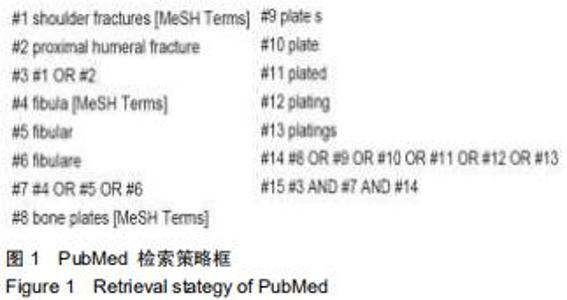
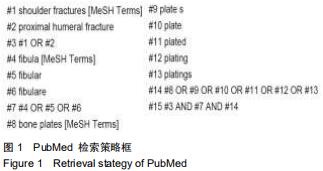
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (36): 5897-5904.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2913
Effect of anatomic locking plate combined with allograft fibula on proximal humerus fracture: a meta-analysis
Xiang Feifan1, Tan Xiaoqi2, Xiang Yong1, Liang Jie1, Zhou Wei1, Luo Liang1, Gu Hao1, Yang Yunkang1
- 1Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, 2Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2020-03-09Revised:2020-03-13Accepted:2020-04-18Online:2020-12-28Published:2020-10-27 -
Contact:Yang Yunkang, MD, Chief physician, Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Xiang Feifan, Master, Physician, Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Project of Southwest Medical University, No. 2017-ZRQN-129; the Project of Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, No. 2017-PT-47
