Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (10): 2124-2131.doi: 10.12307/2025.411
Previous Articles Next Articles
Two-dimensional black phosphorus materials for bone tissue engineering
Chen Jiahan1, Feng Chao2, Huang Xiaoxia1, Niu Minghui3, Wang Xin4, Teng Yong5
- 1Graduate School of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Fourth Clinical College of Medicine, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3College of Pharmacy, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 4Department of Trauma Department, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 5General Hospital of Xinjiang Military Region, Urumqi 830099, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-01-19Accepted:2024-03-09Online:2025-04-08Published:2024-08-23 -
Contact:Teng Yong, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, General Hospital of Xinjiang Military Region, Urumqi 830099, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Chen Jiahan, PhD candidate, Graduate School of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China Feng Chao, Master candidate, Fourth Clinical College of Medicine, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China Chen Jiahan and Feng Chao contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:Regional Fund Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960648; Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2023D01C93 (to TY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Jiahan, Feng Chao, Huang Xiaoxia, Niu Minghui, Wang Xin, Teng Yong. Two-dimensional black phosphorus materials for bone tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2124-2131.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
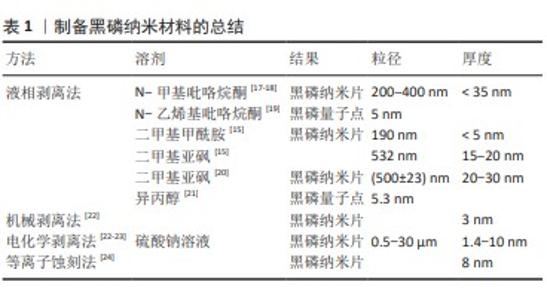
2.1 黑磷材料研究时间线 早在一百年前(1914年),黑磷第一次被美国物理学家珀西·布里奇曼通过将白磷放在高压环境下合成出来[9]。随着石墨烯的问世和兴起,少层黑磷在2014年才被研究者们第一次通过机械剥离的方法制备[10]。随后,一些研究者发现可以通过使用超声剥离的方法,将黑磷制备成粒径只有几百纳米的二维纳米片[11]。研究者发现这种二维纳米材料具有良好的生物相容性、可降解性能以及光热效应,因此被广泛用于生物医学领域[12]。 2.2 纳米黑磷材料的制备 黑磷纳米材料的制备主要为自上而下的顶层剥离方法,主要原理是通过物理或者化学手段削弱黑磷层间的范德华力,得到单层或者少层的磷烯,即黑磷纳米片或量子点。目前,液相剥离法是医学领域研究者最常用的制备黑磷纳米片和黑磷量子点的方法。相比较于其他方法,液相剥离法可以直接制备出各种尺寸的黑磷纳米片,并且通过差速离心分离出研究者需要的尺寸[13],而且具有操作简单、制备量相对较大等优点。液相剥离法最常用的溶剂是N-甲基吡咯烷酮,因为它不含水或任何可能与黑磷发生反应的化学基团[14],其他溶剂包括N-乙烯基吡咯烷酮、二甲基甲酰胺、二甲亚砜和异丙醇也被用于制备黑磷纳米材料。不同的有机溶剂可以影响黑磷纳米材料的产率、尺寸和分散性[15]。除了顶层剥离法之外,自下而上的底层生长方法是其他纳米材料经常采用的制备方法,然而黑磷表面具有较强的化学活性,当它暴露在空气中时容易与氧气发生反应,导致黑磷表面非常脆弱,这不利于黑磷的生长,因此很少有人通过底层生长法来制备黑磷纳米材料,但是仍然有一些成功的案例[16]。在表1中总结了近年来常见的几种顶层剥离方法。"
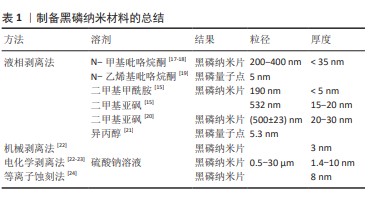
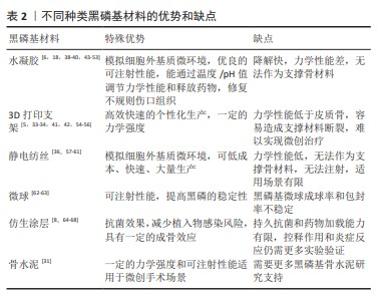
2.3 黑磷纳米材料在骨再生中的优势 虽然骨骼具有强大的愈合能力,但是较大的骨缺损,即临界尺寸缺损是由其他感染疾病等因素引起时,骨的愈合能力将受到极大限制,甚至不愈合[25]。为了预防和解决这一问题,需要通过临床手术干预治疗,人工骨替代物是一种可行有效的选择方案[26-29]。 与其他生物材料相比,黑磷纳米基生物材料在骨再生中具有明显优势,黑磷是磷单质中最稳定的同素异构体,与人体骨中的无机磷元素具有高度的同源性[30],同时黑磷具有良好的生物相容性和降解性能。黑磷的降解性有利于降低局部潜在毒性的累积,黑磷降解后可以形成无毒的磷酸盐并捕获周围的钙离子,形成钙盐沉积,利于骨生长。MA等[31]用含有黑磷的磷酸钙骨水泥共培养小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞(MC3T3-E1),发现黑磷促进了细胞中成骨分化相关蛋白骨形态发生蛋白2、Runx2、骨钙蛋白、骨桥蛋白等的表达,这说明黑磷可以促进成骨分化和诱导。黑磷的层状折叠扶手结构使黑磷获得较高的比表面积,因此可以通过黑磷装载并缓释药物[32]。黑磷还具有优秀的光热性能,红外光可以加速黑磷的降解,继而控制黑磷基材料的力学性能和成骨活性。虽然目前广泛使用的羟基磷灰石和β-磷酸三钙也与人体骨结构相似[29],但是羟基磷灰石不易降解吸收且显示出细胞黏附性低等缺点,β-磷酸三钙虽然具有与黑磷相同的生物相容性、成骨潜能和降解性能,但是显示出较低的力学强度,仍不能完美替代人体骨组织,因此基于黑磷的纳米材料在骨组织工程领域将有更大的发展潜力。 2.4 黑磷在骨组织工程中的研究进展 黑磷优良的理化性质为其在骨组织工程中的应用奠定了良好基础。黑磷在成骨方面具有以下作用:①生物矿化:黑磷降解后产生的磷酸盐可以在材料表面矿化,促进成骨效应[4,33-34];②光热成骨:黑磷的光热作用可以产生轻度的热刺激,上调热休克蛋白、碱性磷酸酶和Ⅰ型胶原表达[35-36],促进骨缺损的修复;③促进血管生成:黑磷能够促进组织周围微血管生成,增加血管生成标记物CD31的表达,进一步帮助周围骨组织的再生[37-38];④促进神经生长:黑磷具有出色的导电性,黑磷基复合材料能促进神经的迁徙和再生[37-39];⑤免疫调节:黑磷能抑制M1巨噬细胞表型并促促进M2巨噬细胞表型[40],抑制炎症分泌[41-42]。