Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (18): 3775-3783.doi: 10.12307/2025.642
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of acupotomy on the expression of fibroblast growth factor family and its receptor in the splenius capitis muscles of rats with cervical spondylosis
Liu Fushui1, Qian Jiaming2, Fang Ting1, Khaliunaa Tumurbaatar2, 3, Zhao Xiaolan2, Zhu Jinchao2, Wang Xiaole1
- 1Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China; 3Institute of Traditional Medicine and Technology, Ulaanbaatar 17032, Mongolia
-
Received:2024-06-13Accepted:2024-07-30Online:2025-06-28Published:2024-11-27 -
Contact:Wang Xiaole, Physician, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Liu Fushui, MD, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82360940 (to LFS); Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, No. 20224ACB206041 (to LFS); Youth Project of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, No. 20232BAB216117 (to WXL); Science and Technology Projects of Jiangxi Education Department, Nos. GJJ211206 (to LFS), GJJ2200984 (to FT), and GJJ2200990 (to WXL); Graduate Student Innovation Special Fund Project of Jiangxi Province, No. YC2023-B223 (to QJM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Fushui, Qian Jiaming, Fang Ting, Khaliunaa Tumurbaatar, Zhao Xiaolan, Zhu Jinchao, Wang Xiaole. Effects of acupotomy on the expression of fibroblast growth factor family and its receptor in the splenius capitis muscles of rats with cervical spondylosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3775-3783.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
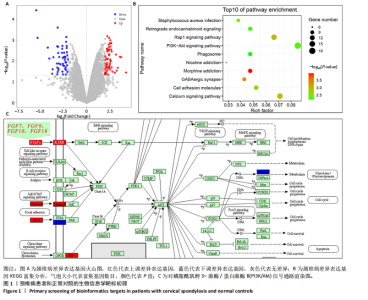
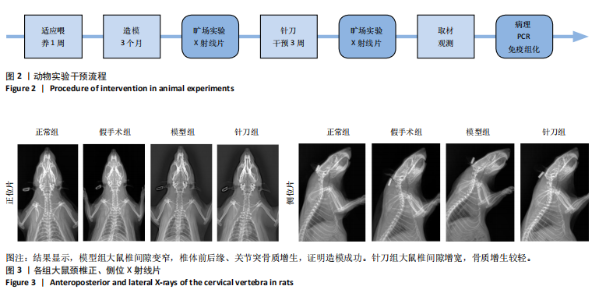
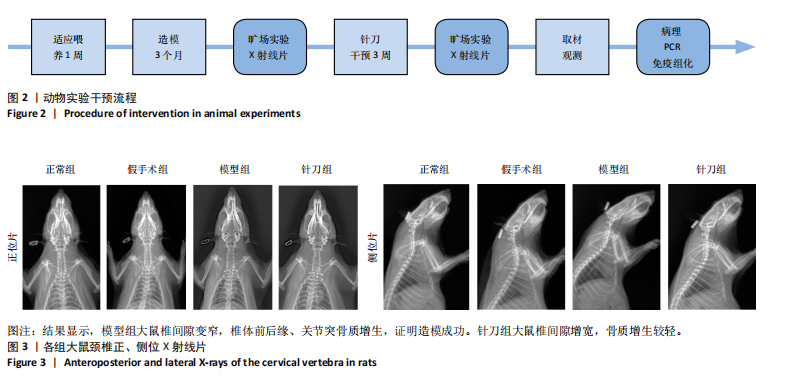
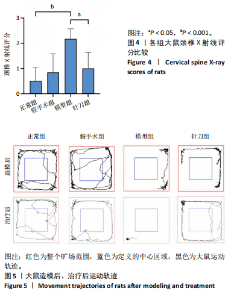
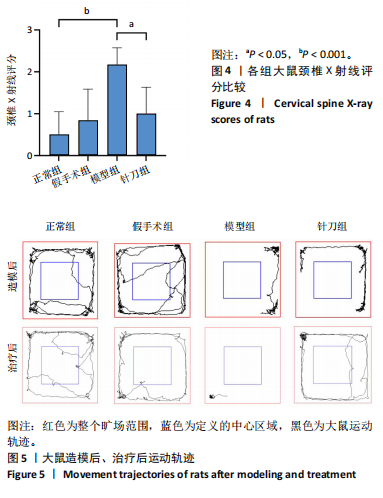
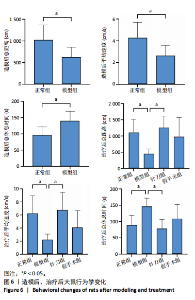
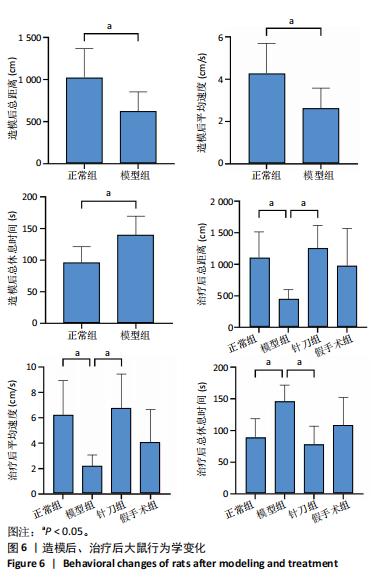
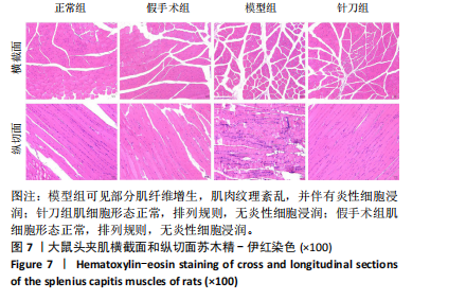
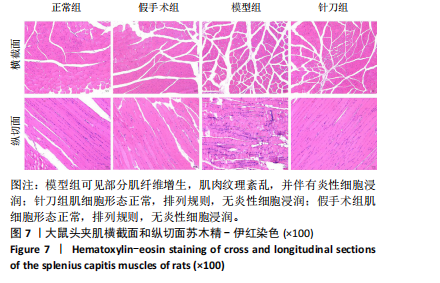
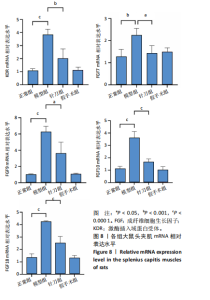
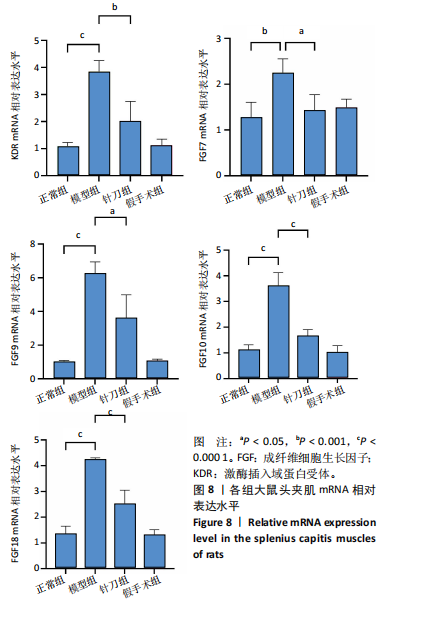
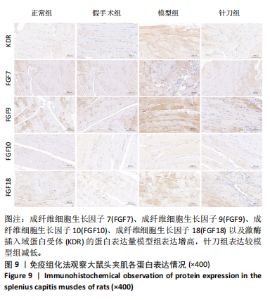