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xiang Feifan, Tan Xiaoqi, Xiang Yong, Liang Jie, Zhou Wei, Luo Liang, Gu Hao, Yang Yunkang. Effect of anatomic locking plate combined with allograft fibula on proximal humerus fracture: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(36): 5897-5904.
share this article
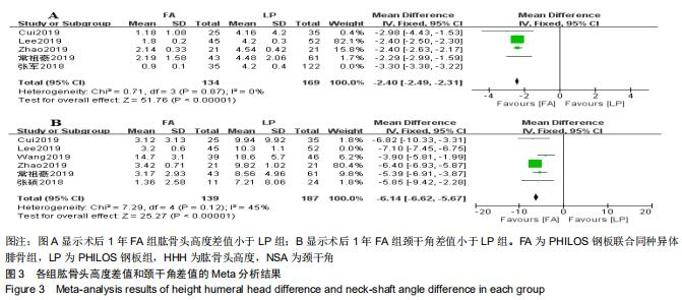
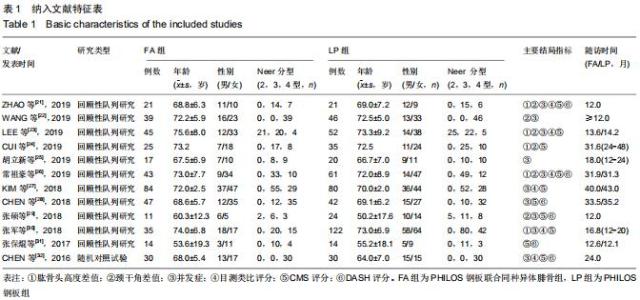
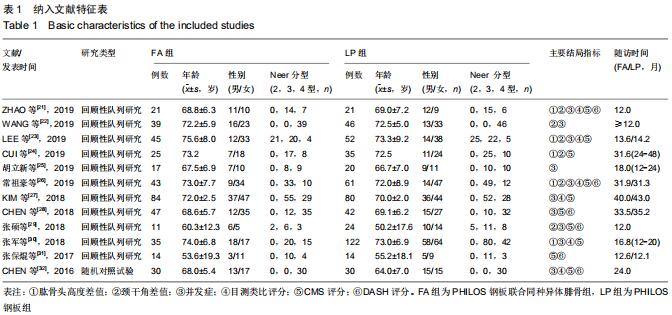
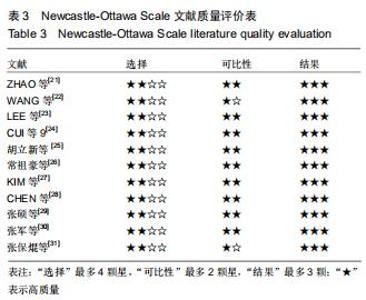
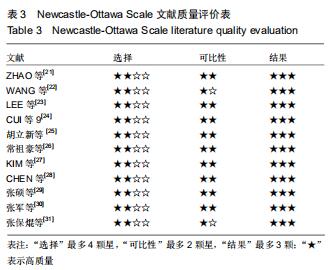
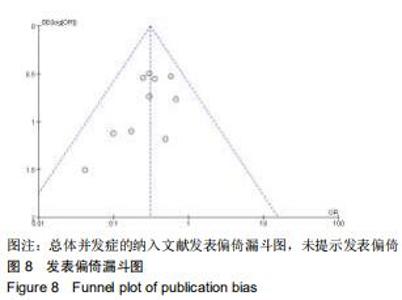
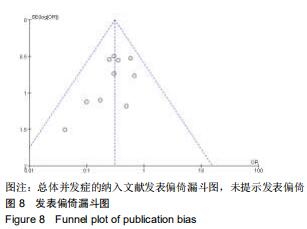
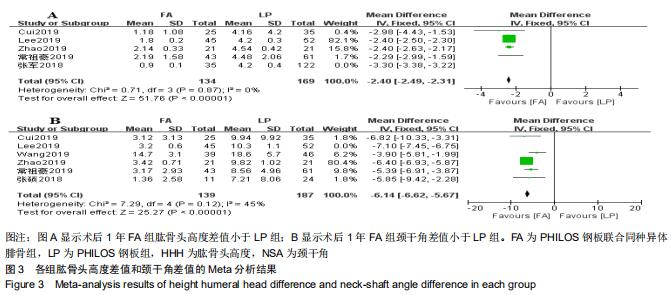
2.3.1 各组影像学数据比较 纳入研究的文献中有5篇报道了FA组和LP组术后1年与术后即刻肱骨头高度差 值[21,23-24,26,30]。5篇文献行Meta分析提示文献异质性较高(I2=98%),进行敏感性分析剔除1篇文献后[30],异质性明显下降(I2=0%),采用固定效应模型。最终4篇文献行Meta分析[21,23-24,26],结果显示术后1年随访FA组的肱骨头高度差值小于LP组(MD=-2.40,95%CI:-2.49至-2.31,P < 0.000 01,I2=0%),见图3A。 纳入研究的文献中有6篇报道了FA组和LP组术后1年与术后即刻颈干角差值[21-24,26,29]。6篇文献行Meta分析提示文献异质性较高(I2=71%),行敏感性分析,剔除1篇文献后[23],异质性明显下降(I2=45%),采用固定效应模型。最终5篇献行Meta分析[21-22,24,26,29],结果显示术后1年随访FA组的颈干角差值小于LP组(MD=-6.14,95%CI:-6.62至-5.67,P < 0.000 01,I2=45%),见图3B。 "
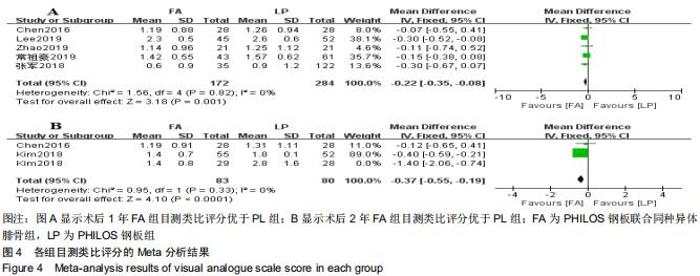
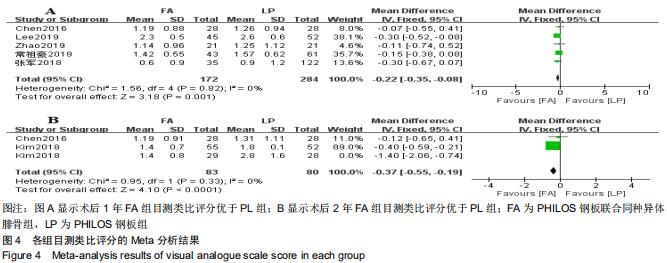
