Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (23): 3744-3750.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0154
Previous Articles Next Articles
Posterior malleolar fractures: how to choose in the face of diversified treatment?
Zhang Yong-duo, Pan De-yue, Li Xue-liang, Zhao Wen-zhi
- Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116023, Liaoning Province, China
-
Online:2018-08-18Published:2018-08-18 -
Contact:Pan De-yue, Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116023, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zhang Yong-duo, Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116023, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yong-duo, Pan De-yue, Li Xue-liang, Zhao Wen-zhi. Posterior malleolar fractures: how to choose in the face of diversified treatment? [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(23): 3744-3750.
share this article
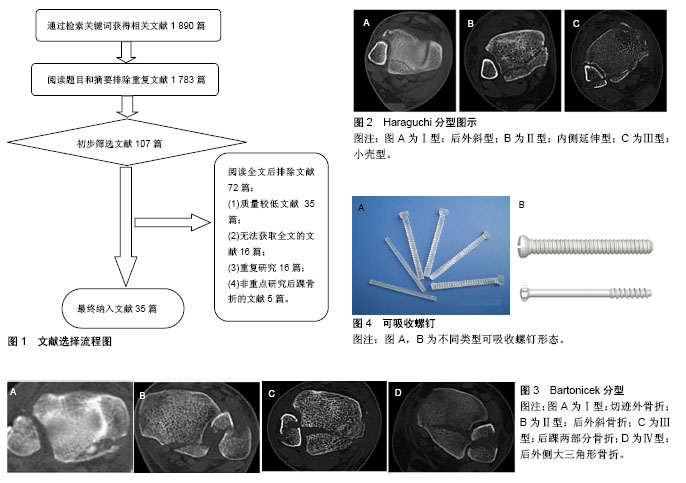
2.1 纳入资料基本概况 纳入的文献包括侧重研究后踝骨折生物力学特性及发生机制的文章7篇[1-7],研究后踝骨折分型的文章5篇[8-12],研究后踝骨折诊断方式的文章4篇[13-16],研究后踝骨折治疗方式的文章17篇[17-33],研究后踝骨折内固定材料的文章2篇[34-35]。见图1。 2.2 纳入资料的研究结果特征 2.2.1 后踝的解剖及生物力学特性 踝关节由胫骨远端、腓骨远端、距骨及其周围的韧带组成,是一个复杂的屈戌关节。研究者将胫骨远端关节面顶部向后下方的延伸形成称为后踝。后踝由皮质骨、松质骨及关节软骨组成,有下胫腓后韧带的起点。研究表明,下胫腓后韧带在维持下胫腓联合稳定性方面发挥42%的作用[3],当后踝发生骨折时,丧失了下胫腓联合后侧稳定性,可使下胫腓联合分离,进而导致踝关节不稳。另外,后踝增加了胫距关节接触面积,有降低踝关节单位面积上的压力的作用。有研究报道,踝关节的压力主要集中在关节面中央1/2处,而后1/4基本不受力[4],因此当后踝骨折块大小超过整个踝关节面的1/4时,将使剩余踝关节面单位面积压力增加,从而导致创伤性关节炎[5-6]。 2.2.2 后踝骨折的发生机制 在惯性的作用下,后踝骨折是由于胫骨整体随躯干继续向前移动,从而使水平剪切、撞击以及地面向上的反作用力发生在后踝与距骨之间,并使两骨相互撞击,造成后踝的骨折[7]。在垂直暴力基础上,常常伴有旋转暴力,因此单纯后踝骨折比较少见。 2.2.3 后踝骨折的分型 根据AO/OTA分型,踝关节骨折A3,B3和C型均伴有后踝骨折。其中A3型(旋后内收损伤)为后内侧骨折,由距骨直接撞击后踝后内侧所致;B3型、C型均为后外侧骨折,多为较大的骨折块,是距骨过度外旋同时向后半脱位并与后踝外侧角直接撞击的结果。在Lauge-Hansen分型中,旋后-外旋型Ⅲ,Ⅳ,旋前-外旋型Ⅳ度和旋前-外展型Ⅱ,Ⅲ度均伴有后踝骨折,这种基于踝关节损伤机制的分型方法对闭合复位治疗的意义较大。但是Lauge-Hansen分型主要强调踝关节整体,尤其内外踝在各种损伤机制中的骨折线走行情况,对于后踝骨折块大小及骨折线延伸方向未有明确的分析,使有些类型的后踝骨折在这两种分型中无法体现,在指导制定治疗方案时,这两种分型仍有涵盖种类不全,影响治疗方式选择等缺点。因此,学者们期望探索一种新的分型方式。 王志生等[8]总结了其88例后踝骨折的分型方式为CT上后踝大小、骨折线以及部位。