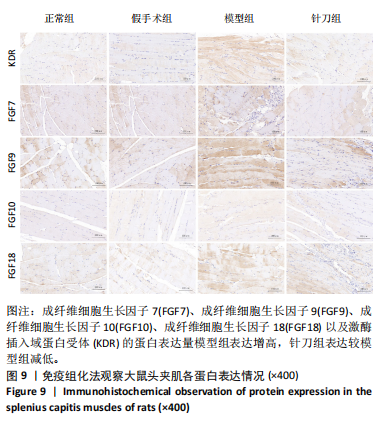
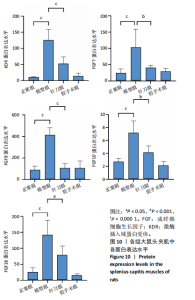
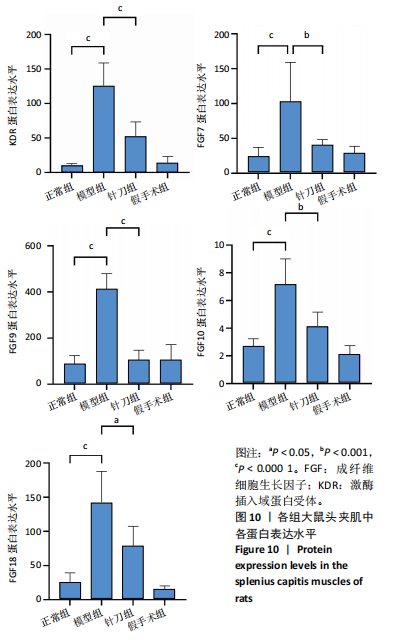
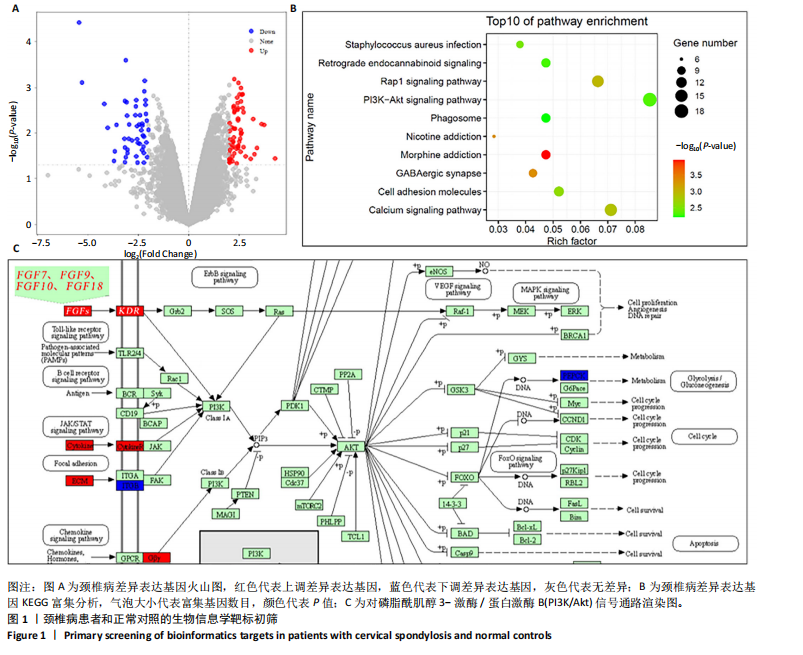
2.1 生物信息学靶标初筛的结果 见图1。正常对照与颈椎病患者比较存在大量差异表达的基因,其中上调表达的基因有60个(P < 0.05,log2FC >2),下调的基因有49个(P < 0.05,log2FC < 2),见图1A。磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路是显著富集的信号通路(P < 0.05),见图1B。对显著富集的磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路研究,结果发现成纤维细胞生长因子家族/激酶插入域蛋白受体是激活磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B上游的重要信号轴,其中成纤维细胞生长因子家族包括成纤维细胞生长因子7、成纤维细胞生长因子9、成纤维细胞生长因子10、成纤维细胞生长因子18,见图1C。 2.2 实验动物数量分析 实验过程无大鼠死亡,实验选用的24只SD大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.3 动物实验干预流程 见图2。 2.4 大鼠颈椎正侧位X射线片检查结果 正常组、假手术组大鼠椎间隙正常,无骨质增生;模型组大鼠椎间隙变窄,椎体前后缘、关节突骨质增生,证明造模成功。针刀组大鼠椎间隙增宽,骨质增生较轻,见图3。颈椎X射线评分表明假手术组与正常组无明显差异(P > 0.05),模型组与正常组比较,颈椎退变明显加重(P < 0.001),而针刀组与模型组比较,颈椎退变减轻(P < 0.05),见图4。 2.5 行为学数据分析 从造模后运动轨迹来看(图5),相较于正常组,模型组大鼠跑动距离短、休息时间长、中心区域时间短。造模后总距离、平均速度模型组小于正常组(P < 0.05),总休息时间模型组长于正常组(P < 0.05),见图6。 从治疗后运动轨迹来看(图5),相较于模型组,针刀组大鼠跑动距离增长、休息时间缩短、中心区域时间延长,提示大鼠活跃度增加。针刀组大鼠治疗后总距离、平均速度大于模型组(P < 0.05),正常组大于模型组(P < 0.05),正常组和假手术组无明显差异(P > 0.05);总休息时间针刀组短于模型组(P < 0.05),正常组短于模型组(P < 0.05),正常组和假手术组无明显差异(P > 0.05),见图6。 2.6 头夹肌病理结果分析 正常组肌细胞形态正常,排列规则,无炎性细胞浸润;模型组可见部分肌纤维增生,肌肉纹理紊乱,并伴有炎性细胞浸润;针刀组肌细胞形态正常,排列规则,无炎性细胞浸润;假手术组肌细胞形态正常,排列规则,无炎性细胞浸润,见图7。"
| [1] WANG C, TIAN F, ZHOU Y, et al. The incidence of cervical spondylosis decreases with aging in the elderly, and increases with aging in the young and adult population: a hospital-based clinical analysis. Clin Interv Aging. 2016;11:47-53. [2] 杨子明, 李放, 陈华江. 颈椎病的分型、诊断及非手术治疗专家共识(2018)[J].中华外科杂志,2018,56(6):401-402. [3] 崔学军, 姚敏. 颈椎病中西医结合诊疗专家共识[J]. 世界中医药, 2023,18(7):918-922. [4] FERNÁNDEZ-DE-LAS-PEÑAS C, ALONSO-BLANCO C, HERNÁNDEZ-BARRERA V, et al. Has the prevalence of neck pain and low back pain changed over the last 5 years? A population-based national study in Spain. Spine J. 2013;13(9):1069-1076. [5] SHIM GY, CHOI J, KIM HJ, et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Spine Pain, 1990-2019: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2024;105(3):461-469. [6] 柯尊华, 王静怡. 