Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (4): 625-630.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0101
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of anti-osteoporotic medications in osteoporotic fractures
Ni Meng-shan1, Chen Xian-zhe1, Chen Yu-xiong1, Guo Wen-jie1, Tian Jing2
- 1Second College of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510282, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510282, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2017-08-25Online:2018-02-08Published:2018-02-08 -
Contact:Tian Jing, Professor, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Zhujiang Hospital,Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510282, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Ni Meng-shan, Second College of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510282, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ni Meng-shan1, Chen Xian-zhe1, Chen Yu-xiong1, Guo Wen-jie1, Tian Jing2. Application of anti-osteoporotic medications in osteoporotic fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 625-630.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
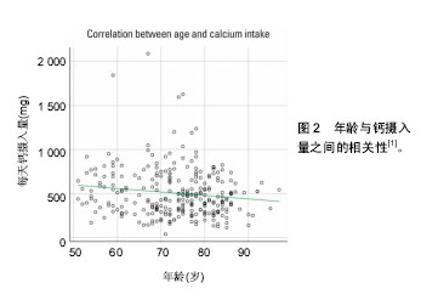
乳酸钙、门冬氨酸钙、葡萄糖酸钙等,吸收较好,对胃部刺激性较小,但需服用较大剂量;后者主要有氯化钙、碳酸钙,其含钙高、作用快、吸收好,但胃刺激性较大,多数患者无法长期服用。现有一种活性钙,吸收率高,将逐渐成为临床应用主流,但其呈强碱性,须根据患者的体质、适应证等予以选择。Yoon等[1]报道,约80%骨质疏松性骨折患者钙和维生素D的饮食摄入量低于临床推荐量(图2)。故临床强调通过食物适当补钙。 2.1.2 维生素D 维生素D可以促进钙的吸收,对骨骼健康、保持肌力、改善身体稳定性、降低骨折风险有益。部分患者摄入钙足量,但仍然缺钙,是因大部分钙剂摄入后经胃肠道流失,未被有效吸收利用所致,降低钙剂的使用效率。维生素D能增加肠道内钙磷吸收,调节甲状旁腺激素分泌及骨细胞分化,促进骨形成。有报道表明,维生素D还可以通过影响神经肌肉的活动和认知,减少患者遭受外力以及摔倒的可能,从而预防骨折的发生[2]。临床常用活性维生素D骨化三醇配合钙剂使用,效果更为明显。同时,户外运动时阳光照射也可增加人体自身合成维生素D。 2.2 骨吸收抑制剂 2.2.1 双膦酸盐 双膦酸盐抑制破骨细胞代谢的作用机制使其在骨折后的临床应用一直备受争议[3]。有Meta分析表明在骨折外科治疗3个月内应用双膦酸盐疗法,无论是影像学上还是临床上,都不会延长骨折的愈合时间,而且骨密度和骨转化指标的变化提示双膦酸盐对骨折愈合有积极意义[4]。 2.2.2 狄诺塞麦 由成骨细胞、骨髓基质干细胞、活化"
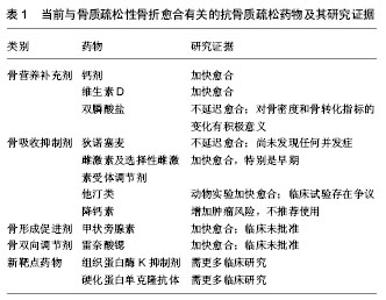
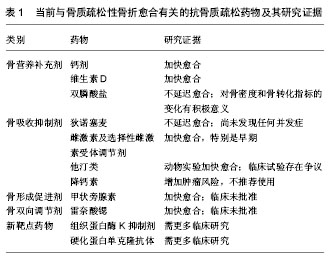