他认为CT在临床诊疗中拥有重要意义,其原因是CT能够明确后踝骨折的解剖学改变。他将后踝骨折分为4型:①Ⅰ型为稳定型,Ⅰ1型:胫骨穹隆后缘的1个或多个小撕脱骨折;Ⅰ2型:胫骨穹隆后外侧的小楔形骨块,所占穹隆面积小于20%;②Ⅱ型为临界型。Ⅱ1型:胫骨穹隆后外侧的小楔形骨块,所占穹隆面积大于20%但小于25%,无原始向后全脱位或半脱位;Ⅱ2型:胫骨穹隆后外侧的小楔形骨块,所占穹隆面积大于20%但小于25%,并伴原始后侧全脱位或半脱位;③Ⅲ型:大楔形骨块,即不稳定型,描述为穹隆后外侧的楔形骨块,所占穹隆面积大于25%;④Ⅳ型:中间贯穿型。骨块所占胫骨穹隆面积大于25%,且骨折线涉及胫骨切迹至内踝。该分型认为,Ⅰ型及Ⅱ1型骨折均可采取保守治疗的方式,Ⅱ2型及以上的后踝骨折则需进行相应的手术内固定治疗。该分型主要体现了CT平扫对于踝关节骨折块面积占整个踝关节面积大小的分析,并指导临床治疗方案的选择,但是也有一定的局限性,其未能结合CT重建,无法直观了解后踝骨折块的大小,也无法体现后踝骨折线向胫骨近端的延伸情况。 Haraguchi等[9]对57例后踝骨折患者进行了病理解剖学研究,并根据CT上胫骨远端关节面水平后踝骨折线方向,将后踝骨折分为3型:其中Ⅰ型:后外斜型,骨折块呈楔形,累及胫骨远端关节面后外角,该类型后踝骨折在临床中最为常见;Ⅱ型:内侧延伸型,骨折线自胫骨远端切迹延伸至内踝,骨折块可包括后外和后内两部分;Ⅲ型:小壳型,胫骨后缘一个及以上小壳形骨片(图2)。有学者认为,后踝骨折累及内踝后丘的病例符合HaraguchiⅡ型骨折特征[10]。此类骨折多合并距骨脱位(半脱位),后踝骨折块相对较大,且预后较差,这一类骨折被称为后Pilon骨折。Haraguchi分型能很好的体现胫骨远端关节面水平后踝骨折线的走行方向,在临床上已广为应用。但该分型未能明确体现后踝骨折块所占胫骨远端关节面积大小,致使该分型无法帮助临床医生确定手术指征,其对临床选择治疗方案的指导意义尚有待进一步完善。 Mangnus等[11]在Haraguchi分型的基础上通过CT图像的后处理技术对后踝骨折进行研究,利用三踝骨折绘图法对后踝骨折的形态进行定性分析,利用CT重建模型定量分析骨折块的体积和累计胫骨远端关节面的面积,发现后踝骨折主要有两种,即后外斜形和横形。其中后外斜形即Haraguchi分型中的Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型,两者是由同一种暴力导致的不同程度的骨折;横形即HaraguchiⅡ型骨折,骨折线延伸至内侧,并累及内踝后丘。另外,他们认为可将后踝骨折分为两个基本类型,即后外型和后内型,并可根据内侧结构是否稳定决定治疗方案。该分型是对Haraguchi分型的总结和改良,并结合了CT三维重建,更加直观的体现的后踝骨折的空间形态,并强调后踝骨折的稳定性,对手术指征的确定上,比Haraguchi分型更加具有说服力,但其分型不够具体,对于一些复杂类型的后踝骨折,未做具体阐明。 Bartonicek等[12]利用CT三维重建,将后踝骨折依据骨折块位置、大小、形状以及胫骨腓切迹是否完整等因素,将后踝骨折分为以下4型:Ⅰ型:为切迹外骨折,骨折线未累及胫骨腓切迹;Ⅱ型:为后外侧骨折,骨折线主要累及胫骨腓切迹的后1/4至1/3;Ⅲ型:为后踝两部分骨折,后内侧骨折线延伸至内踝后丘或丘间沟,外侧骨折块主要累及胫骨腓切迹的后1/4至1/3;Ⅳ型:为后外侧大三角形骨折,骨折线主要累及胫骨远端内后缘和腓切迹的后1/3至1/2,呈三角形(图3)。另外,他们研究发现Ⅰ型至Ⅳ型骨折中,病例数逐渐增加的特点在后踝骨折块的宽度、高度、累及胫骨远端关节面的面积大小、累及胫骨腓切迹的程度、同时合并距骨脱位或半脱位等方面均有体现。通过矢状位片还发现所有后踝骨折,包括切迹外骨折在内,均会不同程度的累及胫骨远端关节面,部分还可见塌陷骨块。因此,他们认为后踝骨折的损伤机制在这一分型中能被充分展现。该分型对于骨折块的位置、大小、形状以及踝关节稳定性等因素均进行了详细的阐述,在指导临床治疗方案的选择方面能做到全面考虑,值得推广。 2.2.4 后踝骨折的诊断 单纯的后踝骨折非常少见,常合并内外踝骨折。一般踝关节骨折的患者外伤史明确,如交通伤、高处坠落伤、运动伤等。骨折后患者常表现为踝关节周围的疼痛、肿胀并伴有踝关节不同程度的活动受限,局部压痛明显,常不能负重行走。 影像学检查是诊断踝关节骨折必不可少的检查手段,其中X射线检查最为常用。但因为拍摄角度及体位的局限性,常规X射线上常常发现不了后踝骨折。有学者通过实验研究及统计学分析指出在踝部标准正侧位X射线片的基础上加拍外旋侧位X射线片可有效提高后踝骨折的检出率。