Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (20): 5201-5213.doi: 10.12307/2026.154
Previous Articles Next Articles
Puerarin-loaded injectable double-network hydrogel for promoting skin wound healing
Yao Yinxuan, Wen Suru, Chen Chaosheng, Wen Xin, Feng Keying, Kuang Zaoyuan, Zhang Wen
- School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
-
Accepted:2025-04-24Online:2026-07-18Published:2025-11-27 -
Contact:Zhang Wen, PhD, Associate professor, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China Kuang Zaoyuan, PhD, Professor, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Yao Yinxuan, Master candidate, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Guangdong Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 20251096 (to ZW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yao Yinxuan, Wen Suru, Chen Chaosheng, Wen Xin, Feng Keying, Kuang Zaoyuan, Zhang Wen. Puerarin-loaded injectable double-network hydrogel for promoting skin wound healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5201-5213.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
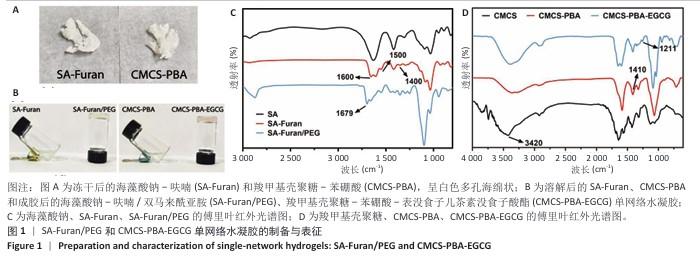
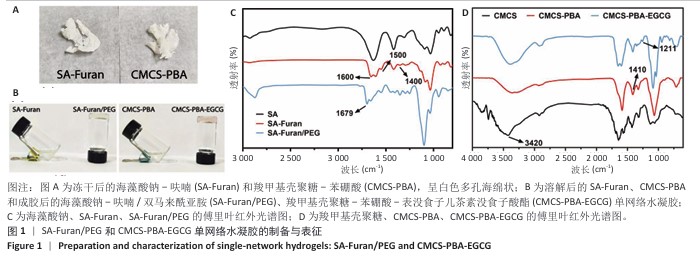
2.1 单网络水凝胶的表征结果 海藻酸钠-呋喃冻干后为白色海绵状固体(图1A),加水溶解后为透明液体(图1B)。海藻酸钠-呋喃中的呋喃和马来酰亚胺基团之间通过Diels-Alder(DA)点击化学反应交联,制备出SA-Furan/PEG单网络水凝胶(图1B)。对冻干后的海藻酸钠-呋喃和SA-Furan/PEG进行傅里叶红外光谱检测,结果如图1C。经过呋喃基团修饰后海藻酸钠在1 400,1 500,1 600 cm-1处出现新的峰,代表呋喃基团的伸缩振动峰,说明海藻酸钠-呋喃制备成功;DA点击化学反应后,位于1 500 cm-1的呋喃吸收峰消失,1 679 cm-1处出现C=O特征峰,说明反应完成SA-Furan/PEG单网络水凝胶制备成功。 羧甲基壳聚糖-苯硼酸中的羟基和表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯中的邻苯二酚结构之间发生交联,制备出CMCS-PBA-EGCG单网络水凝胶(图1B)。对冻干后的羧甲基壳聚糖-苯硼酸和CMCS-PBA-EGCG进行傅里叶红外光谱检测,结果如图1D。