的T 细胞所组成的核因子κB活化受体配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand,RANKL),属于肿瘤坏死因子α家族,与位于破骨细胞表面的核因子κB活化受体(receptor activator of nuclear factor kB,RANK)结合后可活化核因子κB(nuclear factor-kappa B,NF-κB),后者进入细胞核影响相关基因的表达,对破骨细胞的分化、增生、多核化、活化和存活起关键作用。狄诺塞麦是一个完全的作用于RANKL 的人类单克隆抗体,与RANKL有高亲和力,从而抑制破骨细胞活性,提升骨密度,加大骨皮质和骨小梁的强度。一项667名绝经后妇女参与的FREEDOM研究表明,在骨折期间每6个月皮下注射狄诺塞麦60 mg 1次,持续3年,不仅不会引起骨折愈合延迟,甚至还没有任何并发症[5]。故而发生骨质疏松性骨折时可应用狄诺塞麦进行治疗,无需担心其抑制骨折愈合。但是,狄诺塞麦可导致低钙血症,使用前应注意纠正低血钙,尤其是肾功能不全以及接受血液透析的患者。 2.2.3 雌激素及选择性雌激素受体调节剂(selective estrogenreceptor modulators,SERMs) 雌激素通过与相应受体结合,可促进肠道钙吸收和抑制破骨细胞活性,降低骨转化和吸收。停经后妇女体内雌激素水平下降,骨骼失去雌激素保护,易患骨质疏松症。大规模的临床随机对照试验已证明,雌激素替代疗法可降低脊柱和非脊柱骨折发生的风险[6]。因此须严格掌握实施雌激素治疗的适应证和禁忌证。 SERMs是人工合成的非类固醇雌激素类似物,在不同组织中对雌激素受体有截然相反的作用,针对骨组织、心血管中的雌激素受体起激活作用,而在其他器官或组织(如子宫、乳腺)则表现为抑制作用。Pickar等[7]报道了其安全性,甚至可用于预防和治疗乳腺癌。随着SERMs药物的更替,使用SERMs已无肿瘤发生之忧,但静脉血栓栓塞和中风等不良反应仍然值得关注[8]。有诸多报道强调了其在治疗骨质疏松症中的重要地位[9-11]。一项动物实验将雷洛昔芬用于股骨骨折模型小鼠,10 d后接触放射线摄影和组织形态分析表明其加快骨折早期愈合,20 d骨痂矿化加快,骨小梁明显增厚,提示雷洛昔芬在小鼠骨折的整个过程都有促进作用[12]。然而,单独使用SERMs会引起潮热等不良反应。因而,由第3代SERMs巴多昔芬和结合雌激素共同组成的组织选择性雌激素复合物问世。Umland等[13]证明规范使用20 mg巴多昔芬和0.45 mg结合雌激素能抑制骨吸收过程,且降低乳腺癌和子宫内膜癌的发生率。但是Cheung等[14]研究表明,在卵巢切除诱导的骨质疏松性骨折动物模型中雌激素受体的表达推迟。因而,使用雌激素或者SERMs能否达到疗效或者是否能够诱导提高雌激素受体的表达都有待进一步的研究。 2.2.4 他汀类药物 临床上常用于高脂血症的治疗,通过竞争性抑制内源性胆固醇合成限速酶(HMG-CoA)还原酶,使细胞内胆固醇合成减少,从而反馈性刺激细胞膜表面(主要为肝细胞)低密度脂蛋白受体数量和活性增加、使血清胆固醇清除增加、水平降低。近年来,有报道指出该类药物能影响骨代谢,可能成为骨质疏松性骨折的治疗药物之一[15]。其作用机制类似双膦酸盐,能够抑制法尼基焦磷酸合成酶活性,阻碍香叶基焦磷酸向法尼基焦磷酸的合成,破骨细胞活性下降并凋亡,并且提高骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子的表达,促进骨形成[16]。目前他汀类药物口服生物利用度差、肝特异性高,而在骨微环境中分布少,正常用量可能无法达到调节骨代谢的理想浓度,因而有报道称将他汀类和维生素E联合使用,能有效避免高浓度使用带来的不良反应[17]。另外,研发骨特异性他汀类药物或骨靶向药物投送技术也是研究热点。Tan等[18]在CT引导下,将辛伐他汀/泊咯沙姆407水凝胶经皮注射入去除卵巢的小型猪脊柱骨内。3个月后,骨密度提高,骨小梁厚度和骨体积分数增长到原来的150%,同时,骨强度增强一倍之多骨形态发生蛋白2、血管内皮生长因子和骨钙素的表达提高,提示骨靶向投送他汀促进成骨的作用强大。在临床试验方面,该类药物的对骨质疏松性骨折的愈合是否有作用仍然存在很大争议。大样本和长期随访的临床前瞻性双盲随机对照试验是未来的研究重点。 2.2.5 降钙素 由甲状腺素滤泡旁细胞合成和分泌的肽类激素,可降低破骨细胞活性,增强成骨细胞活性。当其作用于骨折处时,与破骨细胞受体结合,使其失去活性和增生能力,从而抑制了骨吸收。另外,降钙素在缓解疼痛上也有着显著的疗效,可能机制为作用于神经中枢特异性受体,升高脑内啡肽水平,阻止钙离子进入神经细胞,抑制疼痛介质前列腺素的合成,从而达到良好的镇痛效果。鲑鱼降钙素作用强于人降钙素40-50倍,故被广泛应用于临床。但是由于降钙素增加某些肿瘤如肝癌风险[19],欧洲药品管理局宣布降钙素鼻喷剂撤出市场,不推荐其用作抗骨质疏松治疗。 2.3 骨形成促进剂——甲状旁腺素 甲状旁腺激素是体内钙平衡的主要调节者,也是当前促进骨形成的代表性药物。原发性或继发性甲状旁腺功能亢进时,持续性甲状旁腺激素刺激引起破骨细胞广泛活化,并使成骨细胞的功能受到抑制,导致骨量丢失。然而,间断性应用甲状旁腺激素可提高成骨细胞的质和量,使骨量增加,改善松质骨和皮质骨结构,增加皮质骨厚度。目前该药物主要包括PTH1-34和PTH1-84两种形式,其中欧洲已经批准这两种药用于治疗骨质疏松症,但美国只批准了PTH1-34(特立帕肽)治疗骨质疏松症。