Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (24): 5187-5194.doi: 10.12307/2025.901
Previous Articles Next Articles
Prostaglandin E2 in repair of skeletal muscle injury
Li Xinlei
- School of Physical Education, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang 453007, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-09-20Accepted:2024-11-12Online:2025-08-28Published:2025-01-25 -
About author:Li Xinlei, MS, Lecturer, School of Physical Education, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang 453007, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Xinlei . Prostaglandin E2 in repair of skeletal muscle injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5187-5194.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
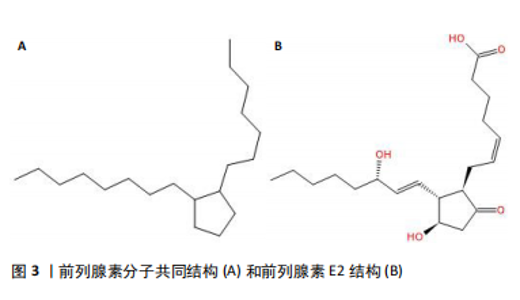
2.1 前列腺素概述 2.1.1 结构 前列腺素(prostaglandin,PG)广泛存在于动物和人体各组织和体液中,是由一类不饱和脂肪酸组成的具有多种生理活性的类激素脂质化合物[6]。前列腺素在体内由花生四烯酸(arachidonic acid)所合成,结构上为一个五元脂肪环和2条侧链(上侧链7个碳原子,下侧链8个碳原子)构成的二十碳不饱和脂肪酸。根据五元脂肪环上取代基(主要是羟基和氢)的不同,将前列腺素分为A、B、C、D、E、F、G、H和Ⅰ等类型,分别用PGA、PGB、PGC、PGD、PGE、PGF,PGH和PGI等表示,其右下角数字则代表侧链的碳碳双键数[7-8]。在前列腺素类化合物中,E型前列腺素(PGE),特别是来自花生四烯酸的前列腺素E2,在动物体内发现最广泛,在体内产生最广泛,表现出的作用最广泛。各前列腺素亚型分子共同结构和前列腺素E2结构见图3。"
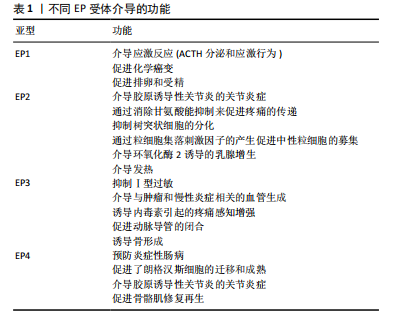
2.1.2 合成 前列腺素是由二十碳不饱和脂肪酸——花生四烯酸经一系列酶促代谢反应产生的一类脂质物质。花生四烯酸在各种生理和病理刺激下经磷脂酶A2(phopholipaseA2,PLA2)催化,由细胞膜膜磷脂释放,在前列腺素H合成酶的环氧化活性和过氧化活性的作用下,转变为前列腺素中间代谢产物PGH2,然后经过下游末端的前列腺素合成酶mPGES-1、mPGES-2和cPGES的催化作用代谢生成前列腺素E2。环氧化酶(cyclooxygenase,COX)是前列腺素合成过程中的关键酶,有COX-1和COX-2两种同工型,以同源二聚体或异源二聚体的形式存在于内质网膜上和核膜上[9-11]。COX-1和COX-2在功能上既有差别,又相互联系,同时参与维持人体内环境稳态和发生炎症时前列腺素的合成过程。mPGES-1主要与COX-2联合以增加前列腺素E2的产生,特别是在炎症因子的刺激条件下,生成的前列腺素E2最后由多药耐药相关蛋白4负责将其转运到细胞外[12-13]。 2.1.3 受体 前列腺素E2通常作用于一组G蛋白偶联受体,即EP1,EP2,EP3,EP4。前列腺素E2同4种受体亚型和EP3亚型的多个剪接亚体可以引起发热、疼痛和炎症等多种反应(表1)。EP亚型在信号转导、组织定位和表达调控方面各有所差异。前列腺素E2受体的这种分子结构和生化异质性使得前列腺素E2成为最广泛通用的前列腺素[14]。前列腺素E2和各种亚型的EP受体结合的Kd值一般在1-40 nmol/L。这些EP受体在不同的细胞类型上"
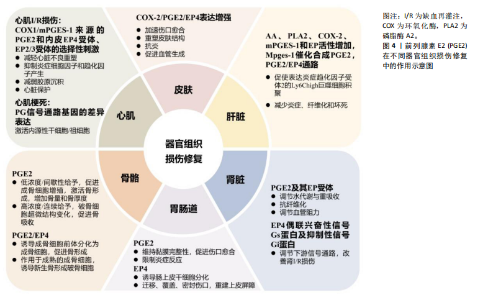
有不同的信号通路和不同的表达模式,每个EP受体的下游功能反映了其耦合的细胞内信号机制:EP1通过Gq蛋白激活磷脂酶C动员细胞内Ca2+,EP2和EP4通过兴奋性G蛋白(stimulatory G protein,Gs)增加环磷酸腺苷(cyclic adenosine monophosphate,cAMP)产生以激活蛋白激酶A,以及EP3通过Gi抑制腺苷环化酶(从而减少环磷酸腺苷)和引起Ca2+动员和磷酸肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidy linositol 3-kinase,PI3K)激活。EP2和EP4已被证实通过β-抑制素途径激活PI3K[15]。 EP4是体内分布和作用最为广泛的EP受体,它作为一种G蛋白偶联受体,其N末端位于胞外,C末端位于胞内,中段为7个跨膜螺旋结构、3个细胞外环和3个细胞内环,胞浆面的第3个环与兴奋性G蛋白偶联,胞外第2环的N-糖基化位点为与配体前列腺素E2结合的重要位置。EP4受体的C末端在所有的前列腺素E2受体中最长。参与跨膜信息传递的G蛋白由α、β和γ 3个亚单位组成,与配体结合后,GTP会与α亚单位结合,而后Gα则与Gβ、Gγ分离。在内源性配体前列腺素E2的刺激下,EP4诱导细胞中环磷酸腺苷水平升高,环磷酸腺苷随后激活蛋白激酶A,蛋白激酶A再使得下游蛋白磷酸化[16-17]。 2.2 前列腺素E2在不同器官组织损伤修复中的作用 近年来的研究已证实前列腺素E2除骨骼肌外还可以增强其他器官组织损伤后的再生和修复,而使用非类固醇抗炎药降低前列腺素E2水平通常对组织修复过程产生不良影响。 在皮肤伤口模型中,皮肤受到损伤后COX-2/PGE2/EP4的表达增强,前列腺素E2水平升高可加速皮肤伤口愈合过程,并重塑具有新毛囊和皮脂腺受伤部位的皮肤结构,还具有明显的抗炎和促血管生成作用。