颈椎病流行病学及发病机理研究进展[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2014,35(1):62-64. [7] SHIN DW, SHIN JI, KOYANAGI A, et al. Global, regional, and national neck pain burden in the general population, 1990-2019: An analysis of the global burden of disease study 2019. Front Neurol. 2022;13: 955367. [8] WONG J J, SHEARER H M, MIOR S, et al. Are manual therapies, passive physical modalities, or acupuncture effective for the management of patients with whiplash-associated disorders or neck pain and associated disorders? An update of the Bone and Joint Decade Task Force on Neck Pain and Its Associated Disorders by the OPTIMa collaboration. Spine J. 2016;16(12):1598-1630. [9] ABOLFOTOUH SM, ALNORI O, CHOMA T, et al. Epidemiology of Work-Related Neck Pain Among Spine Surgeons. Global Spine J. 2024;14(5): 1515-1523. [10] 朱其彬,勾萍,勾俊杰. 针刀治疗颈椎病临床观察[J].中国针灸, 2010,30(S1):12-13. [11] 刘福水,张义,钟鼎文,等. 针刀与针灸治疗颈椎病疗效比较的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(9):1622-1625. [12] 王拥军,施杞,沈培芝,等. 动静力失衡性大鼠颈椎间盘退变模型的动态观察[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2001,21(3):199-202. [13] WANG Y, SHI Q, LU WW, et al. Cervical Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Induced by Unbalanced Dynamic and Static Forces: A Novel In Vivo Rat Model. Spine. 2006;31(14):1532-1538. [14] 刘福水,周凡媛,张义,等.针刀干预对颈椎病兔颈后伸肌B淋巴细胞瘤-2及其相关的x基因、天冬氨酸特异性半胱氨酸蛋白酶-3 mRNA表达的影响[J].针刺研究,2017,42(6):514-517. [15] 杨淑荃. 针刀结合项痹通颗粒对风寒湿颈型颈椎病的疗效及基于自噬的抗炎止痛机制研究[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2023. [16] 余家阔,吴毅文,戴先进,等.颈椎病生物力学发病机制实验研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,1990,15(1):47-51. [17] 姜宁,张亦文,姚彩虹,等.大小鼠抑郁行为实验方法概述[J].中国实验动物学报,2021,29(6):830-838. [18] LIVAK KJ, SCHMITTGEN TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408. [19] 张丽瑾,朱中书,孙钦然,等.针刀松解颈周腧穴对大鼠退变颈椎间盘细胞外基质金属蛋白酶-1、3及其抑制因子-1基因表达的影响与髓核超微结构观察[J].针刺研究,2015,40(5):352-357. [20] 孙钦然,张丽瑾,朱中书,等.针刀松解颈周腧穴对大鼠退变颈椎间盘Ⅰ、Ⅱ型胶原及组织形态学的影响[J]. 针刺研究,2015,40(4): 275-282. [21] 刘福水,金玉立,谢洪武,等.针刀干预对颈椎病兔软骨终板基质金属蛋白酶13、聚集蛋白聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2020,35(6):3146-3150. [22] 徐善达,孔令军,朱清广,等. 