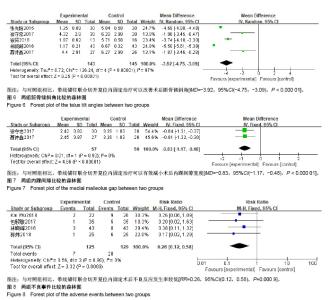
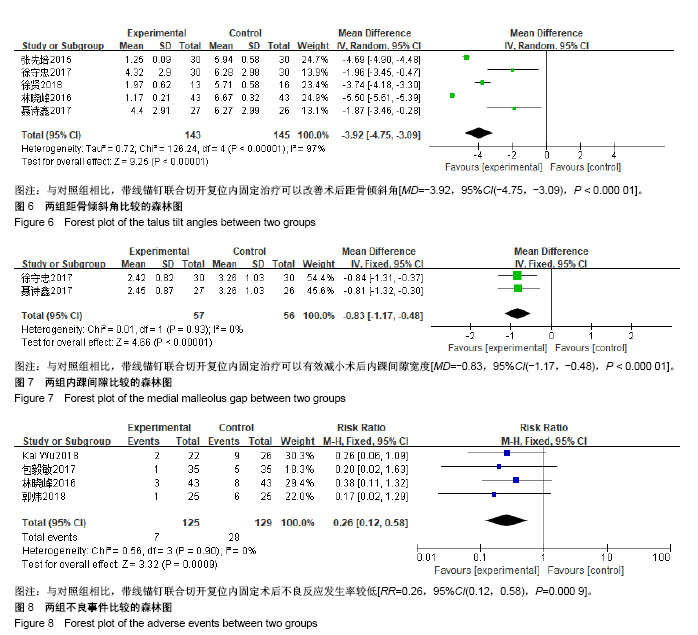
| [1] Kusnezov NA, Eisenstein ED, Diab N, et al. Medial malleolar fractures and associated deltoid ligament disruptions: current management controversies. Orthopedics. 2017;40(2):e216-e222.[2] Halai M, Jamal B, Rea P, et al. Acute fractures of the pediatric foot and ankle. World J Pediatr. 2015;11(1):14-20.[3] 张强,胡彬,彭亮,等. 踝部三角韧带损伤的诊疗进展[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2017,36(6):544-547.[4] 张先培. 锚钉修复治疗外踝骨折合并三角韧带损伤临床研究[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2015,15(76):45-46.[5] 林晓峰. 锚钉修复外踝骨折并三角韧带损伤的临床探讨[J]. 中外医疗, 2016,35(35):91-93.[6] 李鹏. 踝关节损伤时手术修复三角韧带断裂的疗效分析[D]. 太原:山西医科大学, 2016.[7] 包毅敏. 带线锚钉内固定治疗踝关节骨折合并三角韧带损伤临床研究[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2017,23(4):371-374.[8] 聂诗鑫. 带线锚钉联合切开复位内固定治疗踝关节骨折合并三角韧带Ⅱ、Ⅲ度损伤的疗效[J]. 贵州医药, 2017,41(4):390-391.[9] 徐守忠. 带线锚钉联合切开复位内固定在治疗踝关节骨折合并三角韧带Ⅱ、Ⅲ度损伤的效果[J]. 双足与保健, 2017,26(15):117-138.[10] Wu K, Lin J, Huang J, et al. Evaluation of transsyndesmotic fixation and primary deltoid ligament repair in ankle fractures with suspected combined deltoid ligament injury. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2018;57(4):694-700.[11] 郭炜,李冠臣. 锚钉修补结合切开复位内固定治疗踝关节骨折伴三角韧带损伤的效果观察[J]. 中国实用医药, 2018,13(1):51-52.[12] 徐贤,刘林,李聪,等. 踝关节骨折合并三角韧带损伤的手术疗效分析[J]. 浙江临床医学, 2018,20(4):631-633.[13] 伍凯,林健,黄建华,等. 急性踝关节骨折伴三角韧带损伤术中诊断及治疗策略[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2015,36(2):141-145.[14] 佘刚, 邹拥军, 黄靖. 锚钉修补结合切开复位内固定治疗踝关节骨折伴三角韧带损伤的疗效[J]. 安徽医学, 2017,38(10):1262-1265.[15] 胡伟男, 崔海勇. 带线锚钉修复联合切开复位内固定治疗踝关节骨折合并三角韧带损伤[J]. 中国基层医药, 2017,24(14):2147-2151.[16] 秦大山,徐彬,黄万强. 踝关节骨折三角韧带损伤的诊断与治疗进展[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2018,18(16):102-104.[17] Yde J, Kristensen KD. Ankle fractures: supination-eversion fractures of stage IV. Primary and late results of operative and non-operative treatment. Acta Orthop Scand. 1980;51(6): 981-990.[18] Pettrone FA, Gail M, Pee D, et al. Quantitative criteria for prediction of the results after displaced fracture of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983;65(5):667-677.[19] Lindsjo U. Operative treatment of ankle fracture-dislocations. A follow-up study of 306/321 consecutive cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;(199):28-38.[20] Hintermann B, Knupp M, Pagenstert GI. Deltoid ligament injuries: diagnosis and management. Foot Ankle Clin. 2006;11(3):625-637.[21] Femino JE, Vaseenon T, Phisitkul P, et al. Varus external rotation stress test for radiographic detection of deep deltoid ligament disruption with and without syndesmotic disruption: a cadaveric study. Foot Ankle Int. 2013;34(2):251-260.[22] 何河北,董伟强,孙永建,等. 修复三角韧带与不修复对于踝关节骨折合并三角韧带损伤术效果的Meta分析[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014,8(4):497-501. |