心肌缺血再灌注损伤时,COX1/mPGES-1来源的前列腺素E2与内皮EP4受体减轻心脏不良重塑,抑制炎症细胞因子和趋化因子的产生以及减弱胶原沉积来改善缺血再灌注损伤后的心脏功能。此外EP2/3受体的选择性刺激也显示出具有针对缺血再灌注损伤的心脏保护效果[18]。前列腺素信号通路基因表达在心肌梗死中呈现差异表达和变化,前列腺素E2可激活内源性干细胞/祖细胞,促进梗死后心肌再生[19]。在肝损伤期间,AA、磷脂酶A2、COX-2、mPGES-1和EP的活性均显著增加[20]。mPGES-1催化合成前列腺素E2通过PGE2/EP4信号通路促使肝脏内表达炎症趋化因子受体2(CCR2)的Ly6Chigh巨噬细胞积聚来调控肝脏组织修复。前列腺素E2可以通过减少肝脏炎症、纤维化、坏死等来加速肝缺血再灌注损伤的修复[21]。肾细胞产生的前列腺素E2参与调节水分子的代谢与重吸收。水、钠转运,肾小球过滤和血管阻力也受前列腺素E2及其4个EP受体调节[22]。EP4通过偶联兴奋性信号Gs蛋白及抑制性信号Gi蛋白,调节下游多种信号通路,参与各种生理及病理生理过程,与肾功能密切相关,可显著改善肾缺血再灌注损伤。前列腺素E2在急性肾损伤模型中也有着抗纤维化的功能[23]。前列腺素E2可以通过维持黏膜完整性、促进伤口愈合和限制炎症反应来保护胃肠道[24]。肠道损伤时,局部高水平的前列腺素E2可以通过EP4诱导肠上皮干细胞分化为伤口相关上皮细胞,然后伤口相关上皮细胞迁移以覆盖和密封伤口床以重建上皮屏障[25-26]。前列腺素E2是骨代谢过程中的重要调节物质,对骨骼肌组织的修复和再生具有合成代谢作用。研究发现低浓度的前列腺素E2可促进成骨细胞增殖,而较高浓度前列腺素E2则使破骨细胞超微结构变化并促进骨吸收[27]。连续给予前列腺素E2可明显刺激骨吸收,而间歇性给予则可激活骨形成并增加骨量和厚度。PGE2-EP4通过诱导成骨细胞前体分化为成骨细胞促进骨的形成,该信号通路后续可再作用于成熟的成骨细胞,并诱导新生骨形成破骨细胞[28]。前列腺素E2在不同器官组织损伤修复中的作用示意图,见图4。 2.3 骨骼肌损伤修复过程[29-30] 损伤后,骨骼肌大致经历炎症、修复再生和纤维化3个复杂阶段。骨骼肌修复过程中,肌卫星细胞被激活,增殖、分化、形成肌管并与肌纤维融合,以恢复肌肉结构与功能[30]。前列腺素E2作为脂质炎性分子全程参与其中,肌肉损伤初期,机体合成并分泌前列腺素E2激活肌卫星细胞促进其增殖,前列腺素E2已被证明通过影响表皮生长因子受体信号通路促进细胞增殖,通过Bcl-2和核因子kB抑制细胞凋亡,通过诱导血管内皮生长因子促进血管生成,进而多方面促进肌肉再生[5]。 2.4 前列腺素E2促进骨骼肌修复再生的机制 2.4.1 前列腺素E2通过CREB-MPP7-AMOT轴控制肌肉干细胞的增殖和自我更新能力 在肌肉再生过程中前列腺素E2发挥作用主要是通过EP4受体实现的。EP4在肌卫星细胞中稳定表达,而在分化的成肌细胞中逐渐降低到可忽略不计的水平。EP4主要是和激活型G蛋白α偶联,在前列腺素E2刺激下,诱导细胞中环磷酸腺苷水平升高[31]。环磷酸腺苷水平升高激活蛋白激酶A,蛋白激酶A使得下游蛋白磷酸化,其中多数是被称为效应元件结合因子(cAMP response element binding protein,CREBP)的核转录因子[32]。 CREB转录因子家族,由CREB1、CREM和ATF1组成,控制肌肉的发育、生长和存活。CREB1在Ser133位点上的磷酸化以及CREM和ATF1在类似丝氨酸上的磷酸化(统称为pCREB)启动了辅助因子的招募和基因激活的转录机制。它们的转录活性可以从其磷酸化状态中推断出来,A-CREB高度选择性抑制CREB家族。在成人肌肉中,CREB能直接起作用防止肌肉纤维死亡[33]。细胞的自我更新即干细胞具有通过分裂产生保留干细胞特性子细胞维持终"

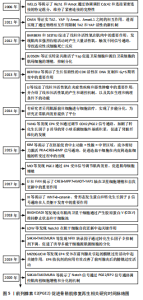
生多分化潜能的能力。CREB活性在静止培养的肌卫星细胞和成肌细胞中较高,赋予了卫星细胞增殖和自我更新的潜能,但在分化的细胞中较低。 为确定CREB的靶点,LI等[34]重点研究了其下调的基因,考虑到干细胞极性,研究人员选择检测膜相关鸟苷酸激酶(MAGUK)p55亚家族成员7(membrane protein,palmitoylated 7,maguk p55 subfamily member 7,MPP7),对卫星细胞来源成肌细胞的染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)分析证实了pCREB与MPP7启动子中的两个半CRE位点结合;检测MPP7在卫星细胞中的亚细胞分布,在肌纤维分离后,MPP7立刻定位于卫星细胞-肌纤维接触的部位(即顶端侧);三维重建证实,MPP7信号优先定位于顶端,大部分被排除在ITGB1+基底侧,但在细胞核中也有所分布;在A-CREB卫星细胞中MPP7水平则低到无法检测到的,并且在维持顶端极性方面存在缺陷。肌生成标记物PAX7、MYOD1、MYOG和肌球蛋白重链(MHC)分别代表干细胞、祖细胞、肌细胞和分化的肌细胞。结合以上指标与A-CREB卫星细胞相比,表达载体卫星细胞中MPP7的强制表达增加了SC簇的大小,并扩大了PAX7+ MYOD1+和PAX7+MYOD1-细胞组分;在WT卫星细胞中,强制表达MPP7没有改变SC簇的大小,但显著增加了PAX7+MYOD1+和PAX7+MYOD1-细胞组分;MPP7恢复了A-CREB卫星细胞的增殖和自我更新能力[34]。上述实验可证明MPP7是卫星细胞中CREB的主要功能靶点,在肌肉再生过程中卫星细胞增殖和生命进程中发挥作用。 WELLS等[35]通过使用293T细胞进行的共免疫共沉淀(co-IP)蛋白质组学分析,检测出含有MPP7、AMOT、AMOTL1和AMOTL2的蛋白复合物。LI等[34]又检测了在对照组和A-CREB 卫星细胞中的AMOT定位,与MPP7一样,AMOT主要定位于静止的卫星细胞顶端,在细胞核附近和核内也存在散在斑点;AMOT和MPP7的IF频信号并没有完全重叠,而大多数A-CREB卫星细胞几乎没有AMOT,但AMOT mRNA水平在A-CREB卫星细胞中没有显著降低,可以认为MPP7-AMOT之间的相互作用是动态的,且需要稳定AMOT。使用邻位连接技术(proximity ligation assay,PLA),发现MPP7-AMOT PLA灶存在于卫星细胞顶端,小部分存在于细胞核,可知卫星细胞中的AMOT水平和顶端富集依赖于CREB活性,且与MPP7作为复合物存在[34]。 