Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (17): 4366-4376.doi: 10.12307/2026.365
Previous Articles Next Articles
Anterior cingulate cortex-targeted inhibition by deep brain stimulation improves depression-like behavior in mice
Yang Haonan1, Yuan Zhengwei2, Xu Junpeng1, Mao Zhiqi1, Zhang Jianning1
- 1The First Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China; 2Chinese Institute for Brain Research, Beijing 102206, China
-
Received:2025-06-17Accepted:2025-09-04Online:2026-06-18Published:2025-12-01 -
Contact:Zhang Jianning, PhD, Chief physician, The First Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China -
About author:Yang Haonan, MS candidate, Physician, The First Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China -
Supported by:A grant from China Brain Project, No. 2021ZD0200407 (to MZQ).
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Haonan, Yuan Zhengwei, Xu Junpeng, Mao Zhiqi, Zhang Jianning. Anterior cingulate cortex-targeted inhibition by deep brain stimulation improves depression-like behavior in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4366-4376.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
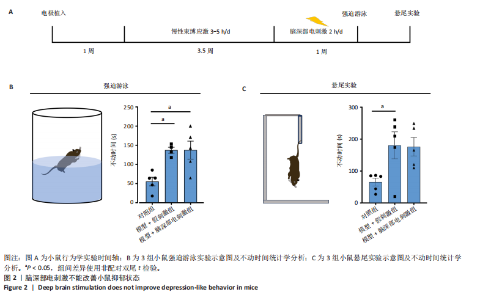
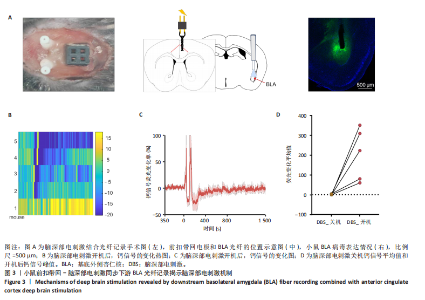
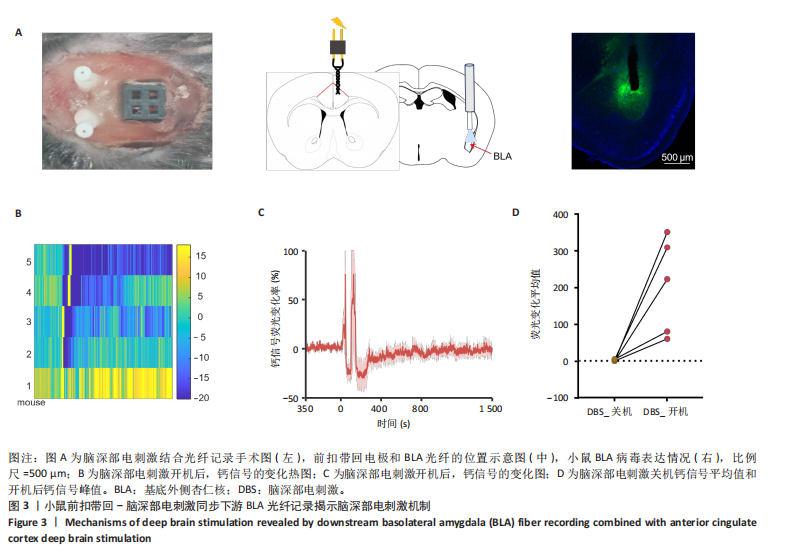
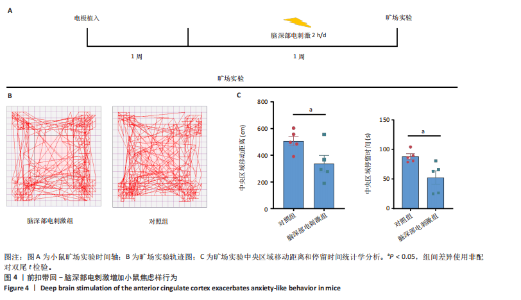
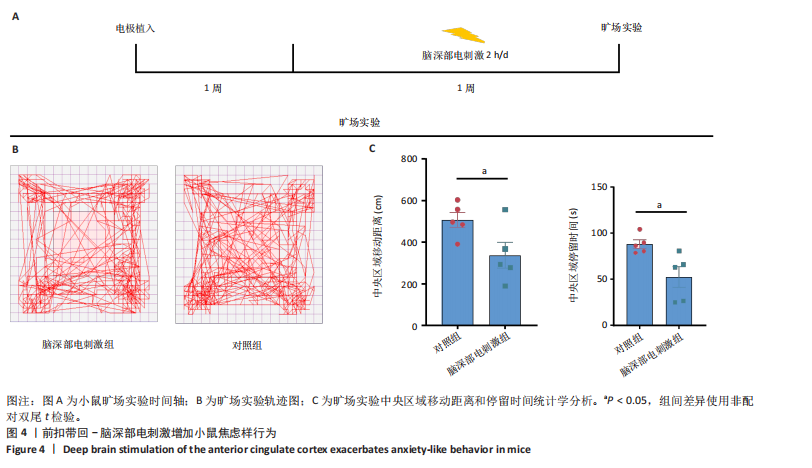
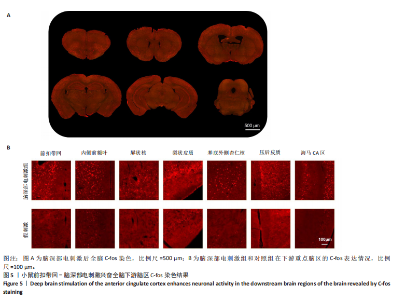
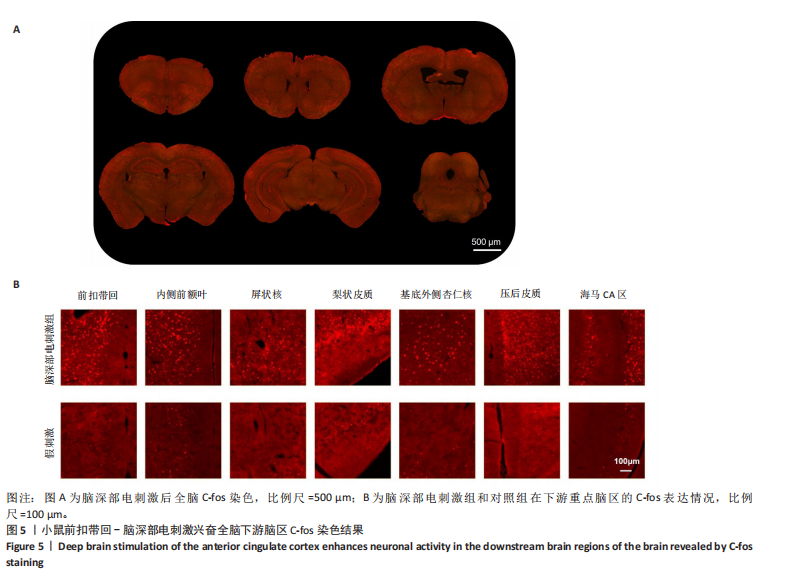
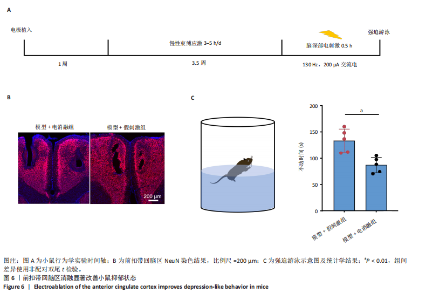
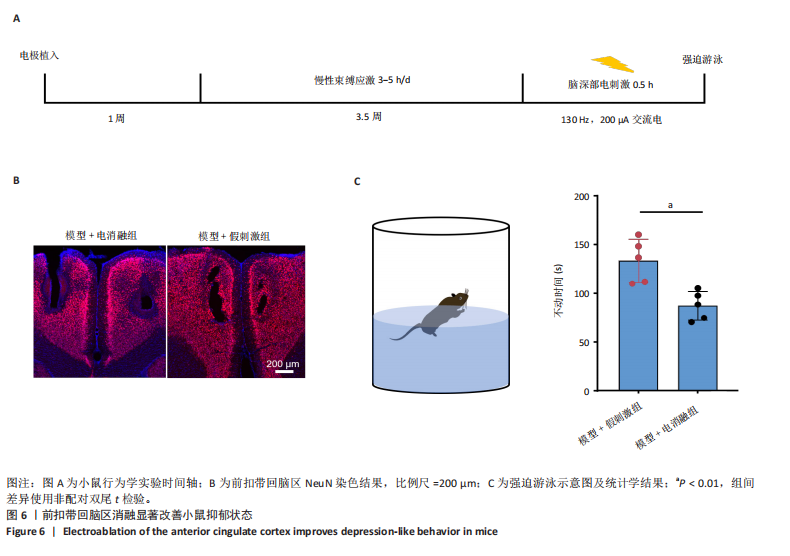
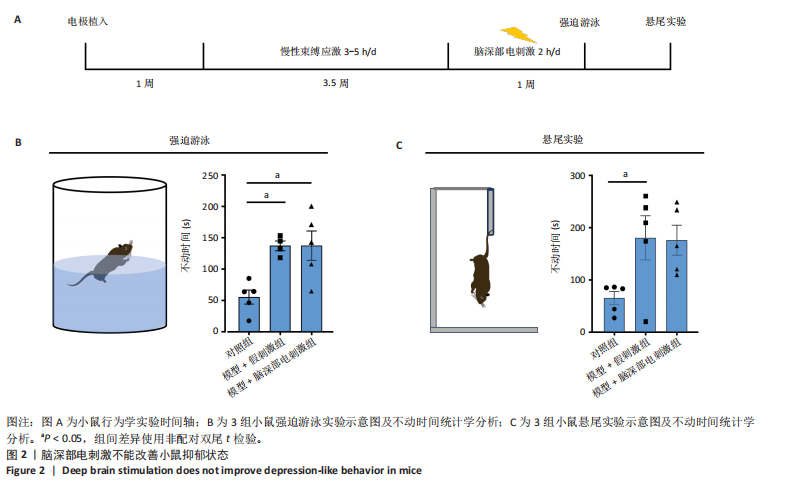
2.1 实验动物数量分析 动物实验共选用小鼠46只,实验过程动物均无死亡,全部进入分析。 2.2 前扣带回-脑深部电刺激并未改善小鼠抑郁状态 对照组、模型+假刺激组和模型+脑深部电刺激组3组小鼠在刺激结束后进行强迫游泳实验和悬尾实验,见图2A。 2.2.1 强迫游泳实验 结果显示,与对照组小鼠强迫游泳不动时间(55.59±11.28) s相比,模型+脑深部电刺激组和模型+假刺激组2组小鼠不动时间均显著延长[(137.40±23.56),(137.10±7.65) s,P < 0.05],但两组间比较差异无显著性意义,图2B。 2.2.2 悬尾实验 结果显示,模型+脑深部电刺激组小鼠悬尾不动时间(175.90±28.47) s与模型+假刺激组不动时间(180.30±42.60) s比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.93),见图2C。 实验结果表明,前扣带回的脑深部电刺激无法逆转小鼠的抑郁样行为。 2.3 前扣带回-脑深部电刺激可以兴奋小鼠前扣带回-BLA神经环路 已有研究表明,抑制前扣带回神经元可改善抑郁样行为,兴奋前扣带回神经元则起到反作用[8]。然而,上述实验未能缓解抑郁。因此,在前扣带回的下游BLA进行光纤记录来进一步探究脑深部电刺激的作用机制。 2.3.1 脑深部电刺激同步光纤记录实验结果 5只小鼠于BLA脑区注射AAV-CaMKII-GCaMP7s病毒并埋置光纤,同时在前扣带回植入刺激电极,见图3A,B。病毒表达2周后,进行脑深部电刺激同步光纤记录实验,开机后发现,小鼠BLA兴奋性神经元的钙信号迅速上升,形成一个尖峰,持续约5 min后逐渐下降并恢复至基线水平见图3C。尽管BLA整体呈现兴奋趋势,但其反应具有显著的异质性。通过对钙信号进行统计学分析,发现小鼠表现出强烈兴奋效应,见图3D。结果表明脑深部电刺激对下游脑区的作用复杂且异质性强,但总体上以兴奋效应为主。 2.3.2 旷场实验结果 脑深部电刺激组和对照组小鼠旷场实验,见图4A。结果显示,对照组小鼠中央区停留时间(88.00±4.53) s 与移动距离(506.40±36.11) cm 均显著高于脑深部电刺激组小鼠中央区停留时间(52.46±11.20) s与移动距离(336.80±61.69) cm(P < 0.05),提示脑深部电刺激可以兴奋神经元,增加焦虑样行为,见图4B,C。 2.4 前扣带回-脑深部电刺激兴奋全脑下游脑区 上述结果实验发现,前扣带回脑区的脑深部电刺激可以激发下游脑区BLA神经元兴奋。因此,利用神经元兴奋标志物C-fos来显示前扣带回脑深部电刺激对全脑神经元的影响。结果显示,脑深部电刺激组小鼠全脑均有C-fos标记,见图5A,说明前扣带回脑深部电刺激会影响整个神经网络。与对照组相比,除了前扣带回之外,C-fos染色揭示了脑深部电刺激小鼠多个相互连接区域出现神经元兴奋,包括BLA、内侧前额叶、屏状核、 压后皮质、梨状皮质和海马CA区,见图5B。"