颈型颈椎病“筋骨失衡”的运动学特性研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(9):4739-4742. [23] PEOLSSON A, PEOLSSON M, JULL G, et al. Preliminary evaluation of dorsal muscle activity during resisted cervical extension in patients with longstanding pain and disability following anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery. Physiotherapy. 2015;101(1):69-74. [24] 张义,郭长青.颈肌改变与颈椎病关系的研究进展[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2012,21(18):2045-2047. [25] 游建宇, 刘福水, 陈明人. 基于筋骨理论探讨针刀在颈椎病防治中的应用[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2022,37(2):753-755. [26] 郭长青,刘福水,马惠芳,等.针刀干预对颈椎病兔颈肌细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 针刺研究,2014,39(1):68-72. [27] GOODARZI F, RAHNAMA L, KARIMI N, et al. The Effects of Forward Head Posture on Neck Extensor Muscle Thickness: An Ultrasonographic Study. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2018;41(1):34-41. [28] 王志彬,丁杰,陈根,等.基于实时应变弹性成像对上交叉综合征患者肌肉功能的康复评定[J]. 科技导报,2023,41(23):35-41. [29] 叶济灵, 徐丽丽, 方仲毅, 等. 急性单侧颈痛伴颈部活动受限患者的压痛阈研究[J]. 医用生物力学,2022,37(5):863-867. [30] LIN YH, CHOU L Y, CHOU HC, et al. The Essential Role of Stathmin in Myoblast C2C12 for Vertical Vibration-Induced Myotube Formation. Biomolecules. 2021;11(11):1583. [31] LIU X, BAI M, SUN Y, et al. FGF7-induced E11 facilitates cell-cell communication through connexin43. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(14): 3862-3874. [32] HUANG J, WANG K, SHIFLETT L A, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 9 (FGF9) inhibits myogenic differentiation of C2C12 and human muscle cells. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(24):3562-3580. [33] 程春芳,万娟,丁恺志,等.成肌细胞增殖与分化及其调控机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(14):2200-2206. [34] SU W, ZHENG X, ZHOU H, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 10 delays the progression of osteoarthritis by attenuating synovial fibrosis via inhibition of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling in vivo and in vitro. Mol Immunol. 