Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (15): 3913-3919.doi: 10.12307/2025.871
Previous Articles Next Articles
A controlled analysis of phenomenon of acupoint sensitization in osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Yao Kexin1, Yang Yidan1, Li Yapeng2, Zhu Xuanye1, Wang Qiuyuan2, Guo Jiayi1, 2, Liu Youwen2, Yue Chen2
- 1College of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Luoyang Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province (Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province), Luoyang 471002, Henan Province, China
-
Accepted:2024-12-20Online:2026-05-28Published:2025-11-07 -
Contact:Guo Jiayi, Chief TCM physician, College of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; Luoyang Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province (Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province), Luoyang 471002, Henan Province, China Liu Youwen, Chief physician, Luoyang Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province (Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province), Luoyang 471002, Henan Province, China Yue Chen, MD, Associate chief physician, Luoyang Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province (Orthopedic Hospital of Henan Province), Luoyang 471002, Henan Province, China -
About author:Yao Kexin, Master candidate, College of Orthopedics and traumatology, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance and Innovation Talent Project (Zhongjing Project) Traditional Chinese Medicine Top Talents, No. 2021 15 (to GJY); 2023 National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project, System Construction, Evaluation and Promotion of Pingle Bone Correction for the Prevention and Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis, No. GZY-KJS-2023-012 (to GJY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yao Kexin, Yang Yidan, Li Yapeng, Zhu Xuanye, Wang Qiuyuan, Guo Jiayi, Liu Youwen, Yue Chen. A controlled analysis of phenomenon of acupoint sensitization in osteonecrosis of the femoral head[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(15): 3913-3919.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
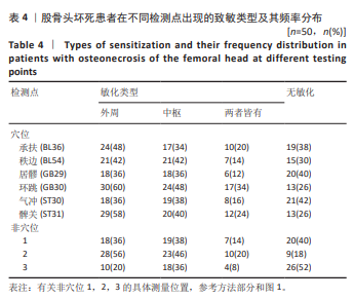
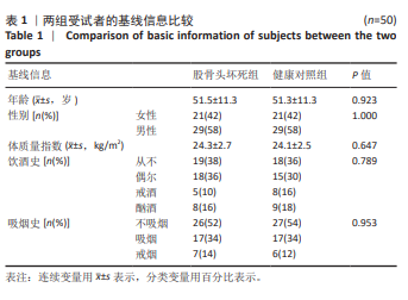
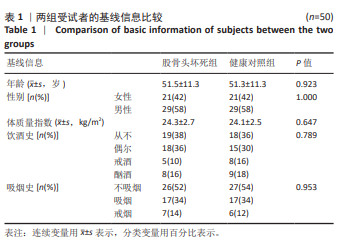
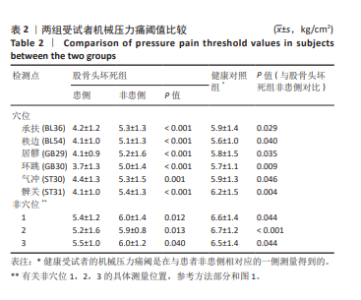
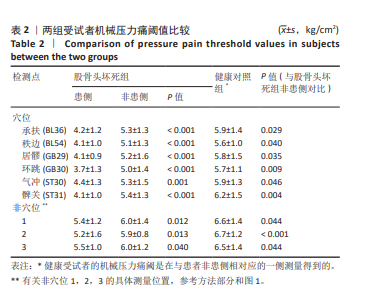
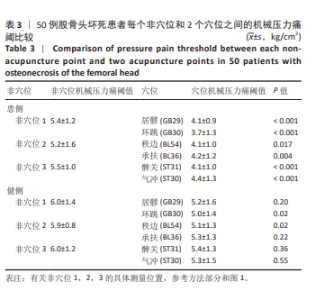
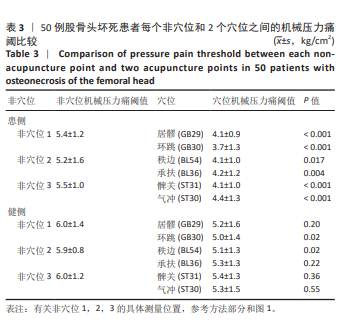
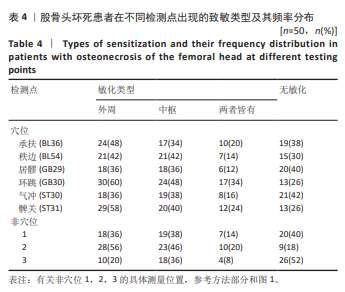
2.6 对患者穴位和非穴位的敏感性评估 进一步根据机械压力痛阈值评估了患者穴位和非穴位的疼痛敏感性,见表4。在所有患者中,观察到所有6个穴位和3个非穴位均出现了疼痛敏感性增加的现象,且穴位的敏感性增加程度更为显著。具体到各个穴位,承扶(BL36)的外周敏感化患者比例为48%,秩边(BL54)为42%,居髎(GB29)为36%,环跳(GB30)为60%,气冲(ST30)为36%,髀关(ST31)为58%。对于非穴位,非穴位1的外周敏化患者比例为36%,非穴位2为56%,非穴位3为20%。在患者的非患侧,如果机械压力痛阈值低于健康对照组相应侧的第25百分位数,则认为存在中枢敏化现象。具体比例为:承扶(BL36)34%,秩边(BL54)42%,居髎(GB29)36%,环跳(GB30)48%,气冲(ST30)38%,髀关(ST31)40%。非穴位1的敏化比例为38%,非穴位2为46%,非穴位3为36%。 这些结果提示,针对敏感穴位的针灸治疗可能对大多数类似此次研究样本的骨坏死患者是有效的。 2.7 股骨头坏死患者在不同检测点出现的致敏类型及其频率分布 在此次研究的样本中,6个穴位和3个非穴位的敏化情况因患者而异,且个体敏化类型(外周和/或中枢)也有所不同,见表4。在6个穴位中,承扶(BL36)、环跳(GB30)和髀关(ST31)在大多数敏化患者中显示出既有中枢敏化也有外周敏化,而其余3个穴位则只显示出其中一种类型的敏感化。根据这些结果推测,针对敏化穴位的针灸治疗或可以根据个体患者进行个性化调整。 2.8 不良事件 在此次试验过程中,未涉及任何药物及侵入性干预,无不良事件发生。"