| [1] BROMET E, ANDRADE LH, HWANG I, et al. Cross-national epidemiology of DSM-IV major depressive episode. BMC medicine. 2011;9:90. [2] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators.Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet (London, England). 2018;392(10159): 1789-1858. [3] WALKER ER, MCGEE RE, DRUSS BG. Mortality in mental disorders and global disease burden implications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72(4):334-341. [4] ROE-SEPOWITZ D. Adolescent female murderers: characteristics and treatment implications. Am J Orthop. 2007;77(3):489-496. [5] GAYNES BN, LUX L, GARTLEHNER G, et al. Defining treatment-resistant depression. Depress Anxiety. 2020;37(2):134-145. [6] MONCRIEFF J, COOPER R E, STOCKMANN T, et al. The serotonin theory of depression: a systematic umbrella review of the evidence. Molecular Psychiatry. 2023;28(8):3243-3256. [7] SANDOVAL-PISTORIUS SS, HACKER ML, WATERS AC, et al. Advances in Deep Brain Stimulation: From Mechanisms to Applications. J Neurosci. 2023;43(45):7575-7586. [8] GILBERT Z, MASON X, SEBASTIAN R, et al. A review of neurophysiological effects and efficiency of waveform parameters in deep brain stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol. 2023;152:93-111. [9] JOHNSON KA, OKUN MS, SCANGOS KW, et al. Deep brain stimulation for refractory major depressive disorder: a comprehensive review. Mol Psychiatry. 2024;29(4):1075-1087. [10] MAYBERG HS, LOZANO AM, VOON V, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. 2005;45(5):651-660. [11] HOLTZHEIMER PE, HUSAIN MM, LISANBY SH, et al. Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: a multisite, randomised, sham-controlled trial. lancet Psychiatry. 2017;4(11):839-849. [12] RAMASUBBU R, ANDERSON S, HAFFENDEN A, et al. Double-blind optimization of subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: a pilot study. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2013;38(5):325-332. [13] UDUPA K, CHEN R. The mechanisms of action of deep brain stimulation and ideas for the future development. Prog Neurobiol. 2015;133:27-49. [14] KRAUSS JK, LIPSMAN N, AZIZ T, et al. Technology of deep brain stimulation: current status and future directions. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021;17(2):75-87. [15] CHIKEN S, NAMBU A. Mechanism of Deep Brain Stimulation: Inhibition, Excitation, or Disruption? Neuroscientist. 2016;22(3):313-322. [16] SHARIM J, POURATIAN N. Anterior Cingulotomy for the Treatment of Chronic Intractable Pain: A Systematic Review. Pain Physician. 