Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (24): 5179-5186.doi: 10.12307/2025.736
Previous Articles Next Articles
Treatment and repair of musculoskeletal degenerative diseases and injuries from the perspective of muscle-bone crosstalk mechanism
Zhang Xingyu, Wu Dou, Zhao Enzhe, Song Xubin, Zhang Xiaolun
- Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University,Shanxi Bethune Hospital,Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences,Tongji Shanxi Hospital,Taiyuan030032,Shanxi Province,China
-
Received:2024-09-21Accepted:2024-10-31Online:2025-08-28Published:2025-01-25 -
Contact:Wu Dou, PhD, Chief physician, Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University,Shanxi Bethune Hospital,Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences,Tongji Shanxi Hospital,Taiyuan030032,Shanxi Province,China -
About author:Zhang Xingyu, MS, Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University,Shanxi Bethune Hospital,Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences,Tongji Shanxi Hospital,Taiyuan030032,Shanxi Province,China -
Supported by:Shanxi Province Basic Research Program Project, No. 202303021222326 (to ZEZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Xingyu, Wu Dou, Zhao Enzhe, Song Xubin, Zhang Xiaolun. Treatment and repair of musculoskeletal degenerative diseases and injuries from the perspective of muscle-bone crosstalk mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5179-5186.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

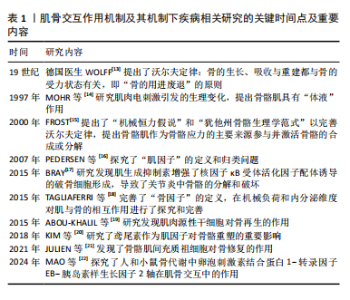
2.2 肌骨的机械交互作用 肌骨的机械交互作用机制是最早被认识并研究的。在解剖学上,骨骼肌通过肌腱与骨骼和关节上牢固的附着点连接,将骨骼节段转变为力学杠杆系统[23],骨骼肌在神经系统指令下完成收缩运动[24];在微观上,肌丝中的肌动蛋白和肌球蛋白异步滑动,表现为宏观的肌肉收缩,从而在关节处产生各向运动的力矩,使骨骼能够多向运动,使人体完成站立、行走、跳跃、面部表情、咀嚼等运动[25]。 沃尔夫定律指出,骨骼的大小和几何形状会根据施加的应力而变化[13],后续完善的“机械稳定器”理论和“犹他州骨骼生理学范式”指出,肌肉收缩产生的应力会诱发其附着骨骼中的合成转换代谢活动[15]。骨细胞是对机械刺激最敏感的细胞,位于骨基质中,被认为是骨重建的主要调节者。一旦成骨细胞被矿化的细胞外基质包围,它们就向骨细胞分化。当骨基质受到机械负荷时,骨细胞可以检测到应力变化。应力检测功能由骨细胞形成的腔隙性小管系统承担,骨细胞可感受伴随小管液快速流动的流体剪切应力和周围电解质浓度,将机械应变转化为生化信号,以募集破骨细胞或成骨细胞对骨进行重塑[26]。在抗阻训练中,施加在骨骼肌上的负荷会作用到骨骼上,这不仅会促进肌肉蛋白质的合成,还会发出高能量需求信号以诱导骨骼的形成,这为肌骨生物力学的相互作用提供了证据[2]。 肌肉和骨骼通过机械负荷相互作用,导致各自的重塑。其中,骨量的发育和维持在很大程度上取决于肌肉产生的机械负荷[15]。骨骼肌质量及肌肉横截面积与不同身体部位的骨量密度呈正相关[27]。从骨的发育来看,骨骼的形状主要由骨骼肌产生的机械负荷决定,在失去骨骼肌机械负荷的发育环境下会导致骨骼发育畸形,失去其固有的生理形状。在一项实验中,小鼠胚胎被敲除骨骼肌发育基因后,骨骼在缺乏骨骼肌附着且无骨骼肌主动收缩的环境下进行发育,该表型的特征是骨矿化严重受损、骨形态改变,表现为异常骨缺损、骨融合、骨发育不全;该研究还提出子宫中运动减少的婴儿会出现暂时性的软骨和关节发育不良[28]。骨骼肌机械负荷还会影响骨隆起的发育,在没有肌肉活动的情况下,骨的生理性隆起会显著减少,甚至完全消失[29]。骨骼肌对骨骼的生长也产生影响,可加剧骨骼生长缺陷。如青少年特发性脊柱侧凸中,凸侧强健的椎旁肌会降低同侧脊柱的机械负荷,从而促进骨骼生长,而凹侧较弱的椎旁肌会增加脊柱负荷并阻碍凹侧骨骼生长,导致弯曲加剧[12]。 虽然肌肉和骨骼之间的相互作用是双向的,但一些观察和研究表明,肌肉相较骨骼在交互协调中起着先行主导作用,在肌骨交互中肌肉变化较骨骼变化较先发生。在一项小鼠后肢悬吊失用实验中,证实股骨和胫骨皮质厚度的减少比腓肠肌和股四头肌质量的降低晚7 d[30]。另一项队列研究表明,从青少年到成人的成长过程中瘦体质量变化先于全身骨密度和骨骼强度的变化[31]。肌萎缩和丢失是航天失重过程中一个难以避免生理过程,被称为失用性肌萎缩和骨丢失,也发生在神经肌肉疾病患者或卧床休息肢体制动的患者。在失重环境下,肌肉骨骼系统失去大量机械刺激,主要是姿势维持骨骼肌受到很大影响,较先发生退变。尽管在太空飞行中采取了运动对策,但仍会发生肌肉萎缩和骨质流失,当宇航员回归地面恢复正常重力时,他们的肌肉恢复速度是骨质恢复速度的6倍[32]。 2.3 肌骨的分泌因子交互 2.3.1 肌因子的交互作用 肌因子根据其在骨代谢中的作用可分为两类:骨形成因子和骨吸收因子。促进骨形成的因子包括鸢尾素、胰岛素样生长因子1、成纤维细胞生长因子2、骨形态发生蛋白1、脑源性神经营养因子、β-氨基异丁酸等;促进骨吸收的肌因子包括肌生长抑制素、白细胞介素等,这些肌因子在骨代谢、骨重建和骨再生中起关键作用[2]。 鸢尾素在肌骨交互的生物学效应中被广泛研究,它是纤连蛋白Ⅲ型结构域5蛋白水解裂解产生的片段,在运动过程中由骨骼肌生成,随后释放到血液循环中[33]。骨骼是鸢尾素的主要靶器官,鸢尾素通过增加骨形成和降低破骨细胞活性促进骨的合成代谢[34]。研究发现,肌肉减少症和骨质疏松症患者血清中的鸢尾素水平明显低于健康对照组,这表明鸢尾素对骨骼肌和骨骼疾病具有高度敏感性。年龄和机械刺激减少是骨质疏松症的重要因素,随着年龄的增长或肢体制动时间延长,血清鸢尾素水平也逐渐降低[35]。鸢尾素已被普遍认为是骨质疏松症、肌肉减少症和肌少-骨质疏松症的预测标志物[36]。 肌生成抑制素又称生长和分化因子8,属于转化生长因子β超家族,是骨骼肌和骨的负调节因子。研究表明,肌生长抑制素可抑制骨细胞来源外泌体miRNA-218的表达,增加抗骨形成代谢因子硬化蛋白、核因子κB受体活化因子配体的产生,以及促进Dickkopf相关蛋白1的产生,其为Dickkopf Wnt信号通路抑制剂[37]。肌肉生长抑制素可以靶向多种骨细胞,包括间充质干细胞、成骨细胞、骨细胞和破骨细胞[38]。肌肉生长抑制素抑制肌细胞的增殖和分化,与肌萎缩和损伤呈正相关。肌生成抑制素作用于骨可促进骨吸收,抑制骨生成[3]。据报道,在中年人群中,高肌肉生长抑制素水平与低皮质骨厚度以及低肌肉质量呈正相关[39]。 β-氨基异丁酸是一种骨骼肌在运动状态下分泌的肌因子,是缬氨酸或胸腺嘧啶的代谢物 [40]。