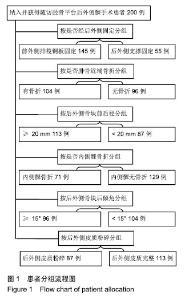
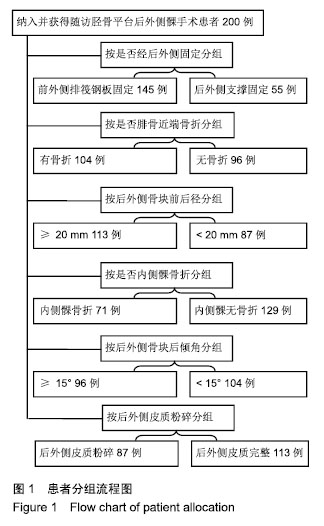
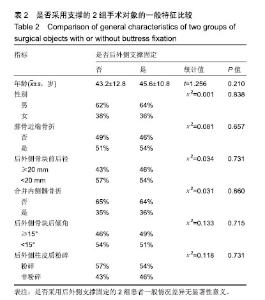
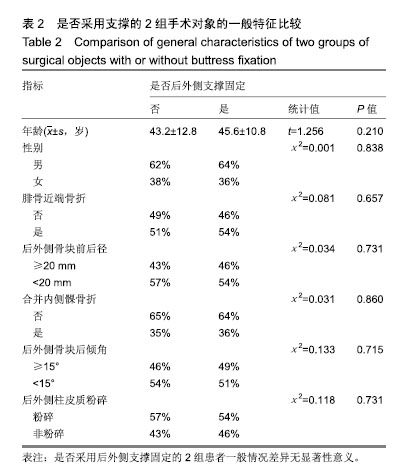
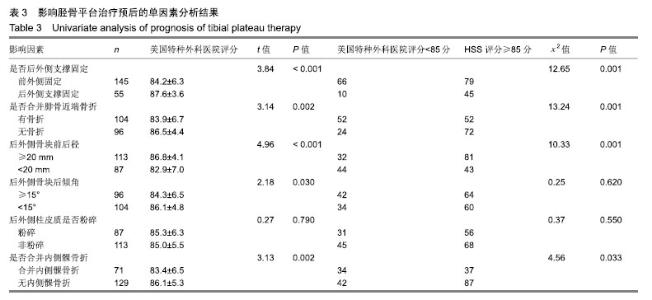
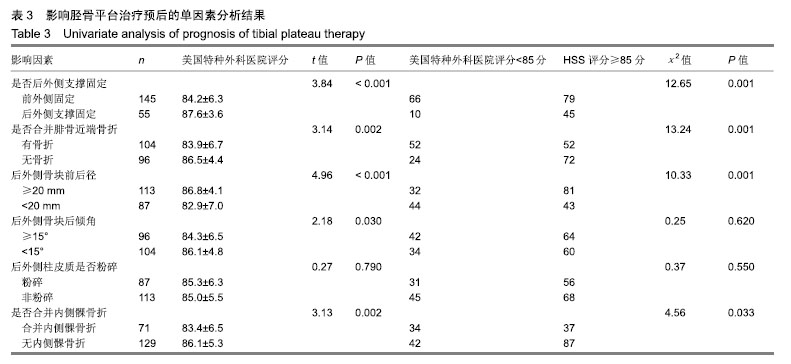
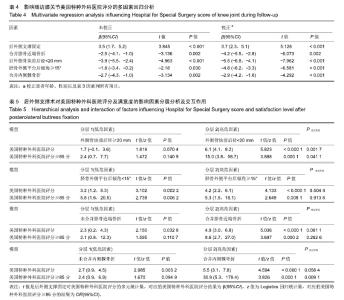
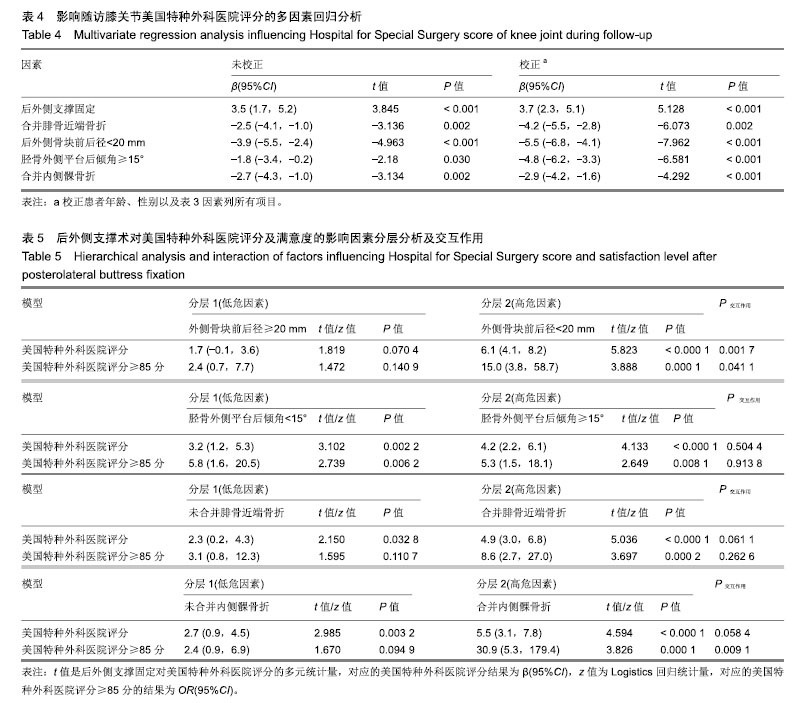
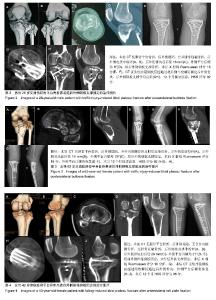
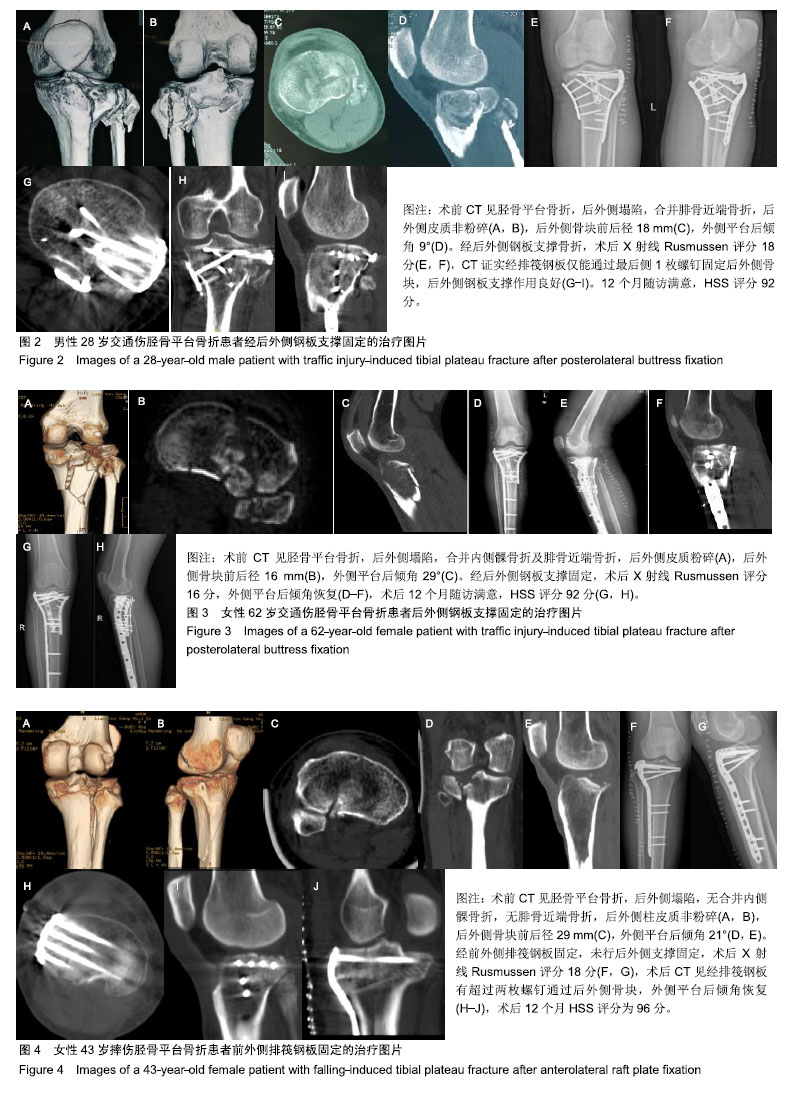
| [1]Galla M, Lobenhoffer P. The direct, dorsal approach to the treatment of unstable tibial posteromedial fracture-dislocations. Unfallehirurg. 2003|106:241-247.[2]Gavaskar A S, Gopalan H, Tummala NC, et al. The extended posterolateral approach for split depression lateral tibial plateau fractures extending into the posterior column: 2 years follow up results of a prospective study. Injury. 2016; 47(7): 1497-1500.[3]Solomon LB, Stevenson AW, Baird RP, et al. Posterolateral transfibular approach to tibial plateau fractures: technique, results, and rationale. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(8): 505-514.[4]张巍,罗从风,曾炳芳.四种不同内固定治疗胫骨平台后外侧剪应力骨折的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2010,12(11): 1069-1073.[5]Rasmussen PS. Tibial condylar fractures.Impairment of knee joint stability as an indication for surgical treatment.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55:1331-1350.