所有AMOT成员均与YAP1结合,YAP1参与驱动C2C12和衍生成肌细胞的增殖和阻止分化[36]。与MPP7和AMOT一样,A-CREB卫星细胞中的YAP1信号严重降低,AMOT与YAP1结合可以解释这一现象,但是否与MPP7有关仍存疑。YAP1的稳定性依赖于AMOT,而AMOT的水平依赖于MPP7,说明它们可能共存于一个稳定的复合物。当这3种蛋白共同表达时,MPP7和YAP1可以相互共同免疫沉淀,这表明AMOT在中间起到桥梁作用。在卫星细胞的细胞核和核周区域的PLA病灶进一步证实了MPP7与YAP1的关系。在激活的卫星细胞(培养36 h)中,YAP1信号高于静止的卫星细胞。在活化的卫星细胞中,MPP7-AMOT PLA灶比在静止的卫星细胞数量更多更分散,MPP7-YAP PLA灶分布于核区域和核周区域以及细胞质内。MPP7-AMOT和MPP7-YAP PLA灶的分散度和数量的增加表明,在卫星细胞激活过程中,MPP7和AMOT起到了增加核YAP1的作用[37]。 AMOT和YAP1的稳定性依赖于MPP7,MPP7再表达可以恢复A-CREB卫星细胞中的AMOT和YAP1。MPP7和AMOT在活化的卫星细胞中持续表达,YAP1维持细胞增殖,增强干细胞生命进程(PAX7+),并阻止分化(MYOG+)[37]。对WT卫星细胞来源的成肌细胞使用siRNA,未检测到A-CREB中复合物存在,进一步阐明MPP7和AMOT在YAP1调控中的作用。MPP7敲除后,核中含有YAP1的成肌细胞数量减少;YAP1转录靶点的下调支持了MPP7在YAP介导的基因激活中的作用,敲除MPP7导致PAX7+和 EdU+细胞数量减少以及MYOG+细胞数量增加。检测AMOT,AMOTl1和AMOTl2敲除后的这些参数,并使用YAP1敲除作为对照,均发现核YAP1数量减少,PAX7+和EdU+细胞数量减少,MYOG+细胞数量增加[34]。已知MPP7和AMOT家族存在于一个蛋白复合物中,可以认为CREB,MPP7,AMOT家族和YAP1形成了一个正调控轴,促进卫星细胞增殖和PAX7+细胞命运。 2.4.2 前列腺素E2对肌卫星细胞自我更新的调节 在成人静息肌中,卫星细胞保持在静止状态,其特征为表达Pax7。当肌肉损伤时,静止卫星细胞被激活并重新表达MyoD,并进入细胞周期进行增殖,增殖的卫星细胞分化并融合成多核肌纤维,以修复受损的肌肉。除此之外还有一部分卫星细胞在分裂后仍具备自我更新能力,以补充干细胞池,从而形成不同功能的细胞群体。骨骼肌卫星细胞即成肌祖细胞,前列腺素E2通过EP4受体激活肌成肌细胞和肌卫星细胞增殖,但它在肌肉分化中的作用尚不清楚。人诱导多能干细胞在广泛扩张后也能被诱导分化为骨骼肌细胞。因此,人诱导多能干细胞有望为细胞治疗提供足够数量的肌肉祖细胞。使用环氧化酶抑制剂检测EP2的上游,抑制COX-1和COX-2的同时,改善了Hu5/KD3细胞与人诱导多能干细胞来源的肌原性祖细胞的融合。而COX-1选择性抑制剂SC-560则没有促进Hu5/KD3细胞和人诱导多能干细胞来源的肌肉祖细胞的分化。相比之下,COX-2选择性抑制剂缬地昔布促进了Hu5/KD3细胞和人诱导多能干细胞来源的肌肉祖细胞的分化。在Hu5/KD3细胞的分化培养中加入前列腺素E2,前列腺素E2以剂量依赖的方式降低了融合指数,但前列腺素E2洗脱后,肌肉分化活性迅速恢复[38-40],这说明COX-2来源的前列腺素E2能够抑制肌肉祖细胞分化。 EP2和EP4均可激活腺苷环化酶,增加细胞内腺苷环化酶浓度,但两种受体的结构和功能不同。SAKAI-TAKEMURA等[30]测试了EP4拮抗剂ONO-AE3-208对肌原细胞分化的影响,ONO-AE3-208并没有增加Hu5/KD3肌原性细胞的融合指数,说明EP4对肌原性祖细胞自我更新的贡献较小;相比之下,EP2特异性激动剂丁前列素增加了单核细胞的百分比,EP2受体拮抗剂TG6-10-123则促进了肌肉祖细胞的融合,EP2的上调阻断了Hu5/KD3细胞的分化,EP2的敲除改善了肌肉祖细胞的融合。以上这些结果表明,COX-2/PEE2/EP2信号在分化条件下抑制了人肌肉祖细胞的分化,从而促进人肌肉祖细胞的自我更新。 g分泌酶抑制剂DAPT主要通过阻断前列腺素E2/EP2受体信号,刺激人肌原细胞的分化。Notch信号的免疫抑制作用主要是通过白细胞介素6和前列腺素E2完成的。在Hu5/KD3细胞中过表达Notch细胞间结构域3(NICD3),如预期所料,NICD3的过表达完全阻止了Hu5/KD3细胞向肌管分化。Notch3与前列腺素E2信号通路有很强的关系,添加前列腺素E2并没有上调NOTCH3,否定了EP2存在对NOTCH3表达的正反馈通路[41]。Notch信号通路上调了人肌肉祖细胞系Hu5/KD3中的EP2,Notch信号通过COX-2/ PGE2/EP2信号以环磷酸腺苷/蛋白激酶A非依赖性信通路抑制分化,从而促进人肌肉祖细胞的自我更新[42]。Notch/PGE2/EP2受体信号通路在调节肌原性祖细胞的细胞命运中发挥了重要作用。但EP2具体促进肌原性祖细胞自我更新的分子机制仍有待确定。 2.4.3 前列腺素E2加速细胞分裂间期G1-S期和调节活性氧促进原代成肌细胞增殖 细胞增殖依赖于细胞周期进程,细胞分裂间期分G1期、S期、G2期。G1又称合成前期,主要合成RNA和核糖体,为下阶段S期DNA复制做物质和能量的准备;S期为DNA合成期,此外还合成组蛋白和DNA复制所需酶;G2期即DNA合成后期,终止合成DNA转而大量合成RNA及蛋白(微管蛋白和促成熟因子等),为有丝分裂做准备。G1-S相受细胞周期蛋白、细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶、细胞周期抑制剂p21Cip1和p27Kip1以及肌肉特异性调节因子肌生长抑制素的调控。 前列腺素E2信号通路已被证明可以通过加速G1-S期的相变来促进细胞周期进程,EP4受体在细胞周期进程中的作用可能为细胞类型依赖性[43]。在小鼠原代成肌细胞的研究中,前列腺素E2或EP4激动剂CAY10598治疗促进G1-S期转变,而EP4拮抗剂L161982导致G0/G1细胞周期阻滞。细胞周期蛋白D和E是监测G1-S相变的两种主要细胞周期蛋白。细胞周期蛋白D的转录诱导开始于G1期早期。细胞周期蛋白D-Cdk4/6复合物的形成可磷酸化细胞周期抑制因子,以启动靶基因的表达,包括细胞周期蛋白E,以加速细胞周期进程。