2016; 19(8): 537-550. [17] BARTHAS F, HUMO M, GILSBACH R, et al. Cingulate Overexpression of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase-1 as a Key Factor for Depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;82(5):370-379. [18] KIM KS, HAN PL. Optimization of chronic stress paradigms using anxiety- and depression-like behavioral parameters. J Neurosci Res. 2006;83(3):497-507. [19] LI Y, ZHONG W, WANG D, et al. Serotonin neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus encode reward signals. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10503. [20] HAMANI C, MAYBERG H, STONE S, et al. The subcallosal cingulate gyrus in the context of major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;69(4):301-308. [21] CAI X, PADOA-SCHIOPPA C. Neuronal encoding of subjective value in dorsal and ventral anterior cingulate cortex. J Neurosci. 2012; 32(11):3791-3808. [22] PALOMERO-GALLAGHER N, HOFFSTAEDTER F, MOHLBERG H, et al. Human Pregenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex: Structural, Functional, and Connectional Heterogeneity. Cereb Cortex. 2019;29(6):2552-2574. [23] YUAN Z, QI Z, WANG R, et al. A corticoamygdalar pathway controls reward devaluation and depression using dynamic inhibition code. Neuron. 2023;111(23):3837-53.e5. [24] GAO Y, GAO D, ZHANG H, et al. BLA DBS improves anxiety and fear by correcting weakened synaptic transmission from BLA to adBNST and CeL in a mouse model of foot shock. Cell Rep. 2024; 43(2):113766. [25] LOWET E, KONDABOLU K, ZHOU S, et al. Deep brain stimulation creates informational lesion through membrane depolarization in mouse hippocampus. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):7709. [26] PUIGDEMONT D, PéREZ-EGEA R, PORTELLA MJ, et al. Deep brain stimulation of the subcallosal cingulate gyrus: further evidence in treatment-resistant major depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012;15(1):121-133. [27] LIN ZJ, GU X, GONG WK, et al. Stimulation of an entorhinal-hippocampal extinction circuit facilitates fear extinction in a post-traumatic stress disorder model. J Clin Invest. 2024;134(22):e181095. [28] SONG N, LIU Z, GAO Y, et al. NAc-DBS corrects depression-like behaviors in CUMS mouse model via disinhibition of DA neurons in the VTA. Mol Psychiatry. 2024;29(5):1550-1566. [29] ASHKAN K, ROGERS P, BERGMAN H, et al. Insights into the mechanisms of deep brain stimulation. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13(9):548-554. [30] PIALLAT B, CHABARDèS S, DEVERGNAS A, et al. Monophasic but not biphasic pulses induce brain tissue damage during monopolar high-frequency deep brain stimulation. Neurosurgery. 