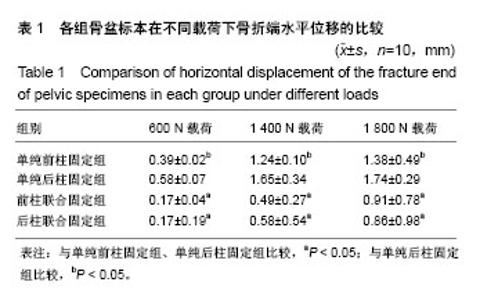
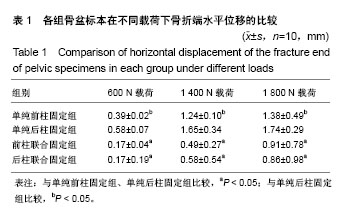
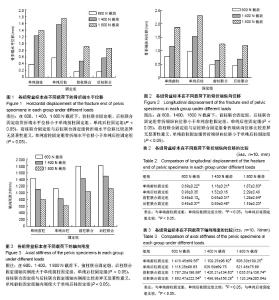
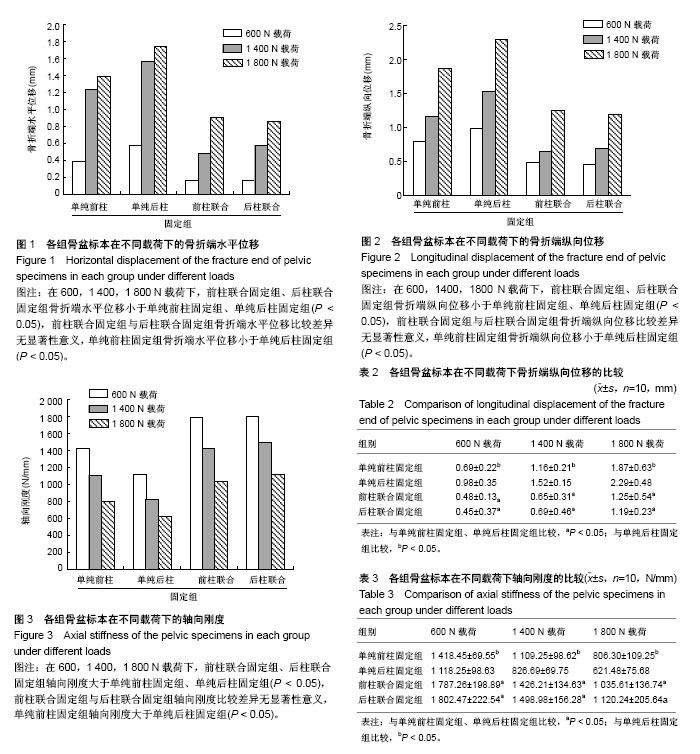
| [1] Karim MA,Abdelazeem AH,Youness M,et al.Fixation of quadrilateral plate fractures of the acetabulum using the buttress screw: A novel technique.Injury.2017;48(8):1813-1818. [2] Dc S,Ramanath SK,Grover A,et al.Uncemented total hip replacement after two years of neglected hip dislocation with fracture of posterior column and wall of the acetabulum. Trauma Mon. 2016;21(5):e25301. [3] 李军,荆珏华.无明显移位的髋臼骨折可以保守治疗吗?[J].临床骨科杂志,2017,20(1):37. [4] 肖长青,杨勇,周恒.切开复位重建钢板内固定治疗复杂髋臼骨折的疗效分析[J].现代诊断与治疗,2016,27(8):1487-1488.[5] 刘波.重建钢板内固定治疗明显移位髋臼骨折的系统性评价[J].临床医学,2016,36(7):53-55.[6] Tan Z,Fang Y,Zhang H,et al.Efficacy of sacroiliac joint anterior approach with double reconstruction plate and computer assisted navigation percutaneous sacroiliac screw for treating tile C1 pelvic fractures.Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.2017;48(5): 668-672. [7] Iwasawa M,Mishima Y,Ohtsubo M.Prevention of mandible reconstruction plate exposure by costal cartilage wrapping. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open.2017;5(8):e1438. [8] Xie P,Ouyang H,Deng Y,et al.Comparison of conventional reconstruction plate versus direct metal laser sintering plate: an in vitro mechanical characteristics study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2017; 12(1):128. [9] 白杨平,林庆培,罗伟初,等.重建钢板内固定治疗锁骨中段骨折的效果分析[J].中国当代医药,2017,24(10):78-80. [10] 韩亚力.重建钢板内固定与克氏针固定治疗锁骨骨折的效果对比[J].世界临床医学,2017,11(15):25. [11] 张小礼,李光涛.微创经皮锁定加压钢板内固定治疗四肢骨折的临床应用价值[J].中国伤残医学,2017,25(14):27-28.[12] 边鹏辉,王占东.掌背侧联合入路锁定钢板固定治疗桡骨远端C3型骨折的临床疗效[J].临床医学研究与实践,2017,2(9):8-10. [13] Ieropoli G,Villafañe JH,Zompi SC,et al.Successful treatment of infected wound dehiscence after minimally invasive locking-plate osteosynthesis of tibial pilon and calcaneal fractures by plate preservation, surgical debridement and antibiotics.Foot (Edinb). 2017;33:44-47.[14] Lee AK,Wagner BR,McPhillips K,et al.Locking compression pilon plate for fixation of comminuted posterior wall acetabular fractures: A Novel Technique.J Orthop Trauma.2017;31(1):e32-e36.[15] Georgiades CH, Matějka J, Pavelka T,et al.Treatment of distal humeral fractures by open reduction and internal LCP-DHP fixation.Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech.2010;77(6):479-483. [16] 罗亮.复杂髋臼骨折的手术治疗[J].