Gonzalez等[13]通过人工合成的后踝骨折模型进行研究,选取的30个模型后踝骨折线与内外踝轴线的平均夹角为21°,每个模型均拍摄踝关节标准侧位和外旋21°侧位X射线片,结果显示标准侧位X射线片上后踝骨折的确诊率为86.67%,外旋21°侧位X射线片上后踝骨折的确诊率为100%。对于典型的后Pilon骨折,后内侧骨块为冠状面骨折,累及内踝后丘甚至部分前丘,后侧骨块通常沿矢状面劈裂为后内和后外侧两部分,后内侧多为塌陷骨折,踝关节X射线片可表现为“双线征”[10,14]。而Ferries等[15]利用常规X射线和CT获得25例三踝骨折患者后踝骨折碎片的大小,其中X射线片与CT片不符的测量结果占54%,从而认为后踝骨折患者的诊断通常不能仅靠X射线片。与X射线相比,CT扫描可对后踝骨折的大小、形态、移位程度、关节面塌陷程度以及可能存在的下胫腓前韧带损伤进行更加准确的评估,并且在此基础上进行CT三维重建,可以更加真实、直观地评估损伤情况,但此种方法也受影像学技师水平的制约。 在后踝骨折的类型中,还有一种特殊类型的骨折更应引起临床医生的重视。该类型骨折为胫骨中下段骨折合并的后踝骨折。其损伤机制现可认为是由于踝关节旋前外翻,小腿外旋造成胫腓骨螺旋骨折的同时,小腿三头肌剧烈收缩,踝关节跖屈,距骨撞击胫骨远端后部从而造成后踝骨折[16]。此种类型的骨折,其后踝骨折多为线样骨折,在早期X射线片上极易漏诊,从而影响踝关节稳定性,导致创伤性关节炎的发生。而CT对此类型骨折的后踝骨折检出率可达90%以上。 总之,对于踝关节损伤的患者,术前进行X射线及CT重建的检查是诊断后踝骨折及确定治疗方案不可缺少的步骤。 2.2.5 后踝骨折的治疗 研究表明,在踝关节损伤伴有后踝骨折时,创伤性关节炎的发生概率明显增加,因此,后踝骨折的正确治疗方案可显著降低创伤性关节炎的发病率。 与其他骨与关节创伤相比,保守治疗和手术治疗也同样均适用于后踝骨折。对于累及关节面积小于25%的后踝骨折来说,保守治疗为首选。保守治疗的方法包括下肢支具、踝关节小夹板以及石膏固定等。对于治疗小于1.0-2.0 mm移位的后踝骨折,不予复位与手术解剖复位对其预后的影响没有明显差异[17]。当后踝骨折块较小且合并外踝骨折时,有效复位固定外踝骨折后,后踝的骨折块常可以自行复位。保守治疗的优点即方便快捷,免除了患者手术的痛苦,并且在花费上要远远低于手术治疗。但是,保守治疗的局限性也很明显。骨折的治疗原则为复位、固定及功能锻炼,而保守治疗时,需要限制整个踝关节的屈伸及旋转功能,无法使踝关节得到早期的功能锻炼,最终致使关节僵硬,给患者拆除外固定后的功能锻炼带来很大的痛苦。如若进行过早的功能锻炼,将会导致外固定失效,导致骨折块继续移位或再移位,最终导致创伤性关节炎。 后踝骨折的手术适应证:后踝骨折的手术指征仍存在较大争议[18]。McLaulghlin回顾性分析大量后踝骨折闭合复位的病例,发现当后踝骨折块大小累及胫骨远端关节面的比例<10%时,并不会发生明显的距骨向后脱位;当骨折块大小比例在10%-25%时,发生距骨脱位的概率为20%;而当比例>25%时,无论最初的手法复位如何精确、复位后外固定措施如何全面,最终无患者可维持最初的复位状态,均发生了不同程度的距骨向后半脱位,并且发生创伤性关节炎。因此,他首次将后踝骨折进行内固定手术与否的分界线界定为胫骨远端关节面的25%。目前大多数外科医生已认同这一观点,并将其视为后踝骨折手术的指征之一。刘志强等[19]为了对后踝关节面进行精确区分、切割,建立了大量踝关节三维有限元模型[20],模拟计算后踝骨折块不同面积范围条件下施加正常应力时的各种参数,其中包括关节软骨的接触面积、最大接触应力、平均接触应力、最大位移等,结果显示,关节面积减小,应力变化增加,关节位移趋势增加等结果多发生于后踝骨折面积超过胫骨远端关节面的1/3时,其预后不良,首选手术复位。Langenhuijsen等[21]认为,在侧位X射线片上,累及关节面积≥10%的后踝骨折中,若内、外踝固定复位后,仍有≥1 mm的移位时,复位固定治疗是必要的。研究发现,Haraguchi分型[9]中,骨折块大小平均累及11.7%的踝关节面的骨折为Ⅰ型骨折,而平均累及29.8%的踝关节面的为Ⅱ型骨折,整个内踝在骨折线向内延伸时,均可被累及。他们认为,外踝固定后的Ⅰ型骨折,在后踝骨折块有明显移位时进行切开复位内固定是必要的。存在两部分骨折块的Ⅱ型骨折,固定内踝后就等同于Ⅰ型骨折。若Ⅱ型骨折在内外踝固定后,仍有后外侧骨块的移位,则需对后踝骨折块行相应的内固定。对于只有一个骨折块的Ⅱ型骨折,则宜行切开复位内固定治疗。龚晓峰等[22]在分析骨折块大小对手术选择的影响时,发现当后踝骨折块面积占比达到15%时,医生选择手术治疗的意愿明显增强。