2.3.2 各组疼痛及功能评分比较 纳入研究的文献中有5篇报道了FA组和LP组术后1年的目测类比评分[21,23,26,30,32]。5篇文献行Meta分析示异质性I2=0%,采用固定效应模型。结果显示,术后1年FA组的目测类比评分优于LP组(MD=-0.22,95%CI:-0.35至-0.08,P=0.001,I2=0%),见图4A。纳入研究的文献中有2篇报道了FA组和LP组术后2年的目测类比评分[27,32]。2篇文献(其中KIM等[27]原文中根据Neer分型分别进行了3部分和4部分骨折数据的统计分析)行Meta分析示异质性I2=79%,行敏感性分析,去除KIM 等[27]中4部分骨折后,异质性明显下降(I2=0),采用固定效应模型。结果显示术后2年FA组的目测类比评分优于LP组(MD=-0.37,95%CI:-0.57至-0.19,P < 0.000 1,I2=0),见图4B。 "
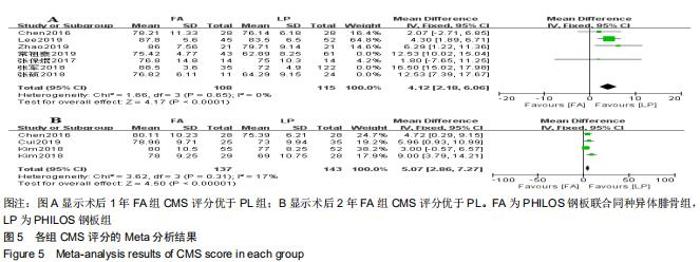
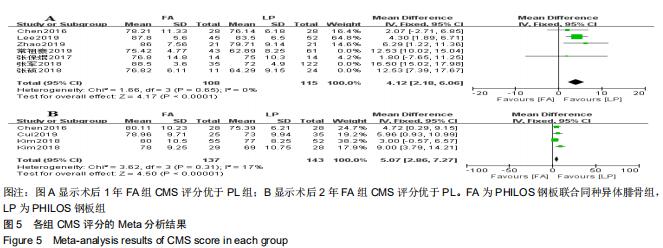
纳入研究的文献中有7篇报道了FA组和LP组术后1年CMS评分[21,23,26,29,30-32]。7篇文献行Meta分析提示文献异质性较高(I2=94%),根据年龄(>65岁和<65岁)、骨折分型、随访时间(>2年和<2年)及中英文文献分别分组,进行亚组分析,均未明显降低文献异质性。再行敏感性分析,剔除3篇文献后[26,29-30],异质性明显下降(I2=0%),采用固定效应模型。最终4篇文献行Meta分析,结果显示术后1年随访FA组CMS评分优于LP组,两组差异有显著性意义(MD=4.12,95%CI:2.18-6.06,P < 0.000 1,I2=0%),见图5A。纳入研究的文献中有3篇报道了FA组和LP组术后2年的CMS评分[24,27,32]。3篇文献行Meta分析示异质性I2= 17%[24,27,32],采用固定效应模型。结果显示术后2年FA组的CMS评分优于LP组,两组差异有显著性意义(MD=5.07,95%CI:2.86-7.27,P < 0.000 01,I2=17%),见图5B。 "

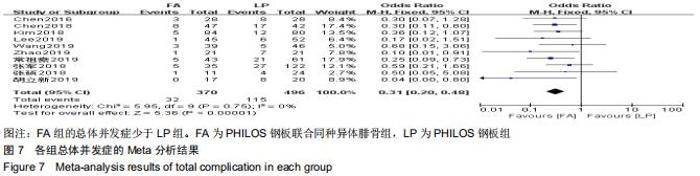
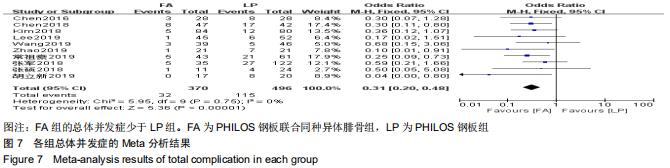
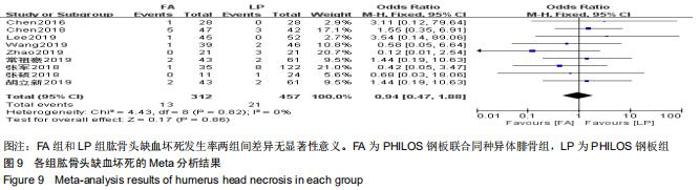