在1 000-1 150 cm-1 波数范围内显示出强峰,这是糖结构的特征峰;波数在 3 420 cm-1 附近的峰归属于-OH 和N-H的伸缩振动,在1 410 cm-1波数处的峰是B-O伸缩振动引起,说明羧甲基壳聚糖-苯硼酸制备成功;利用表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯交联后,在1 211 cm-1波数处出现芳香族O-H伸缩振动峰,说明表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯交联成功,CMCS-PBA-EGCG单网络水凝胶制备成功。 "

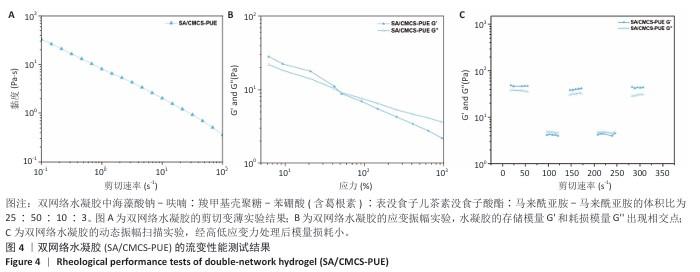
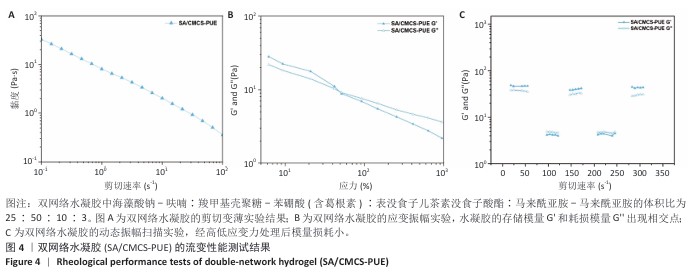
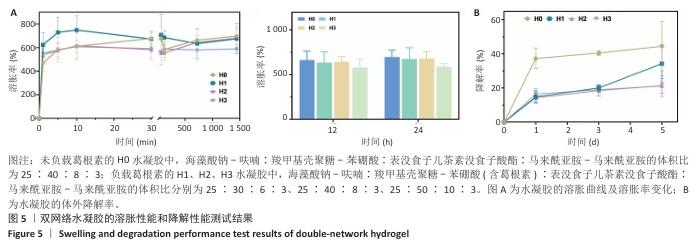
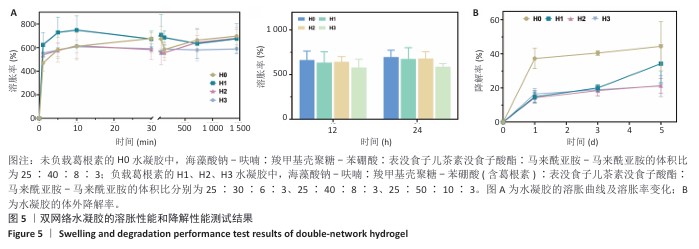
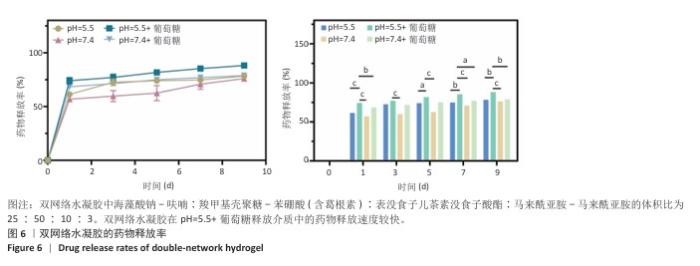
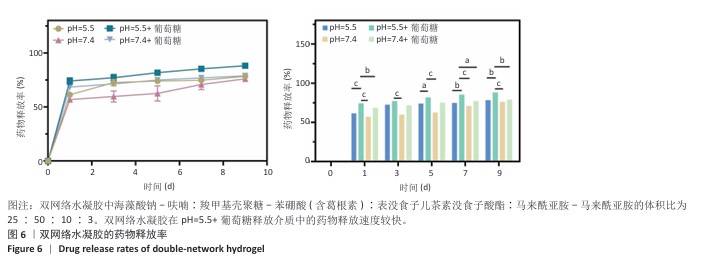
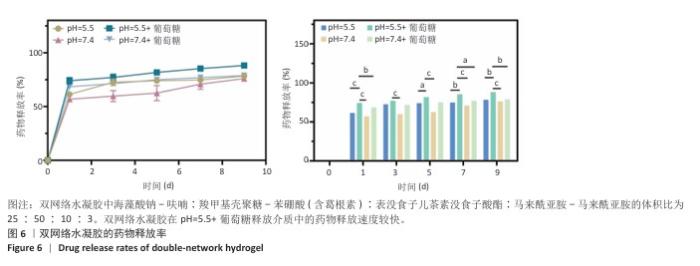
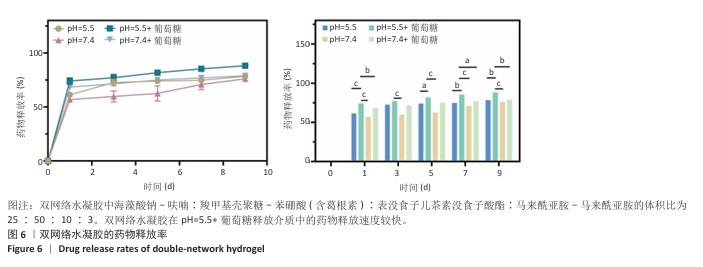
2.2 双网络水凝胶的表征结果 双网络水凝胶成胶结果如图2A,B,H1、H2、H3和H0均能凝固成胶,并且凝固时间在3-5 min内。根据葛根素溶液质量浓度(0.5 mg/mL)可计算出,H1水凝胶中葛根素质量浓度为0.234 mg/mL,H2水凝胶葛根素质量浓度为0.263 mg/mL,H3水凝胶中葛根素质量浓度为0.284 mg/mL。 使用1 mL注射器吸取H1、H2、H3和H0水凝胶观察其可注射性,结果如图2C所示,表明双网络水凝胶具有良好的可注射性。将H1、H2、H3和H0水凝胶置于人体手指关节上,通过运动关节观察其黏附性,如图2D所示,表明双网络水凝胶具有良好的组织黏附性。 使用扫描电镜观察冻干后水凝胶的微观形态,单网络与双网络水凝胶的内部形貌如图3所示。3种水凝胶均有相互连通的三维微孔样结构,单网络水凝胶SA-Furan/PEG和CMCS-PBA-EGCG内部孔数少、孔径大;双网络水凝胶H3中的微孔密集、孔数多、孔径小。 使用流变仪观察了双网络水凝胶的力学性能。通过应变振幅扫描实验观察到H3水凝胶从溶胶到凝胶的转变,如图4A存储模量(G’)和耗损模量(G’’)的相交出现说明水凝胶状态的成功转变。H3水凝胶的可注射性与其剪切变薄行为相关联,如图4B所示。另外,在应变振幅扫描实验的基础上,使用1%和1 000%的连续变换应变扫描观察了水凝胶的自愈合性,如图4C,在高低应变转换后H3水凝胶的模量恢复且损失不大,表明该水凝胶具有良好的自愈合性。 水凝胶的溶胀能力会直接影响创面渗出液的吸收率和敷料体积变化,是水凝胶作为创面敷料必须考虑的问题。如图5A,在12,24 h内,各组水凝胶皆能达到较高的溶胀率,并在一定时间内保持稳定,最后趋于平衡。各组之间水凝胶溶胀率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。使用含Ⅱ型胶原酶的PBS(1.25 U/mL)作为降解液,对不同比例的双网络水凝胶进行为期5 d的体外降解实验,结果见图5B。H0、H1、H2、H3水凝胶均可进行自身降解,与其余水凝胶相比,H0水凝胶降解快,在第1天的降解率即可达到40%;H1、H2、H3水凝胶的体外降解率相近,降解缓慢,都能够保持稳定的形态,有利于对创面的持续保护和药物释放。 在不同的释放介质中,H3水凝胶中葛根素的释放速度不同。如图6所示,与其他释放介质相比,在pH=5.5、葡萄糖存在的释放介质中,葛根素的释放较快,在第1天时药物释放率能够达到74%,说明H3水凝胶具有pH值和葡萄糖的双响应性。 可从图7看出,SA-Furan/PEG、CMCS-PBA-EGCG和H3水凝胶皆具有抑制大肠杆菌生长的能力,能够保护创面免受感染损害。 "