p21Cip1可以抑制细胞周期蛋白D-Cdk4/6和细胞周期蛋白E-Cdk2的活性,从而阻碍细胞周期的进展。前列腺素E2信号通路对G1-S期相变的影响可能是通过调控细胞周期蛋白E和p21的表达实现的。使用前列腺素E2或EP4激动剂显著增加了细胞周期蛋白E的表达,并降低了p21Cip1的表达;EP4拮抗剂抑制了细胞周期蛋白E的表达,但增强了p21Cip1的表达,这些结果与细胞计数和细胞周期分析相一致。因肌生成抑制素可诱导细胞周期蛋白D降解,上调肌生成抑制素的EP4拮抗剂可能负责下调细胞周期蛋白E。肌生成抑制素已被认为是治疗肌肉萎缩的主要目标,但控制骨骼肌肌生成抑制素表达的机制尚不清楚,前列腺素E2和EP4信号通路可能在肌生成抑制素的表达调控中发挥重要作用[44]。 活性氧能引起DNA损伤,进而导致细胞周期阻滞或细胞死亡,活性氧也可作为介导信号转导的第二信使。在骨骼肌中,低水平的活性氧有利于线粒体的生物发生和肌肉适应,而氧化应激则会导致肌肉萎缩[45]。Hmox1和Nqo1是L161982处理12 h后仅有的显著上调的2个基因,而这2个基因是由活性氧产生增加诱导的,该结果表明PGE2-EP4信号通路可能在成肌细胞增殖过程中能够调节活性氧。使用前列腺素E2处理12 h对活性氧的产生没有任何明显影响,但在36 h时活性氧能降低18%。在L161982处理后MyoD含量降低表明活性氧的过量产生会导致成肌分化因子MyoD降解。 用EP4拮抗剂L161982处理成肌细胞后,活性氧水平显著升高,活性氧可能是G0/G1周期阻滞的中介因子;与抗氧化剂N-乙酰半胱氨酸或硫酸软骨素共同处理显著逆转了L161982处理对成肌细胞增殖的抑制。这些结果表明,可能存在一个活性氧水平窗口,是促进成肌细胞增殖的最佳窗口。此外,可能有其他途径或机制也参与了N-乙酰半胱氨酸和硫酸软骨素诱导的成肌细胞增殖的恢复。以上说明存在着一个潜在的前列腺素E2信号通路在成肌细胞增殖中的作用的分子机制是通过平衡活性氧水平与抗氧化剂之间的关系[44]。 线粒体是细胞中活性氧产生的主要部位。既往研究表明,前列腺素E2可以激活Bcl-2或Bax来调节线粒体功能。前列腺素E2可以增加C2C12成肌细胞分化过程中过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体共激活物1α和超氧化物歧化酶1的表达。前列腺素E2可能刺激线粒体的生物发生,从而增加活性氧的产生。当EP4受体发挥功能时,超氧化物歧化酶1也会被上调以中和活性氧。抑制EP4受体可能会抑制超氧化物歧化酶1的表达,导致活性氧过量产生和Hmox1和Nqo1上调,而这意味着kelch样ech相关蛋白1(kelch-like ech-associated protein 1,Keap1)/NF-e2相关因子2(NF-E2-related factor 2,Nrf2)通路的激活[46]。前列腺素E2如何调控成肌细胞线粒体功能和活性氧产生,以及前列腺素E2信号通路与Keap1/Nrf2通路的关系则有待进一步研究。 前列腺素E2(PGE2)促进骨骼肌修复再生相关研究时间脉络图,见图5。 2.5 前列腺素E2在骨骼肌修复中的应用 2.5.1 外源性手段抑制前列腺素E2分解促进肌肉再生 15-羟基前列腺素脱氢酶是前列腺素E2的代谢酶,SW033291是一种针对15-羟基前列腺素脱氢酶的小分子抑制剂,能促进前列腺素E2的生成,促进骨、肌肉、肌腱等多种组织的再生。在内源性肾脏前列腺素E2代谢的情况下,在缺血再灌注损伤之前使用SW033291,除可减少炎症反应外,还观察到相关损伤评分、肾小管凋亡和肾损伤生物标志物(如血尿素氮、肌酐和嗜中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质肼)降低[47]。使用含有肌肉来源干细胞和SW033291的纤维蛋白凝胶可以修复胫骨前肌缺损,SW033291的加入显著促进了缺损区肌纤维和血管的形成,减轻了免疫应答和纤维化程度。无论是在体内还是体外,SW033291都在调节肌源性干细胞肌源性分化和肌肉来源干细胞介导的肌肉再生中发挥着作用。SW033291通过上调一系列肌源性标志物增强了肌源分化和肌管形成。此外,PI3K/Akt通路的激活参与了这些促进作用背后的机制。SW033291对前列腺素E2生物活性的促进作用呈剂量依赖性,其最大作用浓度的50%(EC50)在50-100 nmol/L"


之间,在500 nmol/L水平时效果最好[48]。细胞外各种应激,即物理、化学和生物因素,都可能会影响到细胞的生物行为,包括细胞增殖、分化、凋亡和衰老。尤其要注意的是,已有研究证明,即使是干细胞,在经受外源性高压力之后也容易发生衰老现象,而不能正常凋亡[22]。SW033291促进前列腺素E2的产生,而前列腺素E2在炎症过程中起着关键作用,作为衰老调节过程中的一个重要组成部分,其可以诱导成纤维细胞的衰老。肌肉来源干细胞对小分子抑制剂SW033291具有良好的耐受性,所以SW033291可以作为肌肉来源干细胞产生前列腺素E2的有效诱导剂而不会产生其他不良反应。 2.5.2 缓释手段延长前列腺素E2半衰期 虽然前列腺素E2能有效促进组织再生、但其在体内半衰期短和不能持续释放的特点使得实际投入应用中仍有困难。HUANG等[49]设计并合成了一种新的前列腺素E2,通过化学键合前列腺素E2释放基质到胶原蛋白,有效延长了前列腺素E2在体内外的半衰期和作用时长,通过生物发光成像(BLI)证实前列腺素E2基质显著改善了新生血管的形成;前列腺素E2基质通过激活MyoD1介导的肌肉干细胞,在后肢缺血模型中表现出优越的治疗效果,这与骨骼肌加速的结构恢复一致。前列腺素E2与胶原化学键合的方法实现了前列腺素E2缓释,并可能促进基于前列腺素E2疗法的发展,从而显著改善组织再生。此外还有使用含碳化艾草和前列腺素E2的聚乙烯醇可溶性微针贴片(MNP)贴在骨骼肌受损部位的方法有效促进了修复,引入的碳化艾草赋予了贴片近红外光加热特性,提高了前列腺素E2递送的效率,同时也促进了受损肌肉区域的循环;与传统的艾灸治疗相比,该疗法在肌肉损伤小鼠模型中可以更快地恢复肌肉力量和肌肉束纤维的横截面积;此外还成功地诱导了肌肉干细胞的增殖和分化,以有效修复受伤的肌肉组织[50]。"

