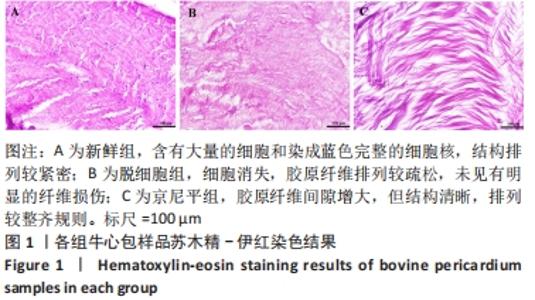
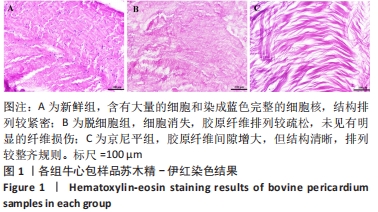
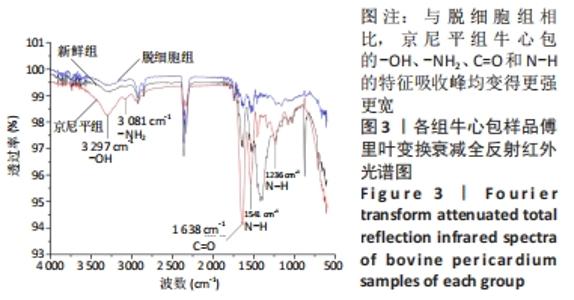
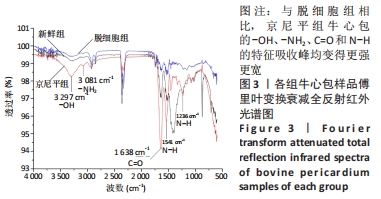
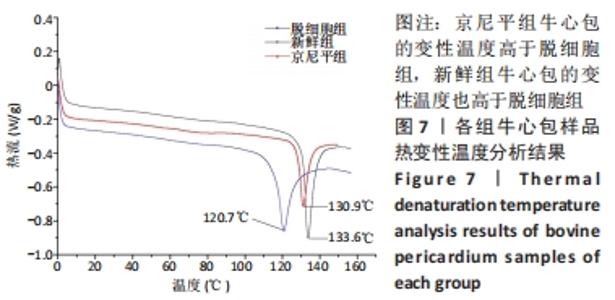
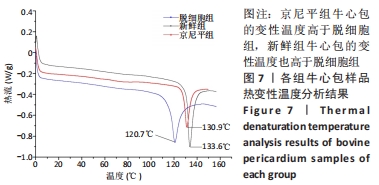
[1] KHOSHHAL F, HASHEMI H, HOOSHMAND E, et al. The prevalence of refractive errors in the Middle East: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Ophthalmol. 2020;40(3):1571-1586.
[2] 王素景.高度近视视网膜脱离患者对侧眼视网膜病变及激光治疗的效果[J].河南医学研究,2017,26(11):2011-2012.
[3] XIAO O, GUO X, WANG D, et al. Distribution and Severity of Myopic Maculopathy Among Highly Myopic Eye. Invest Ophth Vis Sci. 2018;59(12):4880-4885.
[4] 蔺琪,于刚,崔燕辉,等.改良四片式后巩膜加固术治疗儿童进行性高度近视临床研究[J].中国斜视与小儿眼科杂志,2016,24(3):27-28+26+61+5.
[5] 袁梦克,高新晓,魏航,等.病理性近视黄斑劈裂的黄斑区脉络膜厚度及相关影响因素[J].中华眼视光学与视觉科学杂志,2016,18(9):542-545.
[6] 刘亚妮,赵小莹,唐蓓,等.改良的后巩膜加固术治疗高度近视的疗效评估及护理[J].中国药物与临床,2020,20(3):483-485.
[7] LI X, YANG X, LI Q, et al. Posterior scleral reinforcement for the treatment of pathological myopia. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016;9(4):580-584.
[8] 陈珣,王晓瑛,周行涛,等.后巩膜加固术(PSR)后ICL植入术矫正成人高度近视的临床观察[J].复旦学报(医学版),2020,47(3):404-410.
[9] 胥静,谢立科,郝晓凤,等.后巩膜加固术实验研究及临床进展[J].中国医药导报,2019,16(32):42-46.
[10] 张景尚,万修华.后巩膜加固材料在高度近视眼手术治疗中的应用进展[J].国际眼科杂志,2019,19(1):59-62.
[11] 高婷婷,邴启斌,龙琴.后巩膜加固术研究新进展[J].临床眼科杂志, 2017,25(4):381-383.
[12] 过文泰,胡民辉,黄榕康,等.疝外科材料学百年发展及未来展望[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2018,21(7):828-832.
[13] 王彦,刘德成.脱细胞牛心包补片在义眼台置换术中的应用[J].中华眼外伤职业眼病杂志,2017,39(7):545-548.
[14] 周希彬,黄一飞,吴志鸿,等.牛心包生物补片对后巩膜加固区的生物力学特性及其作用机制[J].武警医学,2015,26(6):609-612.
[15] 欧阳朝祜,褚仁远,赵梅,等.牛心包补片应用于后巩膜加固术的早期安全性与生物相容性[J].中华眼视光学与视觉科学杂志,2016,18(5): 259-263.
[16] 易姝,易娟,余时智.后巩膜加固术治疗青少年病理性近视的疗效观察[J].国际眼科杂志,2016,16(4):732-734.
[17] 王旻,笪琳萃,谢艳,等.京尼平作为交联剂在天然生物材料改性中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(5):580-585.
