Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (16): 3380-3387.doi: 10.12307/2025.423
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction and performance evaluation of polycaprolactone/nanodiamond-phospholipid composite materials
Tian Jiayu1, 2, Li Duohua1, 2, Zhang Feng1, 2, Feng Hu2, Sun Wei2
- 1Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2024-02-06Accepted:2024-04-03Online:2025-06-08Published:2024-09-03 -
Contact:Sun Wei, Associate professor, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Tian Jiayu, Master candidate, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Xuzhou Science and Technology Project, No. KC21210 (to SW); Xuzhou Medical Youth Reserve Talent Training Project, No. XWRCHT20220038 (to SW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Jiayu, Li Duohua, Zhang Feng, Feng Hu, Sun Wei. Construction and performance evaluation of polycaprolactone/nanodiamond-phospholipid composite materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3380-3387.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
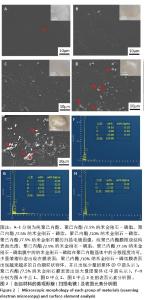
2.2 材料的微观形貌与元素组成检测结果 扫描电镜下观察各组材料中纳米金刚石-磷脂的分布状态,见图2。根据图像可以直观地发现,纯聚己内酯膜微观结构表面光滑;当纳米金刚石-磷脂质量分数在2.5%-7.5%时,纳米金刚石-磷脂在聚己内酯基体中的分散程度均可,少量皱褶形态出现在膜表面(图2B、C);当纳米金刚石-磷脂质量分数继续增加,材料表面出现越来越多的白色颗粒状物体,并且出现少量团聚体(图2D箭头所示);通过点2处(图2D)与点1处(图2A)的元素组成比较证明了白色颗粒状物体是磷脂改性的纳米金刚石;聚己内酯/7.5%纳米金刚石膜表面出现大量团聚体(图2E箭头所示)。 表面元素分析结果显示,纯聚己内酯膜表面的主要元素为C和O;聚己内酯/7.5%纳米金刚石膜表面的主要元素仍为C和O;聚己内酯/7.5%纳米金刚石-磷脂膜表面的元素中出现较多的N、P元素,提示磷脂成功修饰在纳米金刚石上并分散到聚己内酯基体中。通过上述描述,可以得出经磷脂改性的纳米金刚石具有更好的分散性。"

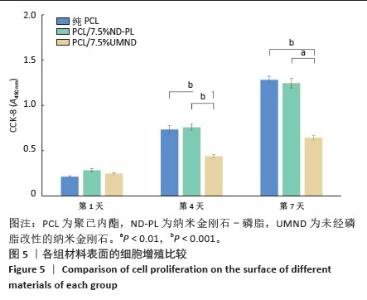
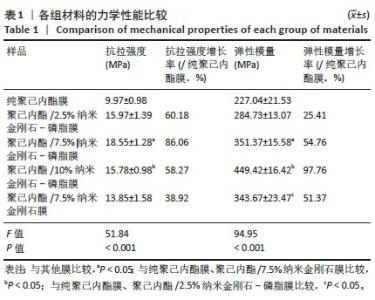
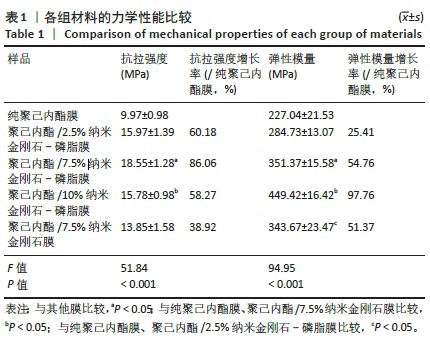
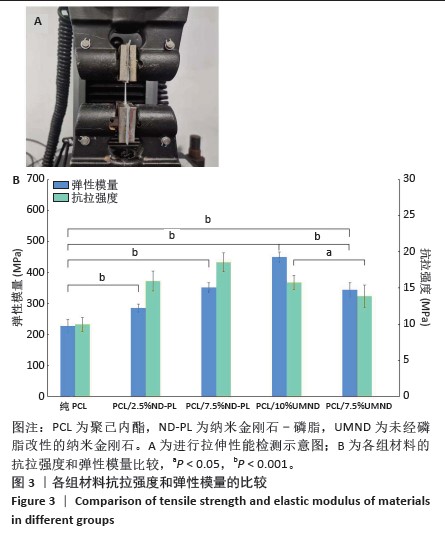
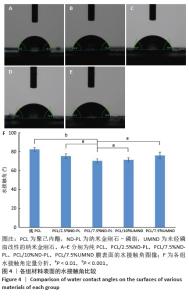
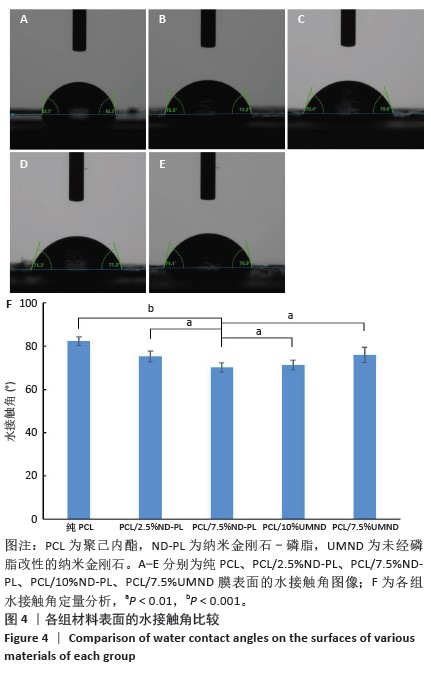
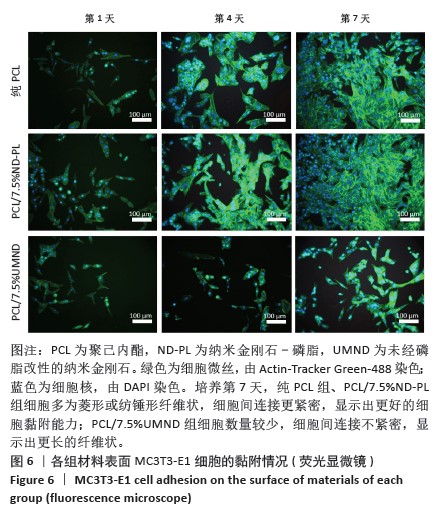
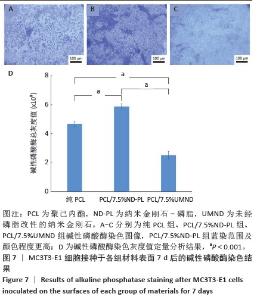
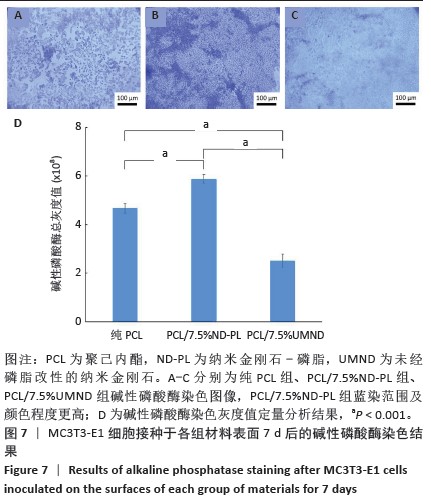
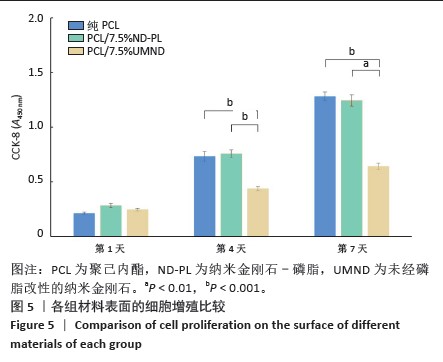
2.5 筛选较佳配比的复合材料 根据各组材料理化性能检测结果,从材料表面特征及纳米金刚石-磷脂分散情况来看,纯聚己内酯/2.5%纳米金刚石-磷脂膜、聚己内酯/7.5%纳米金刚石-磷脂膜表面的纳米金刚石-磷脂分散较为均匀。根据力学实验结果分析,当纳米金刚石-磷脂质量分数增加到7.5%时,复合膜的抗拉强度和弹性模量较纯聚己内酯膜分别增加了86.06%和54.76%,然而随着材料中纳米金刚石-磷脂质量分数增加至10%时,膜的抗拉强度下降。根据水接触角测试分析,当复合材料中纳米金刚石-磷脂质量分数逐渐升高时,材料表面亲水能力逐渐增强。所以,根据上述性能综合结果,选择聚己内酯/7.5%纳米金刚石-磷脂膜为实验组,选择纯聚己内酯膜、聚己内酯/7.5%纳米金刚石膜为对照组进行后续细胞实验。 2.6 各组材料的生物相容性与促成骨性能评价结果 2.6.1 细胞增殖实验 各组材料上的细胞均处于稳定增殖趋势,培养第1天,各组吸光度值比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);培养第4,7天, 聚己内酯/7.5%纳米金刚石组吸光度值低于纯聚己内酯组及聚己内酯/7.5%纳米金刚石-磷脂组(P < 0.05),纯聚己内酯组吸光度值与聚己内酯/7.5%纳米金刚石-磷脂组比较无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图5。细胞增殖实验结果表明,聚己内酯材料中纳米金刚石-磷脂的引入不影响细胞的增殖活力,具有良好的生物相容性。"
