Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (14): 3061-3069.doi: 10.12307/2025.620
Previous Articles Next Articles
Different frequencies of electrical stimulation promote recovery from peripheral nerve injury
Liu Minqi1, Gao Mingwei1, Chu Xiaolei2, Xing Zheng2, Li Shihao2, Ding Ning1, Li Yajie1, Li Qi2
-
Received:2024-05-30Accepted:2024-07-15Online:2025-05-18Published:2024-09-29 -
Contact:Li Qi, MS, Associate chief physician, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Tianjin University Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China -
About author:1College of Exercise & Health, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, Tianjin University Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China Liu Minqi, Master candidate, College of Exercise & Health, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research and Development Program of China under the Key Special Project of “Biology and Information Convergence (BT and IT Convergence),” No. 2023YFF1205200 (to XZ [project participant]); Tianjin Municipal Natural Science Foundation (General Programs), Nos. 22JCYBJC00210 (to LQ) and 22JCYBJC00220 (to CXL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Minqi, Gao Mingwei, Chu Xiaolei, Xing Zheng, Li Shihao, Ding Ning, Li Yajie, Li Qi . Different frequencies of electrical stimulation promote recovery from peripheral nerve injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(14): 3061-3069.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
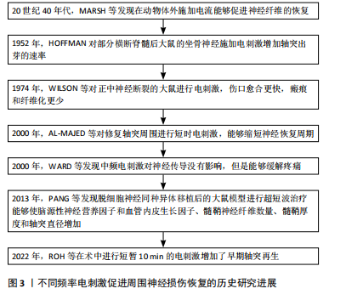
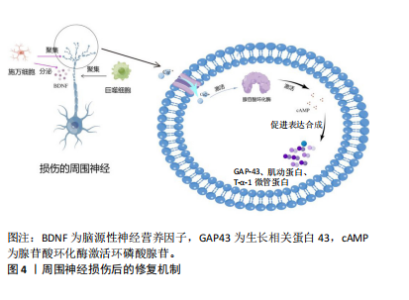
2.1 电刺激促进周围神经损伤恢复的历史研究进展 针对周围神经损伤的治疗有诸多尝试,其中电刺激促进周围神经再生的研究历经数十年发展,取得了显著进展,见图3。20世纪40年代,MARSH等发现在动物体外施加电流能够促进神经纤维的恢复,并能沿着电流方向生长[12]。其中低频电刺激是治疗神经恢复的研究热点。1952年,HOFFMAN[12-13]对部分横断脊髓后大鼠的坐骨神经施加50-100 Hz、10-60 min的电刺激,发现能够增加轴突出芽的速率。2000年,AL-MAJED等[14]研究发现对修复轴突周围进行1 h到2周的20 Hz连续的电刺激,能够缩短神经恢复周期。2016年,CHAN等[15]发现电刺激能够促进施万细胞增殖和脑源性神经生长因子释放。2022年,ROH等[16]发现术中持续10 min的电刺激治疗增加了早期轴突再生,促进了神经横断修复后的功能恢复。 中频电疗法的研究主要集中于缓解慢性疼痛,对于周围神经损伤恢复的较少。2000年,WARD等[17]发现中频电刺激对神经传导没有影响,但是能够缓解疼痛。高频电疗法对于周围神经损伤恢复主要集中在促进炎症反应,加快施万细胞和巨噬细胞的增殖。1974年,WILSON等[12]对正中神经断裂的大鼠进行电刺激,发现未治疗的大鼠在第12天后才和治疗第1天大鼠相同,说明伤口愈合更快,瘢痕和纤维化更少。2013年,PANG等[18]发现脱细胞同种异体神经移植后的大鼠模型同等条件下进行超短波,能够使脑源性神经营养因子和血管上皮生长因子(VEGF)、髓鞘神经纤维数量、髓鞘厚度和轴突直径增加。 2.2 周围神经损伤后修复机制 周围神经受到挤压或者断裂后神经元质膜被破坏,钠离子和钙离子涌入细胞质产生动作电位。损伤部位远端的神经失去与神经元胞体的连接,缺少蛋白质、脂类等能量和营养物质的来源,发生沃勒变性。而钙离子流入轴突损伤部位能够激活蛋白质,主要以腺苷酸环化酶为主,腺苷酸环化酶激活环磷酸腺苷(cAMP)使生长相关蛋白(GAP-43)、肌动蛋白和T-α-1微管蛋白等表达合成,这些微管蛋白支持从近端神经残端萌发的再生生长锥[19]。同时在发生沃勒变性后,大量的施万细胞、巨噬细胞等参与这一过程。由于远端神经元发生"

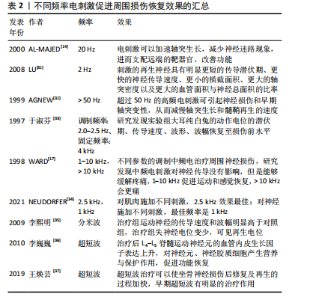