特立帕肽则是甲状旁腺素N端1-34氨基酸残基片段,保留了甲状旁腺激素生物学活性,可与甲状旁腺激素1受体结合,发挥甲状旁腺激素对骨骼的生理作用,同时不存在C端肽对骨代谢的不利影响,已被FDA批准用于绝经后妇女、性腺机能低下男性、激素性骨质疏松症的治疗。若干个病例报告和随机对照试验等表明,特立帕肽可加快骨折愈合,尤其是于桡骨远端骨折、骨盆骨折、脊椎骨折的治疗效果显著。Giannotti等[20]报道1例术后7个月骨不连的股骨骨折绝经后女性患者,特立帕肽治疗2个月后X射线显示骨桥的出现,3个月后骨折完全愈合。在一项Ⅲ期临床研究中,研究者设计随机双盲临床试验,实验组患者每天皮下注射特立帕肽20 μg,持续6个月。由于该研究的样本量不够,特立帕肽组与安慰组的潜在差异未能明显区分,但是试验结果仍然具有一定积极意义[21]。此外,特立帕肽具有逆转长期应用双膦酸盐相关并发症(如双膦酸盐相关的骨坏死、骨重塑抑制)的潜能,显著改善骨重塑的强度,促进骨矿化。一项回顾性队列研究针对双膦酸盐导致的不典型股骨骨折患者进行研究,结果显示特立帕肽组的平均愈合时间是(5.4±1.5)个月,而无特立帕肽组明显加长为(8.6±4.7)个月,并且骨不连或骨延迟愈合的发生率明显降低[22]。目前,特立帕肽仍未被批准用于骨质疏松性骨折的临床治疗,更多设计合理的临床随机双盲试验可能会让特立帕肽成为治疗的主流。 2.4 双向调节剂——雷奈酸锶(strontium ranelate) 锶是人体必需的微量元素之一,可以保持骨更新的速度,在保持骨形成的同时减少骨吸收,改善骨骼的机械强度,但不改变骨结构的晶体,不影响骨骼的矿化,所以锶盐是一种对骨代谢具有双向调节作用的药物。目前临床上的代表药物为雷奈酸锶,主要用于其他治疗无效且无不受控制的高血压、缺血性心脏病、外周血管疾病、脑血管疾病等禁忌证的严重骨质疏松患者[23]。Komrakova等[24]对切除卵巢的SD大鼠进行研究,实验组每天喂食625 mg/kg雷奈酸锶,在第2和第3周即可检测到总骨密度、骨体积分数、愈伤组织的范围和密度、血清碱性磷酸酶、抗酒石酸盐酸性磷酸酶mRNA表达量的提高,核因子κB的骨保护素/受体激活剂配体的mRNA比率的减少以及骨桥的加快形成,提示骨折后仍可继续使用雷奈酸锶或直接对骨质疏松性骨折进行防治。临床有过个例报道,4名骨质疏松性骨折后20个月仍不愈合的患者,每天使用雷奈酸锶2 g,治疗6周到6个月,骨折处出现愈合现象[25]。Negri等[26]也曾报道1名慢性双膦酸盐使用相关的非典型性股骨骨折后不愈合的患者在使用雷奈酸锶后,成骨的标志物快速升高,且骨折在数月后愈合。但是,目前大规模的临床试验仍未开展。 2.5 新靶点药物 2.5.1 新型骨吸收抑制剂——组织蛋白酶K抑制剂(cathepsin-k inhibitors) 破骨细胞能产生若干种用于降解骨基质的蛋白酶,其中一种为组织蛋白酶K,是溶酶体产生的半胱氨酸蛋白酶。它是一种强效地胶原蛋白酶,特别是在酸性环境下,能够溶解骨羟基磷灰石。相反,当组织蛋白酶K功能缺陷时,出现骨量增加,导致致密性成骨不全症的发生。另外,通过动物实验发现,使用组织蛋白酶K抑制剂可提高骨密度值。因骨骼系统以外的皮肤、肺部同样存在组织蛋白酶K,可以引起交叉抑制,导致骨骼系统以外的不良反应,故应使用选择性高的抑制剂。目前,奥当卡替(Odacanatib)是一种具有选择性的组织蛋白酶K抑制剂,是抑制骨吸收强效药物,能明显提高骨密度值[27]。经典的骨吸收抑制剂(如双膦酸盐及狄诺塞麦等)使破骨细胞凋亡,同时阻断破骨细胞与成骨细胞之间的信号转导,骨吸收被明显抑制后骨形成也同时被抑制。相反,新型骨吸收抑制剂奥当卡替使破骨细胞失活,但其与成骨细胞的双向信号转导仍存在,从而维持成骨细胞的骨形成作用。一项开展于399名绝经后妇女的Ⅱ期临床研究表明,每周口服50 mg奥当卡替24个月,实验组腰椎、全髋骨密度分别提升5.5%,3.2%。通过检测发现骨吸收标志物急剧减少,然而骨形成标志物则无明显变化,提示骨形成过程占优势,延伸至3-5年后,药物效应依然存在[28]。另外,一项Ⅲ期临床研究在16 713名65岁低骨密度值的绝经后妇女开展,志愿者被随机分配,实验组每日服用50 mg奥当卡替,对照组每日服用50 mg安慰剂,持续3-5年。随访34个月后,椎体骨折、非椎体、髋部骨折的风险分别下降41%、23%及47%。不典型的转子间骨折及硬皮病样皮肤损害病例正在增加,但尚未出现骨坏死病例,其疗效及安全性还需要在往后临床研究作进一步探索[27]。 2.5.2 新型骨形成促进剂——硬化蛋白单克隆抗体 硬化蛋白是一种由骨细胞SOST基因编码的糖蛋白,通过抑制成骨细胞膜表面的Wnt信号通路,从而降低成骨细胞分化及其功能,最后导致骨的形成受抑制。更重要的是,硬化蛋白是一个理想靶点,因SOST基因只在骨细胞中表达,从而避免了骨骼系统以外的副作用。一种罕见的SOST纯合子突变编码的硬化蛋白可引起严重的骨硬化症,而这些患者往往没有检测到循环的硬化蛋白,甚至出现早死现象。相反,SOST杂合子突变编码的表型是正常的,患者寿命正常,骨质坚硬,故骨折发生风险低。