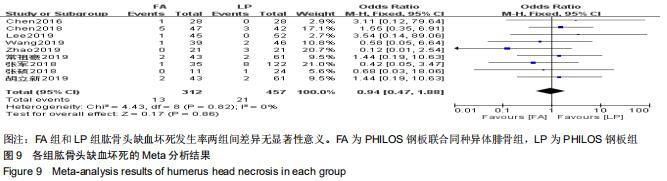
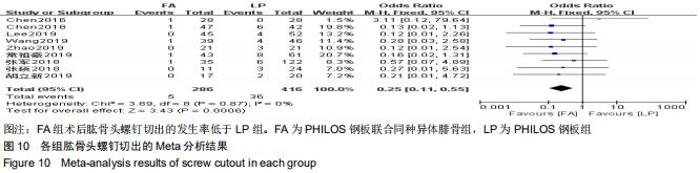
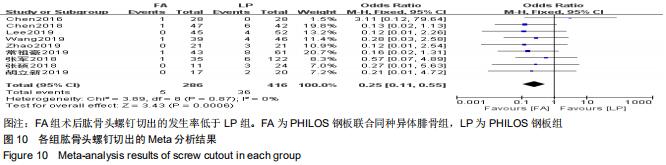
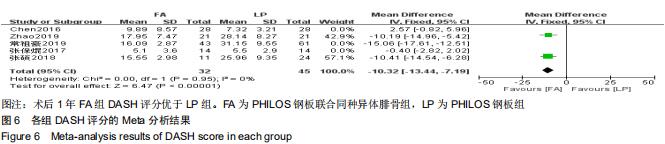
纳入研究的文献中有5篇报道了FA组和LP组术后1年DSAH评分[21,26,29,31-32]。5篇文献行Meta分析提示文献异质性较高(I2=96%),根据年龄(>65岁和<65岁)、骨折分型、随访时间(>2年和<2年)及中英文文献分别分组行亚组分析,均未明显降低文献异质性。再行敏感性分析,剔除3篇文献后[26,31-32],异质性明显下降(I2=0%),采用固定效应模型。最终2篇文献行Meta分析[21,29],结果显示术后1年随访FA组DSAH评分优于LP组,两组差异有显著性意义(MD=-10.32,95%CI:-13.44至-7.19,P < 0.000 01,I2=0%),见图6。 "
|
[1] DAUWE J, WALTERS G, VAN EECKE E, et al. Osteosynthesis of proximal humeral fractures: a 1-year analysis of failure in a Belgian level-1 trauma centre. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020. doi: 10.1007/s00068-020-01323-2.
[2] SEARS BW, HATZIDAKIS AM, JOHNSTON PS. Intramedullary fixation for proximal humeral fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019. doi :10.5435/JAAOS-D-5418-00360.
[3] CONGIA S, PALMAS A, MARONGIU G, et al. Is antegrade nailing a proper option in 2- and 3-part proximal humeral fractures? Musculoskelet Surg. 2019. doi :10.1007/s12306-019-00610-5.
