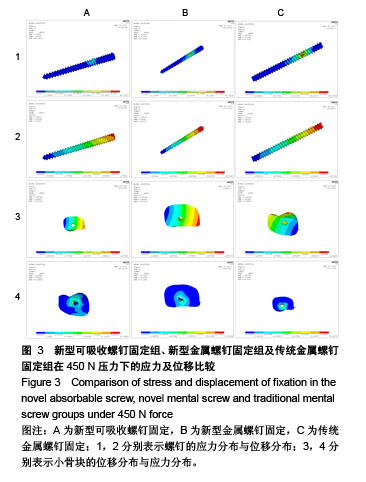
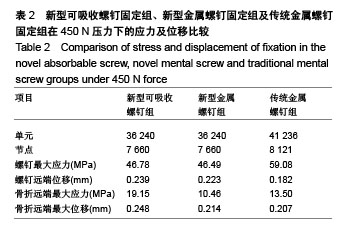
构建包含胫骨的简单内踝骨折模型:实验中包含新型可吸收螺钉固定以及传统螺钉固定组,观察并比较各实验组的应力集中部位以及位移变化。 2.1 新型可吸收螺钉固定组 新型可吸收螺钉固定组共有36 240个单元,7 660个节点。当在垂直于胫距关节与内踝关节方向上共同施加450 N的力时,可吸收螺钉承受的最大应力为46.78 MPa,远端最大位移是0.239 mm;骨折远端承受的最大应力是19.15 MPa,最大位移为0.248 mm。 2.2 新型金属螺钉固定组 传统螺钉固定组共有36 240个单元,7 660个节点。当由胫距关节与内踝关节共同均匀施加450 N的力时,新型金属螺钉所受的最大应力为 46.49 MPa,螺钉远端最大位移是0.223 mm,骨折远端承受的最大应力是10.46 MPa,最大位移是0.214 mm。 2.3 传统金属螺钉固定组 传统螺钉固定组共有41 236个单元,8 121个节点。当由胫距关节与内踝关节共同均匀施加450 N的力时,传统金属螺钉所受的最大应力为 59.08 MPa,螺钉远端最大位移是0.182 mm,骨折远端承受的最大应力是13.50 MPa,最大位移是0.207 mm,如 表2及图3所示。 3个实验组在受到相同的450 N来自胫距关节与内踝关节的压力时,螺钉表现出位移从近端到远端逐渐增大,应力与螺钉两端向中央逐渐增大;集中位置都显示是在螺钉与骨折面接触处,最大位移出现在螺钉的远端,螺钉均未出现明显的滑移。新型可吸收螺钉用于Lauge-Hansen 1型内踝骨折的固定中,应力总体分布均匀,发生断钉可能性小。"
| [1] Cox CL, Spindler KP, Leonard JP, et al. Do newer-generation bioabsorbable screws become incorporated into bone at two years after ACL reconstruction with patellar tendon graft? A cohort study. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2014; 96(3):244-250.[2] Zhang XY, Fang G, Zhou J. Additively manufactured scaffolds for bone tissue engineering and the prediction of their mechanical behavior: a review. Materials (Basel). 2017; 10(1). pii: E50. [3] 翁蔚宗,曹烈虎,周启荣,等.大转子截骨入路可吸收螺钉治疗股骨头骨折疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(6):481-486.[4] 孙和军,李棋,唐新,等.小切口可吸收螺钉内固定治疗前交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折疗效[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014,28(9): 1072-1076.[5] 张斌,王跃,唐孝明.可吸收螺钉及金属螺钉治疗下胫腓联合损伤的疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013,27(12):1442-1445.[6] Liu GT, Balldin BC, Zide JR, et al. A biomechanical analysis of interference screw versus bone tunnel fixation of flexor hallucis longus tendon transfers to the calcaneus. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;56(4):813-816.[7] Sakai A, Oshige T, Zenke Y, et al. Mechanical comparison of novel bioabsorbable plates with titanium plates and small-series clinical comparisons for metacarpal fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(17):1597-1604.[8] Wu CC, Kuo CL, Fan FY, et al. Strontium-impregnated bioabsorbable composite for osteoporotic fracture fixation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(10):3355-3363.[9] Richards DJ, Coyle RC, Tan Y, et al. Inspiration from heart development: Biomimetic development of functional human cardiac organoids. Biomaterials. 2017;142:112-123.[10] 汪金平,杨天府,钟凤林,等.股骨生物力学特性的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(10):931-934.[11] Hosseini HS, Dunki A, Fabech J, et al. Fast estimation of Colles' fracture load of the distal section of the radius by homogenized finite element analysis based on HR-pQCT. Bone. 2017; 97:65-75.[12] Labronici PJ, Pires RE, Franco MV, et al. Medial malleolar fractures: an anatomic survey determining the ideal screw length. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2016;6(5):308-310.[13] Winkler DA. Computational modelling of magnetic nanoparticle properties and in vivo responses. Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(5):483-496.[14] 王伟强,王丽,杨大智,等.血管支架有限元优化设计[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2008,25(2):372-377.[15] 王一民,张晟,王博炜,等.解剖型钢板与锁定钢板固定Sanders Ⅳ型跟骨骨折的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(6): 602-607.[16] 徐学军,郑玉峰.口腔生物力学问题有限元分析的研究进展[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版),2006,42(3):412-419.[17] Yin MC, Yuan XF, Ma JM, et al. Evaluating the reliability and reproducibility of the AO and Lauge-Hansen Classification Systems for ankle injuries. Orthopedics. 2015;38(7): e626-630.[18] Eismann EA, Stephan ZA, Mehlman CT, et al. Pediatric triplane ankle fractures: impact of radiographs and computed tomography on fracture classification and treatment planning. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2015; 97(12):995-1002.[19] Huang X, Zhi Z, Yu B, et al. Stress and stability of plate-screw fixation and screw fixation in the treatment of Schatzker type IV medial tibial plateau fracture: a comparative finite element study. J Orthop Surg Res.2015; 10:182.[20] 曾浪清,陈云丰,张长青,等.