| [1] MIGLIORINI F, LA PADULA G, TORSIELLO E, et al. Strategies for large bone defect reconstruction after trauma, infections or tumour excision: a comprehensive review of the literature. Eur J Med Res. 2021;26(1): 118. [2] KIM HD, AMIRTHALINGAM S, KIM SL, et al. Biomimetic Materials and Fabrication Approaches for Bone Tissue Engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(23).doi:10.1002/adhm.20170061. [3] BHARADWAZ A, JAYASURIYA AC. Recent trends in the application of widely used natural and synthetic polymer nanocomposites in bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;110: 110698. [4] STRATTON S, SHELKE NB, HOSHINO K, et al. Bioactive polymeric scaffolds for tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2016;1(2):93-108. [5] 王培.聚己内酯类生物高分子支架在组织工程领域的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(34):5506-5510. [6] MURUGAN S, PARCHA SR. Fabrication techniques involved in developing the composite scaffolds PCL/HA nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(8):93. [7] MALIKMAMMADOV E, TANIR TE, KIZILTAY A, et al. PCL and PCL-based materials in biomedical applications. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(7-9):863-893. [8] WU J, DU X, ZHANG D, et al. A nanodiamond chemotherapeutic folate receptor-targeting prodrug with triggerable drug release. Int J Pharm. 2023;630:122432. [9] CHAUHAN S, JAIN N, NAGAICH U. Nanodiamonds with powerful ability for drug delivery and biomedical applications: Recent updates on in vivo study and patents. J Pharm Anal. 2020;10(1):1-12. [10] Rehman A, Houshyar S, Wang X. Nanodiamond in composite: Biomedical application. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(4):906-922. [11] ZHANG Q, MOCHALIN VN, NEITZEL I, et al. Fluorescent PLLA-nanodiamond composites for bone tissue engineering . Biomaterials. 2011;32(1):87-94. [12] MORIMUNE-MORIYA S, YADA S, KUROKI N, et al. Strong reinforcement effects of nanodiamond on mechanical and thermal properties of polyamide 66. Compos Sci Technol. 2020;199:108356. [13] FOX K, RATWATTE R, BOOTH MA, et al. High Nanodiamond Content-PCL Composite for Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(5):948. [14] 赵紫薇,高小武,曹文鑫,等.纳米金刚石表面功能化对其性能影响的研究进展[J].人工晶体学报,2022,51(5):852-864. [15] HOUSHYAR S, KUMAR GS, RIFAI A, et al. Nanodiamond/poly-ε-caprolactone nanofibrous scaffold for wound management. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;100:378-387. [16] KHAN M, HAMID A, TIEHU L, et al. Surface optimization of detonation nanodiamonds for the enhanced mechanical properties of polymer/nanodiamond composites. Diam Relat Mate. 2020;107:107897. [17] BOGOJEVIC O, NYGAARD JV, WIKING L, et al. Designer phospholipids - structural retrieval, chemo-/bio- synthesis and isotopic labeling. Biotechnol Adv. 2022;60:108025. [18] BITTMAN R, CLEJAN S. Kinetics of cholesterol and phospholipid exchange between mycoplasma membranes and lipid vesicles. Isr J Med Sci. 1987;23(5):398-402. [19] SHUAI C, LI Y, WANG G, et al. Surface modification of nanodiamond: Toward the dispersion of reinforced phase in poly-l-lactic acid scaffolds. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;126:1116-1124. [20] 孔祥宇,王兴,裴志伟,等.生物支架材料及打印技术修复骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(3):479-485. [21] KOUSHIK TM, MILLER CM, ANTUNES E. Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds: Function of Multi-Material Hierarchically Structured Scaffolds. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(9):e2202766. [22] ALDANA AA, ABRAHAM GA. Current advances in electrospun gelatin-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Int J Pharm. 2017; 523(2):441-453. [23] MAIA FR, BASTOS AR, OLIVEIRA JM, et al. Recent approaches towards bone tissue engineering. Bone. 2022;154:116256. [24] SIDDIQUI N, ASAWA S, BIRRU B, et al. PCL-Based Composite Scaffold Matrices for Tissue Engineering Applications. Mol Biotechnol. 2018; 60(7):506-532. [25] HEGYESI N, HODOSI E, POLYÁK P, et al. Controlled degradation of poly-ε-caprolactone for resorbable scaffolds. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;186:110678. [26] MARTINS AF, FACCHI SP, DA CÂMARA PCF, et al. Novel poly(ε-caprolactone)/amino-functionalized tannin electrospun membranes as scaffolds for tissue engineering. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;525: 21-30. [27] CHEN X, LIN Z, FENG Y, et al. Zwitterionic PMCP-Modified Polycaprolactone Surface for Tissue Engineering: Antifouling, Cell Adhesion Promotion, and Osteogenic Differentiation Properties. Small. 2019;15(42):e1903784. [28] SOLECHAN S, SUPRIHANTO A, WIDYANTO SA, et al. Characterization of PLA/PCL/Nano-Hydroxyapatite (nHA) Biocomposites Prepared via Cold Isostatic Pressing. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(3):559. [29] DONG Q, ZHANG M, ZHOU X, et al. 3D-printed Mg-incorporated PCL-based scaffolds: A promising approach for bone healing . Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;129:112372. [30] 陶圣祥,张之涵,柳辉,等.负载蛋白聚糖4的温度敏感性聚己内酯-聚乙二醇-聚己内酯可注射水凝胶对软骨修复的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2023,40(12):2520-2524. [31] KARAMI P, SALKHI KHASRAGHI S, HASHEMI M, et al. Polymer/nanodiamond composites - a comprehensive review from synthesis and fabrication to properties and applications. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2019;269:122-151. [32] JUNG HS, NEUMAN KC. Surface Modification of Fluorescent Nanodiamonds for Biological Applications. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021;11(1):153. [33] TEGAFAW T, LIU S, AHMAD MY, et al. Production, surface modification, physicochemical properties, biocompatibility, and bioimaging applications of nanodiamonds. RSC Adv. 2023;13(46):32381-32397. [34] TINWALA H, WAIRKAR S. Production, surface modification and biomedical applications of nanodiamonds: A sparkling tool for theranostics. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;97:913-931. [35] 宗薇,柴云鹤,邵小桐,等.基于磷脂-嵌段共聚物杂化囊泡的药物载体[J].