[6]霍永峰,殷照阳,徐刚.胫骨外髁非负重区截骨治疗胫骨平台后外侧髁骨折[J].重庆医学,2018,47(7):919-925. [7]丁浩亮,安智全.后外侧胫骨平台骨折的手术治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(4):362-365.[8]Luo CF, San H, Zhang B, et al. Three-columnfixation for complex tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24: 683-692.[9]Brunner A, Honigmann P, Horisberger MA. Open reduction and fixation of medial Moore type II fractures of the tibial plateau by a direct dorsal approach. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(9):1233-1238.[10]Frosch KH, Balcarek P, Walde T, et al. A new posterolateral approach without fibula osteotomy for the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010; 24(8): 515-520.[11]He X, Ye P, Hu Y, et al. A posterior inverted L-shaped approach for the treatment of posterior bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(1): 23-28.[12]Ghazavi MT, Pritzker KP, Davis AM, et al. Fresh osteochondral allografts for post-traumatic osteochondral defects of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(6): 1008-1013.[13]Solomon LB, Stevenson AW, Lee YC, et al. Posterolateral and anterolateral approaches to unicondylar posterolateral tibial plateau fractures: a comparative study. Injury. 2013; 44(11): 1561-1568.[14]Gilula L, Persenaire M. Subsequent fractures Post-Vertebral augmentation: analysis of a prospective randomized trial in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 34(1): 221-227.