近年来有文献发现后踝骨折块的固定能够恢复下胫腓后韧带的张力,有助于改善下胫腓联合的复位,所获得的稳定性更优于下胫腓螺钉固定的效果,因此甚至有学者认为:只要存在后踝骨折,无论骨折块多大,都应进行解剖重建,以减少下胫腓螺钉的使用。作者认为,在确定后踝骨折的手术指征时,不能单纯依靠单方面的证据,综合考虑后踝骨折面积占胫骨远端关节面大小、骨折块的移位程度、骨折线向胫骨近端延伸情况、骨折的粉碎程度、下胫腓联合的稳定性等因素是必要的。其中,骨折累及关节面积大小及下胫腓联合的稳定性应作为首要评估因素。因为骨折累及关节面积的大小直接决定胫骨远端关节面的受力情况,良好的下胫腓联合稳定性可以有效避免距骨的脱位或半脱位。 后踝骨折的手术方式:对于后踝骨折的手术入路,起决定性作用的是骨折块的位置。后内侧入路、后外侧入路、后内侧联合后外侧入路等为常见的手术入路方式。近年来微创手术越来越受到广大医生的欢迎,采用闭合复位后使用空心钉固定后踝骨折的方式逐渐增多[23-24]。 (1)后外侧入路:踝关节后外侧入路的皮肤切口位于外踝后缘与跟腱的中线,远侧延伸至外踝尖。切开皮肤后,显露皮下组织及深筋膜,注意保护腓肠神经以及小隐静脉,纵向切开深筋膜后显露腓骨肌腱。再将腓骨肌腱向外侧牵开,分离肌间隔后显露拇长屈肌,将其向内侧牵开,即可显露后踝骨折块[25]。操作过程中应注意保护腓动脉、下胫腓后韧带和骨折块上的骨膜。邓建华 等[26]对17例后踝骨折患者均采用改良的后外侧入路行切开复位内固定,术后进行随访,平均随访时间为14.2个月,所有随访的患者中,切口均愈合良好,且内固定物完整、固定牢靠,未见骨折再移位,患者术后均获得骨性愈合,行走时步态正常,无需工具辅助。由此可见,后踝骨折的改良后外侧入路治疗,优点是安全简便、显露清晰,可同时显露腓骨,尤其适用于HaraguchiⅠ型及Ⅲ型骨折,可直视下复位关节面并进行稳定的固定,并且可将钢板置于腓骨外侧或后侧,减少了钢板对皮肤的刺激。 (2)后内侧入路:踝关节后内侧入路是沿胫骨远端内后侧缘和胫后肌腱走行,向距舟关节方向做切口,切开屈肌支持带,向前方牵开胫后肌腱,向后方牵开拇长伸肌腱,或向内踝前方牵开胫后肌腱和拇长伸肌腱,将克氏针临时固定于内踝以辅助维持肌腱牵开;切开胫后肌腱鞘基底和后侧关节囊即可显露骨折。需要注意的是,术毕应缝合屈肌支持带,以防止胫后肌腱脱位[27-28]。该入路适用于HaraguchiⅡ型骨折,而改良的后内侧入路对于严重的后Pilon骨折,能有效的暴露骨折端,从而帮助直视下复位[29]。 (3)后内侧联合后外侧入路:无论后内侧或是后外侧入路,在暴露手术切口对侧的骨折时,均有较大难度。张士波等[30]认为若后踝后外方和后内方同时存在较大骨块时,首选后内侧与后外侧联合入路。邓建华等[26]也认为该手术方式的优点为操作简便,可解剖复位关节面,内固定固定可靠等,治疗效果满意。但是,该入路方式对踝关节内外侧的软组织均需进行较大范围的剥离,对局部血运影响较大,且对内外踝周围的血管、神经及肌腱均有较大可能的损害,不利于骨折的愈合及踝关节功能的恢复。 综上,任何一种类型的后踝骨折均无绝对适用的手术入路。根据骨折的分型个性化的选择手术入路方式不但可以更有效的暴露骨折端,并且尽可能的减小了医源性损伤,在临床工作中,应灵活运用。 (4)微创闭合复位:微创手术现已成为外科手术一大趋势,相对于切开复位内固定,微创闭合复位可以有效减小手术切口,降低手术对骨折端软组织血运的影响。苏文先等[31]随访了9例采用空心加压螺钉经皮微创内固定治疗合并后踝骨折的患者,在侧位X射线片上,这些随访患者的后踝骨折块的特点是大小超过胫骨远端关节面积的25%,且有大于2 mm的移位。术中外踝和内踝首先被复位和内固定,且固定后踝导针的位置与方向是由术前CT决定的。在随访过程中得知,9例患者的后踝骨折均为骨性愈合。因此可见,对于后踝骨折来说,经皮空心加压螺钉内固定为较理想的内固定方式,并且具有创伤小、固定可靠等优势。除了空心加压螺钉外,另外一种微创固定方式也逐渐进入临床医生的视野,即可延伸外固定支架技术。可延伸外固定支架固定方法相对于空心加压螺钉内固定操作更为简便,因空心加压螺钉内固定一般需从胫骨远端,由前至后在C臂透视下进行,术者所受X射线辐射量较大,且对于较薄、较小的后踝骨折块,其加压作用有限,容易造成内固定失效等后果。而外固定支架直接从后踝骨折处进行固定,无需进行大量的术中透视,而且操作更为简便,固定更为牢靠,术后4-6周即可拆除支架,免除了二次手术取出内固定的痛苦。