重建钢板与钛制弹性钉两种内固定方式治疗锁骨中段骨折的有限元分析[J].医用生物力学, 2013, 28(4):441-447.[21] Chen P, Lu H, Shen H, et al. Newly designed anterolateral and posterolateral locking anatomic plates for lateral tibial plateau fractures: a finite element study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):35.[22] Mascarenhas R, Saltzman BM, Sayegh ET, et al. Bioabsorbable versus metallic interference screws in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review of overlapping meta-analyses. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(3):561-568.[23] Sinikumpu JJ, Keranen J, Haltia AM, et al. A new mini-invasive technique in treating pediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures by bioabsorbable elastic stable intramedullary nailing: a preliminary technical report. Scand J Surg.2013;102(4):258-264.[24] 宿玉玺,谢艳,覃佳强,等.可吸收螺钉治疗儿童肱骨外髁骨折中期疗效分析[J].第三军医大学学报,2015,37(3):234-237.[25] Barber FA, Spenciner DB, Bhattacharyya S, et al. Biocomposite implants composed of poly(Lactide-co-Glycolide)/beta-tricalcium phosphate: systematic review of imaging, complication, and performance outcomes. Arthroscopy. 2017;33(3):683-689.[26] Camarda L, Morello S, Balistreri F, et al. Non-metallic implant for patellar fracture fixation: A systematic review. Injury.2016; 47(8):1613-1617.[27] Debieux P, Franciozi CE, Lenza M, et al. Bioabsorbable versus metallic interference screws for graft fixation in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;7:CD009772.[28] 谷洪刚.50例内踝骨折的治疗体会[J].中国医药指南, 2015, 13(28):104-105.[29] Rupprecht M, Spiro AS, Breyer S, et al. Growth modulation with a medial malleolar screw for ankle valgus deformity. 79 children with 125 affected ankles followed until correction or physeal closure. Acta Orthop.2015;86(5):611-615.[30] Bali N, Aktselis I, Ramasamy A, et al. An evolution in the management of fractures of the ankle: safety and efficacy of posteromedial approach for Haraguchi type 2 posterior malleolar fractures. Bone Joint J.2017;99-B(11):1496-1501.[31] Mohammed AA, Abbas KA, Mawlood AS.A comparative study in fixation methods of medial malleolus fractures between tension bands wiring and screw fixation. Springer Plus.2016; 5(1):530.[32] Berggren SS, Tiderius CJ. The Cedell method (cerclage wire and staple) leads to less reoperations than the AO method: a retrospective comparative study of 347 lateral ankle fractures. Acta Orthop.2015;86(3):384-387.[33] 黄俊伍,罗轶,孙华.内踝骨折的新分型及临床应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014,29(4):362-365.[34] Zhou Q, Lu H, Wang Z, et al. Posterolateral approach with buttress plates and cannulated screw fixation for lLarge posterior malleolus fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;56(6): 1173-1179.[35] Nosewicz TL, Beerekamp MS, De Muinck Keizer RJ, et al. Prospective computed tomographic analysis of osteochondral lesions of the ankle joint associated with ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int.2016;37(8):829-834.[36] Yao F, He Y, Qian H, et al. Comparison of biomechanical characteristics and pelvic ring stability using different fixation methods to treat pubic symphysis diastasis: a finite element study. Medicine (Baltimore).2015;94(49):e2207.[37] Ye T, Chen A, Yuan W, et al. Management of grade III open dislocated ankle fractures: combined internal fixation with bioabsorbable screws/rods and external fixation. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2011;101(4):307-315.[38] Hu XJ, Wang H. Biomechanical assessment and 3D finite element analysis of the treatment of tibial fractures using minimally invasive percutaneous plates. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(2):1692-1698.[39] Chevalier Y, Santos I, Muller PE, et al. Bone density and anisotropy affect periprosthetic cement and bone stresses after anatomical glenoid replacement: A micro finite element analysis. J Biomech. 2016;49(9):1724-1733.[40] Haller JM, O'Toole R, Graves M, et al. How much articular displacement can be detected using fluoroscopy for tibial plateau fractures? Injury. 2015;46(11):2243-2247. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||