由于黑磷出色的成骨特性,研究者们将黑磷与多种不同类型的生物材料结合,该文归纳总结了近10年内主流的黑磷基纳米复合材料,主要分为水凝胶、3D打印支架、复合材料支架、静电纺丝、仿生骨膜、微球和仿生涂层(表2)。作者认为黑磷是未来最有潜力的成骨材料之一。2.4.1 黑磷基水凝胶在骨组织工程中的应用 由于水凝胶可以模拟细胞外基质微环境,是黑磷骨组织工程中被研究最广泛的种类之一。近年来,制备黑磷基水凝胶的成分主要有聚乙烯醇水凝胶[43]、壳聚糖水凝胶[18]、胶原蛋白水凝胶[47]、聚(乙二醇)富马酸水凝胶[45-46,51-52]、甲基丙烯酰胺明胶水凝胶等天然成分水凝胶[39]。水凝胶网络系统能够促进细胞的增殖、黏附和分化[69],并且其特有的三维结构具有良好的生物相容性、低抗原性、可降解性[70],但大部分水凝胶缺乏成骨活性,因此研究者将黑磷纳米材料与水凝胶结合来增强其成骨性能。MIAO等[49]开发了一种基于黑磷的甲基丙烯酰基明胶水凝胶,其中的黑磷纳米片可以显著提高其矿化能力,并且具有良好的近红外光热性能和生物相容性,在红外红辐照下纳米复合水凝胶显示出有效的光热抗菌特性,在没有骨诱导因子的情况下促进体外成骨,这与其他研究者得出的结论相同[44,48]。随后,MIAO等[53]又在其基础上加载了Apt19S DNA,制备出新的大孔甲基丙烯酰基明胶水凝胶,发现Apt19S和黑磷纳米片的加入能够高效募集内源性骨髓间充质干细胞,增加CD29和CD44的阳性表达。XU等[38]制备了一种镁修饰的黑磷纳米片甲基丙烯酰胺明胶水凝胶,其中黑磷纳米片和镁离子能够促进血管生成和刺激神经生长分化并增强成骨,证明黑磷纳米片和镁离子能够增强新内皮细胞的标记物CD31(促进血管生成)和神经发生相关神经元标记物β-微管蛋白Ⅲ的含量。JING等[39]的研究也证明,镁修饰的黑磷纳米片能够协同促进施万细胞的迁移和分泌,促进神经突的生长,促进神经支配骨再生。WU等[40]将多巴胺装饰的去铁胺和黑磷纳米片装载进甲基丙烯酸明胶/甲基丙烯酸海藻酸钠混合水凝胶中,发现在近红外诱导下黑磷纳米片能够诱导促进组织血管生成,同时促进MC3T3-E1细胞的碱性磷酸酶活性和钙矿物质沉积,并且黑磷纳米片能够通过影响M2巨噬细胞来调节免疫系统,减少炎症的发生和释放促生长因子,这与XU等[50]的研究结果类似。 虽然水凝胶在骨组织工程中得到了良好的应用和发展,但水凝胶也存在一些自身的不足:首先,水凝胶由于没有足够的力学性能,在遇到人体无法恢复的骨缺损时,无法作为支撑材料为缺损处提供有效的填补;其次,水凝胶在机体中降解速率较快,长期有效且可控的发挥作用仍是水凝胶面临的挑战。 2.4.2 黑磷基3D打印支架在骨组织工程中的应用 近年来,基于黑磷的3D打印支架在骨肿瘤治疗和骨缺损修复中的应用逐渐增加。研究表明,在支架中添加黑磷能够提高3D支架的成骨性能与理化性能。WANG等[5]研发了一种包含黑磷纳米片、盐酸阿霉素和β-磷酸三钙的低温3D支架,通过光热疗和化疗的协同作用可以消融和长期抑制肿瘤复发并改善骨再生,其中黑磷不仅提供了光热作用,而且降低了盐酸阿霉素的化疗毒性。YANG等[55]也通过黑磷的光热作用和生物矿化能力在骨肉瘤治疗中得到了显著效果。WANG等[54]通过将黑磷纳米片和成骨肽加入β-磷酸三钙/聚(乳酸共三甲酯)纳米复合支架中,打印出拥有4D属性的光热响应形状记忆骨组织工程支架,当近红外照射时支架升温使形状重构,便于支架植入,植入完成后支架温度下降恢复形状。LONG等[42]通过将黑磷纳米片加入聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物3D打印支架中,发现黑磷能够招募和刺激M2巨噬细胞极化,抑制炎症,促进人类骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和分化,这与先前WU等[40]得出的结论相同。3D打印支架极大满足了对不规则缺损的适配要求。相较于减材制造,3D打印可以高效快速的个性化生产。虽然3D打印具有高度的可定制化性能,但是“预先制备性”决定其无法在微创手术中发挥作用,对于椎体成形等手术来说,无法将预先制备好的支架通过微创方式放入骨折缺损当中。另外,大部分3D打印支架的力学强度只能到达松质骨的强度但远低于皮质骨,这使得3D打印支架很难独自承担支撑负重骨的任务。力学性能依然是大部分3D打印支架需要面临的挑战。 2.4.3 黑磷基静电纺丝在骨组织工程中的应用 与水凝胶相同,静电纺丝也被广泛用于合成能够有效模拟天然细胞外基质特性的人工支架[71]。静电纺丝是一种通过注射器针喷射高压流体并在收集槽中固化成形的技术,其能够通过混合各种生物材料制备出纳米/微米级的类似于天然细胞外基质的纤维基质[57,72]。LI等[36]通过微流控技术开发了基于黑磷和羟基磷灰石的多孔二氧化硅聚乳酸支架,发现该支架能够通过黑磷纳米片的光热效应促进成骨,在大鼠颅骨模型中,加入黑磷纳米片并进行近红外照射的组显著高于其他实验组。ZHANG等[59]制备了装载了万古霉素/apt19S/黑磷纳米片的聚己酸内酯静电纺丝,同样发现该电纺丝的光热作用能够加速大鼠颅骨的骨再生。SU等[60]利用同轴静电纺丝技术制备了黑磷纳米片/小猪坐骨神经脱细胞的神经基质/聚己内酯仿生骨膜,研究了其在神经源性骨再生中的作用,结果表明该仿生骨膜能够促进轴突生长和神经递质分泌,从而诱导成骨。王文博等[61]通过负载黑磷纳米片和血管内皮生长因子制备了复合纳米纤维骨膜,该骨膜具有良好的生物相容性,体外可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力与血管内皮细胞的成血管能力。虽然静电纺丝和微流控技术使高质量的生物支架成为可能,极大地提高了临床应用前景,但是静电纺丝也存在力学性能不足的缺点[71],这也是静电纺丝材料在骨组织工程中最大的挑战。 2.4.4 黑磷基微球材料在骨组织工程中的应用 微球是一种可以自由流动的微胶囊或微粒,直径为1-1 000 μm,可用于各种药物、生物活性分子和细胞的封装[73]。与普通剂型药物相比,微球可以提高药物的稳定性[74],减少对胃肠道的刺激等[73],因此,将黑磷包载入微球中有助于提高黑磷的稳定性,延长黑磷在体内的作用时间。WANG等[75]报道了通过聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物微球包裹黑磷量子点的生物激发基质囊泡,并与能够靶向成骨细胞的特定适配体功能化,黑磷降解引起的磷酸盐微环境刺激了细胞生物矿化,并且黑磷量子点的光热作用刺激热休克蛋白和碱性磷酸酶的上调表达来进一步促进骨再生。WANG等[62]通过将氯化锶和黑磷纳米片并入聚乳酸共乙醇酸微球,产生了一个近红外光触发药物传递平台,制备的微球由于黑磷而具有有效的近红外吸收和光热效应,并且发现黑磷在被微球包裹后的光热作用效果明显延长,这可能是由于微球避免了黑磷被快速氧化。微球单独使用拥有优秀的可注射性,也可以与生物支架联合使用,增加生物支架的性能[63]。此外,微球是一种可行的能够避免黑磷在体内过快氧化降解的方法之一。目前对于黑磷在微球中的研究文献数量较少,作者认为这可能是由于黑磷主要作为促进成骨的材料而不是药物,并且黑磷不规则的形状可能导致微球成球率下降。近年来,多室或多孔微球具有很好的研究前景[76-77],一个微球可以携带多种药物分子或细胞,这使得黑磷与其他药物或生物因子一同包载入微球成为可能,具有潜在的研究价值。 2.4.5 黑磷基涂层在骨组织工程中的应用 由于植入物感染将产生抵抗宿主免疫细胞和抗生素浸润的生物膜,植入物相关感染可能会导致灾难性的后果[78],因此,如何在确保骨折愈合效果的同时避免与内固定相关的感染已成为外科医生应面对的一个重要临床问题。