| [1] TIDBALL JG, VILLALTA SA. Regulatory interactions between muscle and the immune system during muscle regeneration. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010;298(5):R1173-R1187. [2] SAKUMA K, YAMAGUCHI A. Molecular and cellular mechanism of muscle regeneration. 2012: IntechOpen. [3] XIAO W, LIU Y, LUO B, et al. Time-dependent gene expression analysis after mouse skeletal muscle contusion. J Sport Health Sci. 2016;5(1):101-108. [4] DUMONT NA, BENTZINGER CF, SINCENNES MC, et al. Satellite Cells and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Compr Physiol. 2015;5(3):1027-1059. [5] HO ATV, PALLA AR, BLAKE MR, et al. Prostaglandin E2 is essential for efficacious skeletal muscle stem-cell function, augmenting regeneration and strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(26):6675-6684. [6] YAO C, HIRATA T, SOONTRAPA K, et al. Prostaglandin E₂ promotes Th1 differentiation via synergistic amplification of IL-12 signalling by cAMP and PI3-kinase. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1685. [7] 黄丽丽,杨丹,徐运,等.前列腺素及其类似物治疗和预防脑小血管病的可能性[J].国际脑血管病杂志,2019(1):37-43. [8] 吴珊.穿山甲鳞甲乙醇提取物镇痛抗炎作用及其机制的实验研究[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2012. [9] TRAPPE TA, LIU SZ. Effects of prostaglandins and COX-inhibiting drugs on skeletal muscle adaptations to exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013;115(6):909-919. [10] MURAKAMI M, NARABA H, TANIOKA T, et al. Regulation of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis by inducible membrane-associated prostaglandin E2 synthase that acts in concert with cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(42):32783-32792. [11] WEINHEIMER EM, JEMIOLO B, CARROLL CC, et al. Resistance exercise and cyclooxygenase (COX) expression in human skeletal muscle: implications for COX-inhibiting drugs and protein synthesis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292(6):R2241-R2248. [12] KOROTKOVA M, LUNDBERG IE. The skeletal muscle arachidonic acid cascade in health and inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(5):295-303. [13] OTIS JS, BURKHOLDER TJ, PAVLATH GK. Stretch-induced myoblast proliferation is dependent on the COX2 pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2005;310(2):417-425. [14] SUGIMOTO Y, NARUMIYA S. Prostaglandin E receptors. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(16): 11613-11617. [15] GERARDUZZI C, DI BATTISTA JA. Myofibroblast repair mechanisms post-inflammatory response: a fibrotic perspective. Inflamm Res. 2017;66(6):451-465. [16] DELGHANDI MP, JOHANNESSEN M, MOENS U. The cAMP signalling pathway activates CREB through PKA, p38 and MSK1 in NIH 3T3 cells. Cell Signal. 2005; 17(11):1343-1351. [17] KOBILKA BK. G protein coupled receptor structure and activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1768(4):794-807. [18] 庞磊,孙小婷,魏骐,等.