2009;64(1):156-162; discussion 62-63. [31] BÜHNING F, MIGUEL TELEGA L, TONG Y, et al. Electrophysiological and molecular effects of bilateral deep brain stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle in a rodent model of depression. Exp Neurol. 2022;355:114122. [32] DOURNES C, BEESKÉ S, BELZUNG C, et al. Deep brain stimulation in treatment-resistant depression in mice: comparison with the CRF1 antagonist, SSR125543.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013;40:213-220. [33] ZHANG Y, MA L, ZHANG X, et al. Deep brain stimulation in the lateral habenula reverses local neuronal hyperactivity and ameliorates depression-like behaviors in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;180:106069. [34] SCHOR JS, GONZALEZ MONTALVO I, SPRATT PWE, et al. Therapeutic deep brain stimulation disrupts movement-related subthalamic nucleus activity in parkinsonian mice. Elife. 2022;11:e75253. [35] VAN DEN BOOM BJG, ELHAZAZ-FERNANDEZ A, RASMUSSEN PA, et al. Unraveling the mechanisms of deep-brain stimulation of the internal capsule in a mouse model. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):5385. [36] GONG W K, LI X, WANG L, et al. Prefrontal FGF1 Signaling is Required for Accumbal Deep Brain Stimulation Treatment of Addiction. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025;12(16):e2413370. [37] SPIX TA, NANIVADEKAR S, TOONG N, et al. Population-specific neuromodulation prolongs therapeutic benefits of deep brain stimulation. Science. 2021;374(6564):201-206. [38] MIGUEL TELEGA L, ASHOURI VAJARI D, STIEGLITZ T, et al. New Insights into In Vivo Dopamine Physiology and Neurostimulation: A Fiber Photometry Study Highlighting the Impact of Medial Forebrain Bundle Deep Brain Stimulation on the Nucleus Accumbens. Brain Sci. 2022;12(8):1105. [39] SCHOR JS, NELSON AB. Multiple stimulation parameters influence efficacy of deep brain stimulation in parkinsonian mice. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(9):3833-3838. [40] PAULK AC, ZELMANN R, CROCKER B, et al. Local and distant cortical responses to single pulse intracranial stimulation in the human brain are differentially modulated by specific stimulation parameters.Brain Stimul. 2022;15(2):491-508. [41] MURPHY KR, FARRELL JS, BENDIG J, et al. Optimized ultrasound neuromodulation for non-invasive control of behavior and physiology. Neuron. 2024;112(19):3252-66.e5. [42] VALVERDE S, VANDECASTEELE M, PIETTE C, et al.Deep brain stimulation-guided optogenetic rescue of parkinsonian symptoms. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):2388. [43] ALEXANDER L, JELEN LA, MEHTA MA, et al. The anterior cingulate cortex as a key locus of ketamine’s antidepressant action. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;127:531-554. [44] DIENER C, KUEHNER C, BRUSNIAK W, et al. A meta-analysis of neurofunctional imaging studies of emotion and cognition in major depression. NeuroImage. 2012;61(3):677-685. [45] HOLMES SE, HINZ R, CONEN S, et al. Elevated Translocator Protein in Anterior Cingulate in Major Depression and a Role for Inflammation in Suicidal Thinking: A Positron Emission Tomography Study. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;83(1):61-69. [46] SELLMEIJER J, MATHIS V, HUGEL S, et al. Hyperactivity of Anterior Cingulate Cortex Areas 24a/24b Drives Chronic Pain-Induced Anxiodepressive-like Consequences. J Neurosci. 2018;38(12):3102-3115. [47] MAYBERG HS, LIOTTI M, BRANNAN SK, et al. Reciprocal limbic-cortical function and negative mood: converging PET findings in depression and normal sadness. Am J Psychiatry. 1999;156(5):675-682. [48] PALOMERO-GALLAGHER N, EICKHOFF SB, HOFFSTAEDTER F, et al. Functional organization of human subgenual cortical areas: Relationship between architectonical segregation and connectional heterogeneity. Neuroimage. 2015;115:177-190. [49] KISEL YS, LI A, WARREN N, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of deep brain stimulation for depression. Depress Anxiety. 2018;35(5):468-480. [50] MAYBERG HS.Targeted electrode-based modulation of neural circuits for depression. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(4):717-725. [51] CROWELL AL, RIVA-POSSE P, HOLTZHEIMER PE, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Subcallosal Cingulate Deep Brain Stimulation for Treatment-Resistant Depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(11):949-956. |
| [1] | Haonan Yang, Zhengwei Yuan, Junpeng Xu, Zhiqi Mao, Jianning Zhang. Preliminary study on the mechanisms and efficacy of deep brain stimulation in treating depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Xu Chang, Jiang Mingzhu, Liu Xin, Yan Weijun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of implant anchorage combined with torque auxiliary arch to lower anterior teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1971-1978. |
| [3] | Zhang Di, Zhao Jun, Ma Guangyue, Sun Hui, Jiang Rong. Mechanism of depression-like behavior in chronic social defeat stress mice based on high-throughput sequencing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1139-1146. |
