Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (13): 3370-3378.doi: 10.12307/2026.309
Previous Articles Next Articles
Occurrence and development of plant derived extracellular vesicles in the prevention and treatment of musculoskeletal system diseases
Zhang Yijie1, Hong Bowen1, Zhou Yi1, Shao Yang1, 2, Wu Mao1, 2, Li Shaoshuo1, 2, Wang Jianwei1, 2
- 1Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Wuxi Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Accepted:2025-06-14Online:2026-05-08Published:2025-12-26 -
Contact:Wang Jianwei, MD, Chief physician, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China; Wuxi Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China; Co-corresponding author: Li Shaoshuo, MD, Attending physician, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China; Wuxi Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhang Yijie, Master candidate, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82274546 (to WJW); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82405520 (LSS); Wuxi Municipal Health Commission Research Project, No. Q202232 (to LSS); Wuxi “Double Hundred” Young and Middle-aged Medical and Health Talents, No. HB2023074 (to LSS); Jiangsu Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Development Plan Young Talent Project, No. QN202322 (to LSS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yijie, Hong Bowen, Zhou Yi, Shao Yang, Wu Mao, Li Shaoshuo, Wang Jianwei. Occurrence and development of plant derived extracellular vesicles in the prevention and treatment of musculoskeletal system diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3370-3378.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
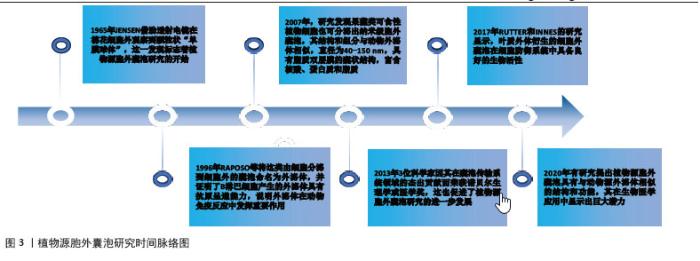
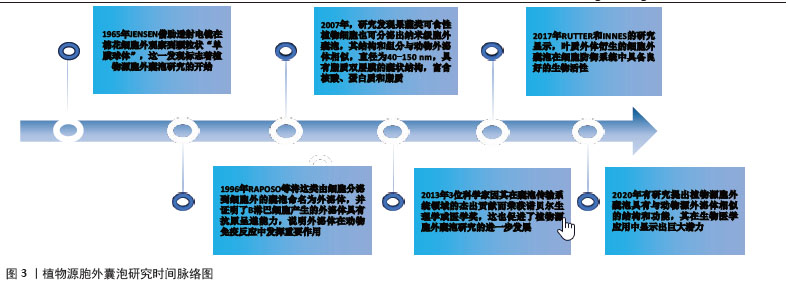
2.1 植物源胞外囊泡研究历程、优势和临床应用前景 2.1.1 研究历程 植物源胞外囊泡的研究起始于20世纪中期,经过研究者数十年的不断探索与总结使这类外泌体样纳米囊泡在疾病治疗中的潜力被逐渐发掘,从而推动这一研究领域快速发展并展现出广阔前景。1965年JENSEN[7]借助透射电镜在棉花细胞外观察到颗粒状“单膜球体”,这一发现标志着植物源胞外囊泡研究的开始。1996年RAPOSO等将这类由细胞分泌到细胞外的囊泡命名为外泌体,并证明了B淋巴细胞产生的外泌体具有抗原呈递能力,说明外泌体在动物免疫反应中发挥重要作用[8]。2007年,研究发现果蔬类可食性植物细胞也可分泌出纳米级胞外囊泡,其结构和组分与动物外泌体相似,直径为40-150 nm,具有脂质双层膜的囊状结构,富含核酸、蛋白质和脂质[9]。2013年3位科学家因在囊泡传输系统领域的杰出贡献而荣获诺贝尔生理学或医学奖,这也促进了植物源胞外囊泡研究的进一步发展[10]。WANG等[11]已经证明葡萄柚来源纳米载体能够有效递送多种治疗剂,包括药物、DNA表达载体、siRNA和抗体,说明这些植物源纳米颗粒在药物递送领域具有潜在应用价值。2017年RUTTER 和 INNES 的研究显示,叶质外体衍生的细胞外囊泡在细胞防御系统中具备良好的生物活性[12]。2020年有研究提出植物源胞外囊泡具有与动物源外泌体相似的结构和功能,其在生物医学应用中显示出巨大潜力[10]。近年来不同植物来源的细胞外囊泡已被证明具有多种生物活性,包括抗癌、抗炎、抗氧化、抗肥胖和再生特性[13]。植物源胞外囊泡的研究历程起始于20 世纪中期的细胞生物学探索,随后逐步发展到当前在生物医学领域的广泛应用研究,体现出它在科学研究和临床应用中的重要价值与发展前景,见图3。"
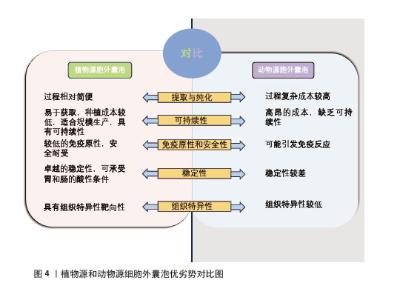
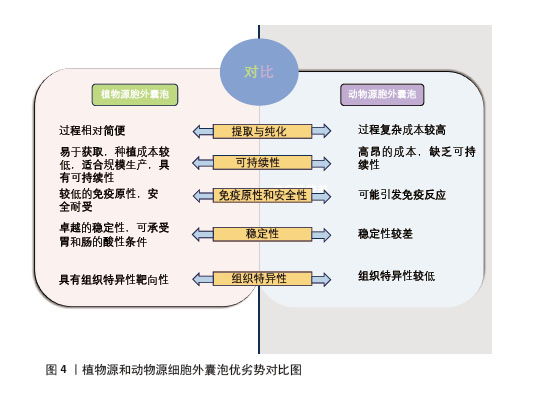