前列腺素受体EP4在心肌肥厚和心肌缺血/再灌注损伤中作用的研究进展[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2016,42(6):1249-1253+1215. [19] STEGBAUER J, COFFMAN TM. Skin tight: macrophage-specific COX-2 induction links salt handling in kidney and skin. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(11):4008-4010. [20] 蔡杰,卢佶翃,高航,等.前列腺素合酶在肝脏疾病中的作用[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2020,36(9):2137-2140. [21] ASLAN M, ÖZCAN F, TUZCU H, et al. Inhibition of neutral sphingomyelinase decreases arachidonic acid mediated inflammation in liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(11):7814-7823. [22] CHENG H, HUANG H, GUO Z, et al. Role of prostaglandin E2 in tissue repair and regeneration. Theranostics. 2021;11(18):8836-8854. [23] HIGASHI AY, ARONOW BJ, DRESSLER GR. Expression Profiling of Fibroblasts in Chronic and Acute Disease Models Reveals Novel Pathways in Kidney Fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;30(1):80-94. [24] MONTROSE DC, NAKANISHI M, MURPHY RC, et al. The role of PGE2 in intestinal inflammation and tumorigenesis. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015; 116-117:26-36. [25] MIYOSHI H, VANDUSSEN KL, MALVIN NP, et al. Prostaglandin E2 promotes intestinal repair through an adaptive cellular response of the epithelium. EMBO J. 2017;36(1):5-24. [26] JAIN U, LAI CW, XIONG S, et al. Temporal Regulation of the Bacterial Metabolite Deoxycholate during Colonic Repair Is Critical for Crypt Regeneration. Cell Host Microbe. 2018;24(3):353-363.e5. [27] HASSAN L, PINON A, LIMAMI Y, et al. Resistance to ursolic acid-induced apoptosis through involvement of melanogenesis and COX-2/PGE2 pathways in human M4Beu melanoma cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 2016;345(1):60-69. [28] 刘芸,和红兵.前列腺素E_2对骨改建作用的研究进展[J].昆明医科大学学报,2021,42(9):149-155. [29] FERNANDO MR, GIEMBYCZ MA, MCKAY DM. Bidirectional crosstalk via IL-6, PGE2 and PGD2 between murine myofibroblasts and alternatively activated macrophages enhances anti-inflammatory phenotype in both cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173(5):899-912. [30] SAKAI-TAKEMURA F, NOGAMI K, ELHUSSIENY A, et al. Prostaglandin EP2 receptor downstream of Notch signaling inhibits differentiation of human skeletal muscle progenitors in differentiation conditions. Commun Biol. 2020;3(1):182. [31] MIZOGUCHI S, WOLF-JOHNSON AS, NI J, et al. The role of prostaglandin and E series prostaglandin receptor type 4 receptors in the development of bladder overactivity in a rat model of chemically induced prostatic inflammation. BJU Int. 2019;124(5):883-891. [32] YANG GX, XU YY, FAN YP, et al. A maladaptive role for EP4 receptors in mouse mesangial cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e104091. [33] KIM