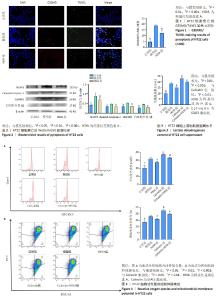
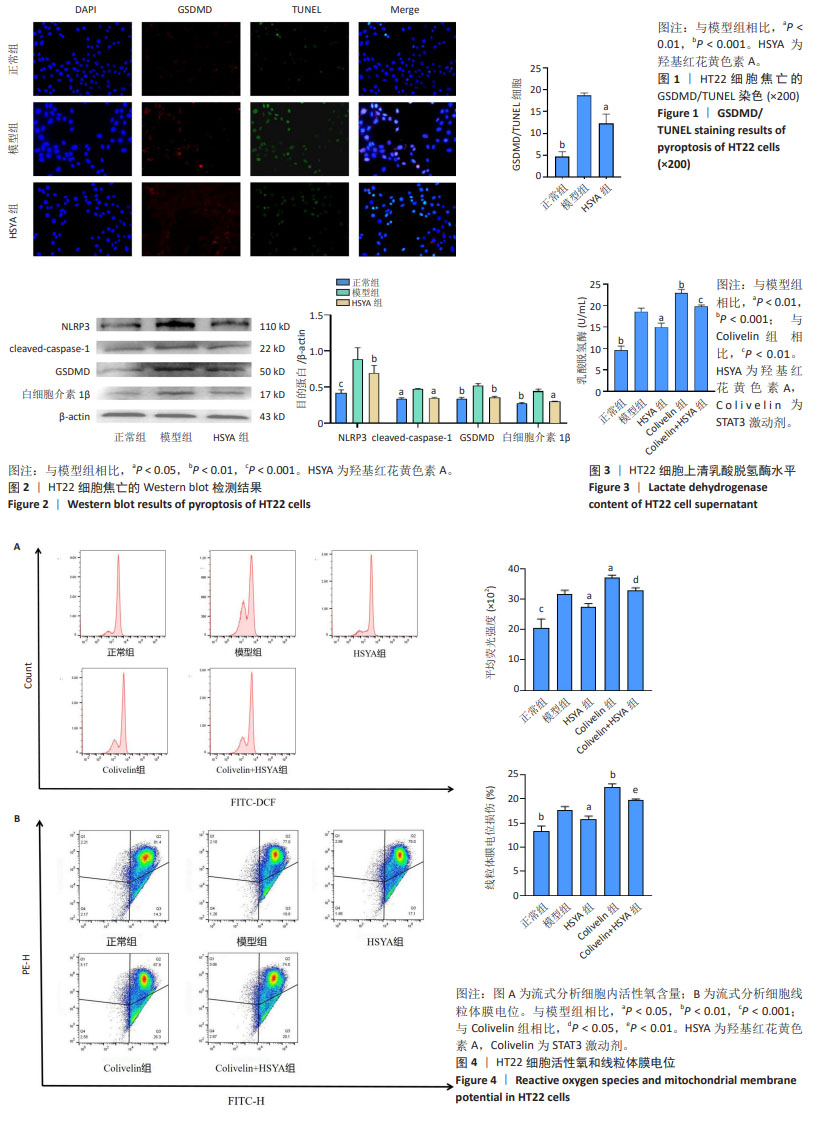
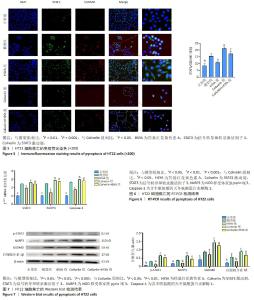
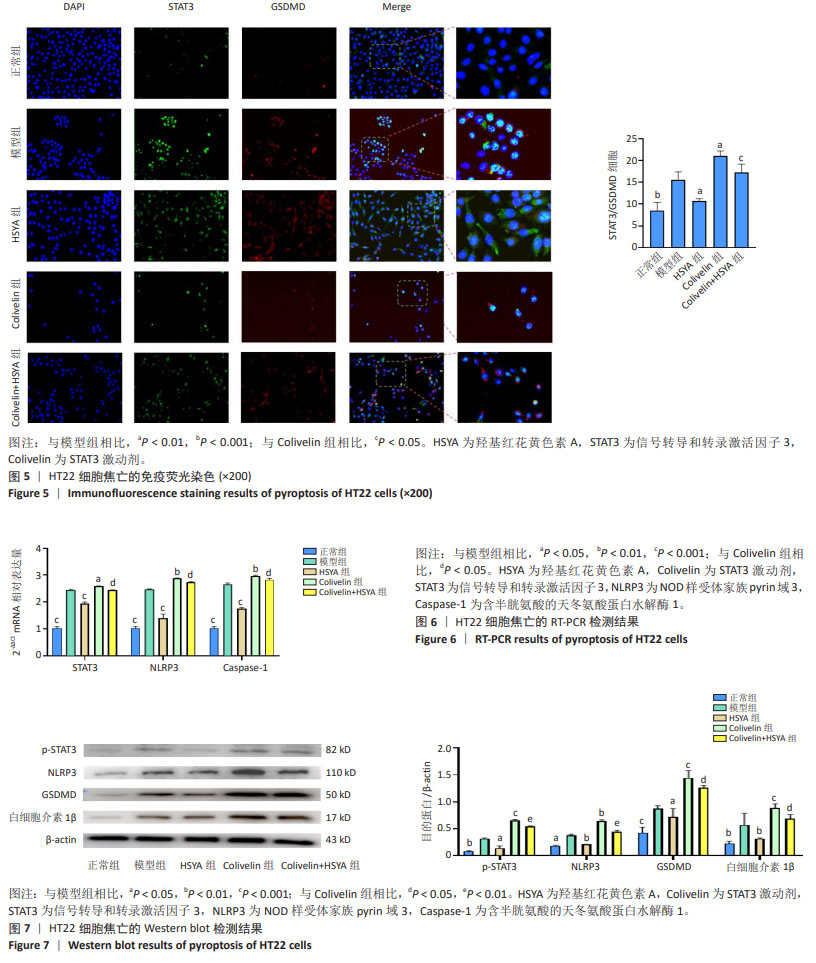
[1] CHEN W, CHEN Y, WU L, et al. Identification of cell death-related biomarkers and immune infiltration in ischemic stroke between male and female patients. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1164742.
[2] ZHU H, HU S, LI Y, et al. Interleukins and Ischemic Stroke. Front Immunol. 2022;13:828447.
[3] LIAO W, WANG M, WU Y, et al. The mechanisms of Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu decoction in treating ischaemic stroke based on network pharmacology and experiment verification. Pharm Biol. 2023;61(1): 1014-1029.
[4] ZHOU S, GAO X, CHEN C, et al. Porcine cardiac blood - Salvia miltiorrhiza root alleviates cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting oxidative stress induced apoptosis through PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;316:116698.
[5] LIN S, LIU X, SUN A, et al. Qilong capsule alleviates ponatinib-induced ischemic stroke in a zebrafish model by regulating coagulation, inflammation and apoptosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;314:116397.
[6] COLL RC, SCHRODER K, PELEGRÍN P. NLRP3 and pyroptosis blockers for treating inflammatory diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022;43(8): 653-668.
[7] 单萍,张继龙.miR-125a-5p通过靶向STAT3减轻戊四唑诱导的癫痫大鼠的神经功能障碍和炎症反应[J/OL].中国免疫学杂志, 1-17[2024-01-02].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/22.1126.r. 20231009.1119.008.html.
[8] SUN Y, XU DP, QIN Z, et al. Protective cerebrovascular effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) on ischemic stroke. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;818:604-609.
[9] YU L, DUAN Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A (HSYA) Improves Learning and Memory in Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion-Injured Rats via Recovering Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:371.
[10] CHEN G, LI C, ZHANG L, et al. Hydroxysafflor yellow A and anhydrosafflor yellow B alleviate ferroptosis and parthanatos in PC12 cells injured by OGD/R. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;179:1-10.
[11] FENG X, DU M, LI S, et al. Hydroxysafflor yellow A regulates lymphangiogenesis and inflammation via the inhibition of PI3K on regulating AKT/mTOR and NF-κB pathway in macrophages to reduce atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. Phytomedicine. 2023; 112:154684.