β-氨基异丁酸的对映体L-β-氨基异丁酸可保护骨细胞免受氧化应激对线粒体功能的破坏,并最终保护骨量,遏制骨细胞的凋亡[41]。 胰岛素样生长因子1和成纤维细胞生长因子2可通过促进成骨细胞的增殖和分化,保持骨量,也是骨修复的强力因子[42]。胰岛素样生长因子1和成纤维细胞生长因子2由肌管分泌,在肌肉损伤后,肌瓣的伤口分泌物中存在高浓度的胰岛素样生长因子1,伴随局部成纤维细胞生长因子2释放增加[43]。最近发现,成纤维细胞生长因子2还可通过抑制骨硬化蛋白基因的信号转导对抗糖皮质激素对骨的吸收作用[44]。一项研究证明了卵泡刺激素结合蛋白1-转录因子EB-胰岛素样生长因子2转导通路与肌萎缩和骨丢失发病机制的联系,肌纤维中卵泡刺激素结合蛋白1的减少诱导转录因子EB的核转位,激活成纤维细胞生长因子2基因的转录和分泌,进而激活破骨细胞内的成纤维细胞生长因子2受体信号传导,刺激破骨细胞生成[22]。 白细胞介素家族的细胞因子大多是促炎递质,由全身多种细胞类型分泌。骨骼肌分泌几种白细胞介素,其中包括白细胞介素6、白细胞介素7和白细胞介素15。白细胞介素6可由肝脏合成,但运动时循环中激增的白细胞介素6由肌肉分泌,白细胞介素6 作用于成骨细胞以促进破骨细胞分化和骨钙素释放[45]。 2.3.2 骨因子的交互作用 骨因子可分为促进肌肉生长的骨因子和促进肌肉退化的骨因子,前者包括骨钙素等,后者包括硬化蛋白和核因子κB受体活化因子配体和转化生长因子β等[2]。 核因子κB受体活化因子配体是骨保护素/核因子κB受体活化因子配体/核因子κB 受体激活剂信号通路中必不可少的一环,主要位于成骨细胞和骨细胞中,核因子κB受体活化因子配体可以与其受体核因子κB 受体激活剂结合而激活下游各信号分子,包括集落刺激因子1受体和核因子κB受体,进而启动破骨细胞分化;另一方面,骨保护素是核因子κB受体活化因子配体的可溶性受体,可阻碍核因子κB受体活化因子配体和核因子κB 受体激活剂的结合,抑制破骨细胞生成 [37]。骨保护素/核因子κB受体活化因子配体/核因子κB 受体激活剂轴功能障碍或核因子κB受体活化因子配体的过表达会导致骨质疏松,而对其的抑制可逆转骨质疏松,增加骨量和强度。骨骼肌中同样表达核因子κB受体活化因子配体,其激活可抑制成肌细胞分化并诱导肌肉萎缩[46-47], 骨钙素是一种由成骨细胞分泌的激素,以羧化、欠羧化和未羧化形式存在于循环中。多项临床研究表明,运动后欠羧化骨钙素增加,欠羧化骨钙素可通过调控GPRC6A基因抑制破骨细胞的早期分化,从而阻止骨吸 收[48]。欠羧化骨钙素也与肌肉质量和功能有关,循环中的欠羧化骨钙素通过抑制肿瘤坏死因子α介导的下游信号通路来抑制炎症因子的表达,抑制肌萎缩[49]。有研究称白细胞介素6/成骨细胞/骨钙素信号传递是肌-骨-肌交互轴的新机制,肌释放白细胞介素6作用于成骨细胞后,激活核因子κB受体活化因子配体表达和促进成骨细胞分化,并释放骨钙素进入循环[45]。 硬化蛋白是由硬化蛋白基因表达的蛋白质,是一种由成熟骨细胞分泌的糖蛋白,可作为骨形成的拮抗剂。硬化蛋白不仅抑制骨形态发生蛋白诱导的Smad蛋白磷酸化,还阻断Wnt/β-catenin通路,进而抑制成骨细胞[50]。此外,硬化蛋白基因抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路减少成肌细胞而分化,对于肌肉质量和功能也产生负面影响[38]。抑制硬化蛋白基因可以有效增加骨质疏松症患者的骨密度及瘦体质量,增强肌肉再生,促进肌肉功能恢复[51-52]。 2.4 肌骨的干细胞交互 近年随着研究的深入,发现肌肉与骨骼间的相互作用不仅涉及机械和分泌功能,肌肉中的干细胞能够间接影响邻近的骨膜和骨骼,甚至迁移至邻近的骨骼直接为骨骼再生提供干细胞来源。骨骼维持其结构和功能很大程度上依赖骨骼干细胞/祖细胞的激活[53]。骨骼干细胞/祖细胞能自我更新,并能分化成骨、软骨和基质[54]。已确认来源于骨髓、骨骺、骨膜等多种骨骼干细胞/祖细胞可用于骨修复,这些细胞群体具有不同的谱系潜能,不同程度参与骨修复过程[55]。 成纤维脂肪祖细胞是分化为骨骼肌的重要祖细胞,成纤维脂肪祖细胞是一种定植于肌组织中的间充质干细胞,具有在组织损伤后活化为成纤维细胞、脂肪细胞和成骨细胞等间充质谱系的能力。肌肉干/祖细胞(也称肌卫星细胞)是一种位于骨骼肌组织中的成体干细胞,主要负责肌肉的生长、修复和再生,肌肉干/祖细胞在骨骼肌再生过程中与成纤维脂肪祖细胞密切配合。一项实验探究了肌源性干细胞在骨折愈合中的作用,通过转基因小鼠的谱系追踪和干细胞移植实验发现肌肉干/祖细胞在骨折断端可以形成软骨细胞[19,56]。 然而,目前尚无证据显示骨骼中的干细胞对肌肉产生直接影响。骨骼干细胞/祖细胞的成肌能力尚未得到深入研究,但成骨不全症患者同时出现骨骼脆弱和肌肉无力可能说明这两种组织之间存在潜在联系[57]。 2.5 肌骨交互机制视域下现有的临床治疗方法 2.5.1 基于机械交互机制 人体骨量在30岁达到峰值,到70岁时骨量通常会进行性减少至30%。人体肌纤维质量在25岁时达到高峰,40岁之前相对稳定,之后肌肉纤维损失加速,直至80岁时肌肉质量损失30%[58]。一项对288名老年受试者的研究表明,患肌少症的老年人患骨质疏松症的风险高4倍[59]。一项横断面研究调查了芬兰2 142名55岁及以上老年人的骨肌肉减少症患病率及其相关性,肌少症、骨质疏松症和肌少-骨质疏松症的患病率分别为13.8%,11.1%和3.9%。骨肌肉减少症与低体质量指数、慢步态速度、行动不便、日常生活的活动能力下降及抑郁有关[60]。肌骨的退行性变与年龄衰老和机体运动功能密切相关,衰老是不可逆转的危险性因素,而对运动功能的干预是可行的措施。体力活动可以抑制肌肉生长抑制素分泌到循环中,而缺乏体力活动和卧床休息则与之完全相反[61]。 运动可以预防和治疗肌骨退行性疾病,不同形式的运动对肌肉和骨骼有不同影响,其中高强度间歇训练的运动方案对机体在细胞和组织层面更有益处[62-63]。过度的高强度运动对骨骼健康不利,反而会在体内引发高水平的氧化应激,对骨组织造成负面影响。而定期进行适度运动则能增强机体的抗氧化防御能力,可以抑制过度的氧化应激反应,促进骨代谢的正平衡,延缓与年龄相关的骨质流失和骨微结构退变,对多种因素引起的骨质疏松症具有预防和治疗作用。同时运动疗法必须遵从个体化的原则并保证患者能长期坚持,以避免造成急性创伤或慢性损害,比如有氧运动,包括慢跑、爬楼梯和踏步运动更适合患骨质疏松症的老年患者[64]。PMP 22蛋白是一种由有氧运动诱导的小鼠骨骼肌细胞因子,与股骨皮质厚度呈正相关,可以抑制卵巢切除小鼠骨密度的下降,体外实验发现其与成骨细胞的形成和破骨细胞的抑制有关[65]。对一组年龄高于70岁女性的横断面研究表明,下肢的适当抗阻训练会使欠羧化骨钙素增加,同时伴随下肢肌肉力量的提高,研究发现未羧化骨钙素和α-ACT蛋白之间呈负相关,α-ACT蛋白是一种与肌肉减少症的炎症机制相关的急性期反应蛋白[66]。 2.5.2 基于生物化学交互机制 在临床实践中,许多药物已被用于单独治疗肌肉减少症和骨质疏松症。用于治疗骨质疏松症的药物包括双膦酸盐、降钙素、甲状旁腺激素类似物和雌激素,大致可分为两类:抑制骨吸收和促进骨生成的药物,从而增加骨量和骨密度并降低骨折风险[67]。目前临床上只有一种药物被专用于治疗肌肉萎缩,重组人生长激素用于治疗人类免疫缺陷病毒相关的消瘦,它有效地维持因抗反转录病毒治疗而生长激素缺乏患者的瘦体质量和体质量。重组人生长激素也被证明改善了肌肉骨骼损伤和失用性萎缩患者的预后。同时还有其他药物可以在一定程度上延缓肌肉衰老、改善肌肉功能,例如活性维生素D、β肾上腺素能受体兴奋剂和血管紧张素转换酶抑制剂[68]。地舒单抗通过靶向结合核因子κB受体活化因子配体竞争性抑制破骨细胞的形成和活性,可以有效增加肌肉质量、强度和功能,在骨折愈合期间改善骨强度和硬度;唑来膦酸通过抑制法尼基酰转移酶等酶的活性降低破骨细胞的信号传导,这两种药在临床上治疗骨质疏松起着关键作用,并对肌肉退化也有正向作用。一项研究在老年髋部骨折患者中前瞻性地比较了地舒单抗与唑来膦酸对骨密度和骨骼肌力量的改善作用, 结果显示地舒单抗的作用优于双膦酸盐[69]。 维生素D通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路刺激骨形成和骨矿化,上调骨骼肌中维生素D受体水平,增加维生素D受体活性,增加肌肉线粒体功能并限制线粒体自噬,从而改善肌肉功能,增强肌肉力量[70]。重组人生长因子治疗通过影响全身生长因子和胰岛素样生长因子1水平发挥作用,从而改善机体功能、肌肉质量和骨密度[71]。