PG, NAKANO H, DAS PP, et al.Flow-induced protein kinase A-CREB pathway acts via BMP signaling to promote HSC emergence. J Exp Med. 2015;212(5):633-648. [34] LI L, FAN CM.A CREB-MPP7-AMOT Regulatory Axis Controls Muscle Stem Cell Expansion and Self-Renewal Competence. Cell Rep. 2017;21(5):1253-1266. [35] WELLS CD, FAWCETT JP, TRAWEGER A, et al.A Rich1/Amot complex regulates the Cdc42 GTPase and apical-polarity proteins in epithelial cells. Cell. 2006;125(3): 535-548. [36] CHAN SW, LIM CJ, CHONG YF, et al. Hippo pathway-independent restriction of TAZ and YAP by angiomotin. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(9):7018-7026. [37] JUDSON RN, TREMBLAY AM, KNOPP P, et al.The Hippo pathway member Yap plays a key role in influencing fate decisions in muscle satellite cells. J Cell Sci. 2012; 125(Pt 24):6009-6019. [38] SAKAI-TAKEMURA F, NARITA A, MASUDA S, et al. Premyogenic progenitors derived from human pluripotent stem cells expand in floating culture and differentiate into transplantable myogenic progenitors. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):6555. [39] XI H, FUJIWARA W, GONZALEZ K, et al. In Vivo Human Somitogenesis Guides Somite Development from hPSCs. Cell Rep. 2017;18(6):1573-1585. [40] HOSOYAMA T, MCGIVERN JV, VAN DYKE JM, et al. Derivation of myogenic progenitors directly from human pluripotent stem cells using a sphere-based culture. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(5):564-574. [41] LOW S, BARNES JL, ZAMMIT PS, et al. Delta-Like 4 Activates Notch 3 to Regulate Self-Renewal in Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2018;36(3):458-466. [42] BAGHDADI MB, CASTEL D, MACHADO L, et al. Reciprocal signalling by Notch-Collagen V-CALCR retains muscle stem cells in their niche. Nature. 2018; 557(7707):714-718. [43] BERTOLI C, SKOTHEIM JM, DE BRUIN RA. Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(8):518-528. [44] MO C, ZHAO R, VALLEJO J, et al. Prostaglandin E2 promotes proliferation of skeletal muscle myoblasts via EP4 receptor activation. Cell Cycle. 2015;14(10): 1507-1516. [45] BARBIERI E, SESTILI P. Reactive oxygen species in skeletal muscle signaling. J Signal Transduct. 2012;2012. doi:10.1155/2012/982794. [46] LI X, FANG P, MAI J, et al. Targeting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species as novel therapy for inflammatory diseases and cancers. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6:19. [47] KIM HJ, KIM SH, KIM M, et al. Inhibition of 15-PGDH prevents ischemic renal injury by the PGE2/EP4 signaling pathway mediating vasodilation, increased renal blood flow, and increased adenosine/A2A receptors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020;319(6):F1054-F1066. [48] ZHANG Y, DESAI A, YANG SY, et al. TISSUE REGENERATION. Inhibition of the prostaglandin-degrading enzyme 15-PGDH potentiates tissue regeneration. Science. 