精细化工,2022,39(11):2290-2296,2336. [36] MA Q, GAO Y, SUN W, et al. Self-Assembled chitosan/phospholipid nanoparticles: from fundamentals to preparation for advanced drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2020;27(1):200-215. [37] DEHGHANI P, AKBARI A, SAADATKISH M, et al. Acceleration of Wound Healing in Rats by Modified Lignocellulose Based Sponge Containing Pentoxifylline Loaded Lecithin/Chitosan Nanoparticles. Gels. 2022; 8(10):658. [38] ZHANG F, SONG Q, HUANG X, et al. A Novel High Mechanical Property PLGA Composite Matrix Loaded with Nanodiamond-Phospholipid Compound for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(2):1087-1097. [39] DU G, LI J, WANG ZB, et al. Effect of Magnesium Addition on Behavior of Collision and Agglomeration between Solid Inclusion Particles on H13 Steel Melts. Steel Res Int. 2017;88(3). doi:10.1002/srin.201600185 [40] GHARIBSHAHIAN M, SALEHI M, BEHESHTIZADEH N, et al. Recent advances on 3D-printed PCL-based composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1168504. [41] ORDUNA L, OTAEGI I, ARANBURU N, et al. Effect of the Simultaneous Addition of Polycaprolactone and Carbon Nanotubes on the Mechanical, Electrical, and Adhesive Properties of Epoxy Resins Cured with Ionic Liquids. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(7):1607. [42] DELAVAR Z, SHOJAEI A. Enhanced mechanical properties of chitosan/nanodiamond composites by improving interphase using thermal oxidation of nanodiamond. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;167:219-228. [43] JEE AY, LEE M. Mechanical properties of polycarbonate and poly(methyl methacrylate) films reinforced with surface-functionalized nanodiamonds. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11(1):533-536. [44] ANITASARI S, WU CZ, SHEN YK. PCL/Graphene Scaffolds for the Osteogenesis Process. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(3):305. [45] Vimalraj S. Alkaline phosphatase: Structure, expression and its function in bone mineralization. Gene. 2020;754:144855. |
| [1] | Sun Xianjuan, Wang Qiuhua, Zhang Jinyi, Yang Yangyang, Wang Wenshuang, Zhang Xiaoqing. Adhesion, proliferation, and vascular smooth muscle differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on different electrospinning membranes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 661-669. |
| [2] | Li Mingzhe, Ye Xiangling, Wang Bing, Yu Xiang. Preparation and osteogenic properties of liquid crystal display light-cured polylactic acid scaffold loaded with nano-tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 670-677. |
| [3] | Xiao Fang, Huang Lei, Wang Lin. Magnetic nanomaterials and magnetic field effects accelerate bone injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 827-838. |
| [4] | Yu Lei, Zhang Wei, Qin Yi, Ge Gaoran, Bai Jiaxiang, Geng Dechun. Repair of femoral condyle defects using mesoporous bioactive glass grafted with bone morphogenetic protein 2 osteogenic peptide inspired by mussel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4629-4638. |