[4] JAWA A, BURNIKEL D. Treatment of proximal humeral fractures: a critical analysis review. JBJS Rev. 2016. doi : 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.O.00003.
[5] SCHMALZL J, JESSEN M, SADLER N, et al. High tuberosity healing rate associated with better functional outcome following primary reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures with a 135 degrees prosthesis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):35-43.
[6] BLONNA D, ASSOM M, BELLATO E, et al. Outcomes of 188 proximal humeral fractures treated with a dedicated external fixator with follow-up ranging from 2 to 12 years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019; 101(18):1654-1661.
[7] NEWMAN JM, KAHN M, GRUSON KI. Reducing postoperative fracture displacement after locked plating of proximal humerus fractures: current concepts. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015; 44(7):312-320.
[8] 周君琳.复杂肱骨近端骨折内固定治疗[J].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2019, 7(1):93.
[9] BARLOW JD, LOGLI AL, STEINMANN SP, et al. Locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures in patients older than 60 years continues to be associated with a high complication rate. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2019.11.026
[10] 徐鹏,苏萍,李雪栋,等.锁定接骨板治疗累及肱骨距的肱骨近端骨折:有效支撑、并发症和功能恢复[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(12):1949-1956.
[11] OPPEBOEN SAO, WIKEROY AKB, FUGLESANG HFS, et al. Calcar screws and adequate reduction reduced the risk of fixation failure in proximal humeral fractures treated with a locking plate: 190 patients followed for a mean of 3 years. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):197.
[12] HE Y, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a novel dualplate fixation method for proximal humeral fractures without medial support. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):72-72.
[13] THEOPOLD J, SCHLEIFENBAUM S, MULLER M, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of hybrid double plate osteosynthesis using a locking plate and an inverted third tubular plate for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0206349.
[14] KNIERZINGER D, CREPAZ-EGER U, HENGG C, et al. Does cement augmentation of the screws in angular stable plating for proximal humerus fractures influence the radiological outcome: a retrospective assessment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020. doi :10.1007/s00402-020-03362-1.
[15] ZHU L, LIU Y, YANG Z, et al. Locking plate fixation combined with iliac crest bone autologous graft for proximal humerus comminuted fracture. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(9):1672-1676.
[16] 朱炼,王博,赵昌平,等.锁定钢板结合同种异体髂骨移植与腓骨移植治疗肱骨近端粉碎性骨折的对比研究[J].河北医科大学学报,2017,38(4): 395-398.
[17] XING F, DUAN X, LIU M, et al. Research progress in treatment of proximal humeral fracture with fibular allograft and locking plate. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(2):260-265.
[18] CHA H, PARK KB, OH S, et al. Treatment of comminuted proximal humeral fractures using locking plate with strut allograft. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(5):781-785.
[19] PARADA SA, MAKANI A, STADECKER MJ, et al. Technique of open reduction and internal fixation of comminuted proximal humerus fractures with allograft femoral head metaphyseal reconstruction. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015;44(10):471-475.
[20] DAVIDS S, ALLEN D, DESARNO M, et al. Comparison of locked plating of varus displaced proximal humeral fractures with and without fibula allograft augmentation. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(4):186-192. [21] ZHAO L, QI YM, YANG L, et al. Comparison of the effects of proximal humeral internal locking system (PHILOS) alone and PHILOS combined with fibular allograft in the treatment of neer three- or four-part proximal humerus fractures in the elderly. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(6):1003-1012.
[22] WANG H, RUI B, LU S, et al. Locking plate use with or without strut support for varus displaced proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients. JBJS Open Access. 2019. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.OA.18.00060.
[23] LEE S H, HAN SS, YOO BM, et al. Outcomes of locking plate fixation with fibular allograft augmentation for proximal humeral fractures in osteoporotic patients: comparison with locking plate fixation alone. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(3):260-265.
[24] CUI X, CHEN H, MA B, et al. Fibular strut allograft influences reduction and outcomes after locking plate fixation of comminuted proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):511-511.