但其不足之处也尤为明显,外固定支架的体积较大,且位于小腿后侧,可能影响患者正常仰卧,给患者日常生活带来不便;除此之外,可延伸的外固定支架对于一些较小的后踝骨折块可能会出现复位困难的情况,这时还需要通过踝关节后外侧切口有限的切开辅助复位。 大量临床研究发现,切开复位钢板内固定相对于微创闭合复位内固定,后踝骨折块将获得更好的解剖复位,有助于骨折端的良好愈合,且对于患者后续踝关节功能恢复上,拥有更高的评分,创伤性关节炎的发病率要明显低于微创闭合复位内固定[32]。Karaca等[33]也认为钢板相对于空心加压螺钉固定后踝骨折,可以使踝关节恢复更优良的背伸能力。因此,对于后踝骨折的患者,作者更加倾向于切开复位,应用钢板对后踝骨折块进行固定。但是,切开直视下复位内踝骨折,对后踝周围软组织的血运破坏较大,且易损伤小隐静脉、腓肠神经及胫后血管等临近结构,手术时应尤为注意。 2.2.6 后踝骨折内固定材料的选择 金属材料和可吸收材料均为后踝骨折可采用的内固定材料。临床上现以金属材料为主,如金属钢板、空心钉及张力带等。因后踝骨折块位于干骺端,该处骨皮质薄弱,骨质构成以松质骨为主,空心加压螺钉常常会穿破骨皮质,这样对骨折块加压作用是很有限的,这种局限性对于伴有骨质疏松的患者表现更加明显。因此,如果固定后踝骨折单纯注重骨折端加压,只注重对抗骨折块的潜在轴向滑移应力是远远不够的。AO首创的动力加压接骨板,螺钉角度多样化,并且可以双向加压,平滑预弯,而放置于中心的螺钉并没有加压效果,想要拥有动力加压效果,螺钉必须放置于偏心位,于接骨板螺孔放置拉力螺钉可以有效增加斜行稳定性,螺钉拧入螺孔时,倾斜螺钉,使之与钢板水平交界处呈钝角、向下、水平方向滑动,完成轴向加压,有限接触-动力加压接骨板与骨接触面积较小,对骨膜的血运干扰减小。 可吸收螺钉由聚乳酸(PLA)、聚乙胶酯(PGA)、聚丙胶酯(PLLA)等生物降解材料制成(图4),具有优良的生物安全性和生物相容性,内固定物加工时经高温、高压等特殊工艺处理,有效提高了内固定物的强度,同时可于体内降解吸收,免除手术取出内固定的二次痛苦,同时,避免了透视下影像对骨折显影的干扰。有研究表明可吸收螺钉置入内固定修复踝关节骨折的疗效与传统钛合金属螺钉的疗效相似,可有效恢复踝关节功能,弹性模量与松质骨相当,生物相容性好,可作为金属内固定物的替代物[34-35]。 "
| [1] 何锦泉,马信龙,马宝通,等.后踝骨折分型及治疗的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(13):863-870.[2] Gonzalez T A, Watkins C, Drummond R, et al. Transfibular approach to posterior malleolus fracture fixation: technique tip. Foot Ankle Int. 2015. DOI:10.1177/1071100715617760.[3] Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Reed SC, Hedman TP. Disruption of the ankle syndesmosis: biomechanical study of the ligamentous restraints. Arthroscopy. 1994;10(5):558-560.[4] Papachristou G, Efstathopoulos N, Levidiotis C, et al. Early weight bearing after posterior malleolar fractures: an experimental and prospective clinical study. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2003;42(2):99-104.[5] Lovisetti G, Irwin TA. Posterior malleolus fracture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22(2):67.[6] Xu H L, Li X, Zhang D Y, et al. A retrospective study of posterior malleolar fractures. Int Orthop. 2012;36(9): 1929-1936.[7] 吴昊天,郭智萍,郭明珂,等.踝部损伤机制与后踝骨折块大小及治疗方法选择的关系[J].中华医学杂志,2011,91(41):2917-2919.[8] 王志生,王志强,李立东,等.