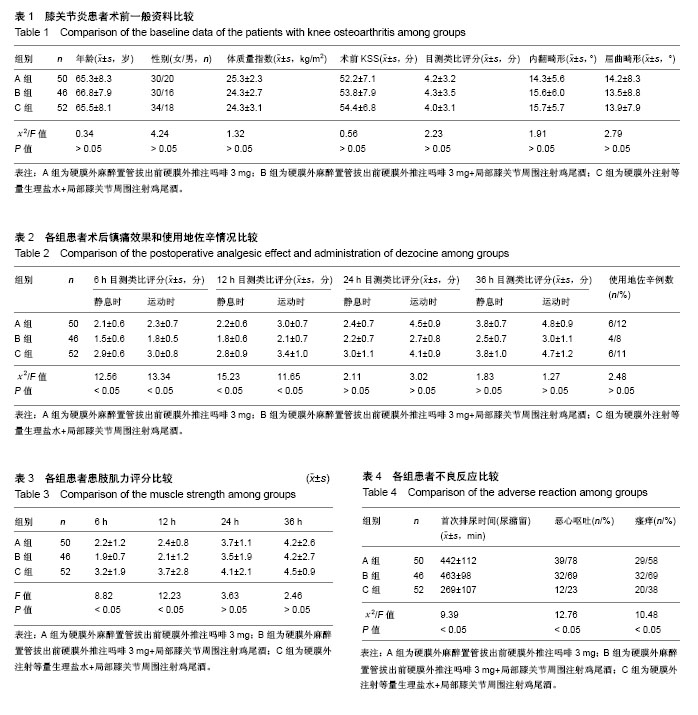
| [1] 杨体敏,斯海波,吴元刚,等.收肌管神经阻滞联合环氧合酶2选择性抑制剂在人工全膝关节置换术后的序贯应用及疗效[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(9):1065-1071.[2] Woolf CJ,Chong MS. Preemptive analgesia--treating postoperative pain by preventing the establishment of central sensitization. Anesth Analg. 1993;77(2): 362-379.[3] Wallace M, Yaksh TL. Characteristics of distribution of morphine and metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma with chronic intrathecal morphine infusion in humans. Anesth Analg. 2012; 115(4) : 797-804.[4] Hozack WJ, Matsen-Ko L. Rapid recovery after hip and knee arthroplasty: a process and a destination. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(4): 517-521.[5] Husted H, Lunn TH, Troelsen A, et al. Why still in hospital after fast- track hip and knee arthroplasty? Acta Orthop. 2011; 82(6): 679-684.[6] Stambough JB, Nunley RM, Curry MC, et al. Rapid recovery protocols for primary total hip arthroplasty can safely reduce length of stay without increasing readmissions. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(4): 521-526.[7] Maradit Kremers H, Larson DR, Crowson CS, et al. Prevalence of total hip and knee replacement in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(17):1386-1397.[8] Petrovic NM, Milovanovic DR, Ignjatovic Ristic D, et al. Factors associated with severe postoperative pain in patients with total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2014; 48(6): 615-622.[9] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会公益性行业科研专项《关节置换术安全与效果评价》项目组,中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组,中国医疗保健国际交流促进会骨科分会关节外科委员会.中国髋、膝关节置换术加速康复——围术期疼痛与睡眠管理专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(2):91-97.[10] 严美娟,楼小侃,吴佳,等.老年人髋关节置换术后硬膜外吗啡和腰骶丛神经阻滞镇痛效果比较[J].中华老年医学杂志,2016,35(6): 634-638.[11] Hsia HL, Takemoto S, van de Ven T, et al. Acute Pain Is Associated With Chronic Opioid Use After Total Knee Arthroplasty. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2018. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000831.[12] Romano C, Lloyd A, Nair S, et al. A Randomized Comparison of Pain Control and Functional Mobility between Proximal and Distal Adductor Canal Blocks for Total Knee Replacement. Anesth Essays Res. 2018;12(2):452-458. [13] Martín-Hernández C, Floría-Arnal LJ, Gómez-Blasco A, et al. Metaphyseal sleeves as the primary implant for the management of bone defects in total knee arthroplasty after post-traumatic knee arthritis. Knee. 2018;25(4):669-675. [14] Berstock JR, Beswick AD, López-López JA, et al. Mortality After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review of Incidence, Temporal Trends, and Risk Factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(12):1064-1070. [15] Guo H, Wang C, He Y. A meta-analysis evaluates the efficacy of intravenous acetaminophen for pain management in knee or hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2018. pii: S0949-2658(18)30130-1.[16] Zhang J, Shi K, Jia H. Ketamine and bupivacaine attenuate post-operative pain following total knee arthroplasty: A randomized clinical trial. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(6): 5537-5543.[17] Sundaram K, Klare CM, Moschetti WE. Proximal tibiofibular osteoarthritis presenting as pain after total knee arthroplasty treated successfully with fusion of the proximal tibial-fibular joint. Arthroplast Today. 2018;4(2):139-142. [18] Leung P, Dickerson DM, Denduluri SK, et al. Postoperative continuous adductor canal block for total knee arthroplasty improves pain and functional recovery: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J Clin Anesth. 2018;49:46-52. [19] Li C, Xu H, Shen B, et al. Effect of continuous and single shot adductor canal blocks for postoperative analgesia and early rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017;31(9):1049-1054.[20] Ikeuchi M, Kamimoto Y, Izumi M, et al. Effects of dexamethasone on local infiltration analgesia in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014; 22(7): 1638-1643.[21] Kwon SK, Yang IH, Bai SJ, et al. Periarticular injection with corticosteroid has an additional pain management effect in total knee arthroplasty. Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(2):493-498.[22] Ng YC, Lo NN, Yang KY, et al. Effects of periarticular steroid injection on knee function and the inflammatory response following Unicondylar Knee Arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(1): 60-65.[23] Sean VW, Chin PL, Chia SL, et al. Single-dose periarticular steroid infiltration for pain management in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, double- blind, randomised controlled trial. Singapore Med J. 2011;52(1): 19-23.[24] Pang HN, Lo NN, Yang KY, et al. Peri-articular steroid injection improves the outcome after unicondylar knee replacement: a prospective, randomised controlled trial with a two-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90(6): 738-744.[25] Bourne MH. Analgesics for orthopedic postoperative pain. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2004;33(3):128-135.[26] Iorio R, Healy WL, Patch DA, et al. The role of bladder catheterization in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(380):80-84. |