[15]Yoon YC, Oh JK, Oh CW, et al. Inside out rafting K-wire technique for tibial plateau fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(2): 233-237.[16]高翔,李杭,郑强,等.胫骨后外侧平台骨折的CT形态学研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(7):709-716.[17]Brunner A, Honigmann P, Horisberger M, et a1.Open reduction and fixation of medial Moore type II fractures of the tibial plateau by a direct dorsal approach. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;24:1233-1238.[18]范鑫斌,张岩,杨铁毅,等.胫骨平台后外侧骨折3种内固定方式的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(22):3510-3516.[19]Moore TM. Fractrue-dislocation of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1981;(156): 128-140.[20]Ogden JA. The anatomy and function of the proximal t ibiofibular joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974;(101):186-191.[21]Espregueira-Mendes JD, Da Silva MV. Anatomy of the proximal tibiofibular joint. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthroac. 2006;14:241-249.[22]霍永峰,殷照阳,厉雷明,等.腓骨近段骨折在后外侧柱复杂胫骨平台骨折中的参考意义[J].重庆医学,2015,44(14):1921-1923, 1927.[23]Pires RE, Gioidano V, Wajnsztejn A, et al. Complications and outcomes of the transfibular approach for posterolateral fractures of the tibial plateau. Injury. 2016;47(10): 2320-2325. |