2015;348(6240):aaa2340. [49] HUANG H, CHEN S, CHENG H, et al. The sustained PGE2 release matrix improves neovascularization and skeletal muscle regeneration in a hindlimb ischemia model. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):95. [50] ZHANG C, JIA S, HUANG J, et al. A carbonized wormwood modified photothermal microneedle patch for the repair of damaged skeletal muscles. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(38):8014-8020. |
| [1] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [2] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [3] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [4] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [5] | Wang Xuanqiang, Zhang Wenyang, Li Yang, Kong Weiqian, Li Wei, Wang Le, Li Zhongshan, Bai Shi. Effects of chronic exposure to low-frequency pulsed magnetic fields on contractility and morphology of the quadriceps muscle in healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1634-1642. |
| [6] | Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Deng Hao, Sun Tao, Cheng Qian. Icariin pretreatment enhances effect of human periodontal stem cells on M1-type macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [7] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [8] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [9] | Sun Yuting, Wu Jiayuan, Zhang Jian. Physical factors and action mechanisms affecting osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1531-1540. |
| [10] | Zhao Ruihua, Chen Sixian, Guo Yang, Shi Lei, Wu Chengjie, Wu Mao, Yang Guanglu, Zhang Haoheng, Ma Yong. Wen-Shen-Tong-Du Decoction promoting spinal cord injury repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1118-1126. |
| [11] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [12] | Zhang Debao, Wang Peng, Li Kun, Zhang Shaojie, Li Zhijun, Li Shuwen, Wu Yimin. Epidural fibrous scar formation in rabbits following autologous ligamentum flavum intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1168-1175. |
| [13] | Ji Huihui, Jiang Xu, Zhang Zhimin, Xing Yunhong, Wang Liangliang, Li Na, Song Yuting, Luo Xuguang, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei. SR9009 combined with indolepropionic acid alleviates inflammation in C2C12 myoblasts through the nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1220-1229. |
| [14] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [15] | Zhao Xiaoxuan, Liu Shuaiyi, Li Qi, Xing Zheng, Li Qingwen, Chu Xiaolei. Different exercise modalities promote functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1248-1256. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||