目前,细菌附着和生物膜形成在种植相关感染中扮演着至关重要的角色,受纳米医学启发在植入物表面覆盖多功能仿生涂层已经变得越来越有吸引力[79]。其中,黑磷被发现可以通过光热作用、纳米刀效应和活性氧效应对革兰阴性菌和革兰阳性细菌产生杀伤作用[67,80-81],因此黑磷作为一种理想的抗菌纳米材料在生物涂层中被广泛研究[64]。YUAN等[65]通过将黑磷混入羟基磷灰石制备出具有光热转化效应和原位生物矿化的生物涂层,研究证明该涂层在消融细菌生物膜和加速骨折愈合方面具有良好的性能,通过采用绝对定量转录组测序随后筛选基因差异表达,鉴定了黑磷可通过代谢相关途径有效调控与骨间充质干细胞分化和骨形成相关核心标志物的表达。BOSE等[66]将黑磷与氧化锌结合制备了钛表面抗菌涂层,能够对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌产生有效杀伤,并且该涂层具有良好的生物相容性和耐腐蚀性。ZENG等[67]通过聚多巴胺修饰黑磷纳米片制备了一种钛植入物的双功能表面涂层,该涂层具有优越的生物相容性、生物活性、光热和声动力转化能力,在10 min近红外照射和20 min超声处理下,体外抗菌活性达到96.6%,体内抗菌活性达到97.3%。MA等[68]用激光在钛镍合金上刻下纳米级沟槽并将负载了阿霉素的黑磷纳米片吸附在沟槽中,最后用聚多巴胺进行修饰,该多功能涂层可以协同近红外进行光热化疗、骨再生和细菌消除,在体外实验中该涂层可以完全根除小鼠骨肉瘤,显著促进骨再生生物活性,对金黄色葡萄球菌(99.2%)和铜绿假单胞菌(99.6%)具有显著的抑菌效果。目前,虽然新型涂层材料可以产生抗菌膜和成骨作用,但这些涂层有机降解产物引起的加载能力有限、控释不理想和过度炎症反应仍然阻碍了其在临床上的应用。 2.4.6 其他黑磷基材料在骨组织工程中的应用 微创治疗是评价修复效果的关键因素之一。从临床角度来看,可注射的材料可以简化外科医生的手术难度,降低感染和瘢痕形成的风险,降低治疗成本和提高患者的舒适度[82-83]。 可注射性骨水泥可能是骨组织工程中最理想的微创材料,也是已经被应用到临床微创治疗的材料之一。虽然,聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯是临床上最常用的生物惰性骨水泥,但是其力学性能过高,容易造成邻近椎体损伤,另外单体毒性、过高的交联温度等缺点也是临床不可忽视的问题[84-85]。因此,研究者们从未放弃寻找具有可生物降解和合适力学性能的可注射骨水泥替代品。近年来,拥有一定力学强度的可注射复合材料被广泛关注,例如磷酸钙骨水泥、硫酸钙骨水泥和聚富马酸丙二醇酯骨水泥等[86-87]。MA等[31]制备了加入黑磷纳米片的磷酸钙骨水泥,该骨水泥具有可调节的固化时间、良好的细胞相容性、优异的光热特性和成骨诱导性。虽然目前研究者已经将更多的目光放在3D打印的研究和发展中,但是可注射生物骨水泥仍是最有希望替代自体骨移植的生物材料之一,作者认为黑磷是一种优秀的成骨材料,在可注射性骨水泥的应用中具有巨大潜力。 "
| [1] CALVO MS, LAMBERG-ALLARDT CJ. Phosphorus. Adv Nutr. 2015;6(6): 860-862. [2] SUN Z, XIE H, TANG S, et al. Ultrasmall Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots: Synthesis and Use as Photothermal Agents. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015;54(39):11526-11530. [3] CHOI JR, YONG KW, CHOI JY, et al. Black Phosphorus and its Biomedical Applications. Theranostics. 2018;8(4):1005-1026. [4] WU Y, LIAO Q, WU L, et al. ZnL2-BPs Integrated Bone Scaffold under Sequential Photothermal Mediation: A Win-Win Strategy Delivering Antibacterial Therapy and Fostering Osteogenesis Thereafter. ACS Nano. 2021;15(11):17854-17869. [5] WANG C, YE X, ZHAO Y, et al. Cryogenic 3D printing of porous scaffolds for in situ delivery of 2D black phosphorus nanosheets, doxorubicin hydrochloride and osteogenic peptide for treating tumor resection-induced bone defects. Biofabrication. 2020;12(3):035004. [6] PAN W, DAI C, LI Y, et al. PRP-chitosan thermoresponsive hydrogel combined with black phosphorus nanosheets as injectable biomaterial for biotherapy and phototherapy treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials. 2020;239:119851. [7] ZHAO Y, PENG X, XU X, et al. Chitosan based photothermal scaffold fighting against bone tumor-related complications: Recurrence, infection, and defects. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;300:120264. [8] JEON S, LEE JH, JANG HJ, et al. Spontaneously promoted osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 preosteoblasts on ultrathin layers of black phosphorus. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;128:112309. [9] GUSMÃO R, SOFER Z, PUMERA M. Black Phosphorus Rediscovered: From Bulk Material to Monolayers. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017; 56(28):8052-8072. [10] LIU H, NEAL AT, ZHU Z, et al. Phosphorene: an unexplored 2D semiconductor with a high hole mobility. ACS Nano. 2014;8(4): 4033-4041. [11] YASAEI P, KUMAR B, FOROOZAN T, et al. High-quality black phosphorus atomic layers by liquid-phase exfoliation. Adv Mater. 2015;27(11): 1887-1892. [12] CHOI JR, YONG KW, CHOI JY, et al. Black Phosphorus and its Biomedical Applications. Theranostics. 