选择性雌激素受体调节剂作为雄激素受体配体,对性腺减退、肌肉萎缩、骨质疏松也有积极的影响[72]。 特立帕肽被称为甲状旁腺激素类似物,连续给予特立帕肽具有分解代谢作用,而间歇给予特立帕肽对骨具有合成代谢作用[73]。特立帕肽对绝经后骨质疏松女性和骨折高风险的骨质疏松患者有较好疗效。甲状旁腺激素1受体是一种在成骨细胞中发现的G蛋白偶联受体,具有甲状旁腺激素调节功能。当甲状旁腺激素1受体被激活时,它刺激多种G蛋白偶联受体相关信号传导,包括PLC/蛋白激酶C、cAMP/蛋白激酶A和细胞外调节蛋白激酶等信号通路,致骨生成增加,还通过抑制硬化蛋白影响Wnt/β-catenin信号传导途径[73]。甲状旁腺激素对肌卫星细胞的增殖和分化具有积极影响[74]。 2.6 肌骨交互机制视域下对相关疾病潜在的干预途径 运动锻炼结合药物治疗对于肌骨退行性疾病有良好效果。在骨折患者中,卧床时间的延长和体力活动的减少是不可避免的,这意味着在短期内难以实施有效的功能恢复和抗阻运动,因此,随着对肌肉与骨骼之间相互作用的深入理解,将两者作为一个整体,开发能够作用于肌骨共同靶点的技术或药物将具有广阔的应用前景。 2.6.1 基于机械交互机制 对骨骼施加的机械应力对于刺激骨代谢和骨修复至关重要。一项动物研究表明,低幅高频振动可以通过刺激肌纤维而影响骨生成,增强骨化性骨折愈合;而且低幅高频振动有助于抵消肌肉力量和活动性的丧失,显著改善IIa型肌纤维的收缩性和横截面积,增加卫星细胞活化和抑制肌生长抑制素表达,从而延缓肌肉减少症动物模型中肌肉减少症的进展[10]。一项对710名社区老年人的随机对照试验显示,低幅高频振动疗法可有效预防跌倒并改善肌肉力量和平衡能力,表明低幅高频振动疗法可用于缓解改善老年人肌肉功能和力量的退化[75]。 2.6.2 基于生物化学交互机制 COLAIANNI等[76]研究发现,缺乏鸢尾素会减缓骨骼生长并降低骨密度,相反,外源性鸢尾素治疗不仅通过促进骨生成和降低破骨细胞活性来增加骨质量和强度,还提升了骨骼肌的质量和强度。对骨质流失小鼠模型注射鸢尾素可促进骨量恢复[77]。在小鼠骨折模型中,鸢尾素处理组的骨痂形成和矿化更快,骨痂的大小和体积及骨折端新生血管的形成相较对照组更显著,体外实验结果表明鸢尾素能促进细胞内成骨和血管生成,提示鸢尾素可能是通过促进骨形成和血管生成来促进骨折愈合的[78]。基于这些发现可开发一种鸢尾素的疗法,用于治疗卧床或航天导致的失用性骨质疏松症,还可用于加快脆性骨折患者的骨折愈合及身体机能的恢复。鱿鱼软骨的Ⅱ型胶原可介导肌源性胰岛素样生长因子1和鸢尾素的产生和释放,从而促进小鼠的骨折愈合[79]。 肌生长抑制素/促活素A信号是肌肉生长的有效抑制剂和肌肉祖细胞分化的调节剂[68]。LEE等[80]研究发现,抑制肌生长抑制素/促活素A信号传导可明显降低小鼠在太空飞行期间骨骼肌和骨骼的损失。有研究表明,肌肉减少症状态下肌生成抑制素水平升高会阻碍骨折愈合,而肌肉生长抑制素抑制剂同时促进骨折愈合和骨骼肌再生[81]。现已有多种肌肉生长抑制素抑制剂进入研制阶段,被证明可增加肌细胞蛋白质合成、减少降解、增强线粒体生物合成,保护肌肉功能[80]。BIALEK等[82]研究表明,可溶性肌生长抑制素诱饵受体对小鼠的肌肉和骨骼质量都呈现了正向作用。 在一项失用后肢模型的小鼠研究中,用L-β-氨基异丁酸处理后可观察到骨细胞凋亡减少,细胞凋亡作用与抗活性氧的保护功能相关,以阻止骨丢失[83]。一项研究证明L-β-氨基异丁酸与低强度机械负荷对肌骨存在正向协同作用,将两者合用可能对难以进行高强度运动的患者具有重要意义[41]。 针对几种骨因子的干预措施也表现出治疗骨质疏松相关骨折的潜力。研究发现骨折后硬化蛋白基因的表达增加,骨折延迟愈合,骨和骨骼肌的质量和强度也发生降低,抑制硬化蛋白基因可以有效增加骨质疏松症患者的骨密度,改善糖尿病或老年小鼠的肌肉质量和功能[84]。另一项研究证明,抑制硬化蛋白基因可缓解乳腺癌骨转移小鼠的骨转移负荷和肌肉无力,同时延长小鼠生存时间[85]。抑制硬化蛋白基因或是治疗与Wnt/β-catenin信号通路介导的细胞内信号级联相关疾病有潜力的治疗靶点。罗莫佐单抗通过靶向抑制骨硬化蛋白促进骨形成并抑制骨吸收[67],现已作为抗骨质疏松药物在国外上市,但其对肌肉的影响还未有确切研究。 抑制核因子κB受体活化因子配体可以改善骨的质量、强度和功能。有研究表明,除骨组织外,核因子κB受体活化因子配体在骨骼肌中同样表达,激活其通路可致快肌Ⅱb肌纤维的选择性萎缩伴无力,此表型通过对核因子κB受体活化因子配体的抑制治疗得到缓解[86]。骨保护素免疫球蛋白片段复合物注射剂用于抗核因子κB受体活化因子配体治疗,已被证实能够增加肌卫星细胞密度和肌纤维横截面积、抑制细胞损害和凋亡,表明骨保护素免疫球蛋白片段复合物对挽救萎缩肌肉的功能和力量、促进损伤后的肌肉再生具有治疗潜力[87]。抗核因子κB受体活化因子配体的单克隆抗体通过影响核因子κB受体活化因子配体和上游核因子κB通路影响骨骼和肌肉的生长发育[88]。 2.6.3 基于干细胞交互机制 转化生长因子β信号通路转导可调节成纤维脂肪祖细胞的激活和分化,转化生长因子β超家族的配体包括转化生长因子β、肌肉生长抑制素和骨形态发生蛋白,可以诱导细胞增殖、肌成纤维细胞分化和细胞外基质沉积。成纤维脂肪祖细胞是促进肌内成骨的关键细胞,其中骨形态发生蛋白2和骨形态发生蛋白9均能推动成纤维脂肪祖细胞向成骨细胞分化[89]。此外,激活素受体在成纤维脂肪祖细胞中的靶向表达也可以激活其在肌肉中异位骨化,是进行性骨化纤维发育不良中异位骨化的成因[90]。这两项研究表明,骨形态发生蛋白和激活素信号传导在调节成纤维脂肪祖细胞成骨分化中的关键作用。 结合成纤维脂肪祖细胞和肌卫星细胞的成骨作用,利用诱导其定向成骨分化因子的能力,在骨折愈合再生中具有广阔前景,为肌肉骨骼疾病的再生医学提供了新的方向。现阶段富血小板血浆、骨髓和脂肪组织是常用的骨科生物制品。富血小板血浆获取操作简便,对组织再生有一定的帮助,但干细胞成分浓度较低。间充质干细胞是再生医学领域最有潜力的干细胞,富含间充质干细胞的脂肪组织和脐带是其有希望的来源[91]。一些研究提出了涉及成纤维脂肪祖细胞在肌肉骨骼疾病治疗中的潜在疗法。肌肉纤维化是创伤、衰老或营养不良的反应,长期损害肌肉功能,还可延缓损伤愈合。成纤维脂肪祖细胞能通过内皮素旁分泌信号通路与肌肉细胞交互,在骨骼肌纤维化中具有关键作用,使用内皮素受体拮抗剂波生坦能够抑制纤维化并促进骨骼肌的再生,该研究将内皮素确定为拮抗人体肌肉纤维化的新成药靶点[21]。在骨肌多发伤情况下,酪氨酸激酶抑制剂伊马替尼可通过减少主要由成纤维脂肪祖细胞引起的持续性愈合组织纤维化来改善骨再生[92]。 干细胞的分泌因子也有可能成为促进骨骼和肌肉再生的潜在治疗药物。成肌细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡中的miRNA-196a-5p可抑制小鼠细胞中破骨细胞样细胞的形成、抑制破骨细胞相关基因的mRNA以及核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导的线粒体能量代谢而保护骨量[93]。在青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者凹侧的肌卫星细胞中,发现其分化必需的雌激素受体1表达下降及其信号传导被破坏,导致肌卫星细胞分化缺陷,而雷洛昔芬在凹侧激活脊髓旁肌雌激素受体1信号可以一定程度上逆转脊柱的病理性侧弯[12]。一项研究强调了骨折愈合过程急性炎症期对正常骨愈合的重要性,对移植的间充质干细胞进行促炎细胞因子共培养或缺氧条件预处理可增强其成骨潜力,对局部炎症进行免疫调节以促进肌肉骨骼组织的愈合和再生,而不同组织来源间充质干细胞的成骨能力还尚在研究中[94]。 肌源性和骨源性干细胞通过自身分化或是激活相关细胞信号转导通路和局部因子的调控,对骨骼肌肉系统的发育、稳态、再生作用是未来可深入探究的领域。"