2.1.2 提取和分离方法 目前分离和纯化植物源胞外囊泡的方法主要有超速离心法和密度梯度超速离心法。随着技术的发展,尺寸排阻色谱法和聚乙二醇沉淀法也展现出良好的应用前景。超速离心法适用于大多数样品,其原理是基于不同物质在均匀悬浮液中沉降速度的差异,然而此方法存在样品可能损失较多、操作耗时较长且可能引入杂质污染等局限性[14]。密度梯度超速离心法是基于颗粒浮力密度分离细胞外囊泡的技术,该方法通过在离心管中加入不同密度的梯度液使囊泡在离心过程中迁移至与其浮力密度相匹配的梯度液位置,该方法虽能有效分离不同大小和密度的植物源胞外囊泡,但操作过程复杂且耗时较长,此外提取效率较低,通常需与超速离心法等其他技术结合以进一步提高纯度,运用该方法分离植物源胞外囊泡一般具有良好的生物活性与稳定性,可用于药物递送、抗炎、抗氧化等多种领域[15]。尺寸排阻色谱的原理是较大分子无法进入色谱柱填充材料的孔隙,而较小分子会进入孔隙导致其迁移速度较慢,从而实现植物源胞外囊泡分离,应用相对有限[16]。聚乙二醇沉淀法是在植物提取液中加入一种非离子型水溶性高分子聚合物溶液以此实现细胞外囊泡的沉淀与富集,该方法提取的囊泡纯度相对较低还容易受到杂质污染可能,需要结合超速离心或尺寸排阻色谱等其他技术进行纯化,但该方法操作简便、成本低廉,很适合大规模提取[17]。不同提取方法都有各有优缺点,选择合适的提取方法需根据研究目的、样本类型以及实验条件综合考量。 2.1.3 优势和临床应用前景 美国生物化学家和医生在寻找凝血因子过程中发现经高速离心处理后的血液沉淀具有凝血功能,他们认为这种沉淀物中不仅包含凝血因子还可能存在血细胞小碎片,这些细胞碎片后来被认定为细胞外囊泡,这标志着动物源胞外囊泡研究的开始。动物源性细胞外囊泡研究历史悠久并显示出潜在的临床疗效,但面临诸多挑战,如成本高昂、持续时间长、缺乏可持续性,以及与大规模动物源胞外囊泡生产相关的细胞培养长期供应不稳定等[18]。另外使用动物源性细胞外囊泡存在免疫反应风险,可能导致不良反应[19]。这些挑战严重限制动物源胞外囊泡在临床实践中的广泛应用并使其转化面临重大障碍。相对于动物源胞外囊泡,植物资源充足易于获取、种植成本较低且植物源胞外囊泡提取和纯化过程相对简单,可依靠超速离心和超滤等纯物理方法达成,这些方法成本效益高、易于标准化且适合规模生产,从而提高生产效率[20]。来自可食用水果和蔬菜的胞外囊泡因免疫原性较低,故更安全且耐受性较好[12]。此外,植物源胞外囊泡表现出卓越稳定性,可承受胃和肠的酸性条件,使其更适合口服给药系统,并且具有更长的体内循环时间和组织特异性靶向性[21],能够穿过血脑屏障,但不能穿过胎盘屏障[22]。因植物源胞外囊泡含有脂质、蛋白质、核酸和次级代谢产物等成分,被视为可持续、绿色、高效的药物输送纳米载体[23]。植物源和动物源细胞外囊泡优劣势对比,见图4。植物源胞外囊泡因独特优势和广泛应用前景日益成为备受关注的热点研究方向,随着进一步研究和技术开发,它们有望在未来的临床实践中发挥更大作用,而深入研究其在疾病中的机制至关重要。"
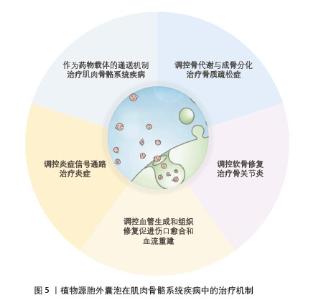
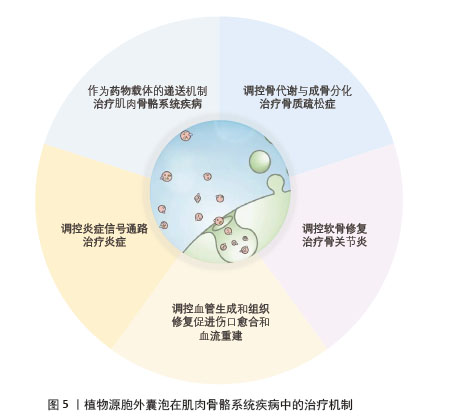
2.2 植物源胞外囊泡在肌肉骨骼系统疾病治疗中的机制 2.2.1 调控骨代谢与成骨分化治疗骨质疏松症 骨质疏松症是一种以骨量减少、骨组织微结构破坏为特征,导致骨脆性增加、易发生骨折的全身性代谢性骨病[24]。传统抗骨质疏松药物主要有:骨吸收抑制剂(如双膦酸盐、降钙素等)、骨形成促进剂(甲状旁腺激素类似物,如特立帕肽)、维生素K2以及活性维生素D及其类似物,如阿法骨化醇、骨化三醇等。这些药物通过不同的机制作用于骨代谢过程,旨在提高骨密度、改善骨质量、减少骨折发生的风险,但同样存在一些不良反应。ZHAN等[25]发现葛根衍生的外泌体样纳米囊泡能够促进原代人骨髓间充质干细胞的分化和矿化。在三甲胺氧化物诱导的绝经后骨质疏松症SD大鼠模型中,研究者通过透射电子显微镜和免疫组化染色观察到植物源性外泌体样纳米颗粒显著促进成骨过程,具体表现为提高骨密度、骨体积分数以及成骨相关标志物的表达,这表明植物源性外泌体样纳米颗粒在骨质疏松症治疗中具有调节骨代谢的潜力。ZHAO等[26]研究表明,从中药骨碎补中提取的细胞外纳米囊泡能够被人骨髓间充质干细胞有效摄取并显著促进细胞增殖和雌激素受体α的表达;骨碎补来源细胞外纳米囊泡还能通过激活雌激素受体α信号通路促进人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化和骨形成,同时抑制破骨细胞的分化和活性进而减少骨吸收;在卵巢切除小鼠模型中,骨碎补来源细胞外纳米囊泡表现出显著的骨靶向性,能够精准聚集于骨组织且未引起其他器官的毒性。有研究证实,人参中的皂甙Rc能够改善骨小梁的微观结构并促进与骨形成相关的基因表达;人参皂甙Rc通过激活β-catenin和Runx2参与的经典Wnt信号通路增强成骨细胞的分化和基质的矿化过程,还通过提高骨形成标志物的表达水平来促进骨形成,因此人参皂甙Rc有潜力作为一种天然的预防和治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的替代疗法[27]。SIM等[28]证明苹果来源纳米囊泡通过激活骨形态发生蛋白2信号通路,进而刺激ERK1/2、JNK1/2和Smad1信号传导,促进成骨前体细胞的生长、分化和矿化,从而增强骨形成,使得苹果来源纳米囊泡有潜力作为一种新的抗骨质疏松症治疗药物。PARK等[29]研究证实从李子中提取的外泌体样纳米囊泡能够通过激活BMP-2/MAPK/Smad-1依赖的Runx2信号通路,增强成骨细胞的分化和矿化过程;在破骨细胞分化调控方面,李子来源外泌体样纳米囊泡能够抑制小鼠原代破骨细胞中抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶阳性细胞数量及抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶活性,这些研究显示李子来源外泌体样纳米囊泡通过促进成骨细胞活化并减少破骨细胞分化来治疗骨质疏松症的。HWANG等[30]研究表明山药衍生的外泌体样纳米囊泡能够刺激成骨细胞增殖、分化和矿化,同时提高骨分化标志物(如骨桥蛋白、碱性磷酸酶和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白)的表达水平;在卵巢切除手术建立的骨质疏松症小鼠模型中,山药衍生的外泌体样纳米囊泡具有促进骨骼纵向生长和增强胫骨矿物质密度的效果,与成骨细胞相关指标的显著提升呈正相关。现有研究表明植物源胞外囊泡在骨质疏松症治疗中展现一定疗效并具备众多优势,其通过多种机制调节骨代谢,包括促进成骨细胞增殖分化、抑制破骨细胞分化、调节关键信号通路以及具备骨靶向性等特性,使其在骨质疏松症治疗领域呈现出广阔的应用前景。同时植物源胞外囊泡作为一种创新的天然药物递送方式,为临床治疗骨质疏松症开辟了新的途径。 2.2.2 调控软骨修复治疗骨关节炎 骨关节炎是一种以关节软骨退行性变为核心病理改变的慢性进行性关节疾病,主要病理特征为关节软骨损伤、滑膜炎症、骨赘形成,疾病后期可能出现活动受限、关节畸形等情况[31]。YILDIRIM等[32]发现番茄衍生的外泌体样囊泡在软骨细胞修复方面显示出巨大潜力,番茄衍生的外泌体样囊泡能够提高软骨细胞标志物的表达水平;此外,番茄衍生的外泌体样囊泡还可促进人脂肪间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化。基于上述发现,番茄衍生的外泌体样囊泡不但在软骨再生领域具有应用前景,也可能成为治疗骨关节炎和其他软骨退行性疾病的新型疗法。