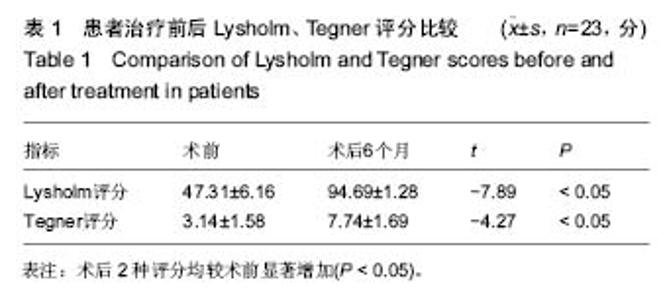
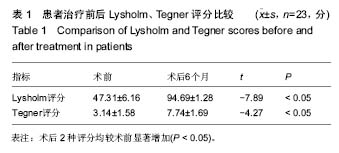
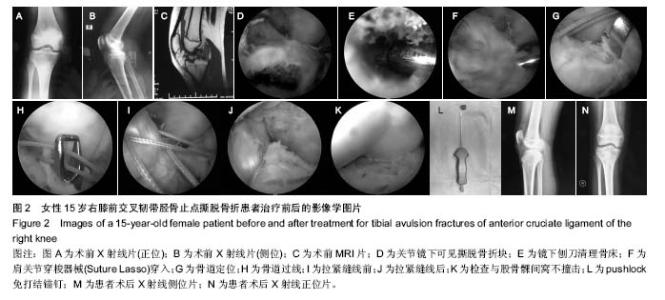
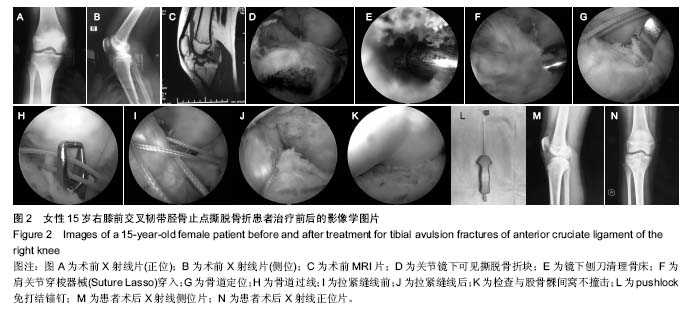
| [1] Anderson CN, Anderson AF. Tibial eminence fractures. Clin Sports Med. 2011;30(4): 727-742[2] 卢华定,史德海,董云旭,等.关节镜下钢丝固定治疗前交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(2): 112-114.[3] Bicer EK, Lustig S, Servien E,et al. Current knowledge in the anatomy of the human anterior cruciate ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(8):1075-1084.[4] Park HJ, Urabe K, Naruse K. Arthroscopic evaluation after surgical repair of intercondylar eminence fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007;127(9):753-757.[5] Lin Y, Wang ZW, Zhang B,et al. Central tendon splitting combined with Suture Bridge double-row technique as a surgical treatment for insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Chin Med J. 2013;20:3860-3864.[6] Smith C, Alexander S, Hill A, et al. A biomechanical comparison of single and double-row fixation in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:2425-2431.[7] 金耀峰,陈刚,戴加平,等. 关节镜下可吸收缝线套扎治疗儿童ACL胫骨止点撕脱骨折[J].中国微创外科杂志,2014,14( 2) : 166-168[8] Boutsiadis A, Karataglis D, Agathangelidis F, et al. Arthroscopic 4-point suture fixation of anterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion fractures.Arthrosc Tech. 2014;3(6): e683-687.[9] 王俭,王文跃,朱海涛,等.关节镜下缝线交叉固定治疗前交叉韧带止点撕脱骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2015,18(3):349-350.[10] Siegel L, Vandenakker-Albanese C, Sigel D. Anterior cruciate ligament injuries: anatomy,physiology, biomechanics, and management.Clin J Sport Med. 2012; 22(4): 349-355.[11] 曹建辉,康慧君,于大海,等.关节镜下空心加压螺钉固定治疗胫骨髁间棘撕脱骨折疗效分析[J]河北医药,2013,35(3):730-731.[12] Gan Y, Xu D, Ding J,et al.Tension band wire fixation for anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture: biomechanical comparison of four fixation techniques.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(5):909-915.[13] Lu XW, Hu XP, Jin C, et al.Reduction and fixation of the avulsion fracture of the tibial eminence using mini-open technique.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(11): 1476-1480.[14] 冯明光,邢斐,杨海涛,等.关节镜下双带线锚钉ACL 止点足印重建治疗胫骨髁间嵴撕脱骨折[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012,31(8) : 673-676[15] Ochiai S, Hagino T, Watanabeet Y,et al. One strategy for arthroscopic suture fixation of tibial intercondylar eminence fractures using the Meniscal Viper Repair System.Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol. 2011;3: 17.[16] Su WR, Wang PH, Wang HN, et al. A simple,modified arthroscopic suture fixation of avulsion fracture of the tibial intercondylar eminence in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011; 20(1) : 17-21.[17] Koukoulias NE,Germanou E,Lola D,et al. Clinical outcome of arthroseopic suture fixation for tibial eminence fractures in adults. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(10):1472-1480.[18] 何秀明,李自振,赵洪涛,等.关节镜下空心钉内固定治疗青少年前交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013, 28(2):162-163.[19] 吕宏升,林洪光,郑佳鹏,等.关节镜下掌骨钢板结合不可吸收缝线固定治疗前交叉韧带止点撕脱骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014,29(4):353-355.[20] 王洪,孙川,孟春庆,等. 关节镜下Orthocord 缝线固定治疗前交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011, 26(12): 1067-1069.[21] 刘阳,孙学斌,李刚,等.关节镜辅助下治疗前交叉韧带胫骨髁间棘撕脱性骨折的临床疗效[J].新疆医科大学学报,2014,37(1): 89-92.[22] 杨坤.关节镜监视下丝线三角形缝合法治疗儿童胫骨髁间嵴撕脱骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(2):159-160.[23] 王法正,梁志林,张军,等. 关节镜下PDS线张力固定前交叉韧带胫骨髁问嵴撕脱性骨折的疗效分析[J]. 新疆医科大学学报, 2014,37(7) : 894-896.[24] 张晓星,邓志龙,曹治东,等. 关节镜下PDS 线交叉缝合固定治疗胫骨髁间棘骨折[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2011,13(5):398-400.[25] 潘铭辉,黄婉容,周敏. 不用内固定法治疗髌骨骨折的体会[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(16):140-141.[26] 朱余龙,朱海涛,王水,等.Arthrex高强度缝线缝合治疗粉碎性髌骨骨折 (附45例报道)[J].医疗前沿,2016,6(19) : 184-185.