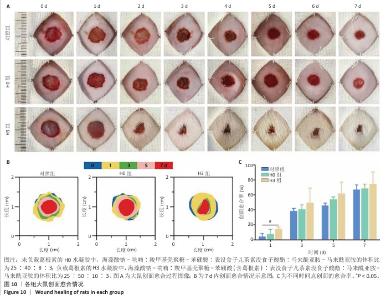
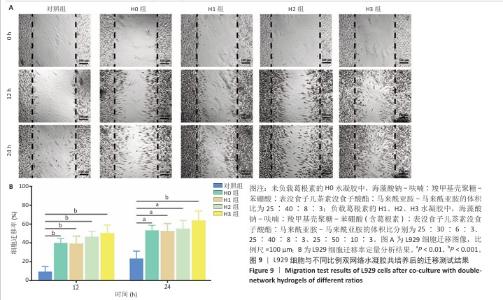
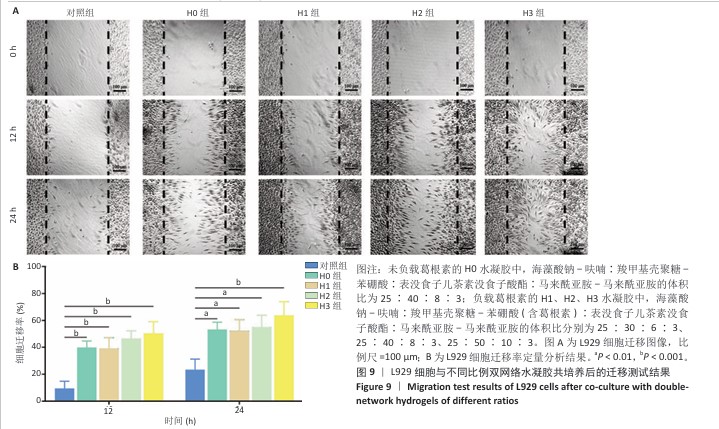
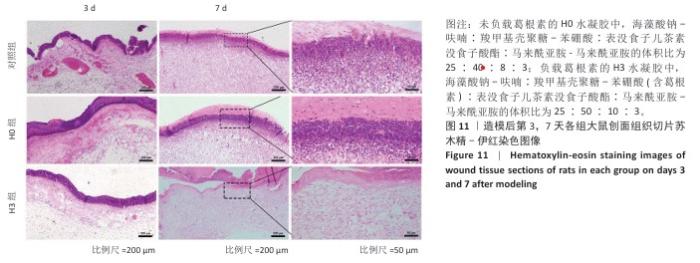
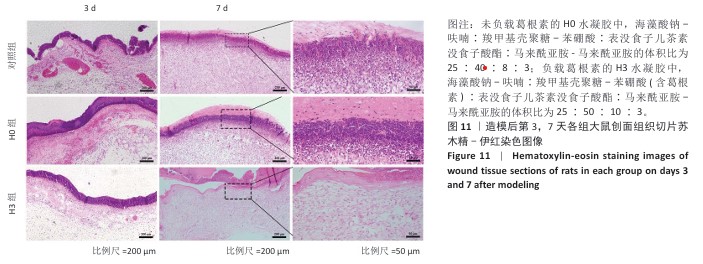
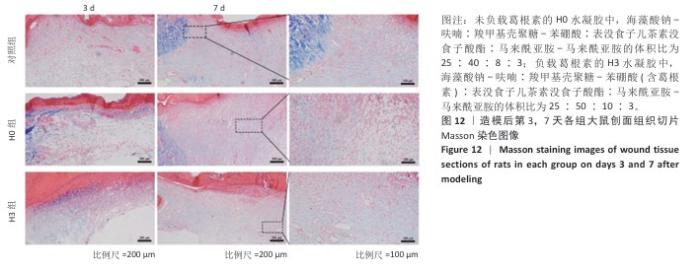
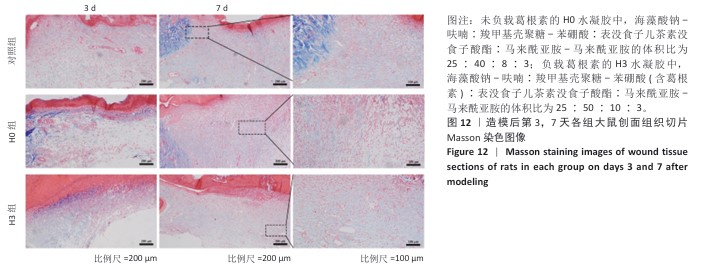
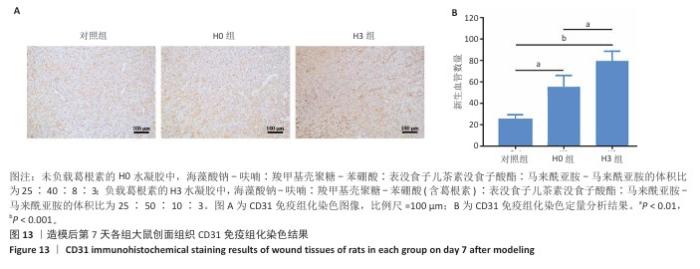
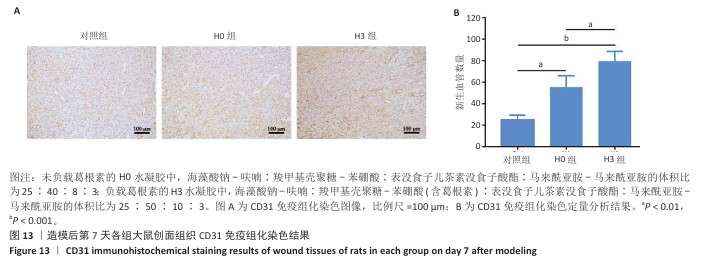
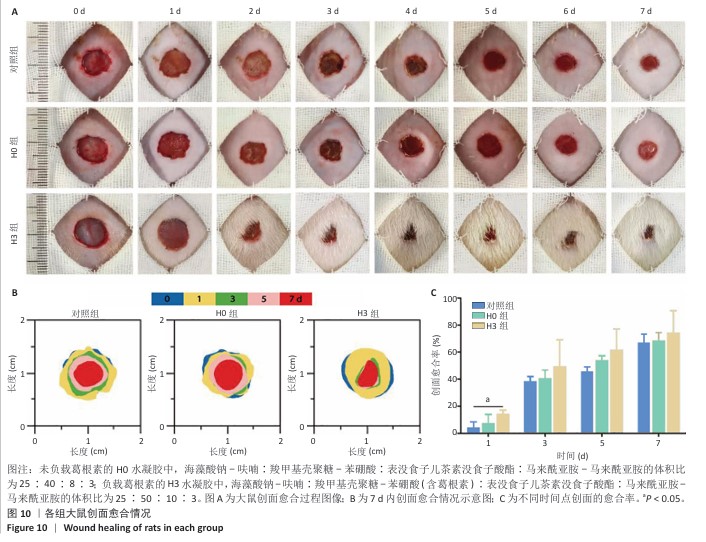
2.4 双网络水凝胶对大鼠创面愈合的影响 2.4.1 实验动物数量分析 9只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.4.2 创面愈合情况 如图10A所示,随着时间的延长,各组创面逐渐愈合,相较于对照组,H0与H3组创面愈合速率较快。由图10B,C可知,造模后第7天,H0组创面愈合率达60%左右,H3组创面愈合率达约70%,表明双网络水凝胶有较好的促创面愈合效果,负载葛根素的H3水凝胶表现出更佳的促愈合效果。 2.4.3 创面组织形态观察 各组大鼠创面组织苏木精-伊红染色图像,见图11。造模后第3天,H3组表皮基底层较H0组染色深,基底层由于细胞质内富含游离核糖体而呈嗜碱性,说明H3水凝胶处理后的组织基底细胞数量多,利于皮肤创伤愈合。造模第7天,3组均有表皮角质层增生现象,H0组、H3组较对照组的增生速度快,并且H3组组织角质层厚度大于其他2组,说明皮肤修复即将完成。表皮和真皮修复结果表明,双网络水凝胶组能够更好地促进皮肤创面愈合,并且H3水凝胶的促进效果更佳。 各组大鼠创面组织Masson染色图像,见图12。造模后第3天,H3组蓝色胶原纤维已开始生成并累积。造模后第7天,H3组皮肤组织中的胶原纤维有序且紧密地堆积,其余2组胶原纤维仍然是无序且稀疏地排列,说明H3水凝胶能够促进创面中的胶原纤维生成与累积。 2.4.4 创面组织CD31免疫组化染色结果 各组大鼠创面组织CD31免疫组化染色图像,见图13A。CD31免疫组化染色定量分析结果显示,H0组、H3组新生血管数量多于对照组(P < 0.01,P < 0.001),H3组新生血管数量多于H0组(P < 0.01),见图13B。 "
| [1] STAN D, TANASE C, AVRAM M, et al. Wound healing applications of creams and “smart” hydrogels. Exp Dermatol. 2021;30(9):1218-1232. [2] YILDIRIMER L, THANH NTK, SEIFALIAN AM. Skin regeneration scaffolds: a multimodal bottom-up approach. Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(12):638-648. [3] VELNAR T, BAILEY T, SMRKOLJ V. The wound healing process: an overview of the cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Int Med Res. 2009;37(5):1528-1542. [4] GURTNER GC, WERNER S, BARRANDON Y, et al. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008;453(7193):314-321. [5] PARANI M, LOKHANDE G, SINGH A, et al. Engineered nanomaterials for infection control and healing acute and chronic wounds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(16):10049-10069. [6] KONDO T, ISHIDA Y. Molecular pathology of wound healing. Forensic sci int. 2010;203(1-3):93-98. [7] QI L, ZHANG C, WANG B, et al. Progress in hydrogels for skin wound repair. Macromol Biosci. 2022;22(7):2100475. [8] 宋杏丽.创面修复的研究进展与启示[J].中国现代医药杂志,2024, 26(8):1-4. [9] 林锦涛,韩晓璐,洪晓轩,等.医用湿性敷料在创面修复的应用及研究进展[J].中国药学杂志,2025,60(4):319-325. [10] 符传亮,张雯静,王任远,等.功能化水凝胶在创面修复应用的研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2025,22(1):64-69,81. [11] 高仪轩,周彪,巴特,等. 新型敷料在创面修复中的应用与进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2022,17(1):68-71. [12] WANG J, CHEN Y, ZHOU G, et al. Polydopamine-coated Antheraea pernyi (A. pernyi) silk fibroin films promote cell adhesion and wound healing in skin tissue repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(38): 34736-34743. [13] YANG J, ZENG WN, XU P, et al. Glucose-responsive multifunctional metal–organic drug-loaded hydrogel for diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2022;140:206-218. [14] KARAMI F, SABER-SAMANDARI S. Synthesis and characterization of a novel hydrogel based on carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate with the ability to release simvastatin for chronic wound healing. Biomed Mater. 2023;18(2):025001. [15] WU J, ZHU J, HE C, et al. Comparative study of heparin-poloxamer hydrogel modified bFGF and aFGF for in vivo wound healing efficiency. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(29):18710-18721. [16] CHEN Y, ZHANG Y, CHANG L, et al. Mussel-inspired self-healing hydrogel form pectin and cellulose for hemostasis and diabetic wound repairing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;246:125644. [17] WANG T, YI W, ZHANG Y, et al. Sodium alginate hydrogel containing platelet-rich plasma for wound healing. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023;222:113096. [18] XU Q, SIGEN A, GAO Y, et al. A hybrid injectable hydrogel from hyperbranched PEG macromer as a stem cell delivery and retention platform for diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2018;75:63-74. [19] DONG Y, HASSAN WU, KENNEDY R, et al. Performance of an in situ formed bioactive hydrogel dressing from a PEG-based hyperbranched multifunctional copolymer. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):2076-2085. [20] YU Q, SUN H, YUE Z, et al. Zwitterionic polysaccharide‐based hydrogel dressing as a stem cell carrier to accelerate burn wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(7):2202309. [21] CHU W, WANG P, MA Z, et al. Lupeol-loaded chitosan-Ag+ nanoparticle/sericin hydrogel accelerates wound healing and effectively inhibits bacterial infection. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;243:125310. [22] LIU Y, CAI S, SHU XZ, et al. Release of basic fibroblast growth factor from a crosslinked glycosaminoglycan hydrogel promotes wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2007;15(2):245-251. [23] SARI MHM, COBRE AF, PONTAROLO R, et al. Status and future scope of Soft nanoparticles-based hydrogel in Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):874. [24] ZHAO L, NIU L, LIANG H, et al. pH and glucose dual-responsive injectable hydrogels with insulin and fibroblasts as bioactive dressings for diabetic wound healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(43): 37563-37574. [25] GUO B, LIANG Y, DONG R. Physical dynamic double-network hydrogels as dressings to facilitate tissue repair. Nat Protoc. 2023;18(11): 3322-3354. [26] 朱琳,陈强,徐昆.高强度双网络水凝胶的增韧机理[J].化学进展, 2014,26(6):1032-1038. [27] 李立清,钟秀敏,章礼旭,等.双网络水凝胶制备及其力学改性[J].化学进展,2023,35(11):1674-1685. [28] DOU C, LI Z, LUO Y, et al. Bio-based poly (γ-glutamic acid)-gelatin double-network hydrogel with high strength for wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;202:438-452. [29] COSTA AMS, MANO JF. Extremely strong and tough hydrogels as prospective candidates for tissue repair–A review. Eur Polym J. 2015; 72:344-364. [30] LIU H, LI Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Novel diabetic foot wound dressing based on multifunctional hydrogels with extensive temperature-tolerant, durable, adhesive, and intrinsic antibacterial properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(23):26770-26781. [31] LI Y, WANG H, NIU Y, et al. Fabrication of CS/SA double‐network hydrogel and application in pH‐controllable drug release. ChemistrySelect. 2019;4(48):14036-14042. [32] WAN J, LIANG Y, WEI X, et al. Chitosan-based double network hydrogel loading herbal small molecule for accelerating wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;246:125610. [33] 张璨琁,冯雨金,贺启元,等.双网络水凝胶在医药领域的应用及研究进展[J].组织工程与重建外科,2024,20(1):135-141. [34] 朱鹏,张兴群,王云龙,等.海藻酸盐医用敷料研究进展[J].