LIANG等[33]利用改造后的外泌体作为载体,将miR-140精准输送至软骨细胞,有效解决了miR-140穿透软骨细胞外致密基质的难题,实现了对软骨细胞的特异性作用。研究表明,miR-140能有效抑制导致软骨降解的蛋白酶活性从而缓解骨关节炎病情,为治疗骨关节炎提供了一种高效且可行的新策略。CHEN等[34]从菠菜中提取出纳米类囊体单元并用软骨细胞膜进行封装,其在自然光照射下可提高细胞内ATP以及NADPH水平,从而推动受损软骨细胞合成代谢,提高软骨组织稳定性,抑制骨关节炎的病理发展进程。LIANG等[35]从钝顶螺旋藻中提取的细胞外囊泡与大黄酸水凝胶结合构建复合体系,其在由内侧半月板失稳和单碘乙酸钠诱导所引发的骨关节炎小鼠模型中可减少软骨降解、增加软骨厚度以及糖胺聚糖含量、降低炎症因子白细胞介素6的表达,同时促进软骨合成相关蛋白Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达。与传统治疗手段(如运动疗法、手术疗法、关节置换术以及使用非类固醇抗炎药和关节内注射剂等药物疗法)相比,植物源胞外囊泡在治疗骨关节炎方面具有多重优势,这些囊泡能够携带核酸、蛋白质等分子,实现精准的药物递送并增强治疗的靶向性。由于免疫原性低,植物源胞外囊泡可以更容易穿透生物屏障被机体吸收。此外植物源胞外囊泡作为药物载体能够提升中药分子的疗效,解决某些中药成分在人体内生物利用度不足的问题[36]。植物源胞外囊泡通过促进软骨细胞标志物和关键蛋白的表达、促进间充质干细胞分化、靶向递送治疗分子、增强细胞代谢能力、抑制软骨降解和炎症反应等多种方式调节软骨修复,在治疗骨关节炎领域有广阔的临床潜力以及应用前景。随着研究的不断推进,这些天然来源的植物源胞外囊泡有望成为治疗骨关节炎的有效手段。 2.2.3 调控血管生成和组织修复促进伤口愈合和血流重建 伤口愈合是身体对损伤产生的自然修复反应,包含炎症、增殖和重塑等一系列复杂生物事件,这些事件共同作用以闭合伤口并恢复受损组织功能[37]。对于缺血或受损组织而言,恢复血液供应是组织再生的重要环节[38-39]。传统疗法如电刺激、生长因子治疗、负压伤口治疗、氧气疗法等均存在一定局限性。YANG等[40]通过体外和体内伤口愈合模型研究证实人参衍生的纳米颗粒具有促进皮肤伤口愈合的潜在作用。人参衍生的纳米颗粒通过激活ERK和AKT/mTOR信号通路,增强细胞增殖和迁移能力,提高伤口愈合相关基因表达,促进血管生成;动物实验显示人参衍生的纳米颗粒可加速小鼠皮肤伤口愈合并减轻愈合后期炎症,为皮肤损伤的治疗策略提供了科学依据。KIM等[41]证明芦荟皂来源的细胞外囊泡能显著抑制促炎细胞因子表达、促进真皮成纤维细胞增殖和迁移,并通过管形成实验展现出良好的血管生成能力,表明芦荟皂来源的细胞外囊泡能够加速营养物质向伤口部位输送,从而促进慢性伤口愈合。?AHIN等[42]利用体外伤口愈合模型探索小麦外泌体促进皮肤伤口愈合的潜在应用,结果显示小麦外泌体能够促进伤口愈合相关基因表达,激活成纤维细胞,并通过提高血管分支数量增加管状结构形成,这说明小麦外泌体具有促进伤口愈合的能力。从仙人掌果实中提取的外泌体可逆转慢性皮肤伤口相关的炎症反应和氧化损伤进而促进伤口愈合[43]。在大鼠皮肤深Ⅱ度烫伤模型中,苦瓜来源胞外囊泡联合莫匹罗星软膏能够显著促进创面愈合,增强组织新生血管的生成并提高血小板-内皮细胞黏附分子的表达水平[44]。植物源胞外囊泡通过促进细胞增殖和迁移、促进血管生成、抑制炎症反应、调节氧化应激等多种方式促进伤口愈合和血流重建。 2.2.4 调控炎症反应 炎症与肌肉骨骼系统存在密切相互作用,适度炎症有助于清除受损组织并启动修复,但持续炎症可能导致免疫紊乱、组织病理变化和肌肉骨骼功能衰退,甚至引起肌肉纤维化并加剧疾病严重程度[45]。植物源胞外囊泡在治疗多种炎症相关疾病方面的潜力日益显著,它们不仅能增强机体的免疫防御能力,还能作为纳米级治疗载体发挥作用[46]。MAMMADOVA等[47]首次通过体外研究分析番茄衍生纳米囊泡的细胞毒性和抗炎潜力,发现3种番茄来源的纳米囊泡组分在无毒水平下能不同程度抑制脂多糖诱导的THP-1细胞炎症。此外番茄中的植物次生代谢产物(如磷脂酸、脂氧合酶、香豆素和番茄红素等)可能影响植物衍生纳米囊泡的生物活性,其中磷脂酸已被证明可以控制炎症发生以及严重程度。TRENTINI等[48]研究表明,在炎症环境中苹果衍生纳米囊泡处理可降低THP-1细胞中白细胞介素1b和白细胞介素8的表达;此外,苹果衍生纳米囊泡还可减少成纤维细胞中炎性细胞因子肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,这说明苹果衍生纳米囊泡具有抗炎作用。研究显示洋葱衍生细胞外囊泡可有效抑制巨噬细胞内的炎症反应,以剂量依赖的方式减少经脂多糖刺激的RAW 264.7细胞中促炎因子的产生[49]。柠檬衍生细胞外囊泡在体外实验中已被证实有抗炎作用,其通过降低ERK1/2的磷酸化水平来抑制核因子κB的活化,同时降低促炎细胞因子水平并促进抗炎分子产生,这种抗炎能力在人类原始T淋巴细胞中也得到了验证[50]。源自马铃薯的外泌体样纳米粒子有调节哺乳动物基因表达的能力,并且可穿透血脑屏障使其成为神经炎症相关疾病治疗的潜在候选物或药物递送载体,能有效缓解微胶质细胞的炎症反应并且与地塞米松等抗炎药物结合时疗效进一步提高,为神经炎症相关疾病治疗提供了可能性和希望[51]。从仙人掌果实中提取的外泌体样纳米囊泡显示出明显抗炎特性,它们能降低促炎细胞因子白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,并在不同浓度下增加抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10的表达,在较高浓度下还可以显著增加白细胞介素4的表达,这说明仙人掌果实中提取的外泌体样纳米囊泡能够以剂量依赖性方式调节炎症反应,减少促炎因子并增加抗炎因子表达[52]。EMMANUELA等[53]的研究首次成功地从龙葵浆果中提取并鉴定植物源性外泌体样纳米粒子并证实具有抗炎作用,特别是在抑制脂多糖诱导RAW264.7细胞中白细胞介素6的表达方面。通过气相色谱-质谱分析发现植物来源的外泌体样纳米颗粒中富含多种化合物,包括具有抗炎作用的单萜类化合物β-柠檬醛,这可能是其发挥抗炎效果的关键因素。植物源胞外囊泡通过促进抗炎分子生成、抑制促炎因子产生、调节关键信号通路、调节 miRNA 表达以及调节免疫细胞功能等多种方式发挥抗炎作用。 2.2.5 作为药物递送载体治疗肌肉骨骼系统疾病 由于关节软骨缺乏血管供应,系统性给药往往难以抵达关节内的靶细胞,因此更倾向于选择直接向关节内注射的方式给药,然而通过关节内注射给药的药物很容易被滑膜血管系统和淋巴系统清除,这导致药物半衰期缩短且在关节腔内停留时间减少。另外关节组织中的胶原纤维和蛋白多糖以及带有高度负电荷的糖胺聚糖,共同构成药物到达软骨深层区域软骨细胞的障碍,这些因素使软骨细胞的精准给药具有挑战性[33]。植物源胞外囊泡作为细胞间通讯的重要递质,通过分子货物传递和表面信号传递来调节多种生物过程[54]。已有研究发现外泌体在递送地塞米松方面具有一定潜力,这种递送方式能有效降低关节炎症、缓解疼痛,还可以刺激软骨进行修复。与全身性给药相比而言,外泌体递送地塞米松还能降低全身性不良反应。经修饰的外泌体可以促进软骨修复和再生、减轻疼痛并降低关节炎症[55-56]。将功能性配体如肝素修饰到柠檬衍生的细胞外囊泡表面,可提高细胞内吞效率并有效减少耐药细胞中的药物外排现象[57]。WU等[58]的研究表明,植物源胞外囊泡还能高效包裹疏水性和亲水性化学物质,在药物递送方面表现出更高的疗效。植物源胞外囊泡可与药物产生协同治疗效果,同时其安全性和高产量的特性也进一步凸显其作为口服药物载体的巨大潜力[57]。植物源胞外囊泡凭借低免疫原性、精准递送药物、增强药物疗效、靶向炎症部位、协同治疗效果、高效包裹和递送药物等特性,在药物递送领域展现出广阔的应用前景,尤其是在口服药物递送系统中能够显著改善药物传递效率。 植物源胞外囊泡在肌肉骨骼系统疾病中的治疗机制,见图5。"