[12] LI Y, LIU XT, ZHANG PL, et al. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Blocks HIF-1α Induction of NOX2 and Protects ZO-1 Protein in Cerebral Microvascular Endothelium. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(4):728.
[13] HUANG P, WU SP, WANG N, et al. Hydroxysafflor yellow A alleviates cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by suppressing apoptosis via mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Phytomedicine. 2021;85: 153532.
[14] ZHOU Z, XU N, MATEI N, et al. Sodium butyrate attenuated neuronal apoptosis via GPR41/Gβγ/PI3K/Akt pathway after MCAO in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021;41(2):267-281.
[15] FANG YY, ZHANG JH. MFG-E8 alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neuronal cell apoptosis by STAT3 regulating the selective polarization of microglia. Int J Neurosci. 2021;131(1):15-24.
[16] PAN Z, WU Q, XIE Z, et al. Upregulation of HSP72 attenuates tendon adhesion by regulating fibroblast proliferation and collagen production via blockade of the STAT3 signaling pathway. Cell Signal. 2020;71:109606.
[17] ZHAO Y, ZHANG X, CHEN X, et al. Neuronal injuries in cerebral infarction and ischemic stroke: From mechanisms to treatment (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2022;49(2):15.
[18] TUO QZ, ZHANG ST, LEI P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med Res Rev. 2022; 42(1):259-305.
[19] YU L, JIN Z, LI M, et al. Protective potential of hydroxysafflor yellow A in cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury: An overview of evidence from experimental studies. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1063035.
[20] ZHANG J, ZHOU R, CAO G, et al. Guhong Injection Prevents Ischemic Stroke-Induced Neuro-Inflammation and Neuron Loss Through Regulation of C5ar1. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:818245.
[21] WEI R, SONG L, MIAO Z, et al. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Exerts Neuroprotective Effects via HIF-1α/BNIP3 Pathway to Activate Neuronal Autophagy after OGD/R. Cells. 2022;11(23):3726.
[22] YU L, LIU Z, HE W, et al. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Confers Neuroprotection from Focal Cerebral Ischemia by Modulating the Crosstalk Between JAK2/STAT3 and SOCS3 Signaling Pathways. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020;40(8):1271-1281.
[23] 刘可心,宋丽娟,吴艺舸,等.羟基红花黄色素A干预脑缺血再灌注损伤后星形胶质细胞脂质运载蛋白2的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(7):1063-1069.
[24] HAN PP, HAN Y, SHEN XY, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation after ischemic stroke. Behav Brain Res. 2023;452:114578.
[25] MAO R, ZONG N, HU Y, et al. Neuronal Death Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategy in Ischemic Stroke. Neurosci Bull. 2022;38(10): 1229-1247.
[26] LONG J, SUN Y, LIU S, et al. Targeting pyroptosis as a preventive and therapeutic approach for stroke. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9(1):155.
[27] BELLUT M, PAPP L, BIEBER M, et al. NLPR3 inflammasome inhibition alleviates hypoxic endothelial cell death in vitro and protects blood-brain barrier integrity in murine stroke. Cell Death Dis. 2021; 13(1):20.
[28] BAI W, HUO S, ZHOU G, et al. Biliverdin modulates the Nrf2/A20/eEF1A2 axis to alleviate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting pyroptosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165:115057.
[29] DONG Z, PENG Q, PAN K, et al. Microglial and Neuronal Cell Pyroptosis Induced by Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation Aggravates Cell Injury via Activation of the Caspase-1/GSDMD Signaling Pathway. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(9):2660-2673.
[30] ZHONG Y, WANG S, YIN Y, et al. Dexmedetomidine suppresses hippocampal astrocyte pyroptosis in cerebral hypoxic-ischemic neonatal rats by upregulating microRNA-148a-3p to inactivate the STAT/JMJD3 axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;121:110440.
[31] LUO L, DENG L, CHEN Y, et al. Identification of Lipocalin 2 as a Ferroptosis-Related Key Gene Associated with Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage via STAT3/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(1):186.
[32] LONG JX, TIAN MZ, CHEN XY, et al. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in ischemic stroke and the intervention of traditional Chinese medicine. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1151196.
[33] XIE Y, LEI X, ZHAO G, et al. mTOR in programmed cell death and its therapeutic implications. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023;71-72: 66-81. |