后踝骨折CT分型及其对临床的指导意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(10):736-738.[9] Haraguchi N, Haruyama H, Toga H, et al.Pathoanatomy of posterior malleolar fractures of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(5):1085-1092.[10] Switaj PJ, Weatherford B, Fuchs D, et al. Evaluation of posterior malleolar fractures and the posterior pilon variant in operatively treated ankle fracture. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;35(9): 886-895.[11] Mangnus L, Meijer DT, Stufkens SA, et al. Posterior malleolar fracture patterns. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(9):428.[12] Bartoní?ek J, Rammelt S, Kostlivý K, et al. Anatomy and classification of the posterior tibial fragment in ankle fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(4):505.[13] Gonzalez O, Fleming JJ, Meyr AJ. Radiographic assessment of posterior malleolar ankle fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2015; 54(3):365.[14] 陆长春,李晓林.后踝骨折的解剖分型及治疗进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(9):821-825.[15] Ferries JS, Decoster TA, Firoozbakhsh KK, et al. Plain radiographic interpretation in trimalleolar ankle fractures poorly assesses posterior fragment size. J Orthop Trauma. 1994;8(4):328.[16] 侯志勇,张英泽,潘进社,等.胫骨下1/3螺旋形骨折合并后踝骨折的致伤机制及漏诊原因分析[J].中华创伤杂志, 2006,22(2): 152-154.[17] Tenenbaum S, Shazar N, Bruck N, et al. Posterior malleolus fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2017;48(1):81.[18] Su FU, Zou ZY, Mei G, et al. Advances and disputes of posterior malleolus fracture. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(20): 3972-3977.[19] 刘志强,都承斐,杨茂伟.利用有限元分析技术探讨后踝骨折的治疗方案[J].北京生物医学工程,2011,30(5):467-470.[20] Alonso-Rasgado T, Jimenez-Cruz D, Karski M. 3-D computer modelling of malunited posterior malleolar fractures: effect of fragment size and offset on ankle stability, contact pressure and pattern. J Foot Ankle Res. 2017;10(1):13.