[25] 胡立新,田大为,张鹏,等.锁定钢板联合异体腓骨移植治疗老年骨质疏松性肱骨近端骨折[J].湖北医药学院学报,2019,38(3):217-221.
[26] 常祖豪,朱正国,齐红哲,等.锁定钢板结合异体腓骨治疗老年肱骨近端粉碎性骨折的中远期疗效观察[J].解放军医学院学报,2019,40(2):106-112.
[27] KIM DS, LEE DH, CHUN YM, et al. Which additional augmented fixation procedure decreases surgical failure after proximal humeral fracture with medial comminution: fibular allograft or inferomedial screws? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(10):1852-1858.
[28] CHEN H, YIN P, WANG S, et al. The augment of the stability in locking compression plate with intramedullary fibular allograft for proximal humerus fractures in elderly people. Biomed Res Int. 2018. doi: 10.1155/2018/3130625.
[29] 张硕,汪秋柯,陈云丰,等.锁定钢板结合异体腓骨治疗头内翻型肱骨近端骨折[J].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2018,6(1):19-24.
[30] 张军,庄云强,李东贞,等.锁定钢板结合异体腓骨支撑治疗老年肱骨近端Neer三、四部分骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(11):946-952.
[31] 张保焜,刘敬文,丁坚,等.异体腓骨辅助解剖复位对肱骨近端骨折预后的影响[J].上海医学,2017,40(6):359-362.
[32] CHEN H, JI X, GAO Y, et al. Comparison of intramedullary fibular allograft with locking compression plate versus shoulder hemi-arthroplasty for repair of osteoporotic four-part proximal humerus fracture: consecutive, prospective, controlled, and comparative study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016;102(3):287-292.
[33] JABRAN A, PEACH C, REN L. Biomechanical analysis of plate systems for proximal humerus fractures: a systematic literature review. Biomed Eng Online. 2018;17(1):47.
[34] PANCHAL K, JEONG JJ, PARK SE, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of unstable proximal humeral fractures treated with a locking plate and fibular strut allograft. Int Orthop. 2016;40(3):569-577.
[35] SHAH KN, SOBEL AD, PAXTON ES. Fixation of a proximal humerus fracture using a polyaxial locking plate and endosteal fibular strut. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32 Suppl 1:S8-S9.
[36] 刘炎,葛鸿庆,管华,等.内侧柱缺失型肱骨近端骨折不同固定方式的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(9):1384-1389.
[37] 郭兵,杨世明,李永威,等.肱骨近端锁定钢板内固定联合自体腓骨植骨治疗Neer四部分骨质疏松肱骨近端骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2019, 34(9):981-982.
[38] 石金柱,黄强,张玉富.解剖锁定钢板结合异体腓骨髓腔内结构植骨治疗复杂肱骨近端骨折[J].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2017,5(4):272-277.
[39] DAVIDS S, ALLEN D, DESARNO M, et al. Comparison of locked plating of varus displaced proximal humeral fractures with and without fibula allograft augmentation. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(4):186-192.
[40] 买买提艾力·吐尔逊,曾浪清,陆叶,等.锁定钢板固定联合同种异体腓骨髓内植入治疗内侧柱粉碎性肱骨近端骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2017, 19(11):928-934.
[41] 沈施耘,李雄峰,吴猛,等.锁定钢板结合不同腓骨植骨方式治疗肱骨近端骨折的生物力学稳定性分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(5):427-431.
[42] CHEN H, ZHU ZG, LI JT, et al. Finite element analysis of an intramedulary anatomical strut for proximal humeral fractures with disrupted medial column instability: a cohort study. Int J Surg. 2020;73: 50-56. [43] 朱正国,常祖豪,齐红哲,等.解剖型腓骨髓内支撑锁定钢板固定肱骨近端骨折的有限元分析[J].解放军医学院学报,2019,40(1):62-67. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [6] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [7] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [8] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [9] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [10] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [11] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [12] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [13] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [14] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [15] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||