| [4] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Zhao Yuxin, Liu Xihua. Effects of different neuromodulatory stimulation modalities on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [5] | Li Zhongxian, Jiao Zitong, Ren Hanyue, Zhang Pan, Peng Min, Huang Yingxin, Li Mengyao, Hu Yuechen, Liang Junquan, Yan Luda, Fu Wenbin, Zhou Peng. Mechanism of depression with insomnia mediated by the locus coeruleus-norepinephrine system: an assessment based on resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3083-3090. |
| [6] | Wang Jiaying, Xu Chun, Mayila · Abudukelimu. Global research status, trends and hotspots of anxiety/depression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2920-2932. |
| [7] | Song Andong, , Fu Huiling, , Yuan Bo, Li Guohua, Jia Xusheng, Jia Menghui . Dodder intervenes with chronic stress depression in a mouse model: changes in NLRP3 inflammasome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2440-2448. |
| [8] |
Li Tian, Ren Yuhua, Gao Yanping, Su Qiang.
Mechanism of agomelatine alleviating anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in APP/PS1 transgenic mice #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1176-1182.
|
| [9] | Tian Jinxin, Zhao Yuxin, Hu Tong, Cui Tiantian, Ma Lihong. Effects of different transcranial magnetic stimulation modes on refractory depression in adults: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7639-7648. |
| [10] | Du Juan, Zhang Yi, Hao Quanshui. Effects of exercise on activation of microglia and astrocytes and neuronal apoptosis in depressed rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6243-6248. |
| [11] | Gao Wenyan, Zheng Zhaoyan, Pan Shang, Wang Peipei, Ji Chunhui, Lyu Shaoping. Bibliometric and visual analysis of Theta burst transcranial magnetic stimulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4389-4400. |
| [12] | Song Yanli, Zhang Xi, Guo Yangbo, Ling Xiaomei, Li Linhai, Yang Zixin, Su Xiaoyun, Cui Jianmei. Effects of treadmill exercise on hippocampal autophagy-induced apoptosis in ovariectomized stressed rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3848-3855. |
| [13] | Ma Sicong, Chen Jing, Li Yunqing. Functions and roles of connective tissue growth factor in nervous systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 615-620. |
| [14] | Wang Xiaoge, Liu Jiwen, Yang Shuai, Bao Jinyu, Li Cui. Effects of exercise on depression-like behaviors in chronic unpredictable mild stress rodent models: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 813-820. |
| [15] | Hu Yue, Zhu Yuanliang, Wan Tenggang, Xu Fangyuan, Xu Zhangyu, Li Jiyang, Li Dan, Wang Jianxiong. Depression-like behavior characteristics of rats with neuropathic pain and expression of mGluR5 and NMDAR2B in the left dorsal agranular insular area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3216-3223. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||