| [1] CUI L, ZHUANG Q, LIN J, et al. Multicentric epidemiologic study on six thousand three hundred and ninety five cases of femoral head osteonecrosis in China. Int Orthop. 2016;40(2):267-276. [2] ZHAO DW, YU M, HU K, et al. Prevalence of Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head and its Associated Risk Factors in the Chinese Population: Results from a Nationally Representative Survey. Chin Med J(Engl). 2015;128(21):2843-2850. [3] ZHAO DW, HU YC. Chinese experts’ consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults. Orthop Surg. 2012;4(3):125-130. [4] COHEN SP, VASE L, HOOTEN WM. Chronic pain: an update on burden, best practices, and new advances. Lancet. 2021;397(10289): 2082-2097. [5] VAN WILGEN CP, KEIZER D. The sensitization model to explain how chronic pain exists without tissue damage. Pain Manag Nurs. 2012; 13(1):60-65. [6] COHEN SP, MAO J. Neuropathic pain: mechanisms and their clinical implications. Bmj. 2014;348:f7656. [7] CURATOLO M. Central Sensitization and Pain: Pathophysiologic and Clinical Insights. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(1):15-22. [8] WANG XY, NIE ZY, YU QQ, et al. Acupuncture Enhances Signals at Sensitized Acupoints to Elevate Pressure Pain Threshold in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients. Chin J Integr Med. 2022;28(12):1105-1110. [9] FERNáNDEZ-HERNANDO D, FERNáNDEZ-DE-LAS-PEñAS C, PAREJA-GRANDE JA, et al. Management of auricular transcutaneous neuromodulation and electro-acupuncture of the vagus nerve for chronic migraine: a systematic review. Front Neurosci. 2023;17: 1151892. [10] JIN Y, ZHOU J, FANG Y, et al. Electroacupuncture prevents the development or establishment of chronic pain via IL-33/ST2 signaling in hyperalgesic priming model rats. Neurosci Lett. 2024; 820:137611. [11] TAN H, TUMILTY S, CHAPPLE C, et al. Acupoints sensitization in people with and without chronic low back pain:A matched-sample cross-sectional study. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023;36(1):137-146. [12] YAN CQ, ZHANG S, LI QQ, et al. Detection of peripheral and central sensitisation at acupoints in patients with unilateral shoulder pain in Beijing: a cross-sectional matched case-control study. BMJ Open. 2017;7(6):e014438. [13] SUN M, GENG G, CHEN J, et al. Acupuncture for chronic neck pain with sensitive points: study protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2019;9(7):e026904. [14] BIRCH S. Trigger point--acupuncture point correlations revisited. J Altern Complement Med. 2003;9(1):91-103. [15] DORSHER PT. Can classical acupuncture points and trigger points be compared in the treatment of pain disorders? Birch’s analysis revisited J Altern Complement Med. 2008;14(4):353-359. [16] KIM DH, RYU Y, HAHM DH, et al. Acupuncture points can be identified as cutaneous neurogenic inflammatory spots. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1): 15214. [17] TAN H, TUMILTY S, CHAPPLE C, et al. Understanding Acupoint Sensitization: A Narrative Review on Phenomena, Potential Mechanism, and Clinical Application. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019; 2019:6064358. [18] JIN H, LI L, YU W, et al. The efficacy of acupuncture and moxibustion for early and middle-stage osteonecrosis of the femeral head: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine(Baltimore). 