2018;8(4):1005-1026. [13] GUO Z, ZHANG H, LU S, et al. From Black Phosphorus to Phosphorene: Basic Solvent Exfoliation, Evolution of Raman Scattering, and Applications to Ultrafast Photonics. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;25(45): 6996-7002. [14] GUO Z, CHEN S, WANG Z, et al. Metal-Ion-Modified Black Phosphorus with Enhanced Stability and Transistor Performance. Adv Mater. 2017; 29(42). doi: 10.1002/adma.201703811. [15] YASAEI P, KUMAR B, FOROOZAN T, et al. High-quality black phosphorus atomic layers by liquid-phase exfoliation. Adv Mater. 2015;27(11): 1887-1892. [16] ZHANG Y, RUI X, TANG Y, et al. Wet-Chemical Processing of Phosphorus Composite Nanosheets for High-Rate and High-Capacity Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2016;6(10):1502409. [17] 张一弛,祁成创,黄泳糠,等.钆基水凝胶微球在光热抗肿瘤和骨修复中的应用研究[J].中国稀土学报,2023,41(1):159-167. [18] LI S, QING Y, LOU Y, et al. Injectable thermosensitive black phosphorus nanosheet- and doxorubicin-loaded hydrogel for synergistic bone tumor photothermal-chemotherapy and osteogenesis enhancement. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;239:124209. [19] WANG W, NIU X, QIAN H, et al. Surface charge transfer doping of monolayer molybdenum disulfide by black phosphorus quantum dots. Nanotechnology. 2016;27(50):505204. [20] PASSAGLIA E, CICOGNA F, COSTANTINO F, et al. Polymer-Based Black Phosphorus (bP) Hybrid Materials by in Situ Radical Polymerization: An Effective Tool To Exfoliate bP and Stabilize bP Nanoflakes. Chem Mater. 2018;30(6):2036-2048. [21] CHEN W, LI K, WANG Y, et al. Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots for Hole Extraction of Typical Planar Hybrid Perovskite Solar Cells. J Phys Chem Lett. 2017;8(3):591-598. [22] GUAN L, XING B, NIU X, et al. Metal-assisted exfoliation of few-layer black phosphorus with high yield. Chem Commun (Camb). 2018;54(6): 595-598. [23] ERANDE MB, PAWAR MS, LATE DJ. Humidity Sensing and Photodetection Behavior of Electrochemically Exfoliated Atomically Thin-Layered Black Phosphorus Nanosheets. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(18):11548-11556. [24] JIA J, JANG SK, LAI S, et al. Plasma-Treated Thickness-Controlled Two-Dimensional Black Phosphorus and Its Electronic Transport Properties. ACS Nano. 2015;9(9):8729-8736. [25] LI W, WU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Self-healing hydrogels for bone defect repair. RSC Adv. 2023;13(25):16773-16788. [26] WANG S, ZHAO S, YU J, et al. Advances in Translational 3D Printing for Cartilage, Bone, and Osteochondral Tissue Engineering. Small. 2022;18(36):e2201869. [27] VERMEULEN S, TAHMASEBI BIRGANI Z, HABIBOVIC P. Biomaterial-induced pathway modulation for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2022;283:121431. [28] AMIRYAGHOUBI N, FATHI M, PESYAN NN, et al. Bioactive polymeric scaffolds for osteogenic repair and bone regenerative medicine. Med Res Rev. 2020;40(5):1833-1870. [29] MISHCHENKO O, YANOVSKA A, KOSINOV O, et al. Synthetic Calcium-Phosphate Materials for Bone Grafting. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(18): 3822. [30] GAHARWAR AK, CROSS LM, PEAK CW, et al. 2D Nanoclay for Biomedical Applications: Regenerative Medicine, Therapeutic Delivery, and Additive Manufacturing. Adv Mater. 2019;31(23):e1900332. [31] MA S, WEI Y, SUN R, et al. Calcium Phosphate Bone Cements Incorporated with Black Phosphorus Nanosheets Enhanced Osteogenesis. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(1):292-302. [32] PENG G, FADEEL B. Understanding the bidirectional interactions between two-dimensional materials, microorganisms, and the immune system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;188:114422. [33] WANG X, YU Y, YANG C, et al. Microfluidic 3D Printing Responsive Scaffolds with Biomimetic Enrichment Channels for Bone Regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31:2105190. [34] LIU X, MILLER AL 2ND, PARK S, et al. Two-Dimensional Black Phosphorus and Graphene Oxide Nanosheets Synergistically Enhance Cell Proliferation and Osteogenesis on 3D Printed Scaffolds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(26):23558-23572. [35] TONG L, LIAO Q, ZHAO Y, et al. Near-infrared light control of bone regeneration with biodegradable photothermal osteoimplant. Biomaterials. 2019;193:1-11. [36] LI Z, ZHANG X, OUYANG J, et al. Ca(2+)-supplying black phosphorus-based scaffolds fabricated with microfluidic technology for osteogenesis. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11):4053-4064. [37] QIAN Y, YUAN WE, CHENG Y, et al. Concentrically Integrative Bioassembly of a Three-Dimensional Black Phosphorus Nanoscaffold for Restoring Neurogenesis, Angiogenesis, and Immune Homeostasis. Nano Lett. 2019;19(12):8990-9001. [38] XU Y, XU C, HE L, et al. Stratified-structural hydrogel incorporated with magnesium-ion-modified black phosphorus nanosheets for promoting neuro-vascularized bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;16:271-284. [39] JING X, XU C, SU W, et al. Photosensitive and Conductive Hydrogel Induced Innerved Bone Regeneration for Infected Bone Defect Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(3):e2201349. [40] WU M, LIU H, LI D, et al. Smart-Responsive Multifunctional Therapeutic System for Improved Regenerative Microenvironment and Accelerated Bone Regeneration via Mild Photothermal Therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(2):e2304641. [41] QIU M, TULUFU N, TANG G, et al. Black Phosphorus Accelerates Bone Regeneration Based on Immunoregulation. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024; 11(1):e2304824. [42] LONG J, YAO Z, ZHANG W, et al. Regulation of Osteoimmune Microenvironment and Osteogenesis by 3D-Printed PLAG/black Phosphorus Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023; 10(28):e2302539. [43] QING Y, WANG H, LOU Y. Chemotactic ion-releasing hydrogel for synergistic antibacterial and bone regeneration. Mater Today Chem. 2022;24:24. [44] WANG Z, ZHAO J, TANG W, et al. Multifunctional Nanoengineered Hydrogels Consisting of Black Phosphorus Nanosheets Upregulate Bone Formation. Small. 2019;15(41):e1901560. [45] GAIHRE B, LIU X, LU L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell spheroids incorporated with collagen and black phosphorus promote osteogenesis of biodegradable hydrogels. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;121:111812. [46] LIU X, GEORGE MN, LI L, et al. Injectable Electrical Conductive and Phosphate Releasing Gel with Two-Dimensional Black Phosphorus and Carbon Nanotubes for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(8):4653-4665. [47] TAN L, HU Y, LI M. Remotely-activatable extracellular matrix-mimetic hydrogel promotes physiological bone mineralization for enhanced cranial defect healing. Chem Eng J. 2022:431P4. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2021.133382 [48] HUANG K, WU J, GU Z. Black Phosphorus Hydrogel Scaffolds Enhance Bone Regeneration via a Sustained Supply of Calcium-Free Phosphorus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(3):2908-2916. [49] MIAO Y, SHI X, LI Q, et al. Engineering natural matrices with black phosphorus nanosheets to generate multi-functional therapeutic nanocomposite hydrogels. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(10):4046-4059. [50] XU D, GAN K, WANG Y, et al. A Composite Deferoxamine/Black Phosphorus Nanosheet/Gelatin Hydrogel Scaffold for Ischemic Tibial Bone Repair. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:1015-1030. [51] XU H, LIU X, GEORGE MN, et al. Black phosphorus incorporation modulates nanocomposite hydrogel properties and subsequent MC3T3 cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109(9):1633-1645. [52] XU H, LIU X, PARK S, et al. Size-dependent osteogenesis of black phosphorus in nanocomposite hydrogel scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2022;110(8):1488-1498. [53] MIAO Y, LIU X, LUO J, et al. Double-Network DNA Macroporous Hydrogel Enables Aptamer-Directed Cell Recruitment to Accelerate Bone Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(1):e2303637. [54] WANG C, YUE H, LIU J, et al. Advanced Reconfigurable Scaffolds Fabricated by 4D Printing for Treating Critical-size Bone Defects of Irregular Shapes. Biofabrication. 2020;12(4):045025. [55] YANG B, YIN J, CHEN Y, et al. 2D-Black-Phosphorus-Reinforced 3D-Printed Scaffolds: A Stepwise Countermeasure for Osteosarcoma. Adv Mater. 2018;30(10). doi: 10.1002/adma.201705611. [56] MIAO Y, CHEN Y, LUO J, et al. Black phosphorus nanosheets-enabled DNA hydrogel integrating 3D-printed scaffold for promoting vascularized bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2023;21:97-109. [57] LEE YB, SONG SJ, SHIN YC, et al. Ternary nanofiber matrices composed of PCL/black phosphorus/collagen to enhance osteodifferentiation.J Ind Eng Chem. 2019;80:802-810. [58] WANG J, WANG J, QIU S, et al. Biodegradable L-lysine-modified amino black phosphorus/poly(l-lactide-coε-caprolactone) nanofibers with enhancements in hydrophilicity, shape recovery and osteodifferentiation properties. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022; 209(Pt 2):112209. [59] ZHANG X, LI Q, LI L, et al. Bioinspired Mild Photothermal Effect-Reinforced Multifunctional Fiber Scaffolds Promote Bone Regeneration. ACS Nano. 2023;17(7):6466-6479. [60] SU Y, ZENG L, DENG R, et al. Endogenous Electric Field-Coupled PD@BP Biomimetic Periosteum Promotes Bone Regeneration through Sensory Nerve via Fanconi Anemia Signaling Pathway. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(12):e2203027. [61] 王文博,徐敬之,吴亮,等.复合纳米纤维骨膜促进血管化和成骨矿化的体外实验[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(25):4028-4037. [62] WANG X, SHAO J, ABD EL RAOUF M, et al. Near-infrared light-triggered drug delivery system based on black phosphorus for in vivo bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2018;179:164-174. [63] XIN S, CHIMENE D, GARZA JE, et al. Clickable PEG hydrogel microspheres as building blocks for 3D bioprinting. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(3):1179-1187. [64] LEE JH, BAEK SM, LEE G, et al. Biocompatible Magnesium Implant Double-Coated with Dexamethasone-Loaded Black Phosphorus and Poly(lactide- co -glycolide). ACS Applied Bio Materials. 