| [1] LOMBARDI G, ZIEMANN E, BANFI G. Physical activity and bone health: what is the role of immune system? A narrative review of the third way. Front Endocrinol. 2019;10:60. [2] GOMARASCA M, BANFI G, LOMBARDI G. Myokines: The endocrine coupling of skeletal muscle and bone. Adv Clin Chem. 2020;94:155-218. [3] KIRK B, FEEHAN J, LOMBARDI G, et al. Muscle, bone, and fat crosstalk: the biological role of myokines, osteokines, and adipokines. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020;18(4):388-400. [4] STEPPE L, MEGAFU M, TSCHAFFON-MÜLLER MEA, et al. Fracture healing research: Recent insights. Bone Rep. 2023;19:101686. [5] DING P, GAO C, GAO Y, et al. Osteocytes regulate senescence of bone and bone marrow. Elife. 2022;11:e81480. [6] KUBAT GB, BOUHAMIDA E, ULGER O, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and skeletal muscle atrophy: Causes, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. Mitochondrion. 2023;72:33-58. [7] WANG Z. Aging and Aging-Related Diseases: Mechanisms and Interventions. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-1117-8. [8] XIE WQ, HE M, YU DJ, et al. Correlation study between bone metabolic markers, bone mineral density, and sarcopenia. J Endocrinol Invest. 2024;47(6):1559-1572. [9] GIELEN E, DUPONT J, DEJAEGER M, et al. Sarcopenia, osteoporosis and frailty. Metabolism. 2023;145:155638. [10] ZHANG N, CHIM YN, WANG J, et al. Impaired fracture healing in sarco‐osteoporotic mice can be rescued by vibration treatment through myostatin suppression. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):277-287. [11] ZHOU J, YI J, BONEWALD L. Muscle-bone crosstalk in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2015;13:274-279. [12] SHAO X, FU X, YANG J, et al. The asymmetrical ESR1 signaling in muscle progenitor cells determines the progression of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Cell Discov. 2023;9(1):44. [13] WOLFF J. The Classic: on the Inner Architecture of Bones and its Importance for Bone Growth:(Ueber die innere Architectur der Knochen und ihre Bedeutung für die Frage vom Knochenwachsthum). Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(4):1056-1065. [14] MOHR T, ANDERSEN JL, BIERING-SØRENSEN F, et al. Long term adaptation to electrically induced cycle training in severe spinal cord injured individuals. Spinal Cord. 1997;35(1):1-16. [15] FROST HM. The Utah paradigm of skeletal physiology: an overview of its insights for bone, cartilage and collagenous tissue organs. J Bone Miner Metab. 2000;18:305-316. [16] PEDERSEN BK, ÅKERSTRÖM TC, NIELSEN AR, et al. Role of myokines in exercise and metabolism. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007;103(3):1093-1098. [17] BRAY N. Targeting myostatin for direct joint defence. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015;14(10):677-677. [18] TAGLIAFERRI C, WITTRANT Y, DAVICCO MJ, et al. Muscle and bone, two interconnected tissues. Ageing Res Rev. 2015;21:55-70. [19] ABOU-KHALIL R, YANG F, LIEU S, et al. Role of muscle stem cells during skeletal regeneration. Stem Cells. 2015;33(5):1501-1511. [20] KIM H, WRANN CD, JEDRYCHOWSKI M, et al. Irisin mediates effects on bone and fat via αV integrin receptors. Cell. 2018;175(7):1756-1768.e17. [21] JULIEN A, KANAGALINGAM A, MARTÍNEZ-SARRÀ E, et al. Direct contribution of skeletal muscle mesenchymal progenitors to bone repair. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1):2860. [22] MAO Y, YAN, YANG J, et al. Muscle-bone cross-talk through the FNIP1-TFEB-IGF2 axis is associated with bone metabolism in human and mouse. Sci Transl Med. 2024;16(750):eadk9811. [23] FRONTERA WR, OCHALA J. Skeletal muscle: a brief review of structure and function. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015;96:183-195. [24] JAYASINGHE SAL, SCHEIDT RA, SAINBURG RL. Neural control of stopping and stabilizing the arm. Front Integr Neurosci. 2022;16:835852.