实验表明,通过删除小鼠体内SOST基因可促进骨形成,增加骨量和提高骨应力作用。目前,多数研究思路主要是通过抑制骨形成抑制物从而提高骨量,很多硬化蛋白单克隆抗体已经被发掘,但是只有Romosozumab达到Ⅲ期临床研究[27]。 一项Ⅰ期临床研究在32名低骨量的绝经后妇女及低骨量的16名健康男性中进行,结果表明血清中Romosoumab的平均浓度随剂量等比例增高,成骨标志物P1NP升高幅度为66%-147%,骨吸收标志物CTx下降幅度为15%-50%,腰椎骨密度增加了4%-7%[29]。另外,一项Ⅱ期临床研究在419名低骨密度值的绝经后妇女中进行,1年后提升腰椎骨密度11.3%,阿仑膦酸钠组、特立帕肽组、对照组分别为4.1%、7.1%及-0.1%[30]。目前,4个Ⅲ期临床研究实验正在开展以评估其有效性及安全性。对比很多同样处于Ⅲ期临床研究的抗骨质疏松药,Romosoumab抗骨折的优越性最为显著,这也许是抗骨质疏松药物领域的一个突破。另外,Romosoumab可降低患者再发骨折的风险,使之有可能成为严重骨质疏松的推荐药物。 当前与骨质疏松性骨折愈合有关的抗骨质疏松药物及其研究证据见表1。"
| [1] Yoon DS, Lee YK, Ha YC, et al.Inadequate Dietary Calcium and Vitamin D Intake in Patients with Osteoporotic Fracture.J Bone Metab. 2016;23(2):55-61.[2] Marcelli C,Chavoix C,Dargent-Molina P. Beneficial effects of vitamin D on falls and fractures: is cognition rather than bone or muscle behind these benefits?. Osteoporos Int.2015;26(1):1-10.[3] Khosla S,Bilezikian JP,Dempster DW, et al. Benefits and risks of bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(7):2272-2282.[4] Li YT, Cai HF, Zhang ZL.Timing of the initiation of bisphosphonates after surgery for fracture healing: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoporos Int.2015;26(2):431-441.[5] Adami S, Libanati C, Boonen S, et al. Denosumab treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis does not interfere with fracture-healing: results from the FREEDOM trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2012;94(23):2113-2119.[6] Brewer L,Williams D,Moore A.Current and future treatment options in osteoporosis.Eur J Clin Pharmacol.2011;67(4):321-331.[7] Pickar JH, Komm BS. Selective estrogen receptor modulators and the combination therapy conjugated estrogens/bazedoxifene: A review of effects on the breast. Post Reprod Health.2015;21(3):112-121.[8] Ellis AJ,Hendrick VM, Williams R, et al. Selective estrogen receptor modulators in clinical practice: a safety overview. Expert Opin Drug Saf.2015;14(6):921-934.[9] Mcclung MR. New management options for osteoporosis with emphasis on SERMs. Climacteric.2015;18 Suppl 2:56-61.[10] Park SB, Kim CH, Hong M, et al. Effect of a selective estrogen receptor modulator on bone formation in osteoporotic spine fusion using an ovariectomized rat model. Spine J.2016;16(1):72-81.