Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (21): 4458-4468.doi: 10.12307/2025.822
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biomechanical characteristics of lower limbs in female patients with different types of patellofemoral pain syndrome
Dong Youqing1, Wei Zixuan2, Wu Haiou2, Chen Ruixiong2, Duan Peng3, Chen Nan2, Lin Xikai4
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Shishou People's Hospital, Shishou 434400, Hubei Province, China; 2College of Sports Medicine, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China; 3Hubei Province Sports Science Institute, Wuhan 430205, Hubei Province, China; 4Department of Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine Shenzhen Hospital (Longgang), Shenzhen 518172, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-31Accepted:2024-07-26Online:2025-07-28Published:2024-12-05 -
Contact:Lin Xikai, MS, Physical therapist, Department of Tuina, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine Shenzhen Hospital (Longgang), Shenzhen 518172, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Dong Youqing, Associate chief physician, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Shishou People's Hospital, Shishou 434400, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:Hubei Provincial Department of Education Scientific Research Project, No. B2021193 (to LXK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dong Youqing, Wei Zixuan, Wu Haiou, Chen Ruixiong, Duan Peng, Chen Nan, Lin Xikai. Biomechanical characteristics of lower limbs in female patients with different types of patellofemoral pain syndrome[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4458-4468.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
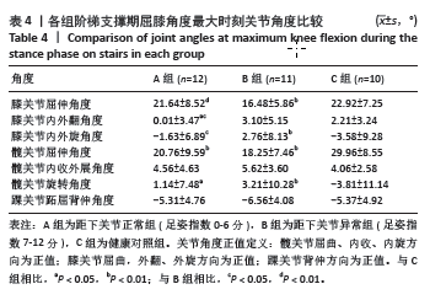
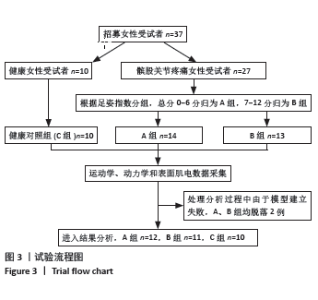
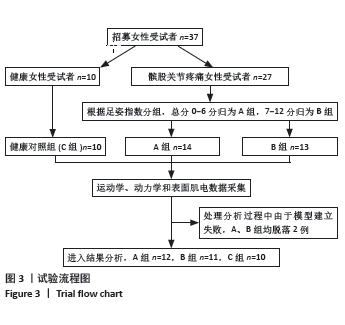
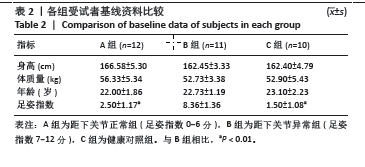
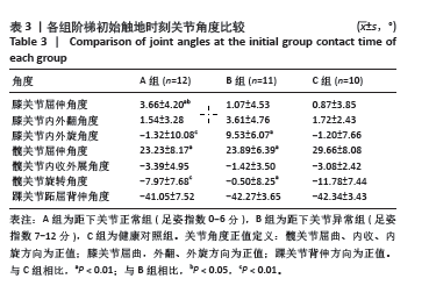
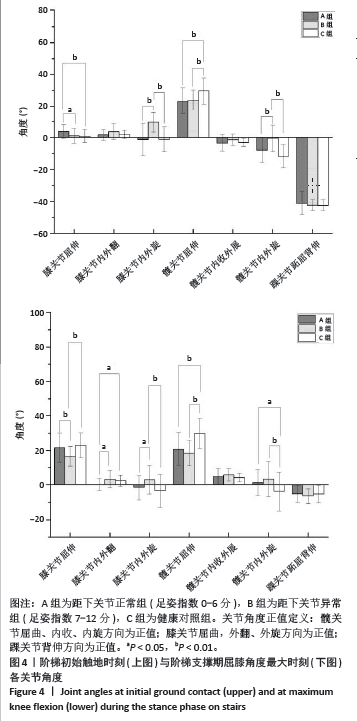
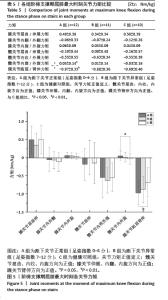
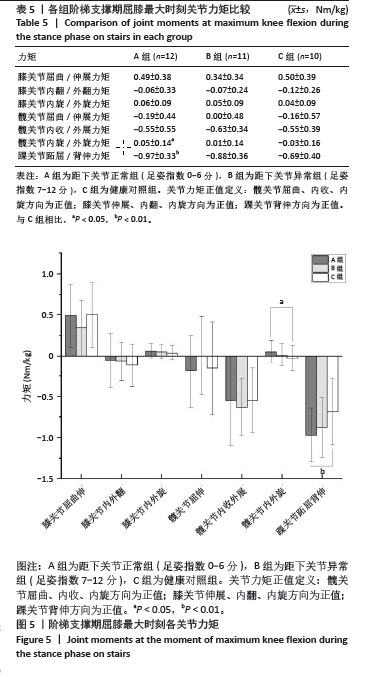
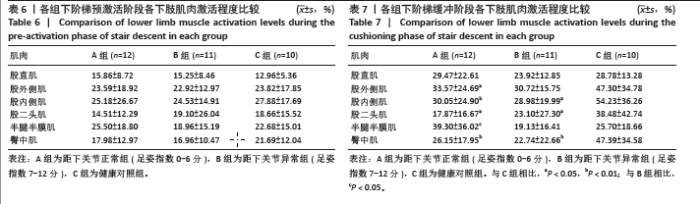
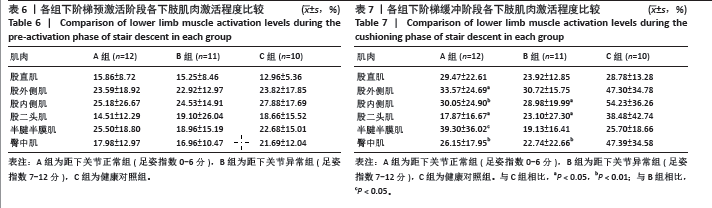
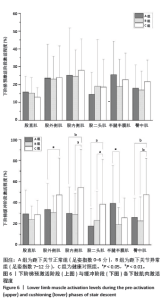
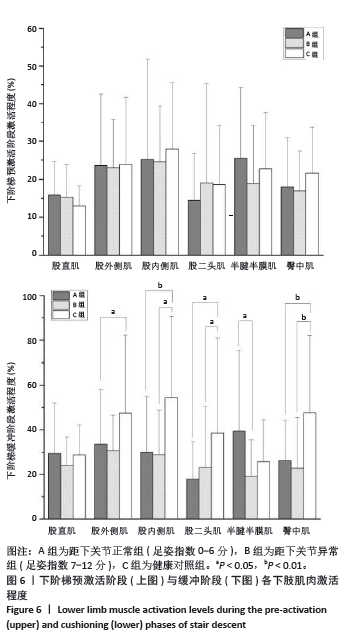
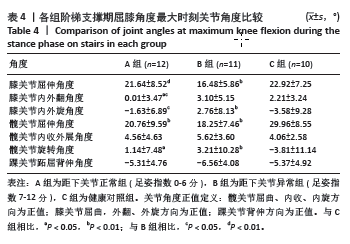
2.5 各组支撑期屈膝角度最大时刻的各关节角度情况 在阶梯支撑期屈膝角度最大时刻,膝关节屈伸角度方面B组与A、C组之间差异均有显著性意义(均P < 0.01);在膝关节内外翻角度方面,A组与B、C组之间差异均有显著性意义(均P < 0.05);在膝关节内外旋角度方面,B组与A、C组之间差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);在髋关节屈伸角度方面,C组与A、B组之间差异均有显著性意义(均P < 0.01)。在髋关节内外旋角度,C组与A、B组之间差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05,P < 0.01)。见表4及图4。 2.6 各组阶梯支撑期屈膝角度最大时刻的各关节力矩情况 在阶梯支撑期屈膝角度最大时刻,髋内外旋力矩方面,A组与C组之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。跖屈背伸力矩方面,A组与C组之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。见表5及图5。"
| [1] CROSSLEY KM, STEFANIK JJ, SELFE J, et al. 2016 Patellofemoral pain consensus statement from the 4th International Patellofemoral Pain Research Retreat, Manchester. Part 1: Terminology, definitions, clinical examination, natural history, patellofemoral osteoarthritis and patient-reported outcome measures. Br J Sports Med. 2016; 50(14):839-843. [2] MARTIMBIANCO A, TORLONI MR, ANDRIOLO BN, et al. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) for patellofemoral pain syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;12(12):CD11289. [3] ZHENG W, LI H, HU K, et al. Chondromalacia patellae: current options and emerging cell therapies. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):412. [4] FELSON DT, LAWRENCE RC, DIEPPE PA, et al. Osteoarthritis: new insights. Part 1: the disease and its risk factors. Ann Intern Med. 2000; 133(8):635-646. [5] CROSSLEY KM. Is patellofemoral osteoarthritis a common sequela of patellofemoral pain? Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(6):409-410. [6] SANGEORZAN A, SANGEORZAN B. Subtalar Joint Biomechanics: From Normal to Pathologic. Foot Ankle Clin. 2018;23(3):341-352. [7] BERNASCONI A, LINTZ F, SADILE F. The role of arthroereisis of the subtalar joint for flatfoot in children and adults. EFORT Open Rev. 2017;2(11):438-446. [8] NAKAGAWA TH, MORIYA ET, MACIEL CD, et al. Trunk, pelvis, hip, and knee kinematics, hip strength, and gluteal muscle activation during a single-leg squat in males and females with and without patellofemoral pain syndrome. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012;42(6):491-501. [9] BOLGLA LA, MALONE TR, UMBERGER BR, et al. Hip strength and hip and knee kinematics during stair descent in females with and without patellofemoral pain syndrome. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008;38(1):12-18. [10] MCKENZIE K, GALEA V, WESSEL J, et al. Lower extremity kinematics of females with patellofemoral pain syndrome while stair stepping. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2010;40(10):625-632. [11] 谢雨馨, 白宇. 髌股疼痛综合征的损伤机制与治疗: 2022年第七届广州运动与健康国际学术研讨会[C].广州,2022. [12] TIBERIO D. The effect of excessive subtalar joint pronation on patellofemoral mechanics: a theoretical model. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1987;9(4):160-165. [13] GROSS KD, FELSON DT, NIU J, et al. Association of flat feet with knee pain and cartilage damage in older adults. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63(7):937-944. [14] DESILVA JM, HOLT KG, CHURCHILL SE, et al. The Lower Limb and Mechanics of Walking inAustralopithecus sediba. Science. 2013; 340(6129):1232999. [15] 蒋学永, 许光旭, 孟殿怀, 等. 距下关节运动控制训练对髌骨外侧高压综合征患者膝关节功能的影响[J]. 湖南师范大学学报(医学版),2020,17(5):76-79. [16] BARTON CJ, MENZ HB, CROSSLEY KM. The immediate effects of foot orthoses on functional performance in individuals with patellofemoral pain syndrome. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45(3):193-197. [17] BARTON CJ, MENZ HB, CROSSLEY KM. Clinical Predictors of Foot Orthoses Efficacy in Individuals with Patellofemoral Pain. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(9):1603-1610. [18] PAVONE V, VESCIO A, PANVINI F, et al. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome in Young Female Athletes: A Case-Control Study. Adv Orthop. 2022; 2022:1907975. [19] LAKSTEIN D, FRIDMAN T, ZIV YB, et al. Prevalence of anterior knee pain and pes planus in Israel defense force recruits. Mil Med. 2010; 175(11):855-857. [20] KOSASHVILI Y, FRIDMAN T, BACKSTEIN D, et al. The correlation between pes planus and anterior knee or intermittent low back pain. Foot Ankle Int. 2008;29(9):910-913. [21] WHEATLEY M, RAINBOW MJ, CLOUTHIER AL. Patellofemoral Mechanics: a Review of Pathomechanics and Research Approaches. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(3):326-337. [22] BOLING M, PADUA D, MARSHALL S, et al. Gender differences in the incidence and prevalence of patellofemoral pain syndrome. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2010;20(5):725-730. [23] MALLIARAS P, COOK J, PURDAM C, et al. Patellar Tendinopathy: Clinical Diagnosis, Load Management, and Advice for Challenging Case Presentations. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2015;45(11):887-898. [24] 熊博文. 针灸联合针刀治疗髌下脂肪垫损伤的临床疗效观察[D]. 合肥:安徽中医药大学,2024. [25] 张新语, 霍洪峰. 足姿指数(FPI):足部姿势及足踝功能的定量表达[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(13):1194-1199. [26] 黄思瑜, 陈建, 胡惠莉, 等. 髌股疼痛综合征下肢特征分析: 第十一届全国体育科学大会[C]. 南京,2019. [27] 陈鹏, 左会武, 王玲, 等. 前交叉韧带重建术后运动员单腿垂直跳跃高度对称性掩盖其异常下肢生物力学[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2023,42(12):939-947. [28] POWERS CM, WITVROUW E, DAVIS IS, et al. Evidence-based framework for a pathomechanical model of patellofemoral pain: 2017 patellofemoral pain consensus statement from the 4th International Patellofemoral Pain Research Retreat, Manchester, UK: part 3. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(24):1713-1723. [29] SALSICH GB, BRECHTER JH, FARWELL D, et al. The effects of patellar taping on knee kinetics, kinematics, and vastus lateralis muscle activity during stair ambulation in individuals with patellofemoral pain. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2002;32(1):3-10. [30] BONACCI J, HALL M, FOX A, et al. The influence of cadence and shoes on patellofemoral joint kinetics in runners with patellofemoral pain. J Sci Med Sport. 2018;21(6):574-578. [31] KOSHINO Y, SAMUKAWA M, CHIDA S, et al. Postural Stability and Muscle Activation Onset during Double- to Single-Leg Stance Transition in Flat-Footed Individuals. J Sports Sci Med. 2020;19(4):662-669. [32] BESIER TF, DRAPER CE, GOLD GE, et al. Patellofemoral joint contact area increases with knee flexion and weight-bearing. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(2):345-350. [33] LENHART RL, THELEN DG, WILLE CM, et al. Increasing running step rate reduces patellofemoral joint forces. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014; 46(3):557-564. [34] 王勇. 鞍座高度对骑行时髌股关节力学特征影响的研究[J]. 体育科学,2018,38(6):60-66. [35] POLLARD CD, SIGWARD SM, POWERS CM. Limited hip and knee flexion during landing is associated with increased frontal plane knee motion and moments. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2010;25(2): 142-146. [36] PANAYIOTOU CHARALAMBOUS C. Knee Biomechanics—Patellofemoral Articulation//Panayiotou Charalambous C. The Knee Made Easy. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022:103-133. [37] ATKINS LT, REID J, ZINK D. The effects of increased forward trunk lean during stair ascent on hip adduction and internal rotation in asymptomatic females. Gait Posture. 2022;97:147-151. [38] HUANG MT, LEE HH, LIN CF, et al. How does knee pain affect trunk and knee motion during badminton forehand lunges? J Sports Sci. 2014;32(7):690-700. [39] BALDON RM, SERRÃO FV, SCATTONE SR, et al. Effects of functional stabilization training on pain, function, and lower extremity biomechanics in women with patellofemoral pain: a randomized clinical trial. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2014;44(4):240-251, A1- A8. [40] 杨辰, 曲峰, 刘卉, 等. 髌股关节痛业余跑者性别特异的下肢生物力学特征[J]. 医用生物力学,2020,35(6):672-678. [41] 杨辰. 基于下肢生物力学特征的髌股关节痛危险因素研究[D]. 北京:北京体育大学,2018. [42] POWERS CM. The influence of altered lower-extremity kinematics on patellofemoral joint dysfunction: a theoretical perspective. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2003;33(11):639-646. [43] SCHWANE BG, GOERGER BM, GOTO S, et al. Trunk and Lower Extremity Kinematics During Stair Descent in Women With or Without Patellofemoral Pain. J Athl Train. 