[25] SYLVESTER AD, LAUTZENHEISER SG, KRAMER PA. A review of musculoskeletal modelling of human locomotion. Interface Focus. 2021;11(5):20200060. [26] INTEMANN J, DE GORTER DJJ, NAYLOR AJ, et al. Importance of osteocyte-mediated regulation of bone remodelling in inflammatory bone disease. Swiss Med Wkly. 2020;150(0506):w20187-w20187. [27] GOODMAN CA, HORNBERGER TA, ROBLING AG. Bone and skeletal muscle: key players in mechanotransduction and potential overlapping mechanisms. Bone. 2015;80:24-36. [28] MURPHY P, ROLFE RA. Building a Co-ordinated Musculoskeletal System: The Plasticity of the Developing Skeleton in Response to Muscle Contractions//Roles of Skeletal Muscle in Organ Development: Prenatal Interdependence among Cells, Tissues, and Organs. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023:81-110. [29] LEEK CC, SOULAS JM, BHATTACHARYA I, et al. Deletion of Fibroblast growth factor 9 globally and in skeletal muscle results in enlarged tuberosities at sites of deltoid tendon attachments. Dev Dyn. 2021; 250(12):1778-1795. [30] WANG L, YOU X, LOTINUN S, et al. Mechanical sensing protein PIEZO1 regulates bone homeostasis via osteoblast-osteoclast crosstalk. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):282. [31] JACKOWSKI SA, LANOVAZ JL, VAN OORT C, et al. Does lean tissue mass accrual during adolescence influence bone structural strength at the proximal femur in young adulthood? Osteoporos Int. 2014;25:1297-1304. [32] LAU P, VICO L, RITTWEGER J. Dissociation of bone resorption and formation in spaceflight and simulated microgravity: Potential role of myokines and osteokines? Biomedicines. 2022;10(2):342. [33] MAAK S, NORHEIM F, DREVON CA, et al. Progress and challenges in the biology of FNDC5 and irisin. Endocr Rev. 2021;42(4):436-456. [34] LIU S, CUI F, NING K, et al. Role of irisin in physiology and pathology. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:962968. [35] ROOMI AB, NORI W, HAMED RM. Lower serum irisin levels are associated with increased osteoporosis and oxidative stress in postmenopausal. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2021;10(1):13. [36] ALSAAWI TA, ALDISI D, ABULMEATY MMA, et al. Screening for sarcopenia among elderly arab females: influence of body composition, lifestyle, irisin, and vitamin D. Nutrients. 2022;14(9): 1855. [37] QIN Y, PENG Y, ZHAO W, et al. Myostatin inhibits osteoblastic differentiation by suppressing osteocyte-derived exosomal microRNA-218: A novel mechanism in muscle-bone communication. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(26):11021-11033. [38] HE C, HE W, HOU J, et al. Bone and muscle crosstalk in aging. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:585644. [39] KURIYAMA N, OZAKI E, KOYAMA T, et al. Evaluation of myostatin as a possible regulator and marker of skeletal muscle-cortical bone interaction in adults. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39:404-415. [40] BONEWALD L. Use it or lose it to age: A review of bone and muscle communication. Bone. 2019;120:212-218. [41] PRIDEAUX M, SMARGIASSI A, PENG G, et al. L BAIBA Synergizes with Sub Optimal Mechanical Loading to Promote New Bone Formation. JBMR Plus. 2023;7(6):e10746. [42] NOVAIS A, CHATZOPOULOU E, CHAUSSAIN C, et al. The potential of FGF-2 in craniofacial bone tissue engineering: a review. Cells. 2021;10(4):932. [43] MAZZIOTTI G, LANIA AG, CANALIS E. Skeletal disorders associated with the growth hormone–insulin-like growth factor 1 axis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022;18(6):353-365. [44] ADHIKARY S, CHOUDHARY D, TRIPATHI AK, et al. FGF-2 targets sclerostin in bone and myostatin in skeletal muscle to mitigate the deleterious effects of glucocorticoid on musculoskeletal degradation. Life Sci. 2019;229:261-276. [45] CHOWDHURY S, SCHULZ L, PALMISANO B, et al. Muscle-derived interleukin 6 increases exercise capacity by signaling in osteoblasts. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(6): 2888-2902. [46] MARCADET L, BOUREDJI Z, ARGAW A, et al. The roles of RANK/RANKL/OPG in cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscles in health and disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:903657. [47] DUFRESNE SS, DUMONT NA, BOULANGER-PIETTE A, et al. Muscle RANK is a key regulator of Ca2+ storage, SERCA activity, and function of fast-twitch skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016;310(8): C663-C672. [48] WANG H, LI J, XU Z, et al. Undercarboxylated osteocalcin inhibits the early differentiation of osteoclast mediated by Gprc6a. PeerJ. 2021;9: e10898. [49] PARK D, KIM DY, BYUN MR, et al. Undercarboxylated, But Not Carboxylated, Osteocalcin Suppresses TNF-α-Induced Inflammatory Signaling Pathway in Myoblasts. J Endocr Soc. 2022;6(8):bvac084. [50] MORETTI A, IOLASCON G. Sclerostin: clinical insights in muscle–bone crosstalk. J Int Med Res. 2023;51(8):03000605231193293. [51] RECKER RR, BENSON CT, MATSUMOTO T, et al. A randomized, double‐blind phase 2 clinical trial of blosozumab, a sclerostin antibody, in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(2):216-224. [52] KIM SP, FREY JL, LI Z, et al. Sclerostin influences body composition by regulating catabolic and anabolic metabolism in adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(52):E11238-E11247. [53] JEFFERY EC, MANN TLA, POOL JA, et al. Bone marrow and periosteal skeletal stem/progenitor cells make distinct contributions to bone maintenance and repair. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29(11):1547-1561.e6. [54] CHAN CKF, GULATI GS, SINHA R, et al. Identification of the human skeletal stem cell. Cell. 2018;175(1):43-56.e21. [55] SEROWOKY MA, ARATA CE, CRUMP JG, et al. Skeletal stem cells: insights into maintaining and regenerating the skeleton. Development. 2020;147(5): dev179325. [56] GIULIANI G, ROSINA M, REGGIO A. Signaling pathways regulating the fate of fibro/adipogenic progenitors (FAPs) in skeletal muscle regeneration and disease. FEBS J. 2022;289(21):6484-6517. [57] PHILLIPS CL, JEONG Y. Osteogenesis imperfecta: Muscle-bone interactions when bi-directionally compromised. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018;16:478-489. [58] 董单,许超,万晴冬,等.肌少-骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2023,39(7):625-631. [59] LOCQUET M, BEAUDART C, BRUYÈRE O, et al. Bone health assessment in older people with or without muscle health impairment. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29:1057-1067. [60] BLOMQVIST M, NUOTIO M, SÄÄKSJÄRVI K, et al. Osteosarcopenia in Finland: prevalence and associated factors. Arch Osteoporos. 2024;19(1):1-11. [61] SMEUNINX B, ELHASSAN YS, MANOLOPOULOS KN, et al. The effect of short‐term exercise prehabilitation on skeletal muscle protein synthesis and atrophy during bed rest in older men. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(1):52-69. [62] CHEN J, ZHOU R, FENG Y, et al. Molecular mechanisms of exercise contributing to tissue regeneration. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):383. [63] SURESH KUMAR H, BARNETT EN, FOWLKES JL, et al. Biomechanical Stimulation of Muscle Constructs Influences Phenotype of Bone Constructs by Modulating Myokine Secretion. JBMR Plus. 2023;7(11):e10804. [64] GAO H, ZHAO Y, ZHAO L, et al. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Multiple Exercise-Regulated Bone Homeostasis. Aging Dis. 2023;14(5):1555. [65] KAWAGUCHI M, KAWAO N, MURATANI M, et al. Role of peripheral myelin protein 22 in chronic exercise‐induced interactions of muscle and bone in mice. J Cell Physiol. 