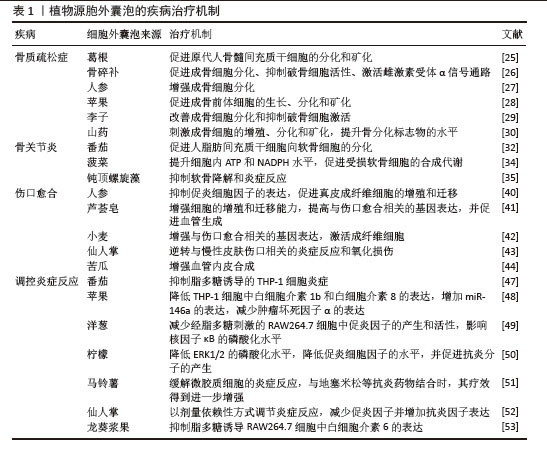
2.2.6 在其他肌肉骨骼系统疾病中的研究 类风湿关节炎是一种常见的自身免疫性疾病,传统治疗手段如非类固醇抗炎药、改善病情抗风湿药、生物制剂和糖皮质激素等,虽能缓解症状、延缓疾病进展,但不良反应明显,还会给患者带来沉重的经济压力。已有研究表明经叶酸修饰的生姜来源胞外囊泡在类风湿关节炎治疗中具有巨大的潜力。在胶原诱导性类风湿关节炎小鼠模型中,生姜来源胞外囊泡能够有效减轻关节炎症和肿胀,改善滑膜炎症以及软骨侵蚀的程度;此外,血清中促炎细胞因子水平也明显下降,骨侵蚀得到了有效抑制[59]。此外,人参来源胞外囊泡能够通过调节炎症信号通路有效抑制促炎细胞因子的产生,减轻肌肉损伤后的炎症反应,加速肌肉组织的修复[60]。有研究团队从西兰花中分离出细胞外囊泡,其能有效负载外源性miRNA并被细胞摄取[61],促进肌腱细胞的增殖和修复。 植物源胞外囊泡的疾病治疗机制汇总,见表1。"
| [1] CAO M, SHENG R, SUN Y, et al. Delivering Microrobots in the Musculoskeletal System. Nanomicro Lett. 2024;16(1):251. [2] GBD 2021 Other Musculoskeletal Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of other musculoskeletal disorders, 1990-2020, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5(11):e670-e682. [3] 张印恩,马铮,倪国骅,等.mFI-5预测老年全膝关节置换术后早期并发症的应用[J].医学研究与战创伤救治,2024, 37(6):593-597. [4] PARK S, RAHAMAN KA, KIM YC, et al. Fostering tissue engineering and regenerative medicine to treat musculoskeletal disorders in bone and muscle. Bioact Mater. 2024;40:345-365. [5] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [6] MAO X, LI T, QI W, et al. Advances in the study of plant-derived extracellular vesicles in the skeletal muscle system. Pharmacol Res. 2024;204:107202. [7] JENSEN WA. The ultrastructure and histochemistry of the synergids of cotton. Am J Bot. 1965;52:238-256. [8] 赵淑举,黄佳欣,李师鹏,等.植物细胞外囊泡研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2024,46(6):1295-1302. [9] 朱珍珠,江睿,廖柳月,等.植物胞外囊泡的结构、生物活性及其在食药递送方面的应用[J].食品工业科技,2022, 43(21):422-432. [10] 赵梦,李思敏,张蕾,等.植物来源囊泡及其生物医学应用研究进展[J].药学学报,2021,56(8):2039-2047+2036. [11] WANG Q, ZHUANG X, MU J, et al. Delivery of therapeutic agents by nanoparticles made of grapefruit-derived lipids. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1867. [12] XU Z, XU Y, ZHANG K, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles (PDEVs) in nanomedicine for human disease and therapeutic modalities. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):114. [13] LIAN MQ, CHNG WH, LIANG J, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: Recent advancements and current challenges on their use for biomedical applications. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022;11(12): 12283. [14] 李俊言,王文苹,张祎,等.植物类中药来源囊泡的研究进展[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2023,52(3):349-360. [15] 蔡鹏,张明真,高博雯.植物源细胞外囊泡在炎症性肠病治疗中的应用[J].现代生物技术研究,2023,1(1):6-11. [16] CALZONI E, BERTOLDI A, CUSUMANO G, et al. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Natural Nanocarriers for Biotechnological Drugs. Processes. 