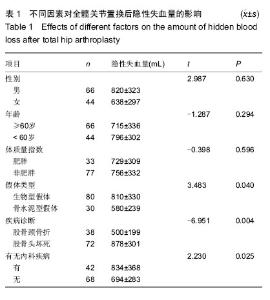
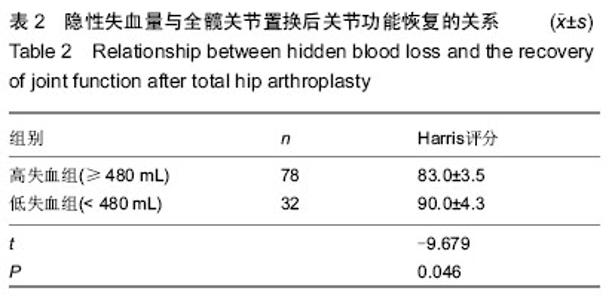
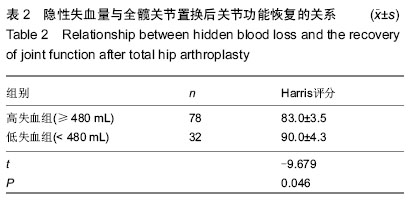
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (13): 1974-1978.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.13.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hidden blood loss after primary total hip arthroplasty: analysis of influential factors
Xu Hai-yong, Zhang Ming, Fang Huai-xi, Le Guo-ping
- Department of Articular Surgery, Liuzhou Worker’s Hospital, Fourth Affiliated Hospital, Guangxi Medical University, Liuzhou 545005, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2015-01-19Online:2015-03-26Published:2015-03-26 -
About author:Xu Hai-yong, Master, Department of Articular Surgery, Liuzhou Worker’s Hospital, Fourth Affiliated Hospital, Guangxi Medical University, Liuzhou 545005, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Hai-yong, Zhang Ming, Fang Huai-xi, Le Guo-ping. Hidden blood loss after primary total hip arthroplasty: analysis of influential factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(13): 1974-1978.
share this article
| [1] Sehat KR, Evans R, Newman JH. How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty: correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee. 2000;7(3): 151-155. [2] Pattison E,Protheroe K,Pringle RM,et al.Reduction in haemoglobin after knee joint surgery. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973; 32(6):582-584. [3] Erskine JG, Fraser C,Simpson R, et al.Blood loss with knee joint replacement, J R Coll Surg Edinb.1981;26(5):295-297. [4] Rosencher N, Kerkkamp JE, Macheras G,et al. Orthopedic surgery transfusion hemoglobin: European overview (OSTHEO) study:blood management in elective knee and hip arthroplasty in Europe.Transfusion. 2003;43(5):459-469. [5] McManus KT, Velchik MG, Alavi A, et al.Non-invasive assessment of postoperative bleeding in TKA patients with Tc-99m RNCs. J Nuclear Med.1987;28:565-567. [6] 王友华,刘瑶,王洪,等.人工全髋关节置换对红细胞脂质过氧化的影响[J].江苏医药,2006,32(7):615-617. [7] Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman J. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty. correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(4):561-565. [8] Ward CF, Alfery DD, Benumof JL. Hypertension following nitroprusside. Anesthesiology. 1980;52(6):525-526. [9] Gross JB. Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology. 1983;58(3): 277-280. [10] Nadler SB, Hidalgo JH, Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;51(2): 224-232. [11] 刘旭东,张先龙,曾炳芳,等.全髋关节置换术后的隐性失血分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(12):995-997. [12] Smith H, Tsang J, Molyneux S,et al.The hidden blood loss after hip fracture. Injury. 2010;7(19):911-913. [13] 高福强,李子剑,刘延青,等.初次全膝关节置换术后肢体肿胀程度与隐性失血量的相关性研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(3): 99-202. [14] 覃健,余存泰,徐中和,等.全髋关节及全膝关节置换术后隐性失血的临床影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2006, 26(5):323-326. [15] 徐浩.全膝关节置换术隐性失血及其危险因素研究[D].青岛大学, 2009. [16] 李征,曹光磊,沈惠良.全膝关节置换术的隐性失血及影响因素分析[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2010,26(9):831-834. [17] Bowditch MG, Villar RN. Do obese patients bleed more? A prospective study of blood loss at total hip replacement. Ann Royal Coll Surg Eng. 1999;81(3):198. [18] 罗涛,黄伟杰,吴伟,等.肥胖对半髋关节置换术围手术期失血的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(17):1419-1422. [19] 邱旭升,陈东阳,徐志宏,等.全膝关节置换术后隐性失血危险因素的分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2012,18(6):510-512. [20] 李洪飞,吕德成,张卫国,等.人工关节置换术隐性失血量及其相关因素分析[J].中国医师进修杂志:综合版, 2011, 34(11): 23-27. [21] Portnoi AS,Begunov AV. The assessment of the State of the blood lipid spectrum, hemostasis, hormonal and hemodynamics in the early diagnosis and drug correction of the cardiovascular changes in prostatic cancer patients undergoing estrogen therapy. Urol Nefrol (Mosk).1992;3(1): 6-11. [22] 肖鹏,吴学建刘宏建.人工关节置换术后隐性失血的相关分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(4):635-638. [23] Reilly IA, FitzGerald GA. Eicosanoid biosynthesis and platelet function with advancing age. Thromb Res. 1986;41(4):545-554. [24] Balleisen L,Bailey J,EppingPH, et al. Epidemiological study on factor VII.Factor VII and fibrinogen in industrial population: I. baseline data on the relation to age. Gender, body-weight,smoking, alcohol, pill-using, and menopause. Thromb Haemost.1985;54(2):475-479. [25] Aillaud MF, Pignol F, Alessi MC, et al. Increase in plasma concentration of plasminogen activator inhibitor, fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor, factor VII: C and in erythrocyte sedimentation rate with age. Thromb Haemost. 1986;55(3):330-332. [26] Yamamoto K, Shimokawa T, Yi H, et al. Aging accelerates endotnxin-induced thrombosis:increased responses of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and lipopolysaccharide signaling with aging. Am J Pathol. 2002;161(5):1805-1814. [27] 许杰,马若凡,李亮平,等.应用低分子肝素对初次全髋及全膝关节置换后失血的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(48):8963-8967. [28] 丛宇,曾晓峰,包倪荣,等.人工关节置换术后隐性失血的影响因素及相关机制[J].医学研究生学报,2011,24(6):611-614. [29] 刘志刚,张上上,陈如见,等.全髋关节置换后的隐性失血[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(13): 2305-2312. [30] 王志岩,周建生,李昭程,等.人工髋关节置换术后并发有症状下肢深静脉血栓临床分析[J].解剖与临床,2012,17(4):288-291. [31] 张晨,李苗,王坤正,等.彩色多普勒超声检查联合超声弹性成像对初次全髋关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的分期诊断价值[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2012,6(4):12-15. [32] 高玉镭,李佩佳,田敏,等.人工全膝关节置换术隐性失血的发生机制及影响因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012, 20(3): 209-212. [33] Liu X, Zhang X, Chen Y, et al. Hidden blood loss after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26(7): 1100-1105. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||