生损害。其原因一可能为过大的电流强度打破了细胞的电化学平衡,阻碍并延缓了神经再生,原因二可能是激活附近支配拮抗肌的神经纤维从而抑制了疗效[23],也易导致肌肉疲劳。反之,较小的电流强度不能达到目标部位的阈值,延缓再生的进程,易出现“神经交错现象”。对于刺激时间来说,ZUO等[24]认为1 h的电刺激能够加速受损的小鼠坐骨神经轴突生长。Charous等[25]发现,30 min的电刺激对于小鼠的面神经功能恢复有显著帮助。因为时间长则容易出现电刺激耐受性,出现兴奋性降低也易导致肌肉疲劳,极大地降低了患者的依从性,刺激时间不能做到规范化统一,不利于判断与处方制定。不同的电刺激方式受到肌肉厚度、脂肪层等外部环境影响。通过研究,Huang等[26]发现在不同强度和频率的电场下,大鼠施万细胞增殖速度及神经生长因子的释放显著增加,发现周围神经对电信号的反应与其频率和幅度密切相关。当刺激信号到达一定强度时,神经的反应大多依赖于频率,且通过研究发现不同频率的电刺激已被证明对接受手术患者的免疫功能、应激反应和血清糖皮质激素水平存在着不同的影响[11] ,因此频率对于周围神经修复和再生的研究有着巨大意义。SticklerY等[27]表示单因素研究可阐明各参数对肌肉收缩的各类作用, 因此电刺激从频率方面进行深入研究具有重要的临床意义。 2.4 不同频率的电刺激机制 电刺激可以改变神经膜上分子分布状态,而神经生长因子的电荷为正容易被吸引,促进了神经生长因子在受损神经部位的集聚,诱发增加钙离子进入,激活细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)磷酸化[28],促进脑源性神经营养因子等神经营养因子上调,加快轴突生长与成熟。且钙离子在新生的轴芽处浓度较高,协同加速了轴芽的生长。这种离子运动刺激神经末梢,扩张受损处血管,产生血管活性肽,改善了损伤神经节段的血液循环,促进神经再生。因此,对比在不同环境下电刺激的生理基础和作用机制具有重要意义,这有助于不同情况下最佳电刺激参数的设置,见表2。常见的电刺激包括低频电刺激、中频电刺激、高频电刺激。低频电刺激涉及的是频率低于1 000 Hz的电流刺激[29];而中频电刺激则指的是频率在1 kHz至100 kHz范围内的电流刺激;至于高频电疗法,它利用的是频率在100 kHz至300 GHz之间、波长在3 000 m至1 mm之间的高频电流[30]。 2.4.1 低频电疗法机制 低频电刺激广泛应用于临床研究,通过电刺激周围神经使钙离子和钠离子向神经元胞体涌"

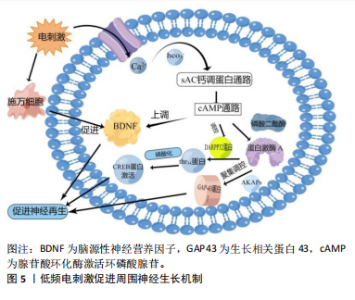
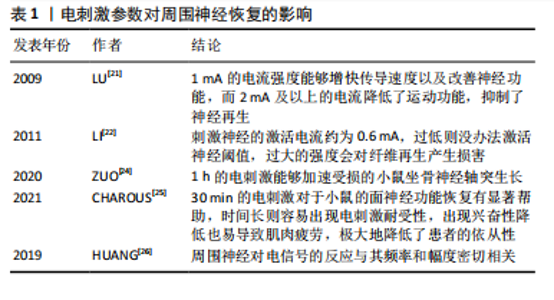
入,钙离子内流进入细胞体,使细胞内的脑源性神经营养因子和Trk B调节上调,相关研究发现,脑源性神经营养因子能够抑制降解cAMP的磷酸二酯酶,从而维持cAMP的细胞内水平含量[38]、激活cAMP反应元件结合蛋白(cAMP-response element binding protein,CREB)、增加T-α-1微管蛋白的合成,这些微管蛋白支持从近端神经残端萌发的再生生长锥[39]。相关研究发现,电刺激能够通过p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase,p38 MAPK)途径激活CREB。在使用特异性p38/MAPK的抑制剂后,CREB的表达被抑制,这表明电刺激诱导的p38/MAPK通路的激活在促进神经轴突生长中具有重要作用[38]。电刺激还可能影响施万细胞行为,如影响体外电刺激后细胞增殖和加速细胞内神经生长因子表达[40],促进巨噬细胞募集和浸润,加速髓磷脂碎片的清 除[41],从而促进体内受损轴突的髓鞘再生,见图5。神经损伤后一两天促进炎症反应的M1巨噬细胞明显增加,损伤后三四天M1型巨噬细胞逐渐分化为抵抗炎症反应的M2型巨噬细胞,从而减少局部炎症反应,促进神经生长[42]。 对于小于1 000 Hz的电刺激主要通过影响细胞周期和合成DNA增强细胞增殖。WITZEL等[43]发现,低频电通过改善早期神经元的状态,开启再生路径,缩短再生时间。然而,过高的频率容易降低患者依从性。AL-MAJED等[14]通过对切断股神经的大鼠施用频率20 Hz、脉冲0.1 ms的电刺激后发现,20 Hz的电刺激可以加速轴突生长,减少神经迷路现象,进而支配远端的靶器官,改善功能。而LU等[31]研究发现,在2 Hz频率下,刺激的再生神经具有明显更短的传导潜伏期、更快的神经传导速度、更小的横截面积、更大的轴突密度以及更大的血管面积与神经总面积的比率。AGNEW等[32]也报道,超过50 Hz的高频电刺激可引起神经损伤和早期轴突变性,从而减慢轴突生长和髓鞘再生的速度。"

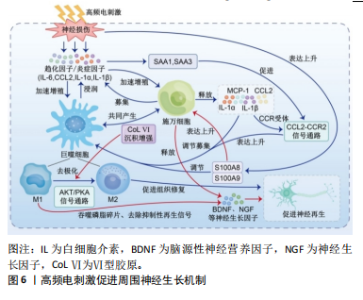
2.4.2 中频电疗法机制 中频电疗法能够缓解疼痛、刺激深层肌肉和神经,使肌肉产生收缩,加快血液和淋巴系统循环,延缓肌肉萎缩,加快传导速度,促进神经修复再生。于淑芬等[33]使用方波、波宽为0.1 ms、调制波频率为2.0-2.5 Hz、固定频率为4 kHz的调制中频脉冲电对坐骨神经损伤后的大耳纯白兔进行每次30 min、连续2-6个月的治疗,研究发现实验组大耳纯白兔的动作电位的潜伏期、传导速度、波形、波幅恢复至损伤前水平,同时实验组兔的血清肌酸磷酸激酶值及神经营养障碍性坏死明显低于对照组,说明中频电疗可以促发损伤部位神经组织的修复,恢复其生物电活动。 对于中频电疗法治疗周围神经损伤的研究较少,大多数研究使用中频电疗法进行镇痛作用。WARD等[17]应用不同参数的调制中频电治疗周围神经损伤,研究发现中频电刺激对神经传导没有影响,但是能够缓解疼痛,1-10 kHz促进运动和感觉恢复,> 10 kHz会更痛。干扰电疗法(interferential current therapy ,IFC)是中频电疗法之中的一种,相关研究认为100 Hz的干扰电频率可以激活大直径、低阈值的Aβ神经纤维,关闭小直径的C纤维和Aδ纤维实现镇痛[44]。NEUDORFER等[34]发现对肌肉施加不同刺激,2.5 kHz效果最佳;对神经施加不同刺激,最佳频率是1 kHz,作用效果依据电流方向与纤维的方向成角各有不同。 WYNDAELE等[45]发现调制频率的最佳频率因肌纤维类型的不同成分而异,较低频率(25-33 Hz)对主要为Ⅰ型(慢肌纤维)的肌肉更好,较高频率(50-66 Hz)对主要为ⅡA型(快肌纤维)的肌肉更好。对于不同的损伤部位,需要结合表面肌电图、超声等手段来辅助找到更合适的频率以及更合适的贴敷位置来促进神经肌肉功能恢复、缓解疼痛等。 2.4.3 高频电疗法机制 高频电疗法根据频率的不同分为微波疗法、短波疗法和超短波疗法。