[27] 安佰京,邢更彦. 关节镜下Pushlock 免打结技术治疗复发性肩关节不稳临床效果分析[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2016, 8(3):21-24.[28] Kocher MS, Micheli LJ, Gerbino P, et al. Tibial eminence fractures in children:prevalence of meniseal entrapment. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(3):404-407.[29] Yang SW, Lu YC, Teng HP, et al. Arthroscopic reduction and suture fixation of displaced tibial intercondylar eminence fractures in adults. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2005;125(4): 272-276[30] 王健, 敖英芳. 青少年ACL损伤流行病学研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2002,21(5) : 471-474.[31] 陈梓锋, 陈爱民, 侯春林. 不同部位贯穿伤对骺板生长发育影响的实验研究[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究,2009,6 ( 5) : 7-12.[32] 陆振飞, 赵金忠, 皇甫小桥.关节镜下跨骺板8字缝线固定法治疗前交叉韧带胫骨止点撕脱骨折后的随访研究[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2008,29(12):639-643.[33] 吴术红,刘毅,熊华章,等.关节镜下“8”字缝线固定治疗青少年前交叉韧带胫骨止点骨折[J]. 重庆医科大学学报,2011,36(7): 863-865.[34] May JH, Levy BA, Guse D, et al. ACL tibial spine avulsion: mid-term outcomes and rehabilitation. Orthopedics. 2011; 34(2):89.[35] Montgomery KD, Cavanaugh J, Cohen S, et al. Motion complications after arthroscopic repair of anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fractures in the adult. Arthroscopy. 2002; 18(2):171-176.[36] Eggers AK, Becker C, Weimann A, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of different fixation methods for tibial eminence fractures. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(3):404-410.[37] Hapa O, Barber FA, Süner G, et al. Biomechanical comparison of tibial eminence fracture fixation with high-strength suture, EndoButton, and suture anchor. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(5):681-687.[38] In Y, Kwak DS, Moon CW, et al. Biomechanical comparison of three techniques for fixation of tibial avulsion fractures of the anterior cruciate ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(8):1470-1478.[39] Seon JK, Park SJ, Lee KB, et al. A clinical comparison of screw and suture fixation of anterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion fractures. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37:2334-2339.[40] 吴宇峰,苏培基,伍中庆,等.前交叉韧带胫骨棘止点撕脱骨折不同内固定方式的生物力学研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(9): 868-871.[41] Thaunat M, Camelo Barbosa N, Tuteja S, et al. A Fluoroscopy-Free Technique for Percutaneous Screw Positioning During Arthroscopic Treatment of Depression Tibial Plateau Fractures. Arthrosc Tech. 2016;5(3):e507-511.[42] Tomás-Hernández J, Monyart JM, Serra JT, et al. Large fracture of the anteromedial tibial plateau with isolated posterolateral knee corner injury: case series of an often missed unusual injury pattern. Injury. 2016;47 Suppl 3: S35-S40. [43] Tosun O, Ocguder A, Annac G, et al. Significant associated MRI findings in patients with anterior cruciate ligament stump entrapment. Skeletal Radiol. 2016;45(9):1269-1276.[44] Wang Y, Cao F, Liu M, et al. Incidence of Soft-Tissue Injuries in Patients with Posterolateral Tibial Plateau Fractures: A Retrospective Review from 2009 to 2014. J Knee Surg. 2016; 29(6):451-457. [45] Mitchell JJ, Mayo MH, Axibal DP, et al. Delayed Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction in Young Patients With Previous Anterior Tibial Spine Fractures. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(8):2047-2056. [46] Brunner S, Vavken P, Kilger R, et al. Absorbable and non-absorbable suture fixation results in similar outcomes for tibial eminence fractures in children and adolescents. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(3):723-729. [47] Zehir S, Elmal? N, ?ahin E, et al. Posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction via tibial inlay technique in multiligament knee injuries. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015;49(6):579-585. |