2022;237(5):2492-2502. [66] LEVINGER I, SCOTT D, NICHOLSON GC, et al. Undercarboxylated osteocalcin, muscle strength and indices of bone health in older women. Bone. 2014;64:8-12. [67] PANA A, SOURTZI P, KALOKAIRINOU A, et al. Sarcopenia and polypharmacy among older adults: a scoping review of the literature. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2022;98:104520. [68] RODGERS BD, WARD CW. Myostatin/activin receptor ligands in muscle and the development status of attenuating drugs. Endocr Rev. 2022;43(2):329-365. [69] RUPP T, VON VOPELIUS E, STRAHL A, et al. Beneficial effects of denosumab on muscle performance in patients with low BMD: a retrospective, propensity score-matched study. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(10):2177-2184. [70] BASS JJ, KAZI AA, DEANE CS, et al. The mechanisms of skeletal muscle atrophy in response to transient knockdown of the vitamin D receptor in vivo. J Physiol. 2021;599(3):963-979. [71] ALTOWATI MA, SHEPHERD S, MCGROGAN P, et al. Effects of recombinant human growth hormone in children with Crohn’s disease on the muscle-bone unit: a preliminary study. Horm Res Paediatr. 2018;90(2):128-131. [72] ELAHMER NR, WONG SK, MOHAMED N, et al. Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Strategies in Osteoporosis: A Comprehensive Review. Biomedicines. 2024;12(8):1635. [73] BRENT MB, STOLTENBORG FE, BRÜEL A, et al. Teriparatide and abaloparatide have a similar effect on bone in mice. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:628994. [74] ROMAGNOLI C, ZONEFRATI R, LUCATTELLI E, et al. In Vitro Effects of PTH (1-84) on Human Skeletal Muscle-Derived Satellite Cells. Biomedicines. 2023;11(4):1017. [75] LEUNG KS, LI CY, TSE YK, et al. Effects of 18-month low-magnitude high-frequency vibration on fall rate and fracture risks in 710 community elderly-a cluster-randomized controlled trial. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25:1785-1795. [76] COLAIANNI G, CUSCITO C, MONGELLI T, et al. The myokine irisin increases cortical bone mass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(39):12157-12162. [77] COLAIANNI G, MONGELLI T, CUSCITO C, et al. Irisin prevents and restores bone loss and muscle atrophy in hind-limb suspended mice. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):2811. [78] KAN T, HE Z, DU J, et al. Irisin promotes fracture healing by improving osteogenesis and angiogenesis. J Orthop Translat. 2022;37:37-45. [79] LI Z, TIAN Y, ZHANG L, et al. Type II collagen from squid cartilage mediated myogenic IGF-I and irisin to activate the Ihh/PThrp and Wnt/β-catenin pathways to promote fracture healing in mice. Food Funct. 2021;12(14):6502-6512. [80] LEE SJ, LEHAR A, MEIR JU, et al. Targeting myostatin/activin A protects against skeletal muscle and bone loss during spaceflight. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020; 117(38):23942-23951. [81] ZHANG N, CHIM YN, WANG J, et al. Impaired fracture healing in sarco-osteoporotic mice can be rescued by vibration treatment through myostatin suppression. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):277-287. [82] BIALEK P, PARKINGTON J, LI X, et al. A myostatin and activin decoy receptor enhances bone formation in mice. Bone. 2014;60:162-171. [83] KITASE Y, VALLEJO JA, GUTHEIL W, et al. β-aminoisobutyric acid, l-BAIBA, is a muscle-derived osteocyte survival factor. Cell Rep. 2018;22(6): 1531-1544. [84] RAMLI FF, CHIN KY. A review of the potential application of osteocyte-related biomarkers, fibroblast growth factor-23, sclerostin, and dickkopf-1 in predicting osteoporosis and fractures. Diagnostics. 