微波疗法是波长为10-30 cm、频率为2 450 MHz的电磁波,可以分为分米波、厘米波和毫米波;短波疗法为波长100-10 m、常用频率为13.56 MHz(波长22.12 m)和27.12 MHz(波长11.06 m);超短波疗法波长为10-1 m、常用频率为40.68 MHz(波长7.37 m)和50.0 MHz(波长为6.0 m)[30];主要分为热效应和非热效应。通过动物实验观察高频电下暴露对蛙坐骨神经复合动作电位传导的影响,发现复合动作电位传导有微小变化而且电刺激后神经恢复所需的时间减少了[46]。李熙明等[35]研究发现通过分米波对腓总神经损伤患者进行12周的治疗后治疗组失神经电位变少,可见再生电位,原理可能是通过加强局部血液循环、抑制炎性反应、改善周围组织缺氧,提供良好的微环境;其中S-100蛋白表达水平显著提高,促进施万细胞增殖,加速损伤神经轴突再生及再髓鞘化、促进再生神经结构成熟,延缓运动终板并促进了终板的再生,从而促进神经再生和功能恢复。ZHAO等[47]利用S-100蛋白作为施万细胞标记物,发现微波疗法诱导再生神经中S-100蛋白的表达上升,其促进神经再生的机制可能涉及上调脊髓和肌肉中脑源性神经生长因子和血管内皮生长因子的表达以及受损神经中S-100蛋白的表达。田德虎[48]使用微波对周围神经损伤后的大鼠进行干预后发现,实验组神经纤维中神经生长因子蛋白及mRNA表达明显高于相同时间点对照组,证明了分米波可通过升高神经组织中神经生长因子水平,使逆转运速度加快,从而抑制神经断端轴突变性反应,促进损伤轴突对神经生长因子蛋白的摄取,加速轴突逆行运输神经生长因子蛋白的过程,进而保护脊髓前角运动神经元,减少细胞凋亡,促进轴突再生[49]。李巍巍等[36]通过超短波对坐骨神经损伤的大鼠干预后发现,超短波治疗后L4-L5脊髓运动神经元的血管内皮生长因子表达上升,可能的原因是作用于神经细胞膜上的酪氨酸激酶受体(VEG-FR)触发了神经再生信号传导,直接对神经元、神经胶质细胞产生营养与保护作用,促进功能恢复。血管内皮生长因子可作为一种神经生长因子和化学趋向因子,其释放能为再生轴索提供必要的附着表面,从而促进轴突和髓鞘的形成。O’BRIEN等[50]研究发现,损伤神经在缺氧的环境下,募集巨噬细胞并上调血管内皮生长因子以促进随后的血管生成。c-Jun蛋白有控制周围神经再生的潜力,c-Jun蛋白可将受损神经的施万细胞重新编程至髓鞘形成表型,以生成再生所必需的修复细胞,同时,c-Jun蛋白的缺失可能会导致功能失调的修复细胞的形成和神经元死亡[51]。研究发现,小剂量超短波有促进神经再生的作用,大剂量则有抑制作用[36]。王焕芸[37]使用足印法及苏木精-伊红染色法评估大鼠坐骨神经功能指数(SFI)及观察神经再生,发现超短波治疗可以使坐骨神经损伤后修复及再生的过程加快,表示早期超短波有明显的治疗作用,且微热量较无热量能更好地促进神经再生。高频电疗法能够穿透较深的组织,并且通过改变神经、肌肉和血管周围的微环境,使施万细胞以及巨噬细胞增殖,加快吞噬和清除细胞碎片,促进神经生长因子的分泌,加快轴突和髓鞘恢复,促进神经再生,见图6。 2.5 不同频率电刺激的临床应用 2.5.1 低频电疗法的临床应用 低频电疗法是临床中应用广泛的电刺激治疗之一。低频电疗法能够促进感觉、运动神经元恢复,缓解疼痛,改善患者的运动功能。ELABD等[52]发现感觉神经横断后,只有约40%神经元的再生轴突能"


长入原来的分支,而应用低频电刺激能将其提高到75%左右。POWER等[53]对肘管减压术后的31例患者进行1 h的电刺激后发现,术后1年,电刺激患者最大复合肌肉动作电位(compound muscle action potential,CMAP)振幅、握力和捏紧强度的客观测量值与对照组相比显著增加;并且在随访中,电刺激组术后1年和3年的运动单位数目较对照组显著增加。FRANZ等[54]发现低频电刺激可以促进运动神经元中多聚唾液酸(PSA)的高表达,加强支配靶器官的精确性。低频电疗法包括神经肌肉电刺激疗法(neuromuscular electrical stimulation,NMSE)与经皮电刺激疗法(transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation,TENS)等,神经肌肉电刺激疗法通过低频脉冲对运动神经元的募集与激活,刺激肌肉恢复功能。研究发现,神经肌肉电刺激疗法通过激活运动轴突产生收缩,诱发收缩主要由刺激部位下运动轴突的直接去极化所驱动[55],这种外周机制的刺激配合康复方案的主动运动激发中枢机制的调节,双重作用更好地促进了神经功能的恢复速度,促进更多的选择性神经再支配[56]。许多研究认为,在进行常规康复训练的基础上进行神经肌肉电刺激疗法在恢复股四头肌力量方面比单独使用传统的康复计划更有效,并且在受伤或手术后尽早且频繁地实施才能达到最佳效果,因此在周围神经损伤后的早期要尽早应用电刺激联合传统康复训练,防止失神经支配后肌肉快速萎缩。CAMPOS等[57]发现经过神经肌肉电刺激疗法联合早期运动的ICU患者的患者站立所需时间更少、住院时间更短、神经元募集更多、肌肉力量更好。研究发现,静脉血栓风险的增加会加快周围神经损伤以及抑制周围神经修复[58]。而有研究发现,神经肌肉电刺激疗法能够降低静脉血栓的风险,FLODIN等[59]在股四头肌应用36 Hz的神经肌肉电刺激疗法可能会最大增加股静脉的峰值静脉速度(PVV),降低静脉血栓的风险,并且没有产生不适感。 经皮电刺激疗法是一种采用低频脉冲电流通过皮肤直接输入人体的治疗方法。在对比研究中,观察到经皮电刺激的脉冲持续时间通常长于植入电极的脉冲持续时间[60],这在一定程度上反映了其渗透性相对较差、作用强度不够强以及靶向性较低的特点。通过临床观察和评估,发现高强度的经皮电刺激在长时间应用时会产生热效应,这种热效应累积到一定程度后,可能会对患者皮肤造成烧伤的风险[47]。这一现象的出现,主要是由于经皮电刺激疗法的低穿透效率限制了刺激电流在人体组织内的有效流动和分布,导致大部分刺激能量在皮肤附近衰减,产生耐受效应[61]。有研究者发现短暂应用或在频率和幅度变化的情况下,经皮电刺激疗法会出现不同的效果,从而防止出现对电流的耐受效应[62]。因此,在面对不同体型的患者时需要特别注意治疗方法的调整。对于体型较瘦的患者,由于皮下脂肪层较薄,电刺激在浅表处的作用更直接,这可能会增加皮肤烧伤的风险,因此在给这类患者进行治疗时,需要特别控制刺激的强度和持续时间,以避免不必要的皮肤损伤。