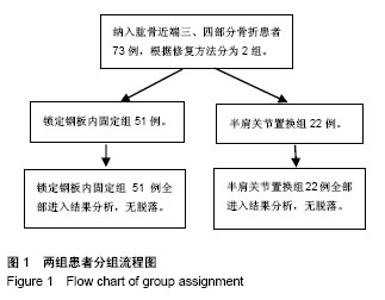
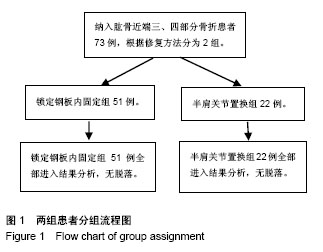
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (19): 2974-2980.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0228
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical outcomes of three- or four-part complex proximal humerus fractures: hemiarthroplasty versus locking plate fixation
Feng Shuo, Zha Guo-chun, Guo Kai-jin, Yang Zhi, Chang Bu-qing, Yang Shuo, Xu Chong-jun, Chen Xiang-yang
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Online:2018-07-08Published:2018-07-08 -
Contact:Chen Xiang-yang, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Feng Shuo, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Youth Medical Talent Project of Jiangsu Province, No. QNRC2016800; the Science and Technology Plan Project of Xuzhou City, No. KC16SL111; the General Program of Health Planning Commission of Jiangsu Province, No. H201528; the Key Social Development Project of Jiangsu Province, No. BE2015627; the Science and Technology Program of Xuzhou City, No. KC14SH091
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Feng Shuo, Zha Guo-chun, Guo Kai-jin, Yang Zhi, Chang Bu-qing, Yang Shuo, Xu Chong-jun, Chen Xiang-yang. Clinical outcomes of three- or four-part complex proximal humerus fractures: hemiarthroplasty versus locking plate fixation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(19): 2974-2980.
share this article
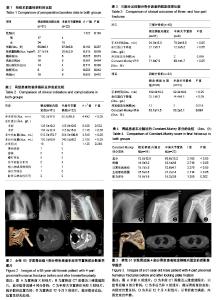
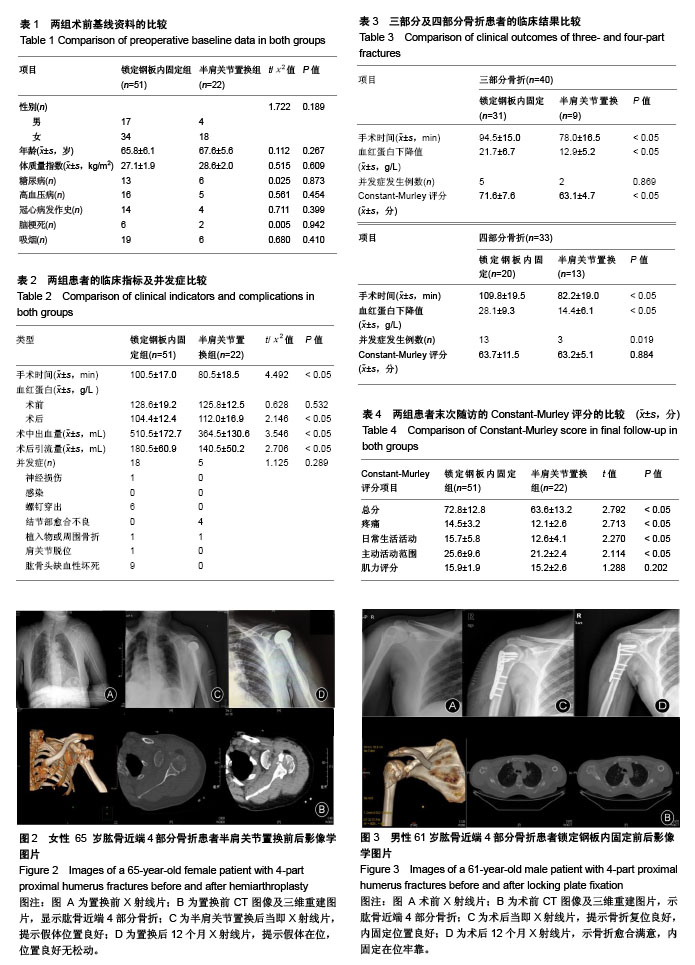
2.2 两组术前基线资料的比较 锁定钢板内固定组与半肩关节的患者的性别、年龄、体质量指数及术前合并症进行比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),2组资料具有可比性,见表1。 2.3 两组患者的临床手术指标及并发症比较 锁定钢板内固定组的手术时间明显长于半肩关节置换组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。2组患者术前血红蛋白水平相比,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但术中出血量、术后引流量、术后血红蛋白量相比,2组差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 在并发症方面,锁定钢板内固定组中最常见的并发症组为肱骨头缺血性坏死9例,其次是螺钉穿出6例;而在半肩关节置换组中,4例出现大小结节愈合不良。2组均无患者发生感染。锁定钢板内固定组中1例出现神经损伤,1例出现钢板断裂,1例出现术后肩关节再次脱位;这些在肩关节置换组中都未出现,仅有1例术后出现假体周围骨折。锁定钢板内固定组的总并发症发生率为35%,半肩关节置换组并发症发生率为23%,锁定钢板内固定组的总并发症发生率虽然高于半肩关节置换组,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表2。 2.4 按肱骨近端三、四部分骨折进行分组的临床结果比较 在肱骨近端三及四部分骨折中锁定钢板内固定组的手术时间明显长于半肩关节置换组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。肱骨近端三及四部分骨折采用锁定钢板内固定血红蛋白下降量较半肩关节置换更低,二者相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。肱骨近端三部分骨折采用锁定钢板内固定与半肩关节置换在并发症方面的比较,并发症发生例数分别为5,2例,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);但肱骨近端四部分骨折采用锁定钢板内固定与半肩关节置换并发症发生例数分别为13,3例,采用锁定钢板内固定的并发症发生率明显高于半肩关节置换,且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。对于三部分骨折锁定钢板内固定组的患者末次随访的Constant-Murley评分明显优于半肩关节置换组,且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);而四部分骨折2组患者的末次随访Constant-Murley评分差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表3。 2.5 肩关节功能Constant-Murley评分的比较 末次随访锁定钢板内固定组患者的Constant-Murley总评分明显优于半肩关节置换组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。在Constant-Murley评分项目中,疼痛、日常生活活动、主动活动范围3个部分中锁定钢板内固定组患者的评分均高于半肩关节置换组,且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);仅肌力评分2组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表4。 2.6 典型病例 典型病例1:女性患者,65 岁,肱骨近端4部分骨折,半肩关节置换前X射线、CT图像及随访12个月时的术后X射线见图2。 典型病例2:男性患者,61 岁,肱骨近端4部分骨折,行锁定钢板内固定术前X射线、CT图像及随访12个月的术后X射线片见图3。 "
| [1] Courtbrown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: A review. Injury. 2006;37(8): 691.[2] Baron JA, Barrett JA, Karagas MR. The epidemiology of peripheral fractures. Bone.1996;18(3): 209S-213S.[3] Khatib O, Onyekwelu I, Zuckerman JD. The incidence of proximal humeral fractures in New York State from 1990 through 2010 with an emphasis on operative management in patients aged 65 years or older. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014; 23(9): 1356-1362.[4] Palvanen M, Kannus P, Niemi S, et al. Update in the epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;442: 87-92.