2020;10(3):145. [85] MAUREL DB, MATSUMOTO T, VALLEJO JA, et al. Characterization of a novel murine Sost ERT2 Cre model targeting osteocytes. Bone Res. 2019;7(1):6. [86] HAMOUDI D, BOUREDJI Z, MARCADET L, et al. Muscle weakness and selective muscle atrophy in osteoprotegerin-deficient mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2020;29(3): 483-494. [87] BOUREDJI Z, HAMOUDI D, MARCADET L, et al. Testing the efficacy of a human full-length OPG-Fc analog in a severe model of cardiotoxin-induced skeletal muscle injury and repair. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021;21:559-573. [88] ONO T, HAYASHI M, SASAKI F, et al. RANKL biology: bone metabolism, the immune system, and beyond. Inflamm Regen. 2020;40:1-16. [89] JUBAN G, SACLIER M, YACOUB-YOUSSEF H, et al. AMPK activation regulates LTBP4-dependent TGF-β1 secretion by pro-inflammatory macrophages and controls fibrosis in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Cell Rep. 2018;25(8):2163-2176.e6. [90] LEES-SHEPARD JB, YAMAMOTO M, BISWAS AA, et al. Activin-dependent signaling in fibro/adipogenic progenitors causes fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):471. [91] FANG WH, VANGSNESS JR CT. Food and Drug Administration’s Position on Commonly Injected Biologic Materials in Orthopaedic Surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(12):3414-3421. [92] BENSALAH M, MURAINE L, BOULINGUIEZ A, et al. A negative feedback loop between fibroadipogenic progenitors and muscle fibres involving endothelin promotes human muscle fibrosis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(3):1771-1784. [93] TAKAFUJI Y, TATSUMI K, KAWAO N, et al. MicroRNA-196a-5p in extracellular vesicles secreted from myoblasts suppresses osteoclast-like cell formation in mouse cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021;108:364-376. [94] MARUYAMA M, RHEE C, UTSUNOMIYA T, et al. Modulation of the inflammatory response and bone healing. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:386. |
| [1] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [2] | Sun Jiahe, Shi Jipeng, Zhu Tianrui, Quan Helong, Xu Hongqi. Effect of exercise intervention in elderly individuals with sarcopenia and its comorbidities: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 997-1007. |
| [3] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [4] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [5] | Li Guangzheng, Li Wei, Zhang Bochun, Ding Haoqin, Zhou Zhongqi, Li Gang, Liang Xuezhen. A prediction model for sarcopenia in postmenopausal women: information analysis based on the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 849-857. |
| [6] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [7] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [8] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [9] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [10] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [11] | Cai Yaohao, Lang Lyu, Li Hong. Assessing the bone mass of the residual alveolar ridge in the first molar for implant placement by cone-beam computed tomography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1572-1577. |
| [12] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [13] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [14] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [15] |
Huang Xiaobin, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, He Yanyan, Xue Lipeng.
Mechanisms of different yin nourishing and kidney tonifying methods on osteoclastysis pathway in ovariectomized rats #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219.
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||