相反,对于肥胖患者,由于皮下脂肪层较厚,电刺激在穿透皮肤后需要达到更深层的神经组织才能发挥作用,这使得准确作用于目标神经部位变得更具挑战性[63]。在这种情况下,可能需要使用更高强度的刺激或采取其他辅助措施,如改变电极的位置或调整刺激的频率,以确保治疗的有效性;同时,也需要密切关注患者的反应,并根据需要调整治疗方案。CHU等[64]通过超声定位损伤神经,并且采用有限元建模,以电流密度和激活功能为优化指标,建立最佳经皮神经刺激参数,对23例正中神经断裂修复术后的患者进行经皮电针刺激,发现患者的感觉功能、运动功能和握力均有改善。因此临床中可能需要借助肌电图、超声等辅助进行精准定位,以及相应的有限元建模对刺激参数进行更准确的应用。 综上所述,低频电作为临床中常用的电刺激方式,衍生了各种的作用方式,如利用电针或植入电极技术可以显著提升治疗作用的靶向性。然而,高靶向性的实现往往伴随着有创性的操作,可能导致患者的低依从性。这种有创性治疗方式和患者较低的配合度,极大地限制了治疗方法的主动性和整体效果。因此,如何在保证治疗效果的同时,降低有创性操作并提高患者的依从性,成为亟待深入研究和解决的关键问题。 2.5.2 中频电疗法的临床应用 临床较为常用的中频电疗法可以分为干扰电疗法、调制中频电疗法。中频电流能够使组织的电阻降低,作用到较深的位置,中频交流电疗法越来越受到人们的重视。调制中频电疗法是用载波频率2 000-5 000 Hz,调制频率10-150 Hz的电流进行治疗,其中连续波与断续波在临床上被证明可以改善神经功能,促进神经支配肌肉收缩。唐伟等[65]使用电脑中频和低频电刺激辅助治疗周围神经损伤,进行2个疗程后,观察组痊愈达到了观察组痊愈显效率为72.4%,对照组为42.9%,说明中频电刺激能够加速周围神经恢复。有研究发现,中频交流电刺激会抑制周围神经无关活动和不适配的肌肉力量的产生[66],目前实验探究了植入式电极的作用,对于片状电极的相关作用还未得到证实,但发现10 kHz是刺激皮下组织的最佳频率,并且发生不适感较少,在此基础能够启发找到疗效显著的调制电频率。 干扰电是将两种不同频率的正弦电流,交叉地输入人体,在深部组织产生低频调制的脉冲电流[67]。干扰电有较高的穿透频率,能够在内部生成电场,减少了对电极附近的皮肤的刺激[68],避免了经皮神经电刺激可能出现的电流烧伤且比侵入性疗法方法更安全、更方便。以高频电流作载体促进穿透,进入深层组织,凭借低频电流刺激神经[61],因为皮肤对中频通过的阻力很小,所以与低频电流时相比,中频电流能够穿透组织的深度更深,治疗效果更佳[44]。ALMEIDA等[69]对175例慢性腰痛患者进行不同频率(2 kHz/100 Hz,2 kHz/2 Hz,4 kHz/100 Hz,4 kHz/2 Hz)比较,发现频率为4 kHz/100 Hz对慢性腰痛患者的即时镇痛作用最优。目前有人提出,干扰电作为一种非侵入式电刺激可以结合其他方案强化疗效,例如镜像疗法、有氧运动以及血流限制等其他不同运动方式相结合[70],可以增强治疗效果,缩短治疗时间。 2.5.3 高频电疗法的临床应用 高频电疗法主要作用于深部组织,其作用包括改善软组织弹性、增加血管舒张、减少肌肉痉挛、促进慢性炎症组织的愈合,使肿胀和疼痛减轻。李熙明等[35]通过分米波对腓总神经损伤患者进行12周的治疗,发现治疗组的运动神经传导速度和波幅明显高于对照组,其中传导速度能够反映髓鞘功能,波幅反映轴索功能。刘海洋等[71]通过针刺联合超短波疗法治疗面神经炎,发现治疗后最大复合肌肉动作电位波幅、TFGS评分均较治疗前增高。应用10-1 mm微波治疗的方法为毫米波疗法,有部分文献提出小剂量可以促进神经再生[47],毫米波可以驱动周围神经系统的快速温度变化,并调节神经元的放电速率,被认为是一种生物反馈。高频电刺激在临床应用中还针对一些退行性疾病产生的活动受限以及慢性疼痛,例如膝骨关节炎、腰椎间盘突出症、颈椎病、肩周炎等。JAN等[72]将40例膝骨关节炎患者分为3组,分别进行短波治疗、短波联合非类固醇抗炎药治疗以及不治疗,通过超声检查发现2个实验组患者的滑膜囊总厚度均显着小于初始厚度,并且在20次治疗中滑膜囊继续显著变薄,疼痛程度逐渐降低;同时,他们发现用药组并没有显示出比单独短波有更好的疗效。对于高频电疗法是促进神经再生的一种手段,但患者主观能动性较低,仍需要合适的辅助手段来帮助电刺激的疗效。"

| [1] LI NY, ONOR GI, LEMME NJ, et al. Epidemiology of Peripheral Nerve Injuries in Sports, Exercise, and Recreation in the United States, 2009 - 2018. Phys Sportsmed. 2021;49(3):355-362. [2] CHU X, SONG X, LI R, et al. Multielectrode Array-Based Percutaneous Nerve Stimulation Strategy With Ultrasound Guidance for Ulnar Nerve Injury. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2023:PP. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3247164. [3] PADOVANO WM, DENGLER J, PATTERSON MM, et al. Incidence of Nerve Injury After Extremity Trauma in the United States. Hand(N Y). 2022;17(4):615-623. [4] GORDON T. Brief Electrical Stimulation Promotes Recovery after Surgical Repair of Injured Peripheral Nerves. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(1):665. [5] KONG J, TENG C, LIU F, et al. Enhancing regeneration and repair of long-distance peripheral nerve defect injuries with continuous microcurrent electrical nerve stimulation. Front Neurosci. 2024;18:1361590. [6] LI C, LIU SY, PI W, et al. Cortical plasticity and nerve regeneration after peripheral nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(8):1518-1523. [7] SUZUKI K, TANAKA H, EBARA M, et al. Electrospun nanofiber sheets incorporating methylcobalamin promote nerve regeneration and functional recovery in a rat sciatic nerve crush injury model. Acta Biomater. 2017;53:250-259. [8] LOPES B, SOUSA P, ALVITES R, et al. Peripheral Nerve Injury Treatments and Advances: One Health Perspective. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2):918. [9] MATTOS E, GUEDES A, LESSA PIF, et al. Influence of surface peripheral electrical stimulation on nerve regeneration after digital nerve neurorrhaphy: study protocol for a randomized clinical trial. F1000Res. 2021;10:219. [10] GORDON T. Peripheral Nerve Regeneration and Muscle Reinnervation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22):8652. [11] YU X, ZHANG F, CHEN B. Effect of transcutaneous electrical acupuncture point stimulation at different frequencies in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Acupunct Med. 2017;35(2):142-147. [12] WILSON DH, JAGADEESH P, NEWMAN PP, et al. The effects of pulsed electromagnetic energy on peripheral nerve regeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;238:575-585. [13] HOFFMAN H. Acceleration and retardation of the process of axon-sprouting in partially devervated muscles. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1952;30(6):541-566. [14] AL-MAJED AA, NEUMANN CM, BRUSHART TM, et al. Brief electrical stimulation promotes the speed and accuracy of motor axonal regeneration. J Neurosci. 2000;20(7):2602-2608. [15] CHAN KM, CURRAN M W, GORDON T. The use of brief post-surgical low frequency electrical stimulation to enhance nerve regeneration in clinical practice. J Physiol. 2016;594(13):3553-3559. [16] ROH J, SCHELLHARDT L, KEANE GC, et al. Short-Duration, Pulsatile, Electrical Stimulation Therapy Accelerates Axon Regeneration and Recovery following Tibial Nerve Injury and Repair in Rats. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022;149(4):681e-690e. [17] WARD AR, ROBERTSON VJ. Variation in torque production with frequency using medium frequency alternating current. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79(11):1399-1404. [18] PANG CJ, TONG L, JI LL, et al. Synergistic effects of ultrashort wave and bone marrow stromal cells on nerve regeneration with acellular nerve allografts. Synapse. 2013;67(10):637-647. [19] KNOTT EP, ASSI M, PEARSE DD. Cyclic AMP signaling: a molecular determinant of peripheral nerve regeneration. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014:651625. [20] RIGONI M, NEGRO S. Signals Orchestrating Peripheral Nerve Repair. Cells. 2020;9(8):1768. [21] LU MC, TSAI CC, CHEN SC, et al. Use of electrical stimulation at different current levels to promote recovery after peripheral nerve injury in rats. J Trauma. 2009;67(5):1066-1072. [22] LI J, KONG X, GOZANI SN, et al. Current-distance relationships for peripheral nerve stimulation localization. Anesth Analg. 2011;112(1): 236-241. [23] WANG G, DOKOS S. Selective myelinated nerve fiber stimulation via temporal interfering electric fields. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021;2021:6033-6036. [24] ZUO KJ, GORDON T, CHAN K M, et al. Electrical stimulation to enhance peripheral nerve regeneration: Update in molecular investigations and clinical translation. Exp Neurol. 2020;332:113397. [25] CHAROUS S J, HUTZ M J, BIALEK S E, et al. Muscle-Nerve-Nerve Grafting Improves Facial Reanimation in Rats Following Facial Nerve Injury. Front Neurol. 2021;12:723024. [26] HUANG Z, GUO Z, SUN M, et al. A study on graphene composites for peripheral nerve injury repair under electrical stimulation. RSC Adv. 2019;9(49):28627-28635. [27] STICKLER Y, MARTINEK J, HOFER C, et al. A finite element model of the electrically stimulated human thigh: changes due to denervation and training. Artif Organs. 2008;32(8):620-624. [28] CHU XL, SONG XZ, LI Q, et al. Basic mechanisms of peripheral nerve injury and treatment via electrical stimulation. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(10):2185-2193. [29] 朱东明,薛军,蒋毅. 低频电刺激治疗周围神经损伤的研究进展 [J].现代实用医学,2023,35(9):1250-1252. [30] FU T, LINEAWEAVER WC, ZHANG F, et al. Role of shortwave and microwave diathermy in peripheral neuropathy. J Int Med Res. 2019; 47(8):3569-3579. [31] LU MC, HO CY, HSU SF, et al. Effects of electrical stimulation at different frequencies on regeneration of transected peripheral nerve. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2008;22(4):367-373. [32] AGNEW WF, MCCREERY DB, YUEN TG, et al. Evolution and resolution of stimulation-induced axonal injury in peripheral nerve. Muscle Nerve. 1999;22(10):1393-1402. [33] 于淑芬,佟俐,刘淑芳,等. 调制中频脉冲电促进周围神经功能恢复的研究 [J]. 中华理疗杂志,1997(1): 3-7. [34] NEUDORFER C, CHOW CT, BOUTET A, et al. Kilohertz-frequency stimulation of the nervous system: A review of underlying mechanisms. Brain Stimul. 2021;14(3):513-530. [35] 李熙明,王爱华,张宏. 分米波治疗腓总神经损伤疗效观察 [J].河北医药,2009,31(16):2073-2074. [36] 李巍巍,苑秀华,张立新,等. 超短波对大鼠坐骨神经损伤后神经传导速度及其损伤运动神经元内VEGF表达的影响 [J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2010,16(8):744-747+801. [37] 王焕芸. 不同剂量超短波对大鼠坐骨神经损伤后的修复及再生作用 [J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2019,40(16):1992-1994.
