Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (13): 2125-2132.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.13.029
Model of reduced pediatric supracondylar humeral fracture with residual displacements: a finite element analysis of mechanical responses
Chen Lin-wei, Zhao Jing-tao, Zheng Ting-qu, He Chang-qiang, Sun Han-qiao, Huang Feng, Zheng Xiao-hui, Gan Yan-qun
- Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2015-01-16Online:2015-03-26Published:2015-03-26 -
Contact:Zhao Jing-tao, Master, Associate professor, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Chen Lin-wei, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Lin-wei, Zhao Jing-tao, Zheng Ting-qu, He Chang-qiang, Sun Han-qiao, Huang Feng, Zheng Xiao-hui, Gan Yan-qun. Model of reduced pediatric supracondylar humeral fracture with residual displacements: a finite element analysis of mechanical responses[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(13): 2125-2132.
share this article
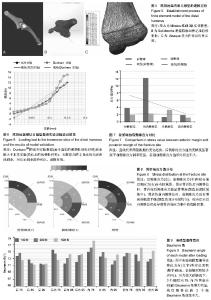
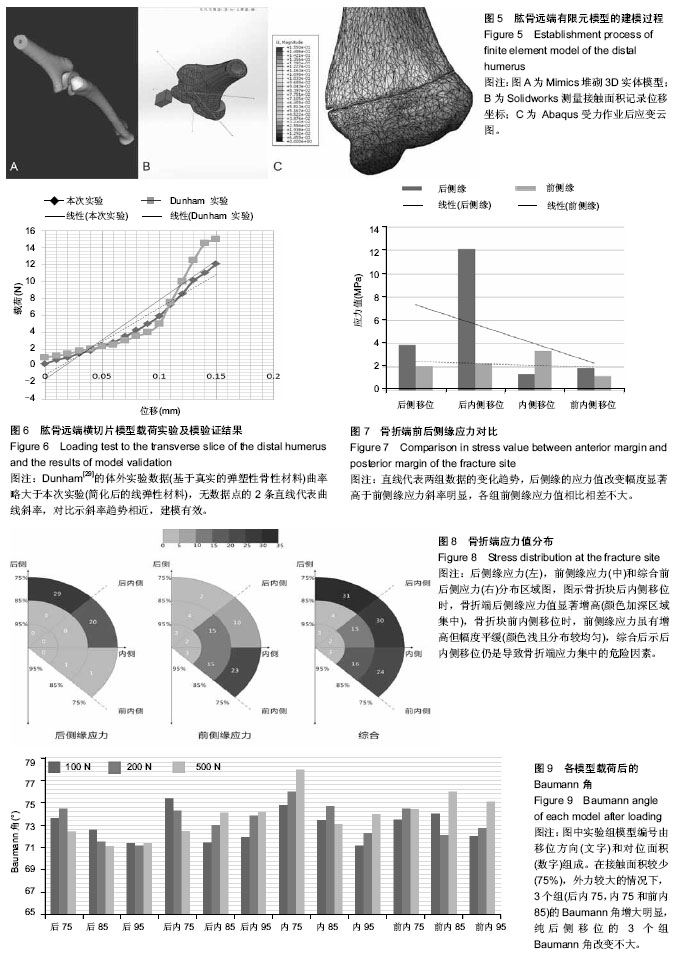
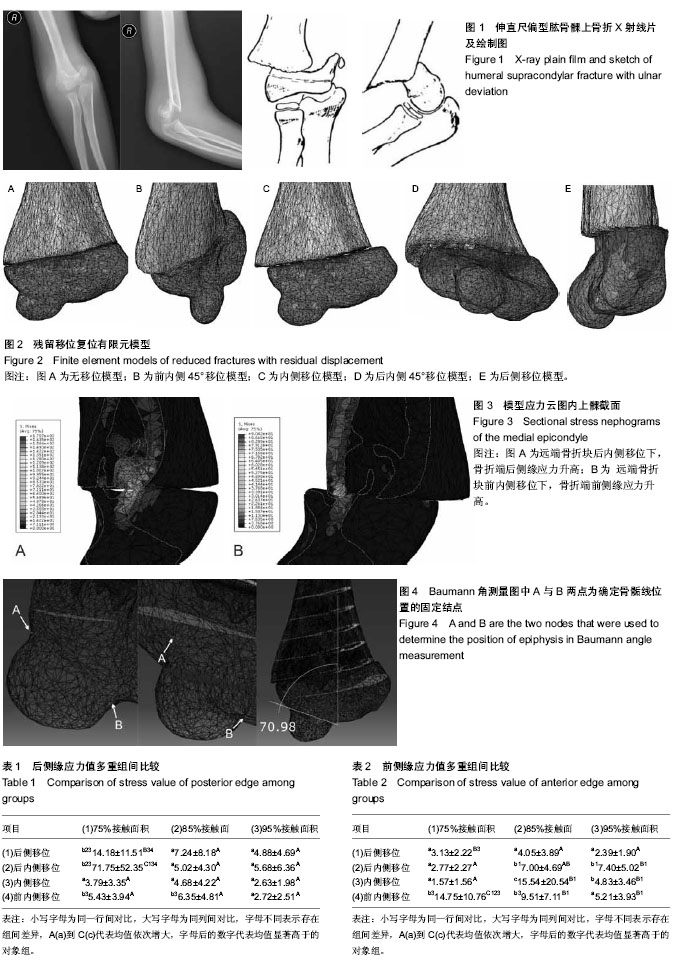
2.1 模型建立 图5为建模过程,实际建成肱骨远端有限元模型共含有四面体单元89 252个单元,48 752个节点。 2.2 模型验证 在体外尸体骨实验中,Dunham等[29]对肱骨远端骨组织的力学性能进行了测试,按照其描述的分层和取值方法,本次实验所建有限元模型相应分层应力加载结果与Dunham等提供数据对比见图6,Dunham等研究的对象为成人骨,载荷-位移曲线反映骨材料具有一定的弹塑性,且弹性阶段线斜率高于本实验模型,本次实验模型所用CT图像来自于儿童,材料赋值时设定为不均质弹性,所得曲线斜率较一直,弹性模量略低于Dunham实验,总体而言本次实验所建立的模型在材料属性上与真实情况贴近,能够反映肱骨远端骨组织加载后的响应特征,可以用于下一步的生物力学分析。 2.3 后侧缘应力 方差齐性检验示差异无显著性意义(P=0.09),可进行下一步方差分析,主效应检验结果示移位方向、接触面积的主效应及它们之间交互作用对骨折端后侧缘应力值影响显著(P < 0.01),事后检验示骨折端后侧缘的平均应力由大到小排列依次为:后内侧移位、后侧移位、前内侧移位、无移位及内侧移位,其中后内侧移位下应力值显著高于其余4组(P < 0.01),其余4组组间对比差异均无显著性,当接触面积为75%时,骨折端后侧缘的应力值显著增高(P < 0.01),表1示多重组间比较结果与事后检验相符,同移位方向内比较,接触面积小者应力值大,同接触面积下比较,后内侧移位组应力值大,应力高值出现在75%接触后内侧移位组,75%接触后侧移位组次之,此两组应力值与其他各组相比差异存在显著性意义,其余组间对比差异基本无显著性意义。 2.4 前侧缘应力 方差齐性检验示无显著性(P=0.36),主体效应检验中移位方向、接触面积的主效应及它们之间交互作用对骨折端前侧缘应力值影响显著(P < 0.01),事后检验示前内侧移位、内侧移位、后内侧移位、后侧移位及完全复位下骨折端前侧缘应力值逐渐降低,方向刚好与后侧缘应力值结果相反,对比下前内侧移位与后内侧移位、完全复位应力值差异有显著性意义,接触面积比较结果呈现"
| [1] 陆春.儿童肱骨髁上骨折的内固定治疗[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2007,15(20):1550-1552. [2] Mulpuri K, Wilkins K. The treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures: evidence-based guideline. J PediatrOrthop. 2012;32Suppl 2:S143-152. [3] 廖世杰,赵劲民,丁晓飞.儿童肱骨髁上骨折的分型与治疗进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(8):714-716. [4] Omid R, Choi PD, Skaggs DL. Supracondylar humeral fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(5): 1121-1132. [5] Young S, Fevang JM, Gullaksen G, et al. Deformity and functional outcome after treatment for supracondylar humerus fractures in children: a 5- to 10-year follow-up of 139 supracondylar humerus fractures treated by plaster cast, skeletal traction or crossed wire fixation. J Child Orthop. 2010;4(5):445-453. [6] Ababneh M, Shannak A, Agabi S, et al. The treatment of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. A comparison of three methods. Int Orthop. 1998;22(4): 263-265. [7] Tschopp O, Rombouts JJ. Complications of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Acta Orthop Belg. 1996; 62(Suppl1):51-57. [8] Farnworth CL, Smith PD, Mubarak SJ. Etiology of supracondylar humerusfracture. J Pediatr Orthop. 