[5] Guy P, Slobogean GP, Mccormack RG. Treatment preferences for displaced three- and four-part proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(4): 250.[6] Rabi S, Evaniew N, Sprague SA, et al. Operative vs non-operative management of displaced proximal humeral fractures in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. World J Orthop. 2015;6(10): 838.[7] Slobogean GP, Johal H, Lefaivre KA, et al. A scoping review of the proximal humerus fracture literature. Bmc Musculoskelet Disord. 2015; 16(1): 112.[8] Sebastiáforcada E, Cebriángómez R, Lizaurutrilla A, et al. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for acute proximal humeral fractures. A blinded, randomized, controlled, prospective study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014; 23(10): 1419-1426.[9] Shukla DR, Mcanany S, Kim J, et al. Hemiarthroplasty versus reverse shoulder arthroplasty for treatment of proximal humeral fractures: a meta-analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;25(2): 330-340.[10] Cuff DJ, Pupello DR. Comparison of hemiarthroplasty and reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;22(10): 2050.[11] Wild JR, Demers A, French R, et al. Functional outcomes for surgically treated 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures. Orthopedics. 2011;34(10): e629.[12] Bonnevialle N, Tournier C, Clavert P, et al. Hemiarthroplasty versus reverse shoulder arthroplasty in 4-part displaced fractures of the proximal humerus: Multicenter retrospective study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2016;102(5): 569-573.[13] Andrés-Cano P, Galán A, Arenas J, et al. Results of uncemented hemiarthroplasty as primary treatment of severe proximal humerus fractures in the elderly. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(2): 273-280.[14] Park YK, Kim JK, Kwon J, et al. Intermediate-term outcome of hemiarthroplasty for the comminuted proximal humerus fracture. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016.[15] White JJE, Soothill JR, Morgan M, et al. Outcomes for a large metaphyseal volume hemiarthroplasty in complex fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;26(3): 478-483.[16] Kralinger F, Schwaiger R, Wambacher M, et al. Outcome after primary hemiarthroplasty for fracture of the head of the humerus. A retrospective multicentre study of 167 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(2): 217.[17] Gupta AK, Harris JD, Erickson BJ, et al. Surgical management of complex proximal humerus fractures-a systematic review of 92 studies including 4500 patients. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(1): 54.[18] Fialka C, Stampfl P, Arbes S, et al. Primary hemiarthroplasty in four-part fractures of the proximal humerus: Randomized trial of two different implant systems. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(2): 210-215.[19] Hashiguchi H, Iwashita S, Ohkubo A, et al. The outcome of hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures is dependent on the status of the rotator cuff. Int Orthop. 2015;39(6): 1115-1119.[20] Moineau G, Jr MCW, Trojani C, et al. Prognostic factors and limitations of anatomic shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of posttraumatic cephalic collapse or necrosis (type-1 proximal humeral fracture sequelae). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(23): 2186.[21] Saporito M, Merolla G, Campi F, et al. Malunion of Humeral Tuberosity Fractures: Springer Milan, 2015.[22] Misra A, Kapur R, Maffulli N. Complex proximal humeral fractures in adults--a systematic review of management. Injury. 2001;32(5): 363-372.[23] Gavaskar AS, Karthik BB, Tummala NC, et al. Second generation locked plating for complex proximal humerus fractures in very elderly patients. Injury. 2016;47(11): 2534-2538.[24] Fattoretto D, Borgo A, Iacobellis C. The treatment of complex proximal humeral fractures: analysis of the results of 55 cases treated with PHILOS plate. Musculoskelet Surg. 2016;100(2): 1-6.