2023;159:46-57. [35] SUN J, YAN B, YIN W, et al. Identification of genes associated with osteoarthritis by microarray analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(4): 5211-5216. [36] WAGATSUMA A, TAMAKI H, OGITAF. Sequential expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, Flt-1, and KDR/Flk-1 in regenerating mouse skeletal muscle. Physiol Res. 2006;55(6):633-640. [37] RISSANEN TT, VAJANTO I, HILTUNEN MO, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (KDR/Flk-1) in ischemic skeletal muscle and its regeneration. Am J Pathol. 2002;160(4):1393-1403. [38] LI B, WANG Z, HE Y, et al. Adropin Improves Radiation-Induced Myocardial Injury via VEGFR2/PI3K/Akt Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022:2022:8230214. [39] WANG Y, LU YH, TANG C, et al. Calcium Dobesilate Restores Autophagy by Inhibiting the VEGF/PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:886. [40] 刘福水,方婷,洪滔,等.针刀干预对颈椎病兔颈后伸肌细胞PI3K/Akt信号通路的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(2):918-922. |
| [1] | Han Haihui, Ran Lei, Meng Xiaohui, Xin Pengfei, Xiang Zheng, Bian Yanqin, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling to improve bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1905-1912. |
| [2] | Chen Yuning, Jiang Ying, Liao Xiangyu, Chen Qiongjun, Xiong Liang, Liu Yue, Liu Tong. Buqi Huoxue Compounds intervene with the expression of related factors and autophagy related proteins in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1152-1158. |
| [3] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [4] | Fang Yuan, Qian Zhiyong, He Yuanhada, Wang Haiyan, Sha Lirong, Li Xiaohe, Liu Jing, He Yachao, Zhang Kai, Temribagen. Mechanism of Mongolian medicine Echinops sphaerocephalus L. in proliferation and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7519-7528. |
| [5] | Li Chen, Liu Ye, Ni Xindi, Zhang Yuang. Simulation analysis of real-time continuous stiffness in muscle fibers and tendons of the triceps surae during multi-joint movement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7529-7536. |
| [6] | Yang Bo, Pan Xinfang, Chang Liuhui, Ni Yong. Correlation of echocardiographic parameters with disability at 3 months after acute ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7544-7551. |