1998; 18:38-42. [9] 王建伟,马勇,诸方受,等.肱骨髁上骨折并发肘内翻的生物力学机制研究概况[J].北京中医药大学学报,1998,39(4):58-60. [10] D'Ambrosia RD. Supracondylar fractures of humerus- prevention of cubitusvarus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972; 54(1):60-66. [11] ArinoVL, Lluch EE, Ramirez AM, et al. Percutaneous fixation of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1977;59(7):914-916. [12] 徐华梓,李也白,池永龙,等.儿童肱骨髁上骨折切开复位术后肘内翻畸形[J].中华小儿外科杂志,1995,16(1):28-29. [13] 侯德光.肱骨髁上骨折并发肘内翻的探讨[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,1989,2:28-29. [14] 李海波,田心义.儿童肱骨髁上骨折的治疗及肘内翻机理研究进展[J]. 中医药导报,2006,12(2):78-82. [15] Flynn JC, Matthews JG, Benoit RL. Blind pinning of displaced supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Sixteen years' experience with long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(2):263-272. [16] Smith L. Deformity following supracondylar fractures of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1965;47(8):1668. [17] 霍力为,王广伟,庾伟中,等.黄氏手法配合小夹板治疗儿童Gartland Ⅲ型肱骨髁上骨折临床观察[J].新中医,2011, 43(11): 65-66. [18] 宋冰,刘建科,张伟.手法整复小夹板治疗儿童伸直型肱骨髁上骨折[J].陕西中医学院学报,2008,31(5):37-38. [19] 陈执平,齐振熙,周金水.应用三维有限元分析探讨髓芯减压术后产生的空洞对股骨头应力的影响[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2009,3(5):49-52. [20] 魏秋实,何伟.有限元分析在股骨头坏死领域中的应用研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(19):1611-1614. [21] Bonnick SL. Noninvasive assessments of bone strength.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes.2007;14(6): 451-457. [22] Keaveny TM. Biomechanical computed tomography-noninvasive bone strength analysis using clinical computed tomography scans. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192: 57-65. [23] Rice JC, Cowin SC, Bowman JA. On the dependence of the elasticity and strength of cancellous bone on apparent density. J Biomech. 1988;21(2):155-168. [24] Morgan EF, Bayraktar HH, Keaveny TM. Trabecular bone modulus-density relationships depend on anatomic site. J Biomech. 2003;36(7):897-904. [25] Rho JY, Hobatho MC, Ashman RB, et al. Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med Eng Phys.1995;17:347-355. [26] Bahk MS, Srikumaran U, Ain MC, et al. Patterns of pediatric supracondylar humerusfractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008;28(5):493-499. [27] Shockey JS, von Fraunhofer JA, Seligson D. A measurement of the coefficient of static friction of human long bones. Surf Tech. 1985;25(2):167-173. [28] Schuster I, Korner J, Arzdorf M, et al. Mechanical comparison in cadaver specimens of three different 90-degree double-plate osteosyntheses for simulated C2-type distal humerus fractures with varying bone densities.J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(2):113-120. [29] Dunham CE, Takaki SE, Johnson JA, et al. Mechanical properties of cancellous bone of the distal humerus. ClinBiomech (Bristol, Avon). 2005;20(8):834-838. [30] 徐华梓,林焱,陈跃忠,等. Baumann角测量预测肱骨髁上骨折肘内翻的研究[J].温州医学院学报,1999,40(1):6-8. [31] Williamson DM, Coates CJ, Miller RK, et al. Normal characteristics of the Baumann (humerocapitellar) angle: an aid in assessment of supracondylar fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992;12(5):636-639. [32] Worlock P. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus. Assessment of cubitusvarus by the Baumann angle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986;68(5):755-757. [33] 庄志强,林乔龄,洪嘉志,等.基于Baumann角测定在预测儿童肱骨髁上骨折并发肘内翻的发生率的临床意义[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2012,32(2):27-28. [34] 刘飞,楼跃,唐凯,等.儿童肱骨远端有限元模型的建立及力学分析[J]. 热带医学杂志,2011,11(5):527-528. [35] 王亚斌,周小建,任亚军,等.肱骨远端三维有限元模型的建立及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(22): 4002-4005. [36] 刘剑,黄潮桐,陈隆福,等.肱骨髁上部位局部三维构建及有限元分析[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2012,4(6):427-431. [37] Lamdan R, Liebergall M, Gefen A, et al. Pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures: effect of bone-implant interface conditions on fracture stability. J Child Orthop. 2013;7(6):565-569. [38] Sabalic S, Kodvanj J, Pavic A. Comparative study of three models of extra-articular distal humerus fracture osteosynthesis using the finite element method on an osteoporotic computational model. Injury. 2013;44Suppl 3:S56-61. [39] Worlock P. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus. Assessment of cubitusvarus by the Baumann angle. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1986;68(5):755-757. [40] Silva M, Pandarinath R, Farng E, et al. Inter- and intra-observer reliability of the Baumann angle of the humerus in children with supracondylar humeral fractures. Int Orthop. 2010;34(4):553-557. [41] 左大鹏.闭合治疗儿童肱骨髁上骨折[J].贵阳中医学院学报, 2008, 30(4):48-50. [42] 郭源,王承武,范源,等.儿童“不可复性”肱骨髁上骨折的治疗[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志,1998,19(2):5-7. [43] 凌长敦, 庞国栋. 儿童肱骨髁上移位骨折致肘内翻畸形的探讨与预防[J].广西中医药, 2007,30(4): 50. [44] 刘献祥,林木南,符臣学,等. 肱骨髁上骨折并发症98例临床分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2001,14(4):8-9. [45] 王国平,张玉柱,王人彦,等.屈肘前臂旋前位整复固定治疗肱骨髁上骨折120例[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2002,17(2):150-151. [46] 高光明,杜成高. 肱骨髁上骨折后肘内翻畸形的原因探讨[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,1997,5(6):51-52. |
| [1] | Zhang Lei, Ma Li, Fu Shijie, Zhou Xin, Yu Lin, Guo Xiaoguang. Arthroscopic treatment of greater tuberosity avulsion fractures with anterior shoulder dislocation using the double-row suture anchor technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 895-900. |
| [2] | Zhang Jing, Wang Bin, Lü Xin. Application of anatomic intramedullary nail in tubular bone fractures of limbs: stronger holding force and anti-rotation ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 917-922. |
| [3] | Qin Wan’an, Cai Zhouyu, Wei Gejin, Lin Zhoudan. Finite element analysis of absorbable screws and ethibond sutures for the treatment of humerus shaft fractures caused by grenade throwing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3855-3859. |
| [4] | Liu Gang, Zhang Baolu, Shi Jie, Bao Dingsu, Zeng Shengqiang, Deng Kai, Liu Yang, Wang Guoyou, Fu Shijie. Difference between proximal humeral locking plate and cannulated screw fixation in the treatment of Mutch type II fracture of greater tuberosity of humerus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2863-2868. |