[11] Chaki O.[Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs)].Nihon Rinsho.2015;73(10):1673-1681.[12] Spiro AS, Khadem S, Jeschke A, et al. The SERM raloxifene improves diaphyseal fracture healing in mice.J Bone Miner Metab. 2013;31(6): 629-636.[13] Umland EM, Karel L, Santoro N. Bazedoxifene and Conjugated Equine Estrogen: A Combination Product for the Management of Vasomotor Symptoms and Osteoporosis Prevention Associated with Menopause. Pharmacotherapy.2016;36(5):548-561.[14] Cheung WH,Miclau T,Chow SK,et al.Fracture healing in osteoporotic bone. Injury.2016;47 Suppl 2:S21-S26.[15] Tsartsalis AN,Dokos C,Kaiafa GD,et al.Statins, bone formation and osteoporosis: hope or hype?. Hormones (Athens).2012;11(2):126-139.[16] Ibrahim N, Mohamed N, Shuid AN.Update on statins: hope for osteoporotic fracture healing treatment. Curr Drug Targets.2013; 14(13):1524-1532.[17] Abdul-Majeed S, Mohamed N, Soelaiman IN. A review on the use of statins and tocotrienols, individually or in combination for the treatment of osteoporosis. Curr Drug Targets.2013;14(13):1579-1590.[18] Tan J, Fu X,Sun CG,et al.A single CT-guided percutaneous intraosseous injection of thermosensitive simvastatin/poloxamer 407 hydrogel enhances vertebral bone formation in ovariectomized minipigs. Osteoporos Int.2016;27(2):757-767.[19] Sun LM, Lin M C, Muo CH, et al. Calcitonin nasal spray and increased cancer risk: a population-based nested case-control study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2014;99(11):4259-4264.[20] Giannotti S,Bottai V,Dell'Osso G,et al. Atrophic femoral nonunion successfully treated with teriparatide. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23 Suppl 2:S291-S294.[21] Bhandari M, Jin L, See K, et al. Does Teriparatide Improve Femoral Neck Fracture Healing: Results From A Randomized Placebo-controlled Trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(5):1234-1244.[22] Miyakoshi N, Aizawa T, Sasaki S, et al. Healing of bisphosphonate- associated atypical femoral fractures in patients with osteoporosis: a comparison between treatment with and without teriparatide. J Bone Miner Metab.2015;33(5):553-559.