上海纺织科技,2020,48(11):13-18. [35] 王蕾,吕康宁,李文军,等.两种不同海洋生物材料对大鼠急性创面修复效果的研究[J].海洋科学,2023,47(10):87-93. [36] 吴沥豪,陈功,任康,等.羧甲基壳聚糖基生物医用材料降解代谢行为的研究进展[J].高分子通报,2023,36(2):148-157. [37] 陈锐,王语馨,鲍凡凡,等.壳聚糖在医用敷料领域中的研究进展[J].现代丝绸科学与技术,2020,35(4):36-40. [38] KIM AR, LEE SL, PARK SN. Properties and in vitro drug release of pH-and temperature-sensitive double cross-linked interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels based on hyaluronic acid/poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) for transdermal delivery of luteolin. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118:731-740. [39] FAN X, HUANG J, ZHANG W, et al. A multifunctional, tough, stretchable, and transparent curcumin hydrogel with potent antimicrobial, antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and angiogenesis capabilities for diabetic wound healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(8):9749-9767. [40] JIN SE, SON YK, MIN BS, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of constituents isolated from Pueraria lobata roots. Arch Pharm Res. 2012;35:823-837. [41] LIU CM, MA JQ, SUN YZ. Puerarin protects rat kidney from lead-induced apoptosis by modulating the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012;258(3):330-342. [42] 杨敏,丁传波,马葭葭.葛根素药理活性研究进展[J].人参研究, 2021,33(6):62-64. [43] 刘春丽,闫雨娟,莫礼文,等.葛根素对RAW264.7细胞破骨分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(32):5114-5119. [44] 孙姝婵,龚迪菲,袁天翊,等.葛根素通过改善线粒体呼吸功能减轻血管内皮细胞氧化损伤[J].药学学报,2022,57(5):1352-1360. [45] 郑彩云,戴亨纷,陈莉娜.葛根的药食功效和现代应用探析[J].中国现代中药,2024,26(10):1815-1822. [46] 曹盼,张樱山,魏学明,等.葛根素药理作用研究新进展[J].中成药,2021,43(8):2130-2134. [47] 李欢,张相安.葛根在治疗炎症性肠病中的作用机制和应用研究进展[J].中草药,2025,56(4):1428-1439. [48] 徐珊珊,阎丽颖,范光艳.