[25] Rotini R, Cavaciocchi M, Fabbri D, et al. Proximal humeral fracture fixation: multicenter study with carbon fiber peek plate. Musculoskelet Surg. 2015;99 Suppl 1(1): 1-8.[26] Brunner A, Thormann S, Babst R. Minimally invasive percutaneous plating of proximal humeral shaft fractures with the Proximal Humerus Internal Locking System (PHILOS). J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(8): 1056-1063.[27] Dai J, Chai Y, Wang C, et al. Meta-analysis comparing locking plate fixation with hemiarthroplasty for complex proximal humeral fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(3): 305-313.[28] Duralde XA, Leddy LR. The results of ORIF of displaced unstable proximal humeral fractures using a locking plate. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(4): 480-488.[29] Schliemann B, Theisen C, Kösters C, et al. Complex fractures of the proximal humerus in the elderly—outcome and complications after locking plate fixation. Musculoskelet Surg. 2012;96 Suppl 1(1): S3.[30] Brorson S, Frich LH, Winther A, et al. Locking plate osteosynthesis in displaced 4-part fractures of the proximal humerus. Acta Orthopaedica. 2011;43(7): 475-481.[31] Ortmaier R, Filzmaier V, Hitzl W, et al. Comparison between minimally invasive, percutaneous osteosynthesis and locking plate osteosynthesis in 3-and 4-part proximal humerus fractures. Bmc Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16(1): 297.[32] Aguado HJ, Mingo J, Torres M, et al. Minimally invasive polyaxial locking plate osteosynthesis for 3-4 part proximal humeral fractures: our institutional experience. Injury. 2016;47: S22-S28.[33] Geiger EV, Maier M, Kelm A, et al. Functional outcome and complications following PHILOS plate fixation in proximal humeral fractures. Acta Orthopaedica Et Traumatologica Turcica. 2010;44(1): 1.[34] AS P, S S, U O, et al. Locking plate fixation of three- and four-part proximal humeral fractures. Acta Orthopaedica Et Traumatologica Turcica. 2010;44(2): 97.[35] Thanasas C, Kontakis G, Angoules A, et al. Treatment of proximal humerus fractures with locking plates: a systematic review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(6): 837.[36] Brunner F, Sommer C, Bahrs C, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures using a proximal humeral locked plate: a prospective multicenter analysis. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(3): 163.[37] Schliemann B, Siemoneit J, Ch T, et al. Complex fractures of the proximal humerus in the elderly--outcome and complications after locking plate fixation. Musculoskelet Surg. 2012;96 Suppl 1(1): S3.[38] Hente R, Kampshoff J, Kinner B, et al. Treatment of dislocated 3- and 4-part fractures of the proximal humerus with an angle-stabilizing fixation plate. Der Unfallchirurg. 2004;107(9): 769-782.[39] Peter H, Christian B, Björn E, et al. Does fixed-angle plate osteosynthesis solve the problems of a fractured proximal humerus? Acta Orthopaedica. 2009;80(1): 92-96.[40] Konrad G, Hirschmüller A, Audige L, et al. Comparison of two different locking plates for two-, three- and four-part proximal humeral fractures--results of an international multicentre study. Int Orthop. 2012;36(5): 1051.[41] Aksu N, Gö?ü? A, Kara AN, et al. Complications encountered in proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate fixation. Acta Orthopaedica Et Traumatologica Turcica. 2010; 44(2): 89-96. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [8] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [9] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [10] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [11] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [12] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [13] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [14] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [15] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||