2020;3(12): 8879-8889. [65] YUAN B, ZHOU X, LI Y, et al. Black-Phosphorus-Nanosheet-Reinforced Coating of Implants for Sequential Biofilm Ablation and Bone Fracture Healing Acceleration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(41): 47036-47051. [66] BOSE S, SURENDHIRAN D, CHUN BS, et al. Facile synthesis of black phosphorus-zinc oxide nanohybrids for antibacterial coating of titanium surface. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;219:112807. [67] ZENG J, GU C, GENG X, et al. Combined photothermal and sonodynamic therapy using a 2D black phosphorus nanosheets loaded coating for efficient bacterial inhibition and bone-implant integration. Biomaterials. 2023;297:122122. [68] MA Y, JIANG L, HU J, et al. Developing a Versatile Multiscale Therapeutic Platform for Osteosarcoma Synergistic Photothermo-Chemotherapy with Effective Osteogenicity and Antibacterial Capability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(39):44065-44083. [69] WANG Z, WEI H, HUANG Y, et al. Naturally sourced hydrogels: emerging fundamental materials for next-generation healthcare sensing. Chem Soc Rev. 2023;52(9):2992-3034. [70] ZHOU B, JIANG X, ZHOU X, et al. GelMA-based bioactive hydrogel scaffolds with multiple bone defect repair functions: therapeutic strategies and recent advances. Biomater Res. 2023;27(1):86. [71] LIM DJ. Cross-Linking Agents for Electrospinning-Based Bone Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(10):5444. [72] WANG Z, WANG Y, YAN J, et al. Pharmaceutical electrospinning and 3D printing scaffold design for bone regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;174:504-534. [73] HU L, ZHANG H, SONG W. An overview of preparation and evaluation sustained-release injectable microspheres. J Microencapsul. 2013; 30(4):369-382. [74] WONG CY, AL-SALAMI H, DASS CR. Microparticles, microcapsules and microspheres: A review of recent developments and prospects for oral delivery of insulin. Int J Pharm. 2018;537(1-2):223-244. [75] WANG Y, HU X, ZHANG L, et al. Bioinspired extracellular vesicles embedded with black phosphorus for molecular recognition-guided biomineralization. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2829. [76] ZHANG W, WANG X, LI X, et al. A 3D porous microsphere with multistage structure and component based on bacterial cellulose and collagen for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydrate Polymers: Scientific and Technological Aspects of Industrially Important Polysaccharides. 2020;236:116043. [77] KRIEGEL C, ATTARWALA H, AMIJI M. Multi-compartmental oral delivery systems for nucleic acid therapy in the gastrointestinal tract. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(6):891-901. [78] KOO H, ALLAN RN, HOWLIN RP, et al. Targeting microbial biofilms: current and prospective therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2017;15(12):740-755. [79] LIU Y, SHI L, SU L, et al. Nanotechnology-based antimicrobials and delivery systems for biofilm-infection control. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(2):428-446. [80] XIONG Z, ZHANG X, ZHANG S, et al. Bacterial toxicity of exfoliated black phosphorus nanosheets. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018;161:507-514. [81] LI B, LAI C, ZENG G, et al. Black Phosphorus, a Rising Star 2D Nanomaterial in the Post-Graphene Era: Synthesis, Properties, Modifications, and Photocatalysis Applications. Small. 