2015;50(7):704-712. [44] DIONISIO VC, MARCONI NF, DOS SI, et al. Upward squatting in individuals with and without patellofemoral pain syndrome: a biomechanical study. J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(5):1437-1446. [45] TAN JM, MIDDLETON KJ, HART HF, et al. Immediate effects of foot orthoses on lower limb biomechanics, pain, and confidence in individuals with patellofemoral osteoarthritis. Gait Posture. 2020;76: 51-57. [46] WIRTZ AD, WILLSON JD, KERNOZEK TW, et al. Patellofemoral joint stress during running in females with and without patellofemoral pain. Knee. 2012;19(5):703-708. [47] 向福荣. 全身关节过度活动女性前交叉韧带损伤风险研究[D]. 武汉:武汉体育学院,2023. [48] RIEMANN BL, LEPHART SM. The sensorimotor system, part I: the physiologic basis of functional joint stability. J Athl Train. 2002;37(1): 71-79. [49] GLAVIANO NR, SALIBA S. Differences in Gluteal and Quadriceps Muscle Activation During Weight-Bearing Exercises Between Female Subjects With and Without Patellofemoral Pain. J Strength Cond Res. 2022;36(1):55-62. [50] MIRZAIE GH, RAHIMI A, KAJBAFVALA M, et al. Electromyographic activity of the hip and knee muscles during functional tasks in males with and without patellofemoral pain. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2019;23(1):54-58. [51] TOUMI H, BEST TM, PINTI A, et al. The role of muscle strength & activation patterns in patellofemoral pain. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2013;28(5):544-548. [52] BRIANI RV, DE OLIVEIRA SD, FLÓRIDE CS, et al. Quadriceps neuromuscular function in women with patellofemoral pain: Influences of the type of the task and the level of pain. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e205553. [53] BRINDLE TJ, MATTACOLA C, MCCRORY J. Electromyographic changes in the gluteus medius during stair ascent and descent in subjects with anterior knee pain. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2003; 11(4):244-251. [54] AAGAARD P, SIMONSEN EB, ANDERSEN JL, et al. Neural adaptation to resistance training: changes in evoked V-wave and H-reflex responses. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2002;92(6):2309-2318. [55] DE OLIVEIRA SD, MAGALHÃES FH, FARIA NC, et al. Lower Amplitude of the Hoffmann Reflex in Women With Patellofemoral Pain: Thinking Beyond Proximal, Local, and Distal Factors. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97(7):1115-1120. [56] MOZAFARIPOUR E, SEIDI F, MINOONEJAD H, et al. The effectiveness of the comprehensive corrective exercise program on kinematics and strength of lower extremities in males with dynamic knee valgus: a parallel-group randomized wait-list controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):700. [57] WERNER S. An evaluation of knee extensor and knee flexor torques and EMGs in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome in comparison with matched controls. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 1995; 3(2):89-94. [58] DIETER BP, MCGOWAN CP, STOLL SK, et al. Muscle activation patterns and patellofemoral pain in cyclists. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014;46(4): 753-761. [59] KALYTCZAK MM, LUCARELI P, DOS RA, et al. Kinematic and electromyographic analysis in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome during single leg triple hop test. Gait Posture. 2016;49: 246-251. |
| [1] | Lu Jieming, Li Yajing, Du Peijie, Xu Dongqing. Effects of artificial turf versus natural grass on biomechanical performance of the lower limbs in young females during jump-landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1101-1107. |