2024;12(12):2938. [17] LANGELLOTTO MD, RASSU G, SERRI C, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: a synergetic combination of a drug delivery system and a source of natural bioactive compounds. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025; 15(3):831-845. [18] KIM J, LI S, ZHANG S, et al. Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022;17(1):53-69. [19] ZENG YB, DENG X, SHEN LS, et al. Advances in plant-derived extracellular vesicles: isolation, composition, and biological functions. Food Funct. 2024;15(23): 11319-11341. [20] KIM SQ, KIM KH. Emergence of Edible Plant-Derived Nanovesicles as Functional Food Components and Nanocarriers for Therapeutics Delivery: Potentials in Human Health and Disease. Cells. 2022; 11(14):2232. [21] DING L, CHANG C, LIANG M, et al. Plant‐Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Emerging Tools for Cancer Therapeutics. Advanced Therapeutics. 2024;7(11):2400256. [22] WANG Y, WANG J, MA J, et al. Focusing on Future Applications and Current Challenges of Plant Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022; 15(6):708. [23] SHAO M, JIN X, CHEN S, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles -a novel clinical anti-inflammatory drug carrier worthy of investigation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;169:115904. [24] 郭丰硕,李美艺,张子腾,等.老年骨质疏松风险预测新标杆—TyG-BMI的诊断潜力[J].中国实验诊断学,2025,29(1): 51-55. [25] ZHAN W, DENG M, HUANG X, et al. Pueraria lobata-derived exosome-like nanovesicles alleviate osteoporosis by enhacning autophagy. J Control Release. 2023;364: 644-653. [26] ZHAO Q, FENG J, LIU F, et al. Rhizoma Drynariae-derived nanovesicles reverse osteoporosis by potentiating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via targeting ERα signaling. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024;14(5): 2210-2227. [27] YANG N, ZHANG X, LI L, et al. Ginsenoside Rc Promotes Bone Formation in Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis In Vivo and Osteogenic Differentiation In Vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6187. [28] SIM Y, SEO HJ, KIM DH, et al. The Effect of Apple-Derived Nanovesicles on the Osteoblastogenesis of Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells. J Med Food. 2023;26(1): 49-58. [29] PARK YS, KIM HW, HWANG JH, et al. Plum-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles Induce Differentiation of Osteoblasts and Reduction of Osteoclast Activation. Nutrients. 2023; 15(9):2107. [30] HWANG JH, PARK YS, KIM HS, et al. Yam-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblast formation and prevent osteoporosis in mice. J Control Release. 2023;355:184-198. [31] 李宜金,黎嘉澔,张海涛,等.关节康片干预软骨稳态保护膝骨关节炎小鼠关节软骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2026,30(12): 2994-3004. [32] YILDIRIM M, ÜNSAL N, KABATAŞ B, et al. Effect of Solanum lycopersicum and Citrus limon-Derived Exosome-Like Vesicles on Chondrogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024;196(1):203-219. [33] LIANG Y, XU X, LI X, et al. Chondrocyte-Targeted MicroRNA Delivery by Engineered Exosomes toward a Cell-Free Osteoarthritis Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020; 12(33):36938-36947. [34] CHEN P, LIU X, GU C, et al. A plant-derived natural photosynthetic system for improving cell anabolism. Nature. 