| [5] | Xiang Feifan, Tan Xiaoqi, Xiang Yong, Liang Jie, Zhou Wei, Luo Liang, Gu Hao, Yang Yunkang. Effect of anatomic locking plate combined with allograft fibula on proximal humerus fracture: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(36): 5897-5904. |
| [6] | Wang Qiang, Gu Yong, Chen Liang. Advantages and disadvantages of internal fixation with suture anchors and locking plate in the treatment of the greater tuberosity fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4813-4817. |
| [7] | Qi Yusen, Han Mengguang, Luo Jinwei, Guan Chenwei, Hu Jiayang, Xu Cong, Lü Yongming. Arthroscopic repair for osteoporosis in the greater tuberosity of patients with rotator cuff tear due to chronic moderate to severe tendon retraction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(20): 3140-3145. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhongyan, Li Yubo, Qi Tongning, Chang Tao. Three-dimensional printed polylactic acid resin humerus combined with bioactive coating promotes osteoblast adhesion and increases antibacterial ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(16): 2485-2492. |
| [9] |
She Rongfeng, Zhang Yi, Wang Yuanzheng, Zhang Bin, Chen Peng, Huang Qixiang.
A novel cement-reinforced screw combined with locking plate
fixation versus humeral head
arthroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic fractures of the proximal humerus
|
| [10] | Xu Peng, Su Ping, Li Xuedong, Rui Yongjun. Locking plate in the treatment of proximal humeral fractures involving humeral calcar: effective support, complications and functional recovery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(12): 1949-1956. |
| [11] | Fang Zhirong, Jiang Tao, Hong Weiwu, Huang Yongquan, Peng Jiajie, Liu Zitao, Zhou Lin, Liang Yihao, Su Haitao. Multiloc intramedullary nail versus PHILOS locking plate in the treatment of proximal humerus fracture: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5896-5904. |
| [12] | Gong Dong, Liu Jun, Dong Chenhui, Deng Yinshuan, Zhou Yanfeng, Yang Xinle, Zhen Ping. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma versus glucocorticoid for lateral humeral epicondylitis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(35): 5735-5740. |
| [13] | Ji Qian-yi1, Chen Xiao1, 2, Xu Chang1. Finite element analysis of shear wave velocity influenced by force in muscle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(20): 3155-3160. |
| [14] | Feng Shuo, Zha Guo-chun, Guo Kai-jin, Yang Zhi, Chang Bu-qing, Yang Shuo, Xu Chong-jun, Chen Xiang-yang. Clinical outcomes of three- or four-part complex proximal humerus fractures: hemiarthroplasty versus locking plate fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(19): 2974-2980. |
| [15] | Luo Deng-ke, Chen Ken, Qin Ping, Zhou Na-xin, Yu Ji-zhe, Zou Ji, Chen He-qiang, Xiao Qi-san. Effects of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty versus open reduction and internal plate fixation for the treatment of nonunions of proximal humeral fractures in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(15): 2327-2332. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||