[21] Langenhuijsen JF, Heetveld MJ, Ultee J M, et al. Results of ankle fractures with involvement of the posterior tibial margin. J Trauma. 2002;53(1):55.[22] 龚晓峰,武勇,吕艳伟,等.后踝骨折手术治疗的指征[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(3):232-237.[23] Kim MB, Lee YH, Kim JH, et al. Lateral transmalleolar approach and miniscrews fixation for displaced posterolateral fragments of posterior malleolar fractures in adults: a consecutive study. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(2):105-109.[24] Bennett C, Behn A, Daoud A, et al. Buttress plating versus anterior-to-posterior lag screws for fixation of the posterior malleolar: a biomechanical study. J Orthop Trauma. 2016; 30(12):664.[25] Verhage SM, Boot F, Schipper IB, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of posterior malleolar fractures using the posterolateral approach. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(6):812.[26] 邓建华,吴俊,韩元龙,等.改良后外侧入路固定后踝骨折的疗效[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(1):60-62.[27] Tejwani NC, Pahk B, Egol KA. Effect of posterior malleolus fracture on outcome after unstable ankle fracture. J Trauma. 2010;69(3):666.[28] Benthien RA. The Posterolateral approach to the posterior malleolar: an alternative surgical strategy for unstable trimalleolar ankle fractures. Tech Orthop. 2014;29(1):8-12.[29] Danoff JR, Saifi C, Goodspeed DC, et al. Outcome of 28 open pilon fractures with injury severity-based fixation. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(3):569.[30] 张士波,张露,郜玉忠,等.三踝骨折的新术式及疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2005,20(2):133-134.[31] 苏文先,王埃,孟晓军.经皮微创空心钉内固定治疗后踝骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2011,17(1):92-93.[32] Guo J, Liu L, Yang Z, et al. The treatment options for posterior malleolar fractures in tibial spiral fractures. Int Orthop.2017; 41(9):1-9.[33] Karaca S, Enercan M, Özdemir G, et al. Importance of fixation of posterior malleolus fracture in trimalleolar fractures: a retrospective study. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2016; 22(6):553.