[38] KAWAMURA K, KANO Y. Electrical stimulation induces neurite outgrowth in PC12m3 cells via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Neurosci Lett. 2019;698:81-84. [39] MCGREGOR C E, ENGLISH A W. The Role of BDNF in Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: Activity-Dependent Treatments and Val66Met. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:522. [40] HUANG J, YE Z, HU X, et al. Electrical stimulation induces calcium-dependent release of NGF from cultured Schwann cells. Glia. 2010; 58(5):622-631. [41] LI X, ZHANG T, LI C, et al. Electrical stimulation accelerates Wallerian degeneration and promotes nerve regeneration after sciatic nerve injury. Glia. 2023;71(3):758-774. [42] OSHIMA E, HAYASHI Y, XIE Z, et al. M2 macrophage-derived cathepsin S promotes peripheral nerve regeneration via fibroblast-Schwann cell-signaling relay. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):258. [43] WITZEL C, BRUSHART TM, KOULAXOUZIDIS G, et al. Electrical Nerve Stimulation Enhances Perilesional Branching after Nerve Grafting but Fails to Increase Regeneration Speed in a Murine Model. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2016;32(6):491-497. [44] RAMPAZO ÉP, LIEBANO RE. Analgesic Effects of Interferential Current Therapy: A Narrative Review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(1):141. [45] WYNDAELE JJ. Study on the influence of the type of current and the frequency of impulses used for electrical stimulation on the contraction of pelvic muscles with different fibre content. Scand J Urol. 2016;50(3):228-233. [46] DEWBERRY LS, DRU AB, GRAVENSTINE M, et al. Partial high frequency nerve block decreases neuropathic signaling following chronic sciatic nerve constriction injury. J Neural Eng. 2021;18(2). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abbf03.. [47] ZHAO F, HE W, ZHANG Y, et al. Electric stimulation and decimeter wave therapy improve the recovery of injured sciatic nerves. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(21):1974-1984. [48] 田德虎,张英泽,赵峰,等. 分米波对大鼠再生神经NGF mRNA表达的影响 [J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2005,27(3):16-19. [49] 高杨. 微波对实验性大鼠周围神经损伤后功能恢复的影响 [D].大连:大连医科大学.2011. [50] O’BRIEN AL, WEST JM, SAFFARI TM, et al. Promoting Nerve Regeneration: Electrical Stimulation, Gene Therapy, and Beyond. Physiology (Bethesda). 2022;37(6):0. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00008.2022. [51] ARTHUR-FARRAJ PJ, LATOUCHE M, WILTON DK, et al. c-Jun reprograms Schwann cells of injured nerves to generate a repair cell essential for regeneration. Neuron. 2012;75(4):633-647. [52] ELABD R, ALABDULKARIM A, ALSABAH S, et al. Role of Electrical Stimulation in Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: A Systematic Review. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022;10(3):e4115. [53] POWER HA, MORHART MJ, OLSON JL, et al. Postsurgical Electrical Stimulation Enhances Recovery Following Surgery for Severe Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurosurgery. 2020;86(6):769-777. [54] SINGH B, XU QG, FRANZ CK, et al. Accelerated axon outgrowth, guidance, and target reinnervation across nerve transection gaps following a brief electrical stimulation paradigm. J Neurosurg. 2012; 116(3):498-512. [55] LAGERQUIST O, WALSH LD, BLOUIN JS, et al. Effect of a peripheral nerve block on torque produced by repetitive electrical stimulation. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009;107(1):161-167. [56] DI PALMA M, AMBROGINI P, LATTANZI D, et al. The impact of different exercise protocols on rat soleus muscle reinnervation and recovery following peripheral nerve lesion and regeneration. Front Physiol. 2022;13:948985. [57] CAMPOS DR, BUENO TBC, ANJOS J, et al. Early Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation in Addition to Early Mobilization Improves Functional Status and Decreases Hospitalization Days of Critically Ill Patients. Crit Care Med. 2022;50(7):1116-1126. [58] BERTHELOT JM, DOUANE F, PLOTEAU S, et al. Venous congestion as a central mechanism of radiculopathies. Joint Bone Spine. 2022; 89(2):105291. [59] FLODIN J, WALLENIUS P, GUO L, et al. Wearable Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Quadriceps Muscle Can Increase Venous Flow. Ann Biomed Eng. 2023;51(12):2873-2882. [60] SHAPIRA Y, SAMMONS V, FORDEN J, et al. Brief Electrical Stimulation Promotes Nerve Regeneration Following Experimental In-Continuity Nerve Injury. Neurosurgery. 2019;85(1):156-163. [61] LEE J, PARK E, KANG W, et al. An Efficient Noninvasive Neuromodulation Modality for Overactive Bladder Using Time Interfering Current Method. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2021;68(1):214-224. [62] JU C, PARK E, KIM T, et al. Effectiveness of electrical stimulation on nerve regeneration after crush injury: Comparison between invasive and non-invasive stimulation. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0233531. [63] SINGH V, SANDHU D, XIANG N. Techniques for Peripheral Nerve Stimulator Implantation of the Upper Extremity. Pain Med. 2020; 21(Suppl 1):S27-s31. [64] CHU XL, SONG XZ, LI YR, et al. An ultrasound-guided percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation regimen devised using finite element modeling promotes functional recovery after median nerve transection. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(3):683-688. [65] 唐伟. 电脑中频和低频电刺激辅助治疗周围神经损伤的疗效观察 [J]. 中国疗养医学,2012,21(12):1112. [66] MARIS S, BRANDS M, LENSKENS D, et al. Transcutaneous electrical nerve inhibition using medium frequency alternating current. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):14911. [67] KAYE AD, RIDGELL S, ALPAUGH E S, et al. Peripheral Nerve Stimulation: A Review of Techniques and Clinical Efficacy. Pain Ther. 2021;10(2): 961-972. [68] DIAS LV, CORDEIRO MA, SCHMIDT DE SALES R, et al. Immediate analgesic effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) and interferential current (IFC) on chronic low back pain: Randomised placebo-controlled trial. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2021;27:181-190. [69] ALMEIDA N, PALADINI LH, KORELO RG, et al. Immediate Effects of the Combination of Interferential Therapy Parameters on Chronic Low Back Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain Pract. 2020;20(6):615-625. [70] 赵晓璇, 刘帅祎, 李奇, 等. 不同运动方式促进周围神经损伤后的功能恢复 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025,29(6):1248-1256. [71] 刘海洋, 师燕, 朱一凡. 针刺联合超短波治疗面神经炎的临床研究 [J]. 黑龙江医药科学,2022,45(5):159-160. [72] JAN MH, CHAI HM, WANG CL, et al. Effects of repetitive shortwave diathermy for reducing synovitis in patients with knee osteoarthritis: an ultrasonographic study. Phys Ther. 2006;86(2):236-244. [73] PARK S, LIU CY, WARD PJ, et al. Effects of Repeated 20-Hz Electrical Stimulation on Functional Recovery Following Peripheral Nerve Injury. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2019;33(9):775-784. [74] CHO Y, PARK J, LEE C, et al. Recent progress on peripheral neural interface technology towards bioelectronic medicine. Bioelectron Med. 2020;6(1):23. |
| [1] | Wang Xuanqiang, Zhang Wenyang, Li Yang, Kong Weiqian, Li Wei, Wang Le, Li Zhongshan, Bai Shi. Effects of chronic exposure to low-frequency pulsed magnetic fields on contractility and morphology of the quadriceps muscle in healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1634-1642. |
| [2] | Zhang Shuai, Li Zichun, Xu Yihao, Xie Xiaofeng, Guo Zhongsheng, Zhao Qingyang. Effect of transcranial magneto-acousto-electrical stimulation on the plasticity of the prefrontal cortex network in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1108-1117. |
| [3] | Zhao Xiaoxuan, Liu Shuaiyi, Li Qi, Xing Zheng, Li Qingwen, Chu Xiaolei. Different exercise modalities promote functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1248-1256. |
| [4] | Wen Zixing, Xu Xin, Zhu Shengqun. Correlations between gastrocnemius morphology parameters and physical activity capacity in elderly females under high-frequency ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1058-1063. |
| [5] | Liu Zan, An Ran, Li Baocheng. Effect of pravastatin on functional recovery from sciatic nerve crush injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 942-950. |
| [6] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [7] | Tian Jinxin, Zhao Yuxin, Hu Tong, Cui Tiantian, Ma Lihong. Effects of different transcranial magnetic stimulation modes on refractory depression in adults: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7639-7648. |
| [8] | Yan Rui, Wang Yiyu, Liu Xue, Jiang Yourong, Cheng Huanzhi, Ma Zhe. Application of exosome-loaded hydrogel in nerve injury regeneration and wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7439-7446. |
| [9] | Zhao Xiaoxuan, Liu Shuaiyi, Xing Zheng, Li Qingwen, Chu Xiaolei, Li Qi. Research hotspots and trends in application of tissue engineering in peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6591-6600. |
| [10] | Zheng Xiang, Zhang Mingxing, Huang Ya, Shan Sharui. Improvement of lower limb walking function in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain by biofeedback assisted electrical stimulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 547-553. |
| [11] | Liu Xiaojun, Shang Yuqing, Guan Wenchao, Xu Linlin, Li Guicai. Oriented electrostatically spun polycaprolactone/silk fibroin scaffold loaded with calcium titanate promotes peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6070-6082. |
| [12] | Zhang Tong, Wang Yan, Yang Chunjia, Yue Qingkun, Wu Qingtian. Role of functional hydrogels in tissue repair after traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 6110-6117. |
| [13] | Guan Zhenjie, Li Wenyuan, Geng Rui, Wang Ying. Regulatory mechanisms of the corticospinal tract after spinal cord injury: combined therapeutic strategies targeting transcription factors and signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5158-5170. |
| [14] | Qiao Zhengji, Chai Niubing, Zheng Luyao, Gao Yunna, Wang Yang. Effect of whole‑body vibration training on bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: a meta‑analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5195-5202. |
| [15] | Zhao Yuxin, Zhang Deqi, Bi Hongyan. Effect of different stimulation modalities of non-invasive brain stimulation on cognitive function in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5212-5223. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||