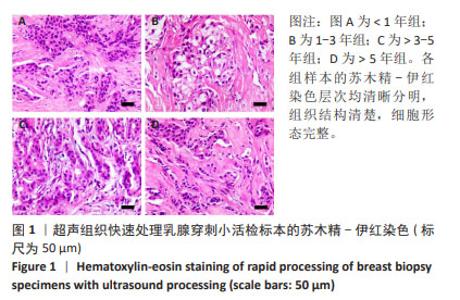
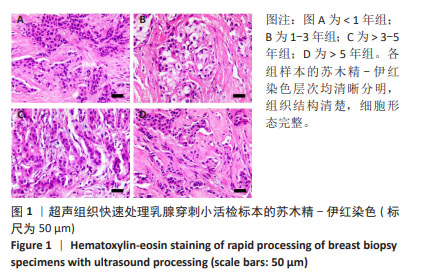
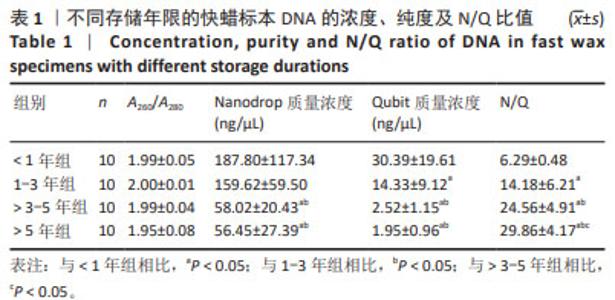
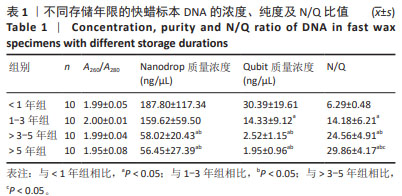
[1] LUDYGA N, GRÜNWALD B, AZIMZADEH O, et al. Nucleic acids from long-term preserved FFPE tissues are suitable for downstream analyses. Virchows Arch. 2012;460(2):131-140.
[2] TORGA G, PIENTA KJ. Patient-Paired Sample Congruence Between 2 Commercial Liquid Biopsy Tests. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(6):868-870.
[3] DO H, DOBROVIC A. Sequence artifacts in DNA from formalin-fixed tissues: causes and strategies for minimization. Clin Chem. 2015;61(1): 64-71.
[4] ELLISON G, AHDESMÄKI M, LUKE S, et al. An evaluation of the challenges to developing tumor BRCA1 and BRCA2 testing methodologies for clinical practice. Hum Mutat. 2018;39(3):394-405.
[5] ROBBE P, POPITSCH N, KNIGHT SJL, et al. Clinical whole-genome sequencing from routine formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens: pilot study for the 100,000 Genomes Project. Genet Med. 2018;20(10):1196-1205.
[6] HEDEGAARD J, THORSEN K, LUND MK, et al. Next-generation sequencing of RNA and DNA isolated from paired fresh-frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples of human cancer and normal tissue. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e98187.
[7] BETTONI F, KOYAMA FC, DE AVELAR CARPINETTI P, et al. A straightforward assay to evaluate DNA integrity and optimize next-generation sequencing for clinical diagnosis in oncology. Exp Mol Pathol. 2017;103(3):294-299.
[8] 杨军,张标,马恒辉,等.FFPE组织提取DNA样本质量评价的多中心调研[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2018,34(6):691-694.
[9] NAGAHASHI M, SHIMADA Y, ICHIKAWA H, et al. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sample conditions for deep next generation sequencing. J Surg Res. 2017;220:125-132.
[10] 李丹,刘亚丽,刘静,等.石蜡组织存放时间对提取DNA质量的影响[J].河南大学学报(医学版),2014,33(1):9-13.
[11] GUYARD A, BOYEZ A, PUJALS A, et al. DNA degrades during storage in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue blocks. Virchows Arch. 2017;471(4):491-500.
