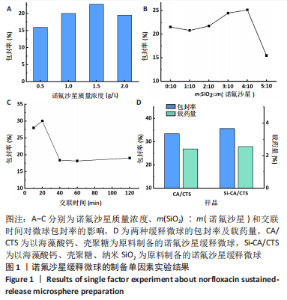
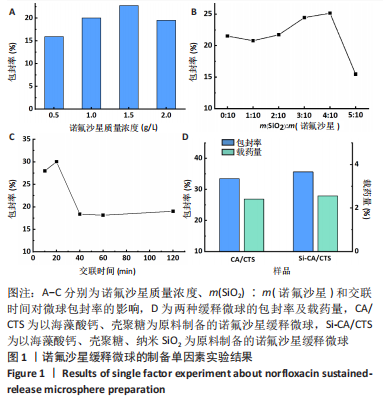
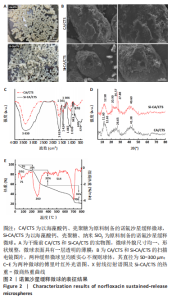
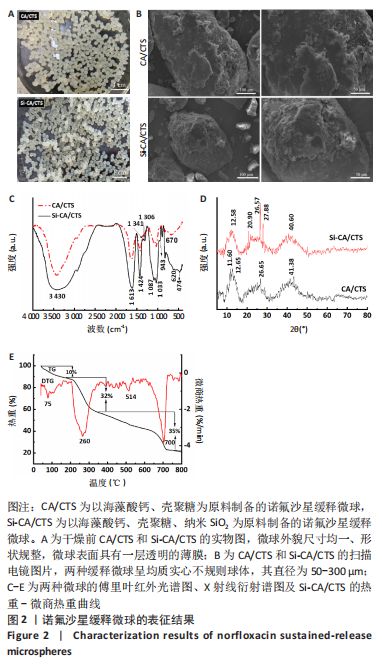
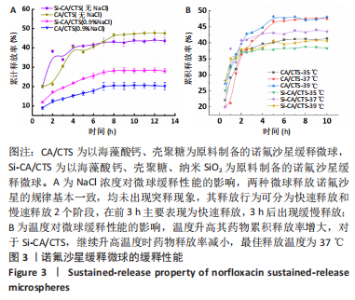
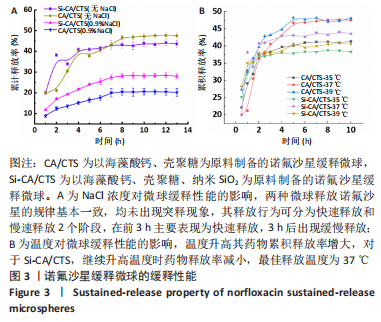
[1] 丁文东,崔康平,郭志,等.纳米银在诺氟沙星胁迫下对黄孢原毛平革菌的毒物兴奋效应[J].生态毒理学报,2020,15(6):141-150.
[2] GUO Q, ZHANG RF, HUA XW, et al. Syntheses, structures, in vitro cytostatic activity and antifungal activity evaluation of four diorganotin(iv) complexes based on norfloxacin and levofloxacin. New J Chem. 2022;46(9): 4314-4324.
[3] 马改大.喹诺酮类抗菌药物的药理作用和临床合理应用探析[J].中国药物与临床,2019,19(8):1347-1348.
[4] 黎丽,刘玉贞,龚咏梅.喹诺酮类抗菌药物的认知与临床用药现状调查[J].现代诊断与治疗,2014,25(23):5326-5327.
[5] ZHANG JL, SRIVASTAVA RS, MISRA RDK. Core-shell magnetite nanoparticles surface encapsulated with smart stimuli-responsive polymer: synthesis, characterization, and LCST of viable drug-targeting delivery system. Langmuir. 2007;23(11):6342-6351.
[6] 周健,方涛林,董健.抗生素缓释载体在慢性骨髓炎治疗中的应用[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2011,5(6):1708-1711.
[7] 周红军,周新华,吴树鸿.毒死蜱/改性膨润土/海藻酸钠复合微球的制备及其缓释性能[J].江苏农业科学,2015,43(1):150-152.
[8] 阎观琼.缓释微球的研究现状[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(93): 39+43.
[9] 李勋,韦祎,马光辉,等.缓释微球制剂的研究进展[J].北京化工大学学报(自然科学版),2017,44(6):1-11.
[10] 赵佩,石磊,刘志龙,等.利福平缓释微球的制备及体外释放特性[J].中国医院药学杂志,2014,34(24):2111-2116.
[11] 韦祎,巩方玲,崔一民,等.微孔膜乳化技术制备缓释微球的研究进展[J].中国医药工业杂志,2018,49(10):1341-1351.
[12] MI Y, ZHOU W, LI Q, et al. Preparation of water-in-oil emulsions using a hydrophobic polymer membrane with 3D bicontinuous skeleton structure. J Membrane Sci. 2015;490:113-119.
[13] YEO Y, BASARAN OA, PARK K. A new process for making reservoir-type microcapsules using ink-jet technology and interfacial phase separation. J Controlled Release. 2003;93(2):161-173.
[14] CAO X, DAI LJ, SUN SC, et al. Preparation and performance of porous hydroxyapatite/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) drug-loaded microsphere scaffolds for gentamicin sulfate delivery. J Mater Sci. 2021;56:15278-15298.