[23] Reginster JY, Brandi ML, Cannata-Andia J, et al.The position of strontium ranelate in today's management of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int.2015;26(6):1667-1671.[24] Komrakova M,Weidemann A,Dullin C, et al. The Impact of Strontium Ranelate on Metaphyseal Bone Healing in Ovariectomized Rats.Calcif Tissue Int.2015;97(4):391-401.[25] Alegre DN, Ribeiro C, Sousa C, et al. Possible benefits of strontium ranelate in complicated long bone fractures. Rheumatol Int.2012; 32(2):439-443.[26] Negri AL, Spivacow FR. Healing of subtrochanteric atypical fractures after strontium ranelate treatment. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab.2012; 9(3):166-169.[27] Chapurlat R.Cathepsin K inhibitors and antisclerostin antibodies. The next treatments for osteoporosis?.Joint Bone Spine.2016;83(3):254-256.[28] Langdahl B,Binkley N,Bone H,et al.Odanacatib in the treatment of postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density: Five years of continued therapy in a phase 2 study. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(11): 2251-2258.[29] Padhi D,Allison M,Kivitz AJ,et al.Multiple doses of sclerostin antibody romosozumab in healthy men and postmenopausal women with low bone mass: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;54(2):168-178.[30] Mcclung MR,Grauer A, Boonen S, et al.Romosozumab in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. N Engl J Med.2014;370(5):412-420. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [6] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [7] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [8] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [9] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [10] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [11] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [12] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [13] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [14] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [15] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