2019;15(8): e1804565. [82] LYKISSAS MG, GIANNOULIS D. Minimally invasive spine surgery for degenerative spine disease and deformity correction: a literature review. Ann Transl Med. 2018;6(6):99. [83] JAHANGIRI M, HUSSAIN A, AKOWUAH E. Minimally invasive surgical aortic valve replacement. Heart. 2019;105(Suppl 2):s10-s15. [84] MOUNIKA C, TADGE T, KEERTHANA M, et al. Advancements in poly(methyl Methacrylate) bone cement for enhanced osteoconductivity and mechanical properties in vertebroplasty: A comprehensive review. Med Eng Phys. 2023;120:104049. [85] GHASEMI F, JAHANI A, MORADI A, et al. Different Modification Methods of Poly Methyl Methacrylate (PMMA) Bone Cement for Orthopedic Surgery Applications. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2023;11(8):485-492. [86] QUAN Q, GONGPING X, RUISI N, et al. New Research Progress of Modified Bone Cement Applied to Vertebroplasty. World Neurosurg. 2023;176:10-18. [87] 栾伟,陈家瀚,滕勇,等.新型可吸收骨水泥的制备及其应用于小牛椎体标本压缩性骨折椎体成形术的生物力学研究[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2022,27(10):721-728. [88] MU X, WANG JY, BAI X, et al. Black Phosphorus Quantum Dot Induced Oxidative Stress and Toxicity in Living Cells and Mice. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(24):20399-20409. [89] FADEEL B, GARCIA-BENNETT AE. Better safe than sorry: Understanding the toxicological properties of inorganic nanoparticles manufactured for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(3):362-374. [90] PARK EJ, PARK K. Oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory responses induced by silica nanoparticles in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol Lett. 2009; 184(1):18-25. [91] LIU X, CHEN K, LI X, et al. Electron Matters: Recent Advances in Passivation and Applications of Black Phosphorus. Adv Mater. 2021; 33(50):e2005924. [92] ESWARAIAH V, ZENG Q, LONG Y, et al. Black Phosphorus Nanosheets: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications. Small. 2016;12(26): 3480-3502. [93] QIU M, WANG D, LIANG W, et al. Novel concept of the smart NIR-light-controlled drug release of black phosphorus nanostructure for cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(3):501-506. [94] OLEFSKY JM, GLASS CK. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2010;72:219-246. [95] VI L, BAHT GS, WHETSTONE H, et al. Macrophages promote osteoblastic differentiation in-vivo: implications in fracture repair and bone homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(6):1090-1102. [96] MOSSER DM, EDWARDS JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12):958-969. |
| [1] | Yu Lei, Zhang Wei, Qin Yi, Ge Gaoran, Bai Jiaxiang, Geng Dechun. Repair of femoral condyle defects using mesoporous bioactive glass grafted with bone morphogenetic protein 2 osteogenic peptide inspired by mussel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4629-4638. |
| [2] | Liu Yunxiang, Zhang Xiaoyu, Li Hao, Zhang Rong, Li Liping, Chen Chongwei. Multiple applications of metal-organic framework materials in bone tissue engineering and orthopedic disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2151-2161. |
| [3] | Wu Zhixin, Jiang Wenwen, Zhan Jianhui, Li Yangshurun, Ren Wenyan, Wang Yiyu. Hydrogels: role and problems in the repair of oral and maxillofacial defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2178-2188. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||