[15] SUNDARAM KMS, CURRY J. Effect of some UV light absorbers on the photostabilization of azadirachtin, a neembased biopesticide. Chemosphere. 1996;32(4):649-659.
[16] 张艳,孟雪.壳聚糖相关的给药系统在血管生成治疗中的作用概述[J].中国药师,2022,25(1):118-123+129.
[17] LACOB AT, LUPASCU FG, APOTROSOAEI M, et al. Recent biomedical approaches for chitosan based materials as drug delivery nanocarriers. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(4):587.
[18] JIANG ZY, ZHAO SJ, YANG MK, et al.Structurally stable sustained-release microcapsules stabilized by self-assembly of pectin-chitosan-collagen in aqueous two-phase system. Food Hydrocoll. 2022;125:107413.
[19] 乐国平,张明,席立成,等.盐酸万古霉素@聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物-壳聚糖-透明质酸复合缓释微球的制备及体外评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2022,26(4):552-558.
[20] 周烨,雷世婵,罗勉,等.海藻酸钠微球制备方法进展[J].生物化工,2021, 7(1):131-133.
[21] ILIESCU RI, ANDRONESCUA E, GHITULICA CD, et al. Montmorillonite-alginate nanocomposite as a drug delivery system-incorporation and in vitro release of irinotecan. Int J Pharmaceut. 2014;463(2):184-192.
[22] 朱玉婉,解英俊,张学文.二氧化硅纳米材料在肝癌治疗中应用进展[J].中国实用外科杂志,2021,41(6):710-713+718.
[23] 李宣民,许永权,赵瑞红,等.介孔二氧化硅-阿维菌素缓释体系的制备与性能研究[J].应用化工,2019,48(6):1274-1278.
[24] AHMADI E, DEHGHANNEJAD N, HASHEMIKIA S, et al. Synthesis and surface modification of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and its application as carriers for sustained drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2014;21(3):164-172.
[25] ZHAO SS, ZHAGN SL, MA J, et al. Double loaded self-decomposable SiO2 nanoparticles for sustained drug release. Nanoscale. 2015;7(39):16389-16398.
[26] XU X, LI J, HAO Z, et al. Characterization and catalytic performance of Co/SBA-15 supported gold catalysts for CO oxidation. Mater Res Bull. 2006;41(2):406-413.
[27] 高奕红,王珊.环保型壳聚糖/SiO2材料制备及吸附染料性能初探[J].化工科技,2018,26(6):1-6.
[28] 曹仕文,张鸿,孟驰涵,等.海藻酸钙-二氧化硅杂化材料的制备及对Cu(Ⅱ)吸附性能[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2020,36(2):169-175,183.
[29] 刘云霞,曾凡桂,孙蓓蕾,等.古交飞灰不同粒径颗粒的XRD及FTIR研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(5):1452-1456.
[30] 黄栋,吴登庆,苏佳雯,等.诺氟沙星和水杨酸药物-药物盐的制备与表征[J].浙江化工,2019,50(11):10-15.
[31] VAIZOGULLAR A I, BALCI A, KULA I, et al. Preparation, characterization, and adsorption studies of core@shell SiO2@CeO2 nanoparticles: a new candidate to remove Hg(II) from aqueous solutions. Turk J Chem. 2016;40:565-575.
[32] 陈慧明. 同轴载药组织工程骨支架缓控释特性研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2020.
[33] 乔永杰,张吕丹,李旭升,等.β-磷酸三钙填充载药微球治疗兔感染性骨缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(11):1013-1018.
[34] 陈歌,曹立冬,赵鹏跃,等.甲氧基丙烯酸酯类农药缓控释制剂的研究进展[J].现代农药,2021,20(2):7-11+22.
[35] 董玉洁,蒋沅岐,陈金鹏,等.中药缓控释制剂的研究进展[J].中草药,2021, 52(8):2465-2472.
[36] 宋子健,丁宇翔,周勤.感觉神经肽与P物质缓释微球对小鼠拔牙窝成骨的作用[J].口腔医学研究,2020,36(1):20-23.
[37] 丁婷婷.负载 BMP-2 的 MPEG-PCL 微球的制备及成骨活性评价[D].济南:山东大学,2018.
[38] MUNICOY S, ÁLVAREZ ECHAZÚ MI, ANTEZANA PE, et al. Stimuli responsive materials for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(13):4724.
[39] 韦祎,巩方玲,崔一民,等.微孔膜乳化技术制备缓释微球的研究进展[J].中国医药工业杂志,2018,49(10):1341-1352.
[40] 刘嘉鑫,张广瑞,卢维新,等.壳聚糖季铵盐在生物材料中的应用[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2020,17(4):59-62.
[41] 吕婷婷.关于丹参素钠-PLGA缓释微球的制备及药剂学性能评价[J].中国社区医师,2019,35(21):8+10.
[42] 于如月,邹茜茜,朱琳,等.粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子缓释微球的研制[J].中国医药工业杂志,2021,52(12):1615-1621.
[43] 赵依妮,李怡,胡鲲,等.诺氟沙星壳聚糖微胶囊缓释作用研究[J].水生生物学报,2014,38(4):675-680.
[44] 冉青,商龙臣,吴少尉,等. SeMet/CS纳米复合微球的制备、缓释性能及抑制肿瘤活性[J].四川大学学报(自然科学版),2018(5):1057-1066.
|