| [1] 尹辉,单平,谭中华.微创经皮加压钢板内固定治疗胫骨干骨折[J].湘南学院学报(医学版),2008,10(2):51-52.
[2] Krettek C.Foreword: concepts of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis.Injury.1997;28(1):1-2.
[3] 王建伟,杨星光,王韬,等.微创内固定系统治疗胫骨近端复杂骨折[J].中国临床医学,2007,14(4):554-557.
[4] 陈新宇.微创内固定技术与传统手术对胫骨平台骨折患者膝关节功能的影响对比[J].中国实用医药,2013,8(10):43-44.
[5] Krieg JC.Proximal tibial fractures: current treatment, results, and problems.Injury.2003;34(1):2-10.
[6] Schandelmaier P,Partenheimer A,Koenemann B,et al.Distal femoral fractures and LISS stabilization.Injury. 2001;32(3): 55-63.
[7] 李亚东,罗先正.带锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折不愈合与延迟愈合[J].中华创伤杂志,2003,19(6):373-374.
[8] 孙文建,王黎明,杨文贵,等.微创与切开复位接骨板内固定治疗膝关节内骨折的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(16): 1201- 1203.
[9] 孙翔,阚世廉,袁天祥.锁定加压钢板置入内固定治疗胫骨骨折的力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4):728-735.
[10] 张勇杰.带锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折不愈合及延迟愈合30例[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2005,14(20):2707-2708.
[11] Young MJ,Barrack RL.Complications of internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures.Orthop Rev.1994;23(2):149-154.
[12] 曹远举.普通加压钢板治疗肱骨下段骨折产生并发症的原因分析(附34例报告)[J].贵州医药,2006,30(8):697.
[13] 李勤勇.单侧外固定支架治疗胫腓骨骨折的并发症及其处理[J].医学信息(中旬刊),2011,24(6):2333-2334.
[14] 王亦璁.如何理解合理的骨折治疗[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2002, 4(1):6-9.
[15] Krettek C,Müller M,Miclau T.Evolution of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) in the femur.Injury.2001; 32(3): 14-23.
[16] Palmer RH.Biological osteosynthesis.Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract.1999;29(5):1171-1185.
[17] Böstman O,Kiviluoto O,Nirhamo J.Comminuted displaced fractures of the patella.Injury.1981;13(3):196-202.
[18] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-5-15. https://www.cnki.net
[19] SCI数据库.Web of Sciencevia ISI Web of Knowledge[DB/OL]. 2013-5-15.http://ip-science.thomsonreuters.com/mjl
[20] 杨景科,庞五宽,岳建民.对单侧多功能外固定支架治疗股骨骨折手术并发症的分析[J].宁夏医学杂志,2000,22(3):157-158.
[21] 刘刚,杨俊刚,范勇,等.四肢骨折外固定支架术后并发症分析[J].四川医学,2011,32(1):108-109.
[22] 罗从风,陈云丰,高洪,等.改良双钢板法治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折[J].华骨科杂志,2004,24(6):326-329.
[23] Wilson W,van Rietbergen B,van Donkelaar CC,et al. Pathways of load-induced cartilage damage causing cartilage degeneration in the knee after meniscectomy.J Biomech. 2003; 36(6):845-851.
[24] 陈路,蔚芃,蒲劲松.微创锁定钢板与传统钢板治疗胫骨近端骨折的比较[J].川北医学院学报,2010,25(6):527-529.
[25] 王星华,姚振均,张庆华,等.带锁髓内钉治疗胫骨骨折38例报告[J].中国临床医学,2003,10(1):47-49.
[26] Safran O,Liebergall M,Segal D,et al.Proximal tibial fractures--should we nail them?Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ).2001;30(9):681-684.
[27] 曾庆敏,丁磊,张键.交锁髓内钉治疗胫骨近端骨折26例分析[J].中国临床医学,2008,15(4):545-546.
[28] Goesling T,Frenk A,Appenzeller A,et al.LISS PLT: design, mechanical and biomechanical characteristics.Injury. 2003; 34(1):11-15.
[29] 李浩,徐龙伟,季卫平,等.LISS钢板在胫骨近端骨折中的应用[J].实用骨科杂志,2007,13(1):45-47.
[30] Schütz M,Kääb MJ,Haas N.Stabilization of proximal tibial fractures with the LIS-System: early clinical experience in Berlin.Injury.2003;34(1):30-35.
[31] Stannard JP,Wilson TC,Volgas DA,et al.Fracture stabilization of proximal tibial fractures with the proximal tibial LISS: early experience in Birmingham, Alabama (USA).Injury.2003; 34(1): 36-42.
[32] 骆锦强,袁权华,陈振宇,等.LISS钢板在胫骨近端骨折中的应用研究[J].中国医学创新,2009,6(22):25-26.
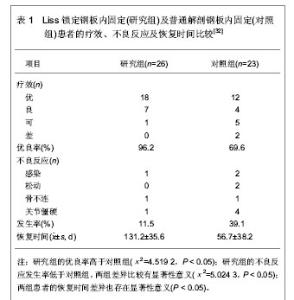
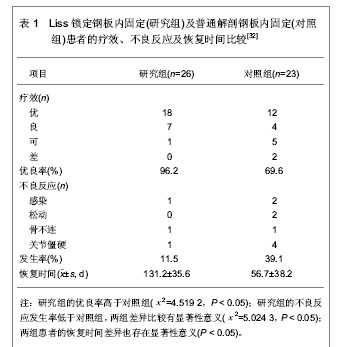
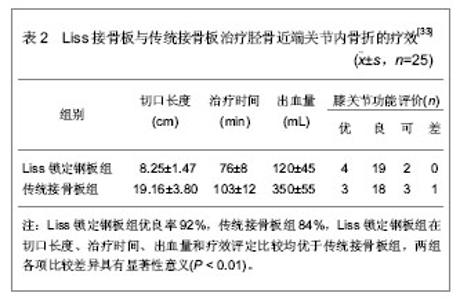
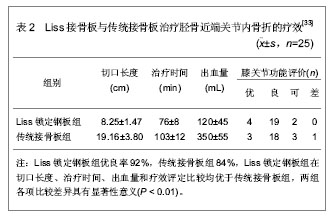
[33] 于水,隋聪,胡孔足,等.不同方法治疗胫骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(2):185-187.
[34] Tejwani NC,Achan P.Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures.Bull Hosp Jt Dis.2004;62(1-2):62-66.
[35] 邱贵兴.四肢长骨干骨折的治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2004, 6(1):8-11.
[36] Schütz M,Müller M,Regazzoni P,et al.Use of the less invasive stabilization system (LISS) in patients with distal femoral (AO33) fractures: a prospective multicenter study.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2005;125(2):102-108. |