| [2] | Wen Zixing, Xu Xin, Zhu Shengqun. Correlations between gastrocnemius morphology parameters and physical activity capacity in elderly females under high-frequency ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1058-1063. |
| [3] | Liu Mengling, Li Yongjie, Liu Hongju. Effect of increased stride length on knee kinematics and dynamics of asymmetric gait after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7109-7115. |
| [4] | Gao Yuan, Xiong Zheyu, Zheng Wei, Chen Haonan, Chen Fangyuqing. Lower extremity biomechanical characterization during step-down test in patients with patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6913-6919. |
| [5] | Guo Ping, Wang Juan. Bilateral lower limb biomechanical abnormalities in patients with unilateral chronic ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6920-6926. |
| [6] | Gou Yanyun, Hou Meijin, Jiang Zheng, Chen Shaoqing, Chen Xiang, Gao Yuzhan, Wang Xiangbin. Biomechanical characteristics of walking in patients with idiopathic scoliosis: cross-sectional analysis of three-dimensional motion capture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 471-477. |
| [7] | Wang Zilong, Meng Xin, Zhang Zhiqi, Xie Yu, Meng Lingyue, Zhang Qiuxia, Kong Lingyu. Biomechanical characteristics of lower extremities during counter movement jump in male patients with functional ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 478-485. |
| [8] | Li Yongjie, Liu Mengling, Zhang Dakuan, Fu Shenyu, Liu Hongju. Effect of unilateral knee osteoarthritis on gait dynamics and muscle activation asymmetry in elderly women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5750-5756. |
| [9] | Zhang Sizhuo, Liu Xiaoqian, Wang Guanglan. Effects of visual interference on biomechanical characteristics of lower limbs in athletes after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4223-4229. |
| [10] | Li Zhenzhen, Zhen Qiaoxia, Chen Keke, Fang Boyan. Effects of different forms of shaker exercises on hyoid muscles activation in healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3791-3797. |
| [11] | Jin Pengfei, Ren Jie. Biomechanical changes of the lower limbs in table tennis players with different foot contact patterns of table tennis forehand loop [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 2995-3001. |
| [12] | Guo Xinfeng, Liang Zhidong, Chen Huiyu, Li Yang. Effects of training modalities and training cycles on visceral and subcutaneous fat in recessively obese individuals [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2340-2346. |
| [13] | Wu Jing, Yao Yingce, Yang Xiaowei, Xue Boshi, Zhao Jianbin, Yang Chen, Luan Tianfeng, Zhou Zhipeng. Intervention of muscle strength training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on lower limb function and biomechanical changes in patients with patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [14] | Han Bing, Liu Hongbin, Wang Hehong, Zhao Hanqing, Zhao Riguang, Sun Yiyan, Zhang Yu. Correlation between lower limb alignment and risk factors of patellofemoral pain syndrome in young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1211-1216. |
| [15] | Wang Tihui, Wang Xu, Wu Jinqing, Chen Jiliang, Wang Xiaolu, Miao Juan. Application of three-dimensional simulated osteotomy of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 905-910. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||