2022; 612(7940):546-554. [35] LIANG F, ZHENG Y, ZHAO C,et al. Microalgae-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Synergize with Herbal Hydrogel for Energy Homeostasis in Osteoarthritis Treatment. ACS Nano. 2025;19(8):8040-8057. [36] 曾斌,梁宇杰,邓志钦,等.细胞外囊泡在治疗膝骨关节炎中的作用与前景[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2023,50(7): 1573-1583. [37] 陈玲玲,程海霞,顾清昕,等.氧疗在伤口愈合中的研究进展[J].护理学,2023, 12(6):1000-1005. [38] CHENG B, FU X. The Role of Stem Cell on Wound Healing After Revascularization-Healing Following Revascularization-Unlocking Skin Potential. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2024;23(1):63-69. [39] LI A, LI D, GU Y, et al. Plant-derived nanovesicles: Further exploration of biomedical function and application potential. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13(8): 3300-3320. [40] YANG S, LU S, REN L, et al. Ginseng-derived nanoparticles induce skin cell proliferation and promote wound healing. J Ginseng Res. 2023;47(1):133-143. [41] KIM M, PARK JH. Isolation of Aloe saponaria-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Investigation of Their Potential for Chronic Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(9):1905. [42] ŞAHIN F, KOÇAK P, GÜNEŞ MY, et al. In Vitro Wound Healing Activity of Wheat-Derived Nanovesicles. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019;188(2):381-394. [43] VALENTINO A, CONTE R, BOUSTA D, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Opuntia ficus-indica Fruit (OFI-EVs) Speed Up the Normal Wound Healing Processes by Modulating Cellular Responses. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(13):7103. [44] 王玮琪,羊月婷,苏志宏,等.植物来源细胞外囊泡在创面修复中作用的研究进展[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2024, 40(12):1199-1204. [45] 丁恺志,龚妍春,李晓诺,等.NLRP3 炎性小体在肌肉骨骼系统疾病中的作用[J].生物工程学报,2024,40(2):337-349. [46] LOU K, LUO H, JIANG X, et al. Applications of emerging extracellular vesicles technologies in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1364401. [47] MAMMADOVA R, MAGGIO S, FIUME I, et al. Protein Biocargo and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Tomato Fruit-Derived Nanovesicles Separated by Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation and Loaded with Curcumin. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(2):333. [48] TRENTINI M, ZANOTTI F, TIENGO E, et al. An Apple a Day Keeps the Doctor Away: Potential Role of miRNA 146 on Macrophages Treated with Exosomes Derived from Apples. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(2):415. [49] KANG SJ, KIM SE, SEO MJ, et al. Suppression of inflammatory responses in macrophages by onion-derived extracellular vesicles. J Ind Eng Chem. 2022;115:287-297. [50] RAIMONDO S, URZÌ O, MERAVIGLIA S, et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of lemon-derived extracellular vesicles are achieved through the inhibition of ERK/NF-κB signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(15):4195-4209. [51] ISHIDA T, KAWADA K, JOBU K, et al. Exosome-like nanoparticles derived from Allium tuberosum prevent neuroinflammation in microglia-like cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2023;75(10):1322-1331. [52] NASELLI F, VOLPES S, CARDINALE PS, et al. New Nanovesicles from Prickly Pear Fruit Juice: A Resource with Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Nutrigenomic Properties. Cells. 2024;13(21):1756. [53] EMMANUELA N, MUHAMMAD DR, IRIAWATI, et al. Isolation of plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles (PDENs) from Solanum nigrum L. berries and Their Effect on interleukin-6 expression as a potential anti-inflammatory agent. PLoS One. 2024; 19(1):e0296259. [54] FENG J, XIU Q, HUANG Y, et al. Plant-Derived Vesicle-Like Nanoparticles as Promising Biotherapeutic Tools: Present and Future. Adv Mater. 2023;35(24):e2207826. [55] LU J, ZHANG Y, YANG X, et al. Harnessing exosomes as cutting-edge drug delivery systems for revolutionary osteoarthritis therapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165: 115135. [56] WANG Q, REN Y, MU J, et al. Grapefruit-Derived Nanovectors Use an Activated Leukocyte Trafficking Pathway to Deliver Therapeutic Agents to Inflammatory Tumor Sites. Cancer Res. 2015;75(12):2520-2529. [57] FANG Z, LIU K. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles as oral drug delivery carriers. J Control Release. 2022;350:389-400. [58] WU P, WU W, ZHANG S, et al. Therapeutic potential and pharmacological significance of extracellular vesicles derived from traditional medicinal plants. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1272241. [59] HAN R, ZHOU D, JI N, et al. Folic acid-modified ginger-derived extracellular vesicles for targeted treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by remodeling immune microenvironment via the PI3K-AKT pathway. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025; 23(1):41. [60] WANG X, XIN C, ZHOU Y, et al. Plant-Derived Vesicle-like Nanoparticles: The Next-Generation Drug Delivery Nanoplatforms. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(5):588. [61] DEL POZO-ACEBO L, LÓPEZ DE LAS HAZAS MC, TOMÉ-CARNEIRO J, et al. Therapeutic potential of broccoli-derived extracellular vesicles as nanocarriers of exogenous miRNAs. Pharmacol Res. 2022;185:106472. |