| [5] | An Jiangru, Zhang Jinyi, Wang Qiuhua, Yang Yangyang, Wang Wenshuang, Zhang Xiaoqing. Mesenchymal stem cells combined with polycaprolactone-hyaluronic acid electrospinning membrane in repair of endometrial injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3369-3379. |
| [6] | Qin Jingjie, Guo Zige, Li Rui, Ma Shiqing, Lu Ruijie, Li Mengjun. Modification with bone forming peptide 1 and polydopamine coating to improve bioactivity of polyetheretherketone surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3318-3325. |
| [7] | Chen Jiahan, Feng Chao, Huang Xiaoxia, Niu Minghui, Wang Xin, Teng Yong. Two-dimensional black phosphorus materials for bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2124-2131. |
| [8] | Wu Yaokun, Liu Chenglin, Fu Jiahao, Song Wei, Chen Hao, Xi Hongzhong, Liu Xin, Du Bin, Sun Guangquan. Combination of effective ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine and bone tissue engineering materials for bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2141-2150. |
| [9] | Liu Yunxiang, Zhang Xiaoyu, Li Hao, Zhang Rong, Li Liping, Chen Chongwei. Multiple applications of metal-organic framework materials in bone tissue engineering and orthopedic disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2151-2161. |
| [10] | Wu Zhixin, Jiang Wenwen, Zhan Jianhui, Li Yangshurun, Ren Wenyan, Wang Yiyu. Hydrogels: role and problems in the repair of oral and maxillofacial defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2178-2188. |
| [11] | Hu Zezun, Yang Fanlei, Xu Hao, Luo Zongping. Effect of surface roughness of polydimethylsiloxane on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under stretching conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1981-1989. |
| [12] | Huang Liping, Li Hui, Wang Xinge, Wang Rui, Chang Bei, Li Shiting, Lan Xiaorong, Li Guangwen. Effects of microstructured bone implant material surfaces on osteogenic function of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1990-1996. |
| [13] | Xu Hui, Kang Bingxin, Zhong Sheng, Gao Chenxin, Zhao Chi, Qiu Guowei, Sun Songtao, Xie Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Pressing local acupoints plus adjustion of the knee joint in a sitting position for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 216-221. |
| [14] | Yu Xingge, Lin Kaili. Application of nanocomposite hydrogels in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5441-5446. |
| [15] |
Zou Gang, You Qi, Shen Mengjie, Zhang Jun, Tang Jingfeng, Jin Ying, Liu Yi.
In vitro construction of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell sheet and its osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4023-4027. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||