[18] SUNG HW, HUANG RN, HUANG LL, et al. In vitro evlauation of cytotoxicity of a naturally occurring cross-linking reagent for biological tissue fixation. J Biomater Sci Polym Edn. 1999;10(1):63-78.
[19] 王建光,刘天起,王雪梅,等.京尼平与戊二醛鞣制牛心包材料的对比研究[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2011,49(5):24-28.
[20] 陈平,李新华,邢万红.京尼平交联的脱细胞牛心包生物支架材料的实验研究[J].中国医药导报,2010,7(6):28-30.
[21] 田聪,万荣欣,刘欣,等.生物交联剂京尼平交联牛心包生物支架材料的性能[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2011,30(2):281-286.
[22] 周希彬.牛心包生物补片应用于后巩膜加固术的实验研究[D].北京:军医进修学院,2012.
[23] 周小婷,周静,周岩,等.眼巩膜生物补片的亚慢性全身毒性试验研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2020,16(6):462-466.
[24] 钟红荣,张岩,包红,等.丝素/明胶/壳聚糖支架材料的构建及表征[J].材料导报, 2018,32(22):3954-3960.
[25] 石敏,陶思洁,李丹,等.面向组织工程应用的再生丝素/海藻酸钙海绵:制备、表征及体内、体外性能研究[J].材料导报,2020,34(4):4158-4165.
[26] 晏飞燕,刘欣,万荣欣,等.牛心包脱细胞支架的制备研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2010,29(4): 607-613.
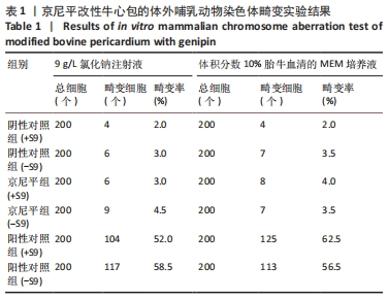
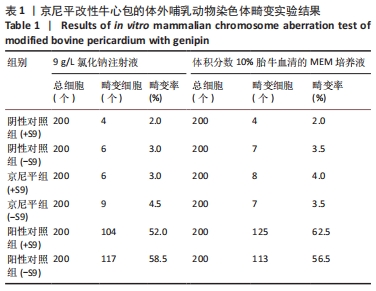
[27] YY/T 0870.2-2013 医疗器械遗传毒性试验第2部分:体外哺乳动物染色体畸变试验[S].
[28] 程祥,郭欢,刘燕萍,等.脱细胞异种生物外科补片的免疫原性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(34):5564-5569.
[29] 赵亮,李霞飞,周坤,等.Triton-x100与丹参酚酸B制备脱细胞血管支架及其生物力学性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(6):951-956.
[30] 郑欣,但年华,陈一宁,等.胶原基生物补片及其抗钙化研究进展[J].生物医学工程与临床,2018,22(5):591-595.
[31] 李丽花,熊健,曹苹,等.改性化学交联脱细胞真皮基质材料的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(26):4206-4211.
[32] 肖宏涛,田社民,查新建,等.不同交联剂对脱细胞牛心包膜生物材料改性的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(10):1301-1306.
[33] 刘其静.单宁酸鞣制对牛心包材料的改性研究[D].武汉:华中农业大学,2019.
[34] 郭岗岗,庞亚博,杨建华,等.采用静电纺丝技术制备丝素纤维蛋白/聚已内酯临时肩袖补片[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(34):5501-5509.
[35] GAO S, YUAN Z, GUO W, et al.Comparison of glutaraldehyde and carbodiimides to crosslink tissue engineering scaffolds fabricated by decellularized porcine menisci. Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;71: 891-900.
[36] 潘腾飞,陶剑,蒋彩云,等.两种脱细胞支架原位植入转归动物试验研究[J].河北工业大学学报,2020,49(3):46-54.
[37] ANDREWS ME, MURALI J, MURALIDHARAN C, et al. Interaction of collagen with corilagin. Colloid Polym Sci. 2003;281(8):766-770.
[38] 刘淑萍,李亮,刘让同,等.羧甲基纤维素钠改性角蛋白膜的结构与性能[J].纺织学报,2019,40(6):14-19.
[39] LIU XH, DAN NH, DAN WH, et al. Feasibility study of the natural derived chitosan dialdehyde for chemical modification of collagen. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;82:989-997.
[40] 白忠祥,但年华,但卫华,等.双醛羧甲基纤维素-胶原复合止血材料的研制[J].材料导报,2018,32(20):3628-3633.
[41] NICKERSON MT, PATEL J, HEYD DV, et al. Kinetic and mechanistic considerations in the gelation of genipin-crosslinked gelatin. Int J Biol Macromol. 2006; 39(4-5):298-302.
[42] 胡康,张伟.胶原蛋白作为医用生物材料对缺损组织修复、再生及重建的作用与意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(2):317-322.
[43] 陈晓松,张建,李建新.一种新型活组织材料的组织学及力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(34):6110-6115.
[44] ZHOU X, TAO Y, CHEN E, et al. Genipin-cross-linked type II collagen scaffold promotes the differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells into nucleus pulposus-like cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(5):1258-1268.
[45] GE TC, XING N, CHEN J, et al. Comparison among several foam dressings in the properties of water-absorption,water-locking and air permeability. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2012;28 (5):349-352.
[46] 田振华,王颖.氧化羧甲基纤维素钠改性胶原膜的制备及表征[J].皮革科学与工程,2020,30(4):7-12.
[47] 高玲玲,侯成立,高远,等.胶原蛋白热稳定性研究进展[J].中国食品学报,2018,8(5):200-212.
|