| [7] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [8] | Gong Yuehong, Wang Mengjun, Ren Hang, Zheng Hui, Sun Jiajia, Liu Junpeng, Zhang Fei, Yang Jianhua, Hu Junping. Machine learning combined with bioinformatics screening of key genes for pulmonary fibrosis associated with cellular autophagy and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7679-7689. |
| [9] | Han Jie, Pan Chengzhen, Shang Yuzhi, Zhang Chi. Identification of immunodiagnostic biomarkers and drug screening for steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7690-7700. |
| [10] | Lu Xiuli, Xu Huazhen, Chen Yuxing, Yao Nan, Hu Zixuan, Huang Dane. Mechanism of Jiangu Formula in treating osteoporosis based on osteoclast-osteoblast coupling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6828-6835. |
| [11] | Yan Laijun, Ge Haiya, Wang Zhengming, Yang Zongrui, Niu Lifeng, Zhan Hongsheng. Mechanism by which Tongdu Huoxue Decoction inhibits macrophage inflammation to delay intervertebral disc degeneration in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6851-6857. |
| [12] | Nigeayi · Aihemaiti, Yilidanna · Dilixiati, An Wei, Maimaitituxun · Tuerdi. Expression of mitochondrial creatine kinase 2 in a rat model of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis and its role in inflammation progression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6877-6884. |
| [13] | Wang Ziheng, Wu Shuang. Oxidative stress-related genes and molecular mechanisms after spinal cord injury: data analysis and verification based on GEO database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6893-6904. |
| [14] |
Zhou Rulin, Hu Yuanzheng, Wang Zongqing, Zhou Guoping, Zhang Baochao, Xu Qian, Bai Fanghui.
Exploration of biomarkers for moyamoya disease and analysis of traditional Chinese medicine targets#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6927-6938.
|
| [15] | Zhao Xuemei, Wang Rui, Ao · Wuliji, Bao Shuyin, Jiang Xiaohua. Effects of Agiophyllum Oligo Saccharides on inflammation and apoptosis of mouse synovial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6939-6946. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||