2021;100(22):e26210. [19] ARANT KR, KATZ JN, NEOGI T. Quantitative sensory testing: identifying pain characteristics in patients with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(1):17-31. [20] CORONADO RA, SIMON CB, VALENCIA C, et al. Experimental pain responses support peripheral and central sensitization in patients with unilateral shoulder pain. Clin J Pain. 2014;30(2):143-151. [21] PAK DJ, YONG RJ, KAYE AD, et al. Chronification of Pain: Mechanisms, Current Understanding, and Clinical Implications. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2018;22(2):9. [22] SANZARELLO I, MERLINI L, ROSA MA, et al. Central sensitization in chronic low back pain: A narrative review. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2016;29(4):625-633. [23] ARENDT-NIELSEN L. Pain sensitisation in osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35 Suppl 107(5):68-74. [24] DING N, JIANG J, QIN P, et al. Mast cells are important regulator of acupoint sensitization via the secretion of tryptase, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and histamine. PLoS One. 2018;13(3):e0194022. [25] HE W, WANG XY, SHI H, et al. Cutaneous neurogenic inflammation in the sensitized acupoints induced by gastric mucosal injury in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017;17(1):141. [26] EIJKELKAMP N, HEIJNEN CJ, CARBAJAL AG, et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 acts as a critical regulator of cytokine-induced hyperalgesia by promoting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and inhibiting p38 signaling. Mol Med. 2012;18(1):556-564. [27] SILVA RL, LOPES AH, GUIMARÃES RM, et al. CXCL1/CXCR2 signaling in pathological pain: Role in peripheral and central sensitization. Neurobiol Dis. 2017;105:109-116. [28] LI AH, ZHANG JM, XIE YK. Human acupuncture points mapped in rats are associated with excitable muscle/skin-nerve complexes with enriched nerve endings. Brain Res. 2004;1012(1-2):154-159. [29] ZHU B, XU WD, RONG PJ, et al. A C-fiber reflex inhibition induced by electroacupuncture with different intensities applied at homotopic and heterotopic acupoints in rats selectively destructive effects on myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers. Brain Res. 2004;1011(2): 228-237. [30] PACE MC, PASSAVANTI MB, DE NARDIS L, et al. Nociceptor plasticity: A closer look. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(4):2824-2838. [31] 许文杰,崔翔,刘坤,等.穴位的敏化特性与C类伤害感受器的关系及研究进展[J].针刺研究,2021,46(12):1048-1056. [32] CUI X, LIU K, GAO X, et al. Advancing the Understanding of Acupoint Sensitization and Plasticity Through Cutaneous C-Nociceptors. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:822436. [33] HAN JS. Acupuncture: neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies. Trends Neurosci. 2003;26(1):17-22. [34] KWON NY, YU JS, KIM DI, et al. Effectiveness of electroacupuncture and acupuncture in alleviating cold hypersensitivity in the hands and feet: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2024;19(11): e0313789. [35] 金新,蔡宛儒.针刺不同敏化状态穴位治疗膝骨关节炎疗效观察[J].湖北中医杂志,2019,14(10):56-57. [36] 任忠陆,齐琳.股骨头坏死中医药治疗的研究新进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2022,31(10):1455-1460. [37] 朱紫燕,张东艳,韩崇涛,等.针刺联合补髓壮骨通络汤治疗早期非创伤性股骨头坏死的疗效及对Harris评分、血清炎症因子、骨代谢水平的影响[J].中医研究,2022,35(12):31-34. [38] 方彬.血府逐瘀汤联合温针灸治疗非创伤性股骨头坏死气滞血瘀证的临床疗效[J].中华养生保健,2024,42(22):34-36+40. [39] DAHMANI D, TAIK FZ, BERRICHI I, et al. Impact of central sensitization on pain, disability and psychological distress in patients with knee osteoarthritis and chronic low back pain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):877. [40] 丁宁,姜婧,王巧侠,等.腧穴敏化的生物物理特性研究进展[J].针灸临床杂志,2017,33(2):69-72. |