心理医生, 2015,21(14):71-72.[17] 谢景瑞,谢文标,林锟.锁定加压钢板内固定术和重建钢板内固定术治疗髋臼骨折疗效对比[J].黑龙江医学, 2014,38(9):1063-1064.[18] 赵勇.锁定加压钢板内固定术治疗复杂性髋臼骨折疗效观察[J].山东医药,2012,52(22):79-80.[19] Liu H, Li L,Wu X,et al. Biomechanical research of different internal fixations using locking reconstruction plate for acetabular transverse fracture.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015;29(9):1084-1087. [20] Zhang Y,Tang Y,Wang P,et al.Biomechanical comparison of different stabilization constructs for unstable posterior wall fractures of acetabulum. A cadaveric study.PLoS One.2013;8(12): e82993. [21] Tadros AM,O'Brien P,Guy P.Fixation of marginal posterior acetabular wall fractures using locking reconstruction plates and monocortical screws.J Trauma. 2010;68(2):478-480. [22] Amato NS,Richards A,Knight TA,et al.Ex vivo biomechanical comparison of the 2.4 mm unilock reconstruction plate using 2.4 mm locking versus standard screws for fixation of acetabular osteotomy in dogs.Vet Surg.2008;37(8):741-748. [23] 代元元,章莹,夏远军,等.四种不同内固定方式治疗髋臼前柱低位骨折的有限元分析比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2016,18(8):702-707.[24] 汤洋,胡小鹏,陆雄伟,等.髋臼后壁骨折固定的生物力学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(8): 925-930.[25] 郑龙龙.髋臼后壁骨折解剖型钢板内固定的生物力学研究[D].安徽医科大学, 2013.[26] 黄晓波,唐述森,武德旺,等.不同钢板内固定方式治疗髋臼横形骨折的生物力学分析[J].创伤外科杂志, 2017,19(3):173-176.[27] 马爱国,裴宝瑞,刘斌,等.髋臼横行后壁骨折不同内固定方式的生物力学研究[J].成都医学院学报,2016,11(6):738-741,746.[28] 高烁,王雷,吴啸波,等.髋臼横行骨折四种内固定方式的生物力学研究[J].中国临床研究,2016,29(4):444-447.[29] Manganaro MS,Morag Y,Weadock WJ,et al.Creating three-dimensional printed Models of acetabular fractures for use as educational tools.Radiographics.2017;37(3):871-880. [30] Jung GH,Lee Y,Kim JW,et al.Computational analysis of the safe zone for the antegrade lag screw in posterior column fixation with the anterior approach in acetabular fracture: A cadaveric study. Injury.2017;48(3):608-614. [31] 张永强,章莹,夏远军,等.髋臼部T形骨折四种不同内固定方式的生物力学有限元分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2017,35(3):312-317.[32] 张潇,杨晓东,夏广,等.经腹直肌外侧切口入路重建钢板辅助后柱顺行拉力螺钉治疗复杂髋臼骨折[J].创伤外科杂志, 2015,17(2): 123-126.[33] Su K,Liu S,Wu T,et al.Posterior column acetabular fracture fixation using a W-shaped angular plate: A biomechanical analysis.PLoS One.2017;12(11):e0187886. [34] 孙玉强,唐明杰,金东旭,等.陈旧性髋臼骨折的手术重建[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(5):496-501.[35] 张明庆.髋臼骨折解剖型锁定钢板内固定的生物力学研究及有限元分析[D].南华大学,2010.[36] 许猛.髋臼骨折解剖锁定钢板的研发及临床应用[D].军医进修学院, 2015. |