[12] ZUGAZAGOITIA J, RUEDA D, CARRIZO N, et al. Prospective Clinical Integration of an Amplicon-Based Next-Generation Sequencing Method to Select Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients for Genotype-Tailored Treatments. Clin Lung Cancer. 2018;19(1):65-73.e7.
[13] 向双,段松,袁怀志,等.超声组织处理仪在胃镜标本HE及幽门螺杆菌PCR检测中的应用[J].临床与试验病理学杂志,2021,37(6):743-745.
[14] 魏雪,冯翠云,李颖,等.脑组织术中快速制片技术在病理诊断中的应用于体会[J].诊断病理学杂志,2020,27(7):516-518.
[15] 郭芳,张杨鸽龄,吴德,等.新型超声组织处理仪配套环保试剂处理小活检组织对分子病理检测的影响[J].中华病理学杂志,2019, 48(10):805-808.
[16] 张茜,杨月红,章宏峰. 超声快速石蜡与常规石蜡在胃肠道间质瘤Sanger测序中结果的对比分析[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志,2020, 36(4):480-482.
[17] 郭连英,向婵,赵瑞英,等.非小细胞肺癌甲醛固定包埋组织保存年限对DNA靶向捕获二代测序的影响[J].中华病理学杂志,2020, 49(6):619-622.
[18] MATSUSHIGE T, KUWAMOTO S, MATSUSHITA M, et al. Detection of Disease-specific Fusion Genes of Soft Tissue Tumors Using Formalin-fixed Paraffin-embedded Tissues; Its Diagnostic Usefulness and Factors Affecting the Detection Rates. Yonago Acta Med. 2019;62(1):115-123.
[19] BERRINO E, ANNARATONE L, MIGLIO U, et al. Cold Formalin Fixation Guarantees DNA Integrity in Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded Tissues: Premises for a Better Quality of Diagnostic and Experimental Pathology With a Specific Impact on Breast Cancer. Front Oncol. 2020;10:173.
[20] FRACASSO T, HEINRICH M, HOHOFF C, et al. Ultrasound-accelerated formalin fixation improves the preservation of nucleic acids extraction in histological sections. Int J Legal Med. 2009;123(6):521-525.
[21] 李颖,冯翠云,魏雪,等.新型超声波快速组织处理仪在纠正蜡块组织处理缺陷时的应用[J].诊断病理学杂志,2020,27(6): 380,390,429.
[22] 郑波,王鹏姣,薛丽燕,等.复合型环保试剂超声组织快速处理技术对肿瘤活检标本蛋白及分子检测的影响[J].中华病理学杂志, 2019,48(2):116-119.
[23] 石晨曦,李秀明,陈志,等.超声组织快速处理技术对小活检组织二代测序质控参数的影响[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2023,39(1): 112-114.
[24] JACKSON CB, GALLATI S, SCHALLER A. qPCR-based mitochondrial DNA quantification: influence of template DNA fragmentation on accuracy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;423(3):441-447.
[25] 雷琎,王媛媛,王一星,等.快速超声法和传统方法处理病理组织制片效果的比较[J].临床与试验病理学杂志,2019,35(8):982-985.
[26] YI QQ, YANG R, SHI JF, et al. Effect of preservation time of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues on extractable DNA and RNA quantity. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(6):300060520931259.
[27] WATANABE M, HASHIDA S, YAMAMOTO H, et al. Estimation of age-related DNA degradation from formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue according to the extraction methods. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(3):2683-2688.
[28] ZHAO R, ZHANG J, HAN Y, et al. Clinicopathological Features of ALK Expression in 9889 Cases of Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer and Genomic Rearrangements Identified by Capture-Based Next-Generation Sequencing: A Chinese Retrospective Analysis. Mol Diagn Ther. 2019; 23(3):395-405.
[29] STOLZ A, JOOß K, HÖCKER O, et al. Recent advances in capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry: Instrumentation, methodology and applications. Electrophoresis. 2019;40(1):79-112.
[30] LU X, WEI Y, SUN J, et al. A Comparative Study of Three Nucleic Acid Integrity Assay Systems. Biopreserv Biobank. 2023;21(6):624-630. |