| [1] | Zhang Di, Zhao Jun, Ma Guangyue, Sun Hui, Jiang Rong. Mechanism of depression-like behavior in chronic social defeat stress mice based on high-throughput sequencing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1139-1146. |
| [2] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [3] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [4] | Li Hanyue, Li Yini, Xiang Linmei, Li Sen. Effects of resistance exercise therapy on pain and function in patients with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 987-996. |
| [5] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Mechanism by which vascular endothelial growth factor A targets regulation of angiogenesis in the treatment of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 671-679. |
| [6] | Zhou Zixiang, Zhao Baoxiang. Research progress in the relationship between nontraumatic necrosis of the femoral head and lipid metabolism and its treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 680-690. |
| [7] | Yang Peng, Xu Chenghan, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie, Li Lin, Shi Jinyu. A meta-analysis of risk factors for residual back pain after vertebral augmentation for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 731-739. |
| [8] | Zhang Anqi, Hua Haotian, Cai Tianyuan, Wang Zicheng, Meng Zhuo, Zhan Xiaoqian, Chen Guoqian . Pain after total knee arthroplasty: current status and trend analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 795-804. |
| [9] | Zhou Feng, Fu Pengfei, Qian Yufan, Xu Pingcheng, Guo Jiongjiong, Zhang Lei. Correlation between spinal sagittal imbalance and knee joint parameters detected by whole-body EOS imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 596-603. |
| [10] | Chen Yiyan, Wang Liyan, Fan Zhiying, Zhou Haibin, Cheng Peng, Lu Aming. Relationship of inertial measurement unit gait stability with pain intensity and kinesiophobia in patients with medial meniscus injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(15): 3839-3847. |
| [11] | Guo Yuqi, Li Jiacheng, Lu Bowen, Zhang Jiahao, Li Gang. Network meta-analysis of core decompression combined with various therapies for early and mid-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(15): 3993-4009. |
| [12] | Zan Yongfeng, Song Keguan, Liu Yuda. Glutamine regulates the effect of hormones on the apoptosis of bone microvascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 2965-2974. |
| [13] | Ren Pengbo, Li Tingwen, Cai Feng, Zhang Jian. Meta-analysis of lumbar bone mineral density, pain score and fall incidence in middle-aged and elderly osteoporosis patients undergoing whole-body vibration training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2569-2575. |
| [14] | Du Yanli, , Wang Yi, , Wang Zhenyu, Wang Xuanhui, , Li Xinye, , Xiong Xifeng, Miao Haixiong, . The role of p53 in musculoskeletal diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2503-2514. |
| [15] | Ao Xiaojing, Li Kun, Liu Yuhang, Yang Xiaoxuan, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Ren Xiaoyan, Zhang Shaojie. Development and application of a three-dimensional digital visualization system for children’s neck acupoints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1834-1840. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||