[34] 王展,张军,张堃,等.内固定材料修复后踝骨折及其生物力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(44):7182-7187.[35] 赵学寨,李海军,孟彩云,等.可吸收螺钉与金属螺钉内固定修复踝关节骨折:生物相容性及踝关节功能比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(31):4687-4692. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [5] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| [6] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [7] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [8] | Nie Shaobo, Li Jiantao, Sun Jien, Zhao Zhe, Zhao Yanpeng, Zhang Licheng, Tang Peifu. Mechanical stability of medial support nail in treatment of severe osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 329-333. |
| [9] | Tan Jiachang, Yuan Zhenchao, Wu Zhenjie, Liu Bin, Zhao Jinmin. Biomechanical analysis of elastic nail combined with end caps and wire fixation for long oblique femoral shaft fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 334-338. |
| [10] | Chen Lu, Zhang Jianguang, Deng Changgong, Yan Caiping, Zhang Wei, Zhang Yuan. Finite element analysis of locking screw assisted acetabular cup fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 356-361. |
| [11] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of multiple implants in treatment of traumatic dislocation of sternoclavicular joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 443-448. |
| [12] | Li Kun, Li Zhijun, Zhang Shaojie, Gao Shang, Sun Hao, Yang Xi, Wang Xing, Dai Lina . A 4-year-old child model of occipito-atlanto-axial joints established by finite element dynamic simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3773-3778. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| [15] | Liu Jinyu, Ding Yiwei, Lu Zhengcao, Gao Tianjun, Cui Hongpeng, Li Wen, Du Wei, Ding Yu. Finite element biomechanical study of full endoscopic fenestration decompression for cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3850-3854. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||