| [1] | Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming. Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [2] | Zeng Xuan, Weng Rui, Ye Shicheng, Tang Jiadong, Mo Ling, Li Wenchao. Two lumbar rotary manipulation techniques in treating lumbar disc herniation: a finite element analysis of biomechanical differences [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [3] | Cheng Qisheng, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xiao Yang, Zhang Chenwei, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [4] | Liu Wenlong, Dong Lei, Xiao Zhengzheng, Nie Yu. Finite element analysis of tibial prosthesis loosening after fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [5] | Chen Long, Wang Xiaozhen, Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin. Biomechanical performance of short-segment screw fixation combined with expandable polyetheretherketone vertebral body replacement in osteoporotic vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [6] | Zhang Nan, Meng Qinghua, Bao Chunyu. Characteristics and clinical application of ankle joint finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2343-2349. |
| [7] | Chen Qiuhan, Yang Long, Yuan Daizhu, Wu Zhanyu, Zou Zihao, Ye Chuan. Peri-knee osteotomy for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: optimization of treatment strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2303-2312. |
| [8] | Zhang Zizheng, Luo Wang, Liu Changlu. Application value of finite element analysis on unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for medial knee compartmental osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2313-2322. |
| [9] |
Dong Chunyang, Zhou Tianen, Mo Mengxue, Lyu Wenquan, Gao Ming, Zhu Ruikai, Gao Zhiwei.
Action mechanism of metformin combined with Eomecon chionantha Hance dressing in treatment of deep second-degree burn wounds#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013.
|
| [10] | Li Qingbin, Lin Jianhui, Huang Wenjie, Wang Mingshuang, Du Jiankai, Lao Yongqiang. Bone cement filling after enlarged curettage of giant cell tumor around the knee joint: a comparison of subchondral bone grafting and non-grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [11] | Cao Yong, Teng Hongliang, Tai Pengfei, Li Junda, Zhu Tengqi, Li Zhaojin. Interactions between cytokines and satellite cells in muscle regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1808-1817. |
| [12] | Hu Xiongke, Liu Shaohua, Tan Qian, Liu Kun, Zhu Guanghui. Shikonin intervention with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves microstructure of femur in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [13] | Cai Ziming, Yu Qinghe, Ma Pengfei, Zhang Xin, Zhou Longqian, Zhang Chongyang, Lin Wenping. Heme oxygenase-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1624-1631. |
| [14] | He Jiale, Huang Xi, Dong Hongfei, Chen Lang, Zhong Fangyu, Li Xianhui. Acellular dermal matrix combined with adipose-derived stem cell exosomes promotes burn wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1699-1710. |
| [15] | Xia Linfeng, Wang Lu, Long Qianfa, Tang Rongwu, Luo Haodong, Tang Yi, Zhong Jun, Liu Yang. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate blood-brain barrier damage in mice with septic encephalopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1711-1719. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||