湿性愈合技术对难愈性创面护理的应用效果[J].新疆中医药,2024,42(2):58-59. [49] 程海霞,陈玲玲,鲍丽超.现代伤口敷料在慢性伤口护理中的研究进展[J].全科护理,2025,23(5):825-827. [50] ANVERY N, SELIM A, KHACHEMOUNE A. The Role of Puerarin in Chronic Wounds: A Review of its Mechanism of Action and Potential Novel Applications. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2024;23(4):492-496. [51] 周晶,吴达莹,杨清,等.葛根素水凝胶对糖尿病大鼠创面血管形成及愈合的影响[J].中药新药与临床药理,2023,34(7):921-928. [52] NGUYEN LTH, AHN SH, CHOI MJ, et al. Puerarin improves dexamethasone-impaired wound healing in vitro and in vivo by enhancing keratinocyte proliferation and migration. Appl Sci. 2021;11(19):9343. [53] YADAV JP, VERMA A, PATHAK P, et al. Phytoconstituents as modulators of NF-κB signalling: Investigating therapeutic potential for diabetic wound healing. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;177:117058. [54] 李蕾,林放,施琳颖,等.缓释生长因子羧甲基壳聚糖支架抑菌功能的研究[J].重庆医学,2020,49(8):1212-1217. [55] 陈泽楚,李婷,陈锦涛.O-羧甲基壳聚糖的制备及其抗菌性能研究[J].化工新型材料,2016,44(9):175-177. [56] OLANIPEKUN EO, AYODELE O, OLATUNDE OC, et al. Comparative studies of chitosan and carboxymethyl chitosan doped with nickel and copper: Characterization and antibacterial potential. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021; 183:1971-1977. [57] 李森池,张扬.羧甲基壳聚糖/纳米银抗菌剂的制备及缓释性能研究[J].化工新型材料,2024,52(1):274-279. [58] 刘琳,班雨,魏悦,等.多功能海藻酸钠海绵的制备及抗菌、止血性能分析[J].分析化学,2021,49(12):1986-1994. [59] 王悦,徐国平,仇巧华,等.聚乙烯醇/海藻酸钠载药复合水凝胶的制备及其抗菌性能[J].现代纺织技术,2023,31(3):145